石墨负极界面SEI膜与锂离子电池热失控
Solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on graphite anode correlated with thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries
石墨负极界面SEI膜与锂离子电池热失控 |
| 张佳怡, 翁素婷, 王兆翔, 王雪锋 |
|
Solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on graphite anode correlated with thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries |
| Jiayi ZHANG, Suting WENG, Zhaoxiang WANG, Xuefeng WANG |
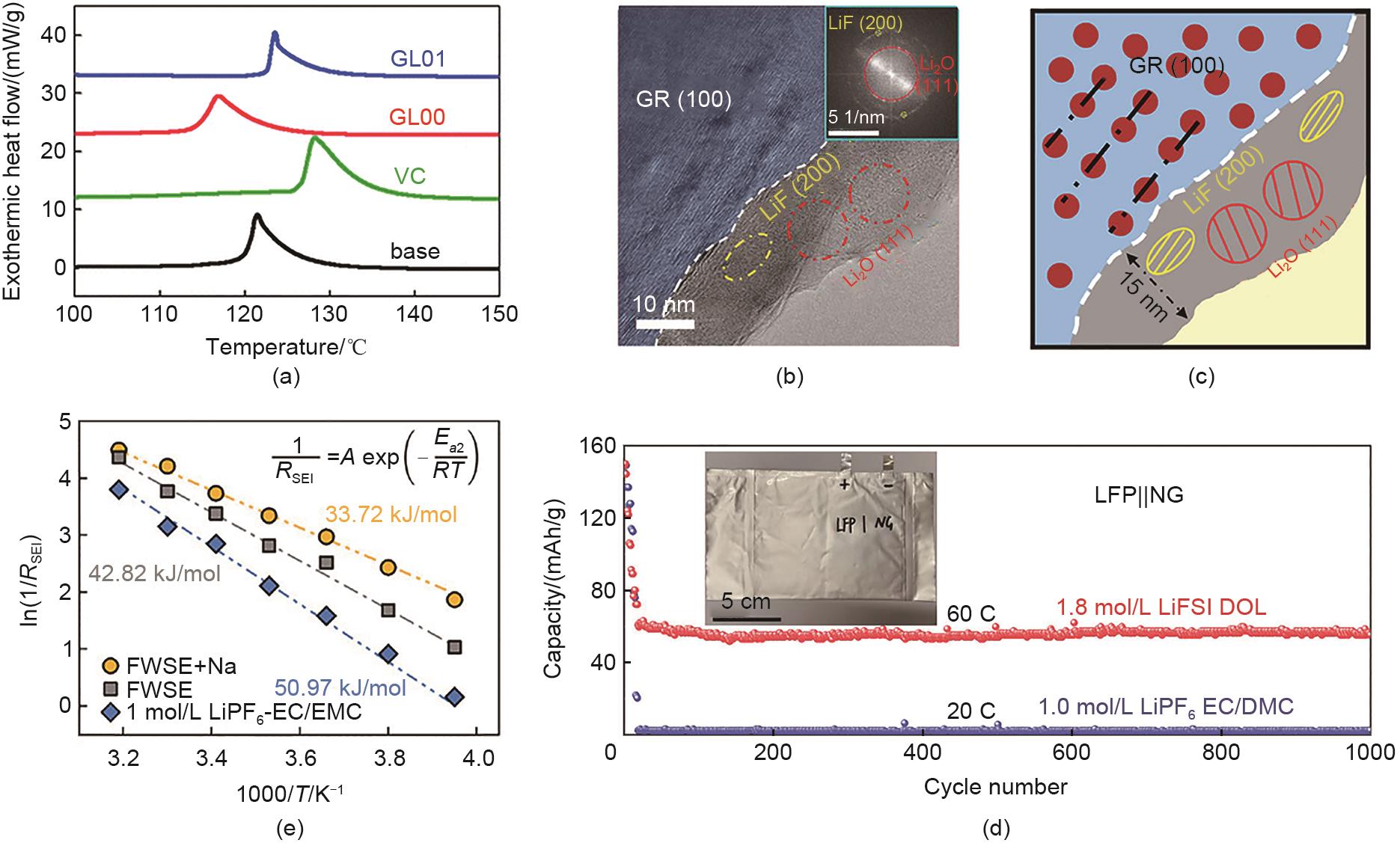
| 图7 (a) 在不含添加剂或含质量分数2% VC/乙交酯(GL00)/GL01添加剂的1 mol/L LiPF6 EC/EMC (体积比1∶2) 电解液中循环1周后的石墨负极DSC曲线[ |
| Fig. 7 (a) DSC curves of the fully de-lithiated graphite anodes collected from the cells cycled in 1 mol/L LiPF6 EC/EMC (volume ratio 1∶2) electrolytes with/without mass fraction 2% VC/glycolide (GL00)/GL01 additives[ |

|