电池电极过程可视化与定量化技术的研究进展
Progresses in visualization and quantitative analysis of the electrode process in rechargeable batteries
电池电极过程可视化与定量化技术的研究进展 |
| 吕思奇, 李娜, 陈浩森, 焦树强, 宋维力 |
|
Progresses in visualization and quantitative analysis of the electrode process in rechargeable batteries |
| Siqi LYU, Na LI, Haosen CHEN, Shuqiang JIAO, Weili SONG |
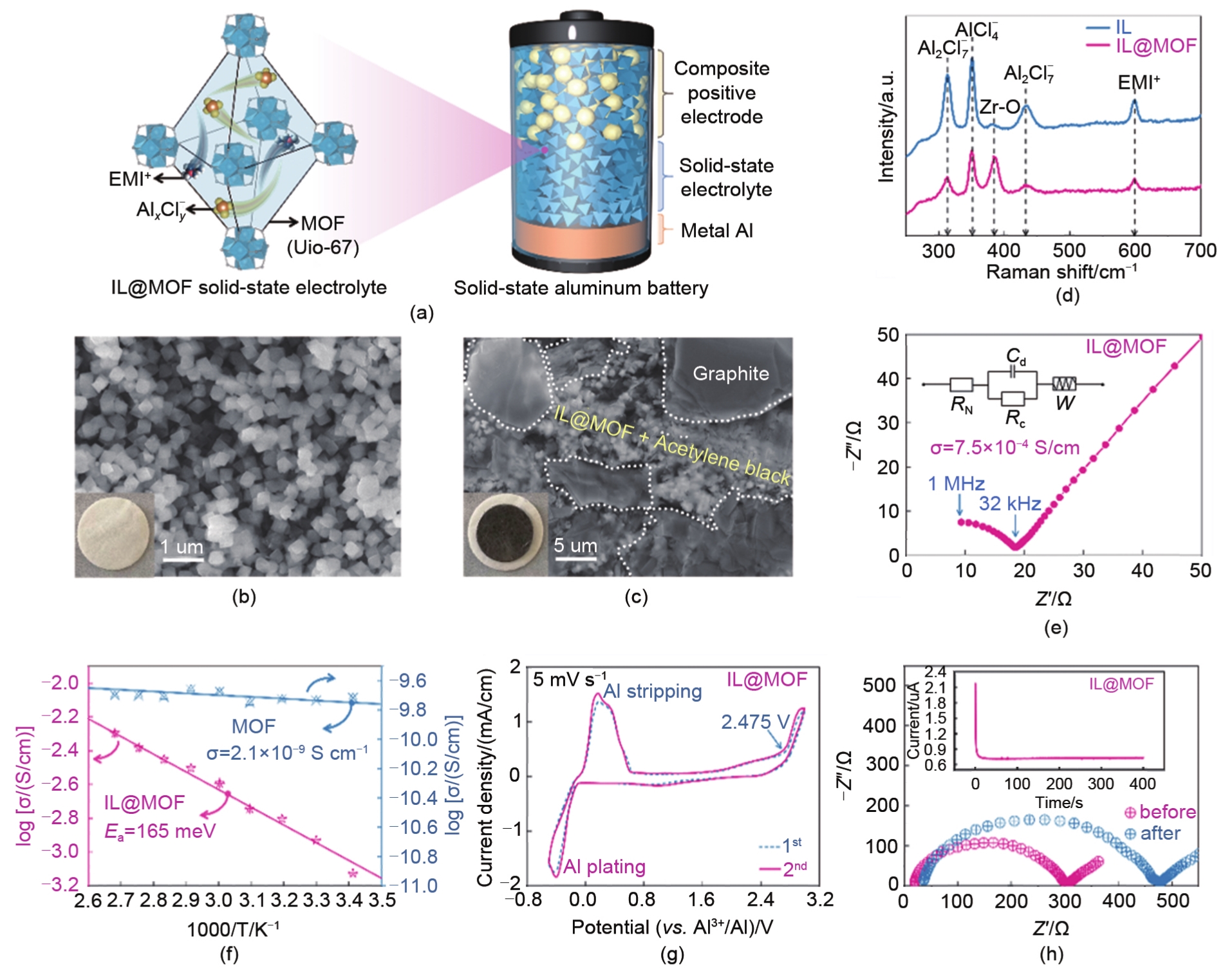
| 图23 (a) IL@MOF电解液内部结构放大示意图及准固态铝电池的结构[迁移的Al x Cl y-和EMIm+ 离子随机显示在Uio-67 MOF的孔隙中,准固态铝电池的复合正极由石墨(黄色球)、IL@MOF电解质(蓝色八面体)和乙炔黑(黑色球)组成];(b) IL@MOF颗粒的SEM形貌(插图为IL@MOF颗粒的照片);(c) 复合正极的SEM形貌(附图为准固态电解质/正极颗粒照片);(d) 原始IL和IL@MOF电解质的拉曼光谱;(e) 对称电池(Mo | IL@MOF | Mo)与等效电路在室温下的EIS图;(f) 纯MOF和IL@MOF的离子电导率的Arrhenius图;(g) 非对称电池(Al | IL@MOF | Mo)的前两个周期扫描速率为5 mV/s的CV曲线;(h) 对称电池(Al | IL@MOF | Al)极化前后的EIS图[ |
| Fig. 23 (a) schematic illustration of the magnification of internal structures in the IL@MOF electrolyte and the architecture of the quasi-solid-state aluminum battery. The migrating Al x Cl y-and EMIm+ ions are randomly displayed in the pores of the Uio-67 MOF, and the composite positive electrode in quasi-solid-state aluminum battery consists of graphite (yellow ball), IL@MOF electrolyte (blue octahedron) and acetylene black (black ball), (b) SEM morphology of IL@MOF particle, and the inset shows the photos of IL@MOF pellet, (c) SEM morphology of the composite positive electrode (inset: the photos of quasi-solid-state electrolyte/positive electrode pellets), (d) Raman spectra of the pristine IL and IL@MOF electrolyte, (e) EIS plot of the symmetric cell (Mo | IL@MOF | Mo) at room temperature with the equivalent circuit, (f) arrhenius plots for the ionic conductivity of pure MOF and IL@MOF, (g) CV curve for the first two cycles of the asymmetric cell (Al | IL@MOF | Mo) at the scan rate of 5 mV/s, (h) EIS plot of symmetric cells (Al | IL@MOF | Al) before and after polarization[ |

|