基于蒙特卡罗模拟的离子导体热力学与动力学特性
Investigating thermodynamic and kinetic properties of ionic conductors via Monte Carlo simulation
基于蒙特卡罗模拟的离子导体热力学与动力学特性 |
| 刘金平, 蒲博伟, 邹喆乂, 李铭清, 丁昱清, 任元, 罗亚桥, 李杰, 李亚捷, 王达, 何冰, 施思齐 |
|
Investigating thermodynamic and kinetic properties of ionic conductors via Monte Carlo simulation |
| Jinping LIU, Bowei PU, Zheyi ZOU, Mingqing LI, Yuqing DING, Yuan REN, Yaqiao LUO, Jie LI, Yajie LI, Da WANG, Bing HE, Siqi SHI |
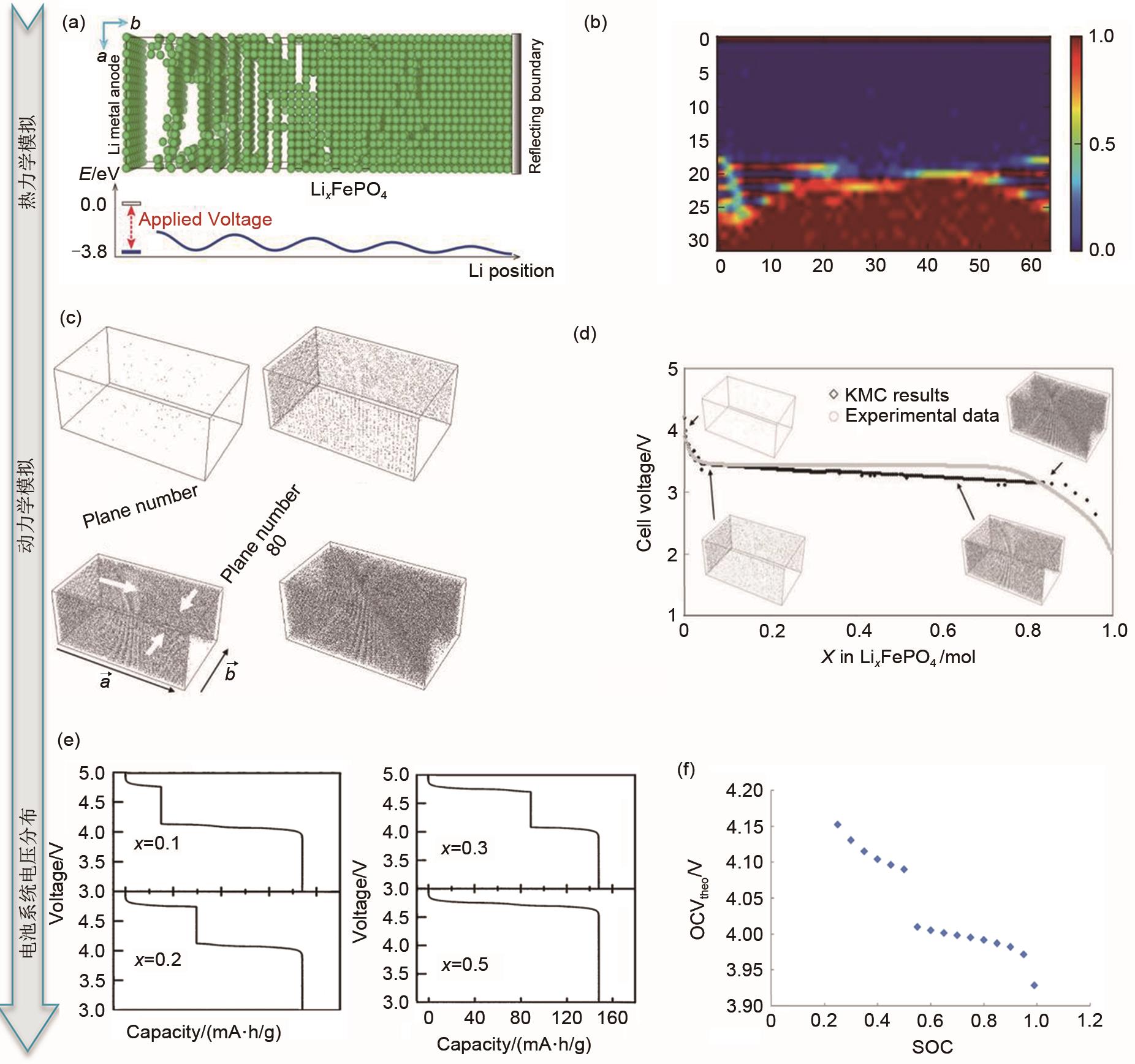
| 图7 MC模拟对正极材料相变与开路电压的分析:(a)MC模拟模型,上图为Li x FePO4 中Li的分布;下图为对应的能量图。绿色的球代表了锂离子[ |
| Fig. 7 MC simulation for phase transition and open circuit voltage of positive material: (a) MC simulation model (The above figure shows the distribution of Li ions in Li x FePO4, the corresponding energy diagram is shown below, the green balls represent Li ions); (b) the arrangement of Li ions along axis a without considering the interaction energy between charges. As shown in the figure, a clear phase boundary is formed between the LiFePO4 and FePO4 phases, and the Li0.5FePO4 phase shrinks to a limited region; (c) MC simulation of constant current discharge process of Li x FePO4 olivine nanocrystals at room temperature. The gray dots represent lithium atoms in the active particles with a surface current density of 0.5 A·m-2. The four groups are 0 s: initial solid solution, 0.0001 s: forming two Li-rich phases and combining together, 0.00056 s:Li-rich phase growth, 10.81 s: the Li-poor phase was almost completely consumed; (d) the relationship between the battery voltage and the concentration of Li ions in the active material; (e) the voltage distribution of Li/LiNi x Mn2-x O4 battery calculated by MC, x = 0.1, x = 0.2, x = 0.3, x = 0.5, respectively; (f) the relationship between the open circuit potential of a full battery (LiMn2O4 anode and carbon cathode) and the Ni occupation of the cathode during discharge |

|