基于蒙特卡罗模拟的离子导体热力学与动力学特性
Investigating thermodynamic and kinetic properties of ionic conductors via Monte Carlo simulation
基于蒙特卡罗模拟的离子导体热力学与动力学特性 |
| 刘金平, 蒲博伟, 邹喆乂, 李铭清, 丁昱清, 任元, 罗亚桥, 李杰, 李亚捷, 王达, 何冰, 施思齐 |
|
Investigating thermodynamic and kinetic properties of ionic conductors via Monte Carlo simulation |
| Jinping LIU, Bowei PU, Zheyi ZOU, Mingqing LI, Yuqing DING, Yuan REN, Yaqiao LUO, Jie LI, Yajie LI, Da WANG, Bing HE, Siqi SHI |
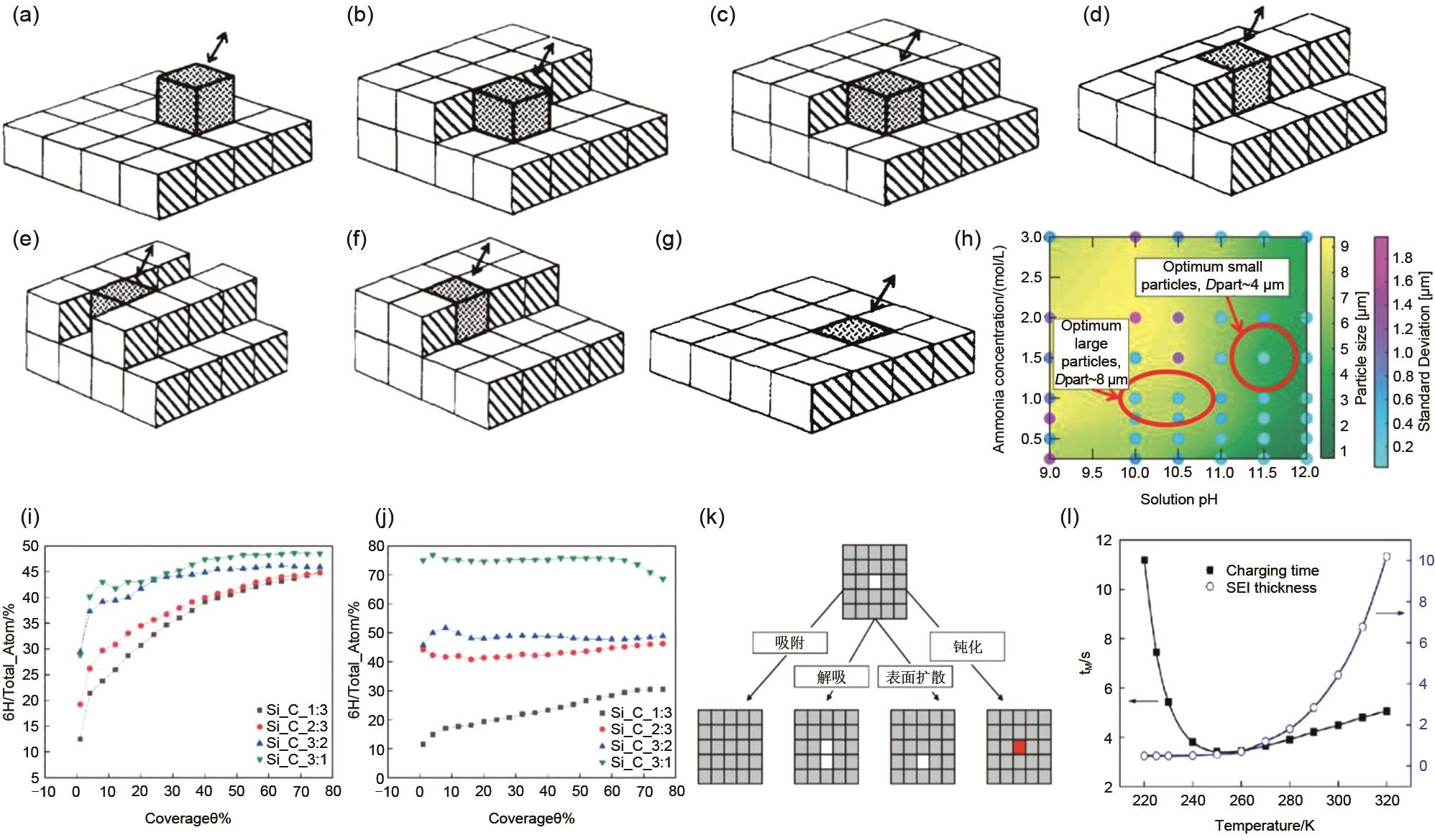
| 图13 (a)~(g)为简单立方晶格表面不同配位下的晶体生长过程[ |
| Fig.13 (a)-(g) the crystal growth process on the surface of a simple cubic lattice under different coordination; (h) Phase diagram of the dependence of crystal size on solution pH and ammonia content. The figure shows the mean particle size of the solution and its corresponding first standard deviation in the case of gaussian particle size distribution. All the data is taken from the computational model. Green areas indicate smaller secondary particles and yellow areas indicate larger secondary particles. The standard deviation of the secondary particle size distribution of the light blue dot is smaller, and the purple dot is larger. Optimum operating conditions, in terms of pH and ammonia content, for precipitating relatively larger (Dpart ~8 μm) and smaller (Dpart ~4 μm) sized secondary active particles, have also been highlighted within the figure (by red circles); (i) under different Si/C ratio conditions at 1100 K, the ratio of 6H-SiC in the growth of the two crystals at the deposition rate F =0.1 ML/s; (j) under different Si/C ratio conditions at 1400 K, the ratio of 6H-SiC in the growth of the two crystals at the deposition rate F =0.1 ML/s; (k) the generation process of SEI film is generally divided into adsorption, desorption, surface diffusion and passivation, etc. (l) the dependence of SEI film thickness, charging speed and temperature |

|