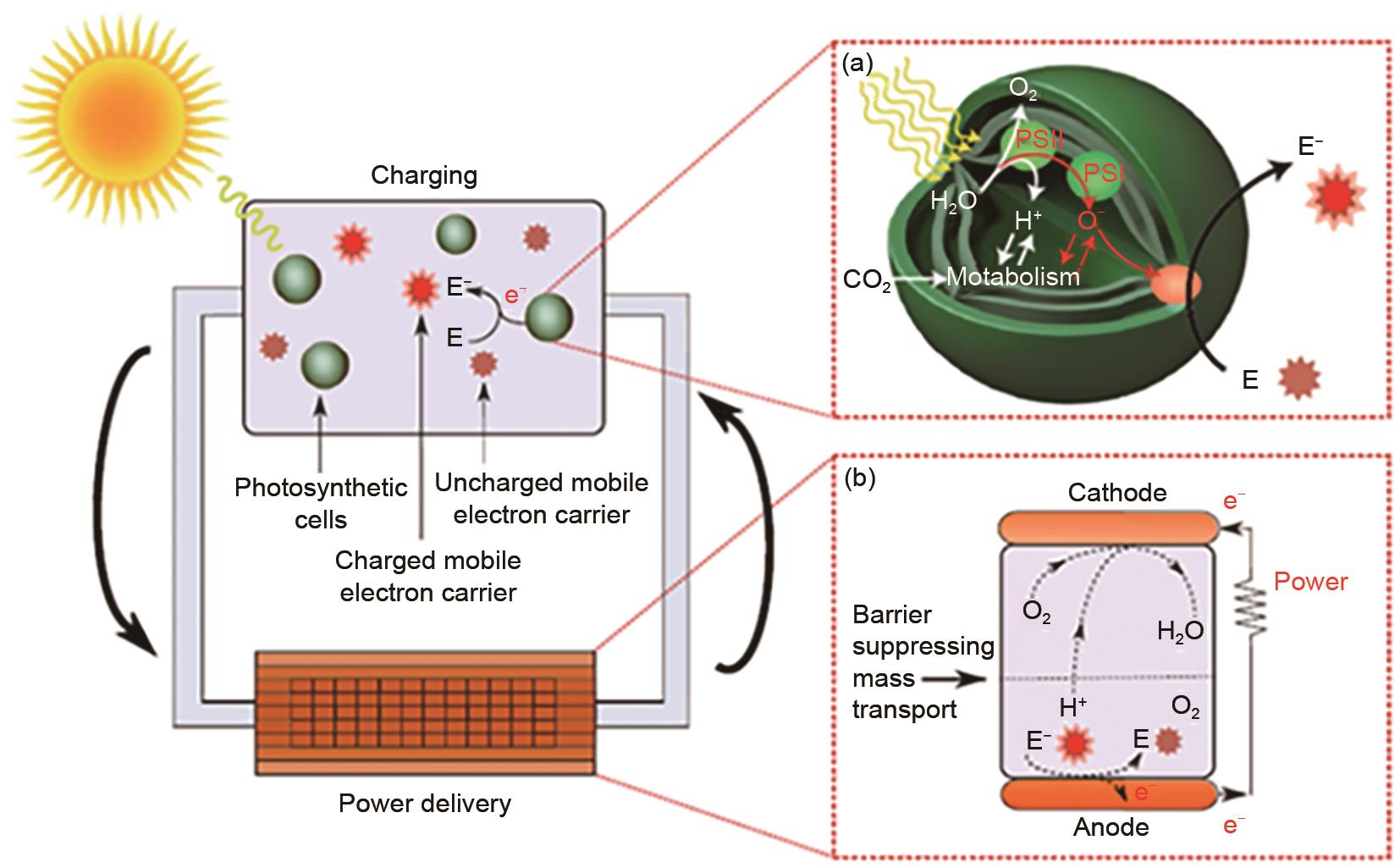
图9. 生物光电电池中的充电、电子迁移和介质输送过程; (a) 光合细胞通过光系统I和II (PSI,PSII)产生高能电子(e-),部分电子通过细胞的外电活性释放到外部环境中以减少载流子(E→E-);(b) 在功率输送装置中,减少的带电荷的载流子(E-)在电子与阳极接触的地方消耗,产生电流。质子(H+)扩散到阴极,在催化作用下产生水,而电子通过外电路到达阴极.(Copyright ? 2018 Nature)
Fig. 9. Process of charging, electron migration and medium transport in bio-photoelectric cells;(a) Photosynthetic cells produce high-energy electrons (e-) through photosystems I and II (PSI, PSII), and some electrons are released into external environment through external electrical activity of cell to reduce carriers(E→E-); (b) ) In power delivery device, reduced charged carriers (E-) are consumed where electrons are in contact with anode, generating current. Protons (H+) diffuse to cathode and produce water under catalysis, while electrons reach cathode through an external circuit. (Copyright ? 2018 Nature)