电解液添加剂稳定水系电池锌负极界面的研究进展
|
|
时文超, 刘宇, 张博冕, 李琪, 韩春华, 麦立强
|
Research progress and prospect on electrolyte additives for stabilizing the zinc anode interface in aqueous batteries
|
|
Wenchao SHI, Yu LIU, Bomian ZHANG, Qi LI, Chunhua HAN, Liqiang MAI
|
|
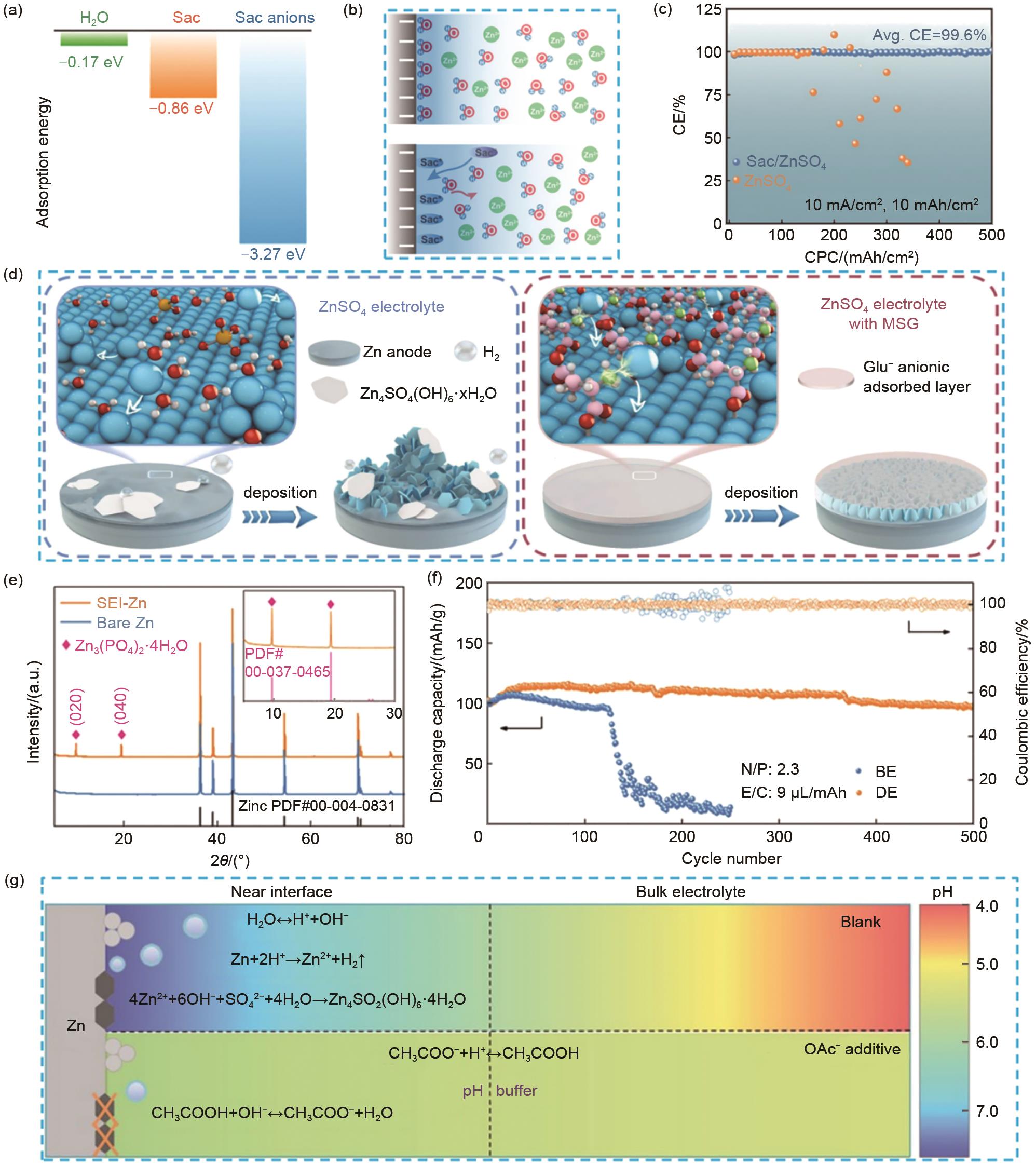
图4 (a) H2O、Sac和Sac阴离子在Zn (0001)表面的吸附能[69];(b) 锌负极界面在引入Sac添加剂前后的EDL结构示意图[69];(c) 在Sac/ZnSO4 和ZnSO4 电解液中Zn-Cu电池的库仑效率[69];(d) 在ZnSO4 和添加MSG的ZnSO4 电解液中,锌/电解液界面沉积行为示意图[78];(e) 在设计的电解液中循环20次前后锌电极的XRD谱图[71];(f) Zn-V2O5 电池在0.8 A/g的电流密度下的长循环性能和效率图[71];(g) 不同电解液pH演变和OAc-阴离子诱导的界面pH缓冲机制的示意图[79]
|
Fig. 4 (a) The adsorption energy of H2O, Sac, and Sac anions on Zn (0001) surface[69]; (b) The schematic descriptions of EDL structure before and after introducing Sac[69]; (c) The CE of Zn-Cu cells using Sac/ZnSO4 and ZnSO4 electrolyte[69]; (d) Schematic of Zn/electrolyte interface behaviors during Zn deposition in ZnSO4 and ZnSO4 electrolyte with MSG[78]; (e) XRD patterns of Zn electrode before and after 20 cycles in the designed electrolyte[71]; (f) Plot of long cycle performance and efficiency of Zn-V2O5 cells at 0.8 A/g current density[71]; (g) Schematic illustration of the pH evolution of different electrolytes and the interfacial pH buffer mechanism enabled by the OAc-anion[79]
|
|
|
|
|

