锂镧锆氧(LLZO)基固态锂电池界面关键问题研究进展
|
|
翟朋博, 常冬梅, 毕志杰, 赵宁, 郭向欣
|
Research progress on key interfacial issues in lithium lanthanum zirconium oxide-based solid-state
|
|
Pengbo ZHAI, Dongmei CHANG, Zhijie BI, Ning ZHAO, Xiangxin GUO
|
|
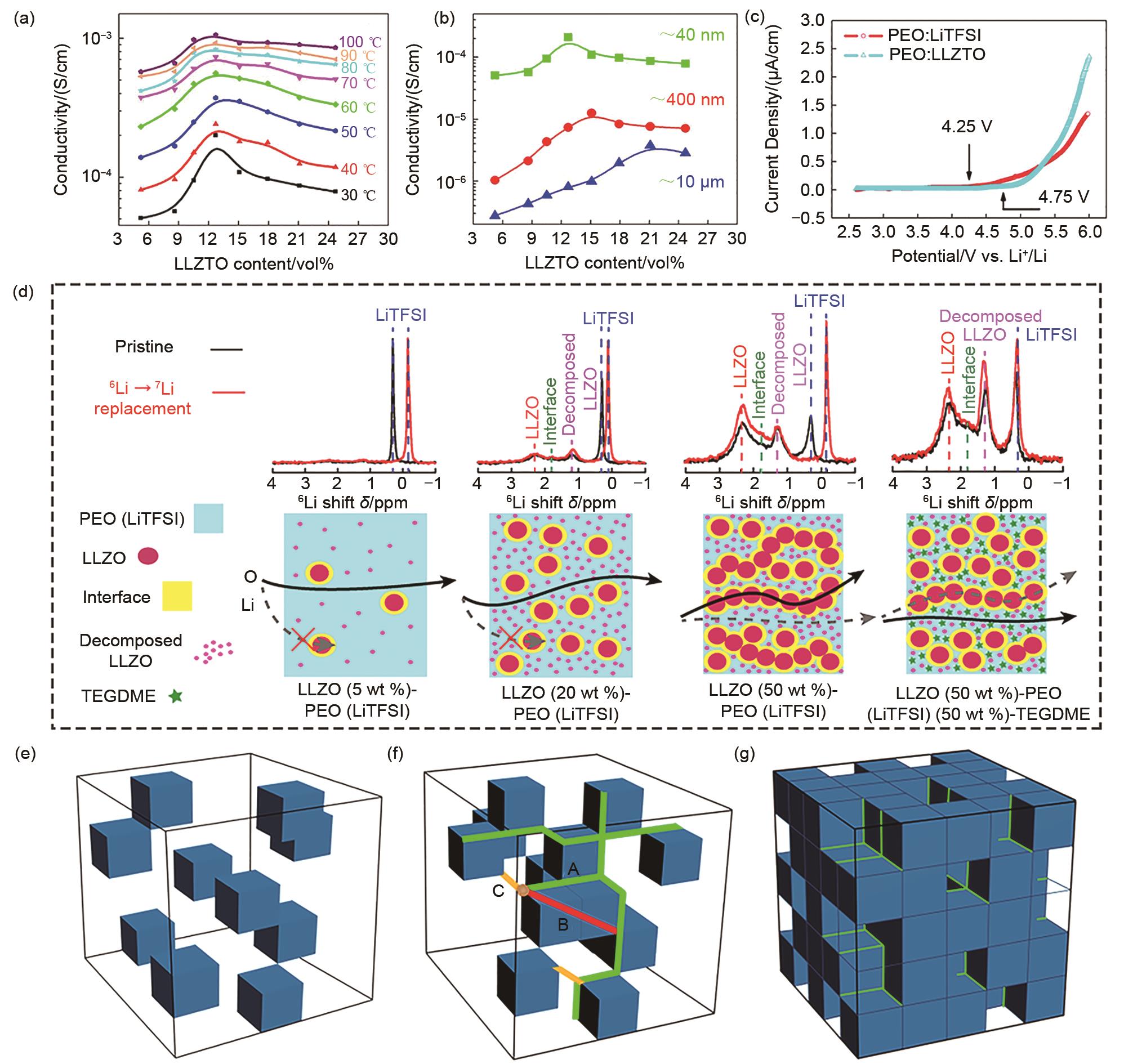
图3 (a) 不同体积分数的PEO/LLZTO复合固体电解质膜在不同温度下的锂离子电导率[44];(b) 使用不同尺寸的LLZTO颗粒作为添加剂的复合电解质膜的锂离子电导率随LLZTO体积分数的变化曲线;(c) PEO: LiTFSI: LLZTO和PEO: LLZTO复合固体电解质膜的LSV曲线;(d) 利用固态核磁技术探究PEO/LLZTO复合固体电解质中的锂离子传输路径[45];PEO/LLZO复合固体电解质中,LLZO添加量(e) 小于渗流阈值;(f) 达到渗流阈值;(g) 超过渗流阈值时的锂离子传输路径示意图[46]
|
Fig. 3 (a) Lithium-ion conductivity of PEO/LLZTO composite solid electrolyte membranes with different LLZTO volume fractions at different temperatures[44]; (b) The Li-ion conductivity as a function of LLZTO volume fraction for the LLZTO particles with different sizes; (c) LSV curves of PEO:LiTFSI: LLZTO and PEO: LLZTO composite electrolyte; (d) Exploring the lithium-ion transfer pathway in PEO/LLZTO composite solid electrolyte using solid-state nuclear magnetic technology[45]; Schematic diagrams of the lithium-ion transfer pathways when the fractions of LLZO is (e) less than the percolation threshold; (f) in the interval of percolation threshold (g) larger than the percolation threshold in the PEO/LLZO composite electrolyte[46]
|
|
|
|
|

