储能科学与技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (3): 913-929.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0006
收稿日期:2025-01-02
修回日期:2025-03-15
出版日期:2025-03-28
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
张隆
E-mail:M202310308@xs.ustb.edu.cn;Zhang-xf2022@163.com;zhanglong25@mail.sysu.edu.cn
作者简介:贾欣媛(2001—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为高安全水系电池,E-mail:M202310308@xs.ustb.edu.cn基金资助:
Xinyuan JIA( ), Xianfu ZHANG(
), Xianfu ZHANG( ), Long ZHANG(
), Long ZHANG( )
)
Received:2025-01-02
Revised:2025-03-15
Online:2025-03-28
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Long ZHANG
E-mail:M202310308@xs.ustb.edu.cn;Zhang-xf2022@163.com;zhanglong25@mail.sysu.edu.cn
摘要:
锌粉作为水系锌金属电池的负极材料之一,因其成本低廉且在实际应用中能够实现较高的锌利用率而受到广泛关注。然而,锌粉的球形微观结构导致的高比表面积及高电化学活性使得锌粉负极在循环过程中易产生枝晶、发生析氢和腐蚀等副反应,严重影响综合电化学性能。本文系统总结了水系锌金属电池锌粉负极的最新研究进展,重点介绍了其在微观修饰与宏观设计方面的改性策略。在微观层面,通过锌粉本体设计、复合锌粉负极构筑及导电网络构建等策略,降低锌粉负极内部阻抗,减轻充放电过程中的体积膨胀,优化锌离子的沉积行为,从而提升其倍率性能和循环稳定性。在宏观层面,通过3D打印和静电纺丝等方法对锌粉材料的空间排列和结构布局进行高精度调控,进一步增强锌粉负极的有序性和功能性,显著改善了电池器件的循环稳定性和库仑效率。此外,流变设计策略通过缓解锌离子沉积应力,为抑制锌粉负极的副反应提供了新的思路。最后,展望了锌粉负极实现高性能和实用化的发展方向。重点强调了先进表征与理论计算对于深入理解锌粉负极失效机理的重要性;提出充分利用锌粉负极的优势,并协同多种改性策略,构筑高稳定性锌粉负极;同时提出突破规模化制备的技术与经济瓶颈是未来推动锌粉负极实用化发展的核心挑战,以期为高性能锌粉负极的进一步开发提供科学指导和理论支持。
中图分类号:
贾欣媛, 张先福, 张隆. 水系锌金属电池锌粉负极研究进展:微观修饰与宏观设计[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 913-929.
Xinyuan JIA, Xianfu ZHANG, Long ZHANG. Research progress on micromodification and macrodesign of Zn powder anodes in aqueous Zn metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 913-929.
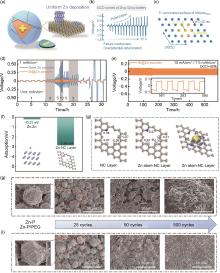
图4
不同包覆材料对锌粉负极的作用机制。MXene@Zn复合材料[33]:(a) MXene@Zn复合材料;(b) 1 mAh/cm2 下未改性的锌粉负极对称电池充放电曲线;(c) MXene(Ti3C2T x )(0002)面和锌沉积物(0002)面的原子排列以及晶格错配;Bi@Zn复合材料[34]:(d) 锌粉负极与Bi@Zn负极的倍率性能;(e) 使用Bi@Zn负极的对称电池在15 mA/cm2/7.5 mAh/cm2(DOD=45%)条件下循环585 h;氮掺杂碳涂层(NC)包覆[35]:(f) 锌(002)表面和NC层上锌的吸附能;(g) 氮掺杂碳层及其与锌原子复合层的模型,以及锌原子-氮掺杂碳层界面电荷密度模型;锌粉表面的聚乙二醇涂层[36]:(h),(i) 不同循环后Zn-P和Zn-P/PEG的SEM图像"
| 1 | 史冬梅, 王晶. 中国、日本、韩国电池技术和产业发展战略态势分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(2): 615-628. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0641. |
| SHI D M, WANG J. Analysis of battery technology and industry development strategy and trend in China, Japan, and South Korea[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 615-628. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0641. | |
| 2 | WANG G Y, ZHANG Q K, ZHANG X Q, et al. Electrolyte additive for interfacial engineering of lithium and zinc metal anodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2025, 15(2): 2304557. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202304557. |
| 3 | 徐冲, 徐宁, 蒋志敏, 等. 锂离子电池产气机制及基于电解液的抑制策略[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(7): 2119-2133. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0212. |
| XU C, XU N, JIANG Z M, et al. Mechanisms of gas evolution and suppressing strategies based on the electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2119-2133. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0212. | |
| 4 | JIANG D, WANG X F, YIN S, et al. Solid-state electrolytes with vertically aligned Li+ transport channels for lithium batteries: A comprehensive review[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2025, 74: 103986. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103986. |
| 5 | ZHANG X F, ZHANG L, JIA X Y, et al. Design strategies for aqueous zinc metal batteries with high zinc utilization: From metal anodes to anode-free structures[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2024, 16(1): 75. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-023-01304-1. |
| 6 | ZHU Y H, LIANG G J, CUI X, et al. Engineering hosts for Zn anodes in aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(2): 369-385. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE03584K. |
| 7 | CHEN S, OUYANG K F, LIU Y F, et al. Non-epitaxial electrodeposition of overall 99% (002) plane achieves extreme and direct utilization of 95% Zn anode and by-product as cathode[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(42): e202409303. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202409303. |
| 8 | 鲁杰, 杜娴, 师玉璞, 等. 高稳定水系锌离子电池PANI包覆钒化合物阴极材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(1): 42-53. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0621. |
| LU J, DU X, SHI Y P, et al. PANI-coated vanadium compound as high-stable aqueous zinc-ion batteries cathode material[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 42-53. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0621. | |
| 9 | GAO Y, YANG N T, BU F, et al. Double-sided engineering for space-confined reversible Zn anodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(5): 1894-1903. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE04292H. |
| 10 | ZHANG M H, HUA H M, DAI P P, et al. Dynamically interfacial pH-buffering effect enabled by N-methylimidazole molecules as spontaneous proton pumps toward highly reversible zinc-metal anodes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(15): 2208630. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202208630. |
| 11 | ZHENG X W, SONG Z Y, ZHANG D, et al. Biomimetic quasi-skin-capillary structure engineering of ionic-electronic conducting full-chain networks for stable zinc powder anodes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(4): 2413990. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202413990. |
| 12 | YAO R, ZHAO Y X, WANG L M, et al. A corrosion-free zinc metal battery with an ultra-thin zinc anode and high depth of discharge[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(9): 3112-3122. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE04320G. |
| 13 | 吴贤文, 龙凤妮, 向延鸿, 等. 中性或弱酸性体系下锌基水系电池负极材料研究进展[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(11): 1983-2001. DOI: 10.7536/PC210453. |
| WU X W, LONG F N, XIANG Y H, et al. Research progress of anode materials for zinc-based aqueous battery in a neutral or weak acid system[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(11): 1983-2001. DOI: 10.7536/PC210453. | |
| 14 | LIU G G, TANG Y C, WEI Y, et al. Hydrophobic ion barrier-enabled ultradurable Zn (002) plane orientation towards long-life anode-less Zn batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(40): e202407639. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202407639. |
| 15 | YANG F H, YUWONO J A, HAO J N, et al. Understanding H2 evolution electrochemistry to minimize solvated water impact on zinc-anode performance[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(45): 2206754. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202206754. |
| 16 | YU H M, CHEN D P, LI Q Y, et al. In situ construction of anode-molecule interface via lone-pair electrons in trace organic molecules additives to achieve stable zinc metal anodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(22): 2300550. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202300550. |
| 17 | ZHANG S J, HAO J N, WU H, et al. Protein interfacial gelation toward shuttle-free and dendrite-free Zn-iodine batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(35): 2404011. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202404011. |
| 18 | ZONG Q, LI R L, WANG J Y, et al. Tailoring the whole deposition process from hydrated Zn2+ to Zn0 for stable and reversible Zn anode[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(41): e202409957. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202409957. |
| 19 | FU B, LIU G Q, ZHANG Y J, et al. Zn powder-based anodes for aqueous Zn metal batteries: Strategies, structures, and perspectives[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(7): 3292-3307. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.4c00628. |
| 20 | ZHANG Z C, WANG X W, KE J Q, et al. Approaching 100% comprehensive utilization rate of ultra-stable Zn metal anodes by constructing chitosan-based homologous gel/solid synergistic interface[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(17): 2313150. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202313150. |
| 21 | LI Q, TANG S H, LUO R Y, et al. Regulating the local chemical environment of Zn powder surface by multi-site anchoring effect to achieve highly-stable Zn anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 66: 103229. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103229. |
| 22 | LI Q, WANG Y B, MO F N, et al. Calendar life of Zn batteries based on Zn anode with Zn powder/current collector structure[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(14): 2003931. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202003931. |
| 23 | LIU D S, XU X L, MENG S B, et al. Harnessing the potential of Zn powder anodes: Innovations and future directions in aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2024, 7(6): e202400071. DOI: 10.1002/batt.202400071. |
| 24 | XIAO J, YUAN C B, XIANG L, et al. Design strategies toward high-utilization zinc anodes for practical zinc-metal batteries[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2024, 30(21): e202304149. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202304149. |
| 25 | YANG Z X, WANG Z Y, CAO J L, et al. Stabilizing zinc powder anodes via bifunctional MXene towards flexible zinc-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 680(Pt A): 657-664. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.10.145. |
| 26 | HUANG J Y, FENG R Q, WU J C, et al. Structural design strategies of zinc powder anode towards rechargeable zinc-based batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2025, 74: 103934. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103934. |
| 27 | CAO P H, MENG Q, LI C C, et al. Dimensionality reduction engineering to construct a highly stable Zn powder anode in aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2024, 7(2): 479-486. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c02385. |
| 28 | ZHAO X, GAO Y, CAO Q H, et al. A high-capacity gradient Zn powder anode for flexible Zn-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(38): 2301741. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202301741. |
| 29 | LI J B, CHENG Z X, LI Z, et al. Rational design of zinc powder anode with high utilization and long cycle life for advanced aqueous Zn-S batteries[J]. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(7): 2436-2444. DOI: 10.1039/D3MH00278K. |
| 30 | WU J C, SHEN X C, ZHOU H T, et al. Zn-In alloying powder solvent free electrode toward high-load ampere-hour aqueous Zn-Mn secondary batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(17): 2308541. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202308541. |
| 31 | LI A X, CHEN M F, TIAN Q H, et al. Conquering poor reversibility of zinc powder electrode through in situ surface engineering towards long-life zinc-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 965: 171337. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171337. |
| 32 | KANG H, KIM S H, AHN D B, et al. Liquid metal-skinned Zn powder anodes enabled by capillary suspension[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(6): 2816-2825. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.4c01009. |
| 33 | LI X L, LI Q, HOU Y, et al. Toward a practical Zn powder anode: Ti3C2Tx MXene as a lattice-match electrons/ions redistributor[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(9): 14631-14642. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano. 1c04354. |
| 34 | CHEN H L, ZHANG W Y, YI S, et al. Zinc iso-plating/stripping: Toward a practical Zn powder anode with ultra-long life over 5600 h[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(9): 3146-3156. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE04333A. |
| 35 | LIN Y H, ZHANG M, HU Y Z, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon coated zinc as powder-based anode with PVA-gel electrolyte enhancing cycling performance for zinc-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 472: 145136. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145136. |
| 36 | HUYAN X D, YI Z H, SANG Z Y, et al. Polyethylene glycol coating on zinc powder surface: Applications in dendrite-free zinc anodes with enhanced utilization rate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 614: 156209. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.156209. |
| 37 | BAYAGUUD A, LUO X, FU Y P, et al. Cationic surfactant-type electrolyte additive enables three-dimensional dendrite-free zinc anode for stable zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(9): 3012-3020. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c01792. |
| 38 | YAN M D, DONG N, ZHAO X S, et al. Tailoring the stability and kinetics of Zn anodes through trace organic polymer additives in dilute aqueous electrolyte[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(9): 3236-3243. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.1c01418. |
| 39 | ZHANG Q, LUAN J Y, FU L, et al. The three-dimensional dendrite-free zinc anode on a copper mesh with a zinc-oriented polyacrylamide electrolyte additive[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(44): 15841-15847. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201907830. |
| 40 | WANG J X, ZHANG H, YANG L Z, et al. In situ implanting 3D carbon network reinforced zinc composite by powder metallurgy for highly reversible Zn-based battery anodes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(10): e202318149. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202318149. |
| 41 | LIN Y H, HU Y Z, ZHANG S, et al. Binder-free freestanding 3D Zn-graphene anode induced from commercial zinc powders and graphene oxide for zinc ion battery with high utilization rate[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(12): 15222-15232. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.2c02872. |
| 42 | LIU G Q, FU B, LIU Z X, et al. Copper oxide-modified highly reversible Zn powder anode for aqueous Zn metal batteries[J]. Rare Metals, 2024, 43(10): 5005-5016. DOI: 10.1007/s12598-024-02869-5. |
| 43 | ZENG L, HE J, YANG C Y, et al. Direct 3D printing of stress-released Zn powder anodes toward flexible dendrite-free Zn batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 54: 469-477. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2022.10.061. |
| 44 | YANG J Y, XU X, GAO Y, et al. Ultra-stable 3D-printed Zn powder-based anode coated with a conformal ion-conductive layer[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(40): 2301997. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202301997. |
| 45 | ZHU J B, HU W X, NI J F, et al. High areal energy zinc-ion micro-batteries enabled by 3D printing[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 196: 183-189. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2024.01.053. |
| 46 | LU H Y, HU J S, ZHANG Y, et al. 3D cold-trap environment printing for long-cycle aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(9): 2209886. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202209886. |
| 47 | LU H Y, HU J S, ZHANG K Q, et al. Microfluidic-assisted 3D printing zinc powder anode with 2D conductive MOF/MXene heterostructures for high-stable zinc-organic battery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(6): 2309753. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202309753. |
| 48 | SHA L, SUI B B, WANG P F, et al. 3D network of zinc powder woven into fibre filaments for dendrite-free zinc battery anodes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 481: 148393. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.148393. |
| 49 | LIU Q, YU Z L, ZHOU R, et al. A semi-liquid electrode toward stable Zn powder anode[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(5): 2210290. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202210290. |
| 50 | YANG Z F, ZHANG Q, LI W B, et al. A semi-solid zinc powder-based slurry anode for advanced aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(3): e202215306. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202215306. |
| 51 | CAO C H, ZHOU K Q, DU W C, et al. Designing soft solid-like viscoelastic zinc powder anode toward high-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(38): 2301835. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202301835. |
| 52 | HUANG X Y, HOU H Q, YU B B, et al. Fully biodegradable and long-term operational primary zinc batteries as power sources for electronic medicine[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(6): 5727-5739. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c12125. |
| 53 | QIN L, ZHOU J Q, SUN M Z, et al. Comprehensive review for zinc powder anodes: Significance, optimizing design, and industrial feasibility in zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2025, 74: 103917. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103917. |
| [1] | 时文超, 刘宇, 张博冕, 李琪, 韩春华, 麦立强. 电解液添加剂稳定水系电池锌负极界面的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
