锂离子电池SEI多尺度建模研究展望
Multiscale modeling of the SEI of lithium-ion batteries
锂离子电池SEI多尺度建模研究展望 |
| 张慧敏, 王京, 王一博, 郑家新, 邱景义, 曹高萍, 张浩 |
|
Multiscale modeling of the SEI of lithium-ion batteries |
| Huimin ZHANG, Jing WANG, Yibo WANG, Jiaxin ZHENG, Jingyi QIU, Gaoping CAO, Hao ZHANG |
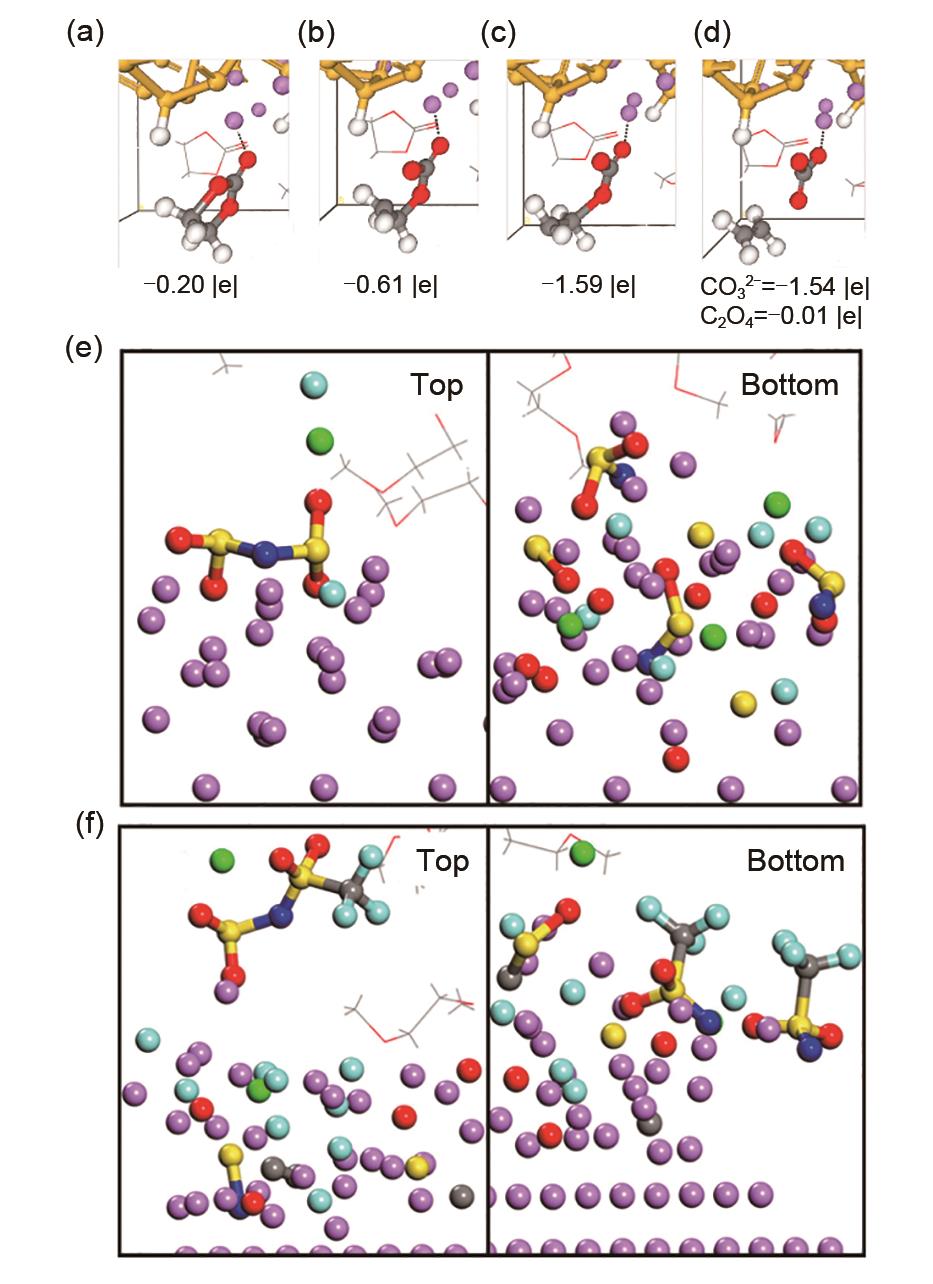
| 图4 EC的分解理论计算示意图:最初,一个电子从表面转移到(a)Li-EC,导致(b)Ccarbonyl —Oring 键断裂;随后,第二个电子转移到EC自由基阴离子(c),触发第二个Ccarbonyl —Oring 键断裂,(d)产生C2H4+CO32-对;给出了EC分子和CO32-/C2H4 产物的净电荷[ |
| Fig. 4 Decomposition of EC. Initially one electron is transferred from the surface to (a) Li-EC, causing a (b) Ccarbonyl —Oring bond to break. Subsequently, a second electron is transferred to (c) the EC- radical anion, triggering the breaking of a second Ccarbonyl —Oring bond and (d) generating the C2H4+CO32-pair. The net charges of the EC molecule and the CO32-/ C2H4 products are shown[ |

|