电解液添加剂稳定水系电池锌负极界面的研究进展
|
|
时文超, 刘宇, 张博冕, 李琪, 韩春华, 麦立强
|
Research progress and prospect on electrolyte additives for stabilizing the zinc anode interface in aqueous batteries
|
|
Wenchao SHI, Yu LIU, Bomian ZHANG, Qi LI, Chunhua HAN, Liqiang MAI
|
|
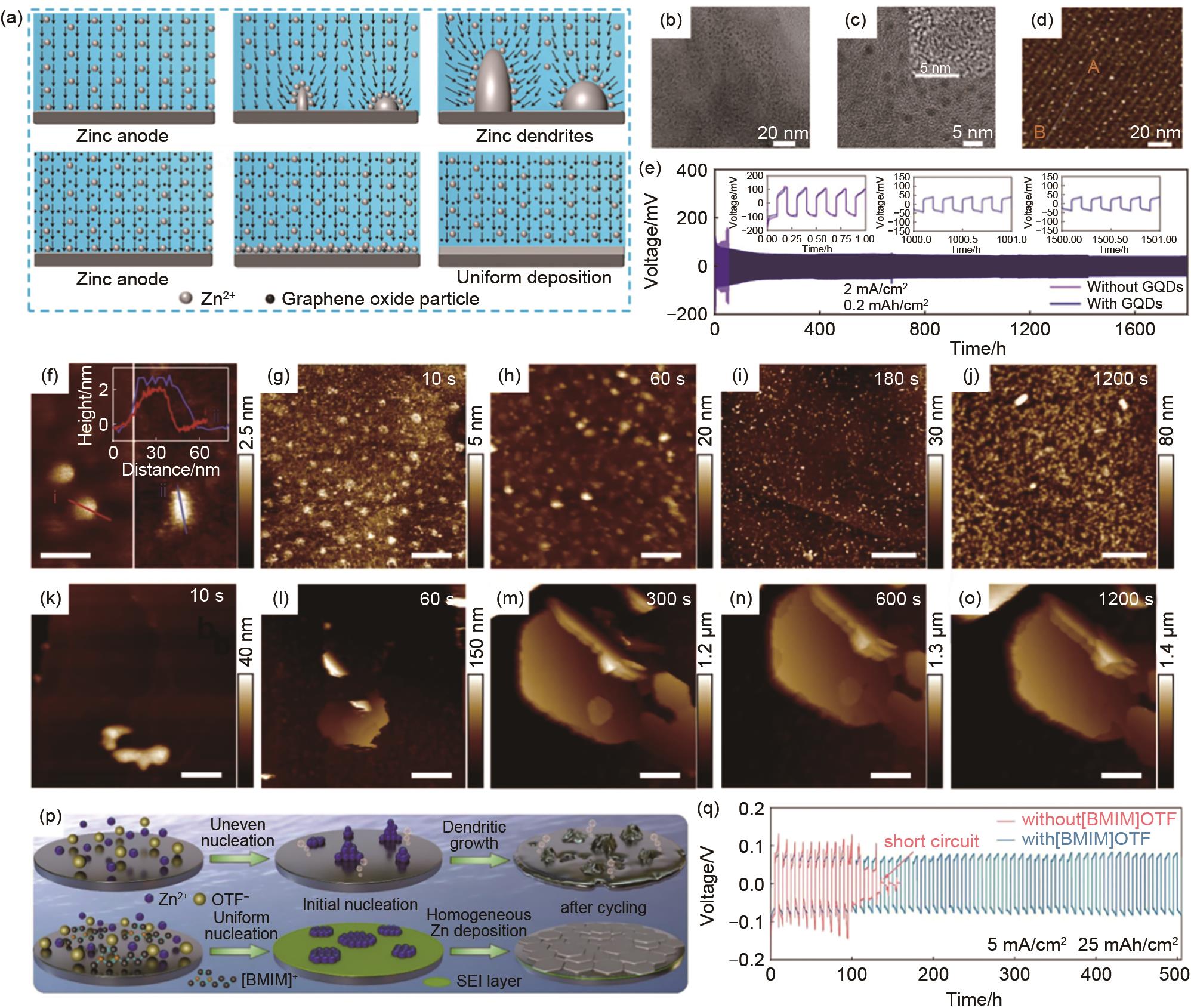
图7 (a) 添加和不添加GO添加剂时锌负极表面电场分布,矢量场描述了电场的方向[91];(b)~(c) 制备的石墨烯量子点TEM图和HRTEM(c中的插图)[92];(d) 云母衬底上GQDs的AFM图和初始线A-B对应的高度剖面[92];(e) 在2 mA/cm2 下,添加和不添加GQDs的Zn||Zn对称电池的长循环曲线和相应的电压曲线[92];(f) 在云母上的纯C3N4QDs(左)和在高定向热解石墨上ZnSO4 水系电解液中的C3N4QDs(右),插图为对应线条的高度轮廓[93];(g)~(o) 在100 μA/cm2 的电流密度下,含C3N4QDs (g)~(j) 和不含C3N4QDs(k)~(o) 的HOPG上Zn沉积的原位AFM图[93];(p) 使用[BMIM]OTF添加剂稳定锌沉积过程的原理图[95];(q) 在5 mA/cm2 和25 mAh/cm2 下的循环性能[95]
|
Fig. 7 (a) The electric field distribution on the surface of zinc anode with and without GO electrolyte additive. The vectorial field describes the direction of the electric field[91]; (b)—(c) TEM and HRTEM (insert in c) images of as-prepared GQDs[92]; (d) AFM image of the GQDs on the mica substrate and corresponding height profile of the origin line A-B[92]; (e) Long-term cycling profiles of the Zn||Zn symmetric cells with and without GQDs additive at 2 mA/cm2 and the corresponding voltage profiles[92]; (f) Pristine C3N4QDs on mica (left) and the C3N4QDs in ZnSO4 aqueous electrolyte on HOPG (right), the inset is the height profiles of the corresponding lines[93]; (g)—(o) In situ AFM images of Zn electrodeposits on HOPG with a current density of 100 μA/cm2 in electrolyte with C3N4QDs (g)—(j) and without C3N4QDs (k)—(o)[93]; (p) Schematic illustration of using [BMIM]OTF additive to stabilize the Zn deposition process[95]; (q) Cycling performances at 5 mA/cm2 and 25 mAh/cm2[95]
|
|
|
|
|

