储能科学与技术 ›› 2022, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (2): 467-486.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0483
冯晓晗1( ), 孙杰1,2(
), 孙杰1,2( ), 何健豪2, 魏义华2, 周成冈1(
), 何健豪2, 魏义华2, 周成冈1( ), 孙睿敏1(
), 孙睿敏1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-15
修回日期:2021-10-19
出版日期:2022-02-05
发布日期:2022-02-08
通讯作者:
周成冈,孙睿敏
E-mail:2215852440@qq.com;sunjie898@aliyun.com;cgzhou@cug.edu.cn;rmsun@cug.edu.cn
作者简介:冯晓晗(1996—),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为磷酸铁锂及普鲁士蓝(白)正极材料,E-mail:基金资助:
Xiaohan FENG1( ), Jie SUN1,2(
), Jie SUN1,2( ), Jianhao HE2, Yihua WEI2, Chenggang ZHOU1(
), Jianhao HE2, Yihua WEI2, Chenggang ZHOU1( ), Ruimin SUN1(
), Ruimin SUN1( )
)
Received:2021-09-15
Revised:2021-10-19
Online:2022-02-05
Published:2022-02-08
Contact:
Chenggang ZHOU,Ruimin SUN
E-mail:2215852440@qq.com;sunjie898@aliyun.com;cgzhou@cug.edu.cn;rmsun@cug.edu.cn
摘要:
锂离子二次电池(LIBs)是当今新能源领域的主流储能器件。磷酸铁锂(LiFePO4)凭借高能量密度、低成本、稳定的充放电平台、环境友好、安全性高等优势,成为应用最为广泛的锂离子电池正极材料之一。如何提高其输出功率以及低温下的能量密度和使用寿命,是磷酸铁锂正极材料面临的主要挑战。本文通过对近期相关文献的探讨,归纳总结了近年来针对磷酸铁锂正极材料的主流改性策略。详细分析了元素掺杂提高材料电化学性能的内在机理,梳理了不同包覆剂对磷酸铁锂的保护机制,这两种手段可有效提高磷酸铁锂正极材料的电子电导率和离子扩散速率,实现材料更高的能量密度、更长的循环寿命和更高的倍率性能。此外也总结了磷酸铁锂常见补锂添加剂的特性及其对正极首圈库仑效率和放电比容量的改善行为。综合分析表明,多种元素共掺杂,先进碳材料包覆和高容量补锂材料的添加有望成为提升磷酸铁锂电化学性能的重要策略。最后,对磷酸铁锂正极未来在商业化生产改良和开发柔性电极等方向的发展前景和面临的挑战进行了展望。
中图分类号:
冯晓晗, 孙杰, 何健豪, 魏义华, 周成冈, 孙睿敏. 磷酸铁锂正极材料改性研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(2): 467-486.
Xiaohan FENG, Jie SUN, Jianhao HE, Yihua WEI, Chenggang ZHOU, Ruimin SUN. Research progress in LiFePO4 cathode material modification[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(2): 467-486.
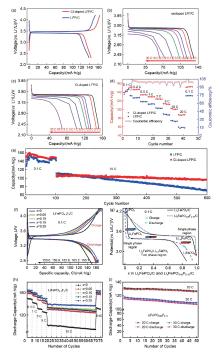
图5
(a) Cl-LFP/C和LFP/C电极材料在0.1 C时的首圈充放电曲线;(b) LFP/C;(c) Cl-LFP/C在不同电流密度下的放电曲线;(d) Cl-LFP/C正极材料和LFP/C正极材料的倍率性能;(e) Cl-LFP/C和LFP/C正极材料分别在0.1 C和10 C电流密度下的循环性能[28];(f) 未掺杂和掺杂F的LiFePO4/C样品在0.1 C倍率下的初始充放电曲线;(g) LiFePO4/C和LiFePO4-xFx/C(x=0.15)样品在0.1 C倍率下的初始充/放电曲线;(h) 未掺杂和掺杂F的LiFePO4/C样品的倍率和循环性能;(i) LiFePO4-xFx/C(x = 0.15)样品在20 C、30 C高倍率下的循环性能[29]"
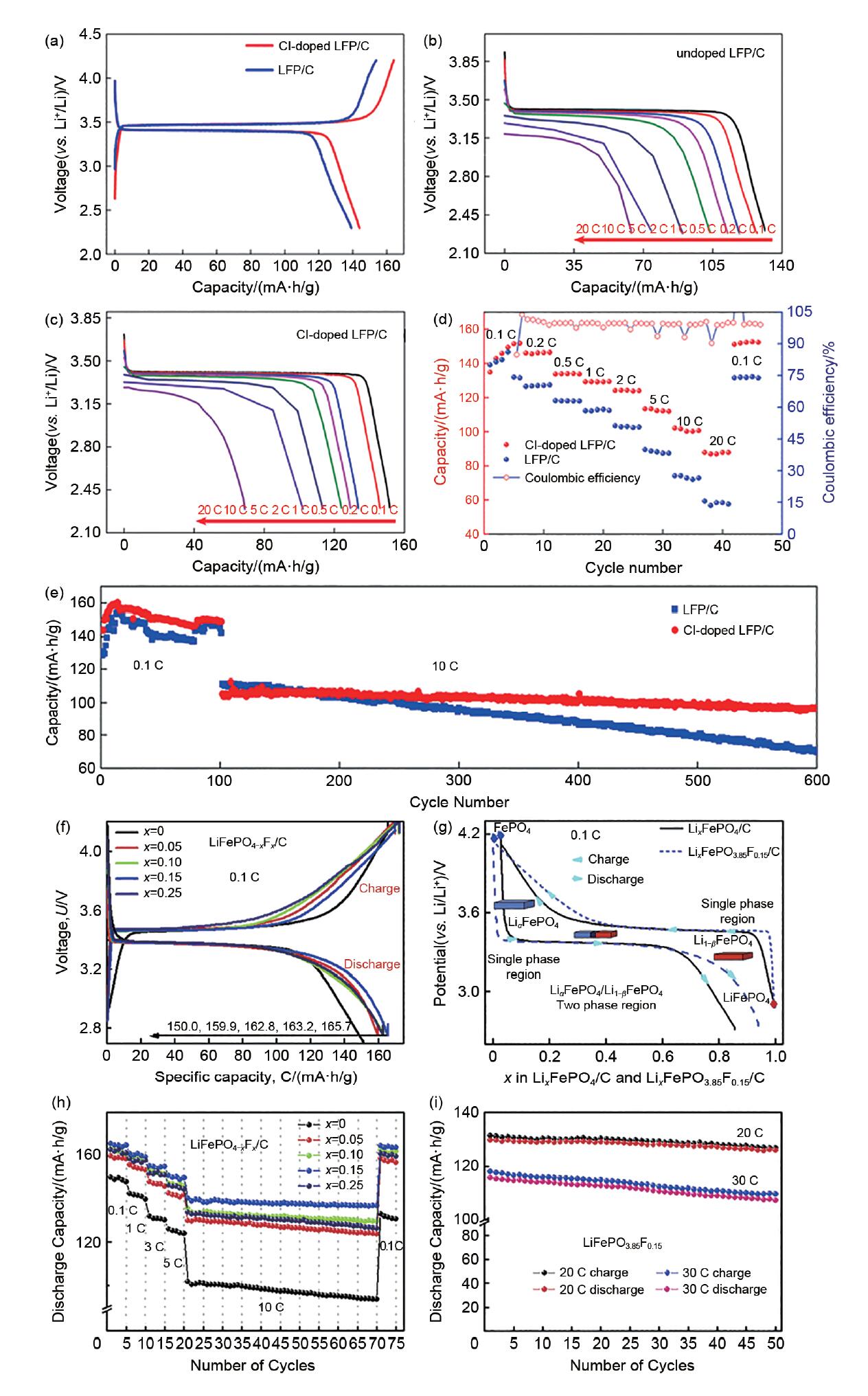
表1
磷酸铁锂元素掺杂改性电化学性能概述"
| 掺杂元素 | 掺杂位点 | 最佳掺杂量 | 电化学性能(初始容量;循环性能) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na[ | Li位 | Li0.99Na0.01FePO4 | 80.9 mA·h/g(10 C);86.7%(10 C,500圈) |
| Nb[ | Li位 | Li0.95Nb0.01FePO4 | 96.7 mA·h/g(10 C);96%(10 C,200圈) |
| Al[ | Li位 | Li0.97Al0.01FePO4 | 95 mA·h/g(0.2 C) |
| Mn[ | Fe位 | LiFe0.77Mn0.23PO4 | 80.9 mA·h/g(1 C);84%(1 C,100圈) |
| Mo[ | Fe位 | LiFe0.98Mn0.02PO4 | 141.5 mA·h/g(0.1 C);98%(0.1 C,100圈) |
| V[ | Fe位 | LiFe0.95V0.05PO4 | 119 mA·h/g(1500 mA/g);98%(1500 mA/g,100圈) |
| Ti[ | Fe位 | LiFe0.98Ti0.02PO4 | 160 mA·h/g(0.2 C);98%(0.2 C,50圈) |
| S[ | O位 | LiFePO3.78S0.22 | 112.7 mA·h/g(10 C);98%(0.2 C,50圈) |
| Cl[ | O位 | LiFePO3.98Cl0.02 | 164.1 mA·h/g(0.1 C);105.3 mA·h/g(10 C);91.5%(10 C,500圈) |
| F[ | O位 | LiFePO3.85F0.15 | 165.7 mA·h/g(0.1 C);115.7 mA·h/g(30 C);92.8%(30 C,50圈) |
| Mg&Ti[ | Mg(Fe位) Ti(Fe位) | LiFe0.985Mg0.005Ti0.01PO4 | 161.5 mA·h/g(0.2 C);139.8 mA·h/g(5 C);92.9%(5 C,100圈) |
| Zr&Co[ | Zr(Li位) Co(Fe位) | Li0.99Zr0.0025Fe0.98Co0.02PO4 | 139.9 mA·h/g(0.1 C);85%(0.1 C,50圈) |
| Ni&Mn[ | Ni(Fe位) Mn(Fe位) | LiFe0.95Ni0.02Mn0.03PO4/C | 164.3 mA·h/g(0.1 C);146 mA·h/g(1 C);98.7%(1 C,100圈) |
| V&F[ | V(Fe位) F(O位) | LiFe0.96V0.02PO3.97F0.06 | 165.7 mA·h/g(0.1 C);154.9 mA·h/g(1 C);95.7%(1 C,500圈) |
| V&Y[ | Y(Fe位) F(O位) | LiFe0.95V0.033PO3.95F0.1 | 148.6 mA·h/g(5 C);96.88%(5 C,700圈) |
| Ni&Mn&Co[ | Ni(Fe位) Mn(Fe位) Co(Fe位) | LiFe0.84Ni0.06Co0.06Mn0.04PO4 | 160.1 mA·h/g(0.1 C);110.8 mA·h/g(10 C);98.3%(10 C,50圈) |
| 1 | LI H, PENG L, WU D B, et al. Ultrahigh-capacity and fire-resistant LiFePO4-based composite cathodes for advanced lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(10): 1802930. |
| 2 | 刘仕强, 王芳, 马天翼, 等. 磷酸铁锂动力电池备电工况寿命试验研究及分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 638-644. |
| LIU S Q, WANG F, MA T J, et al. Cycle life test and analysis of lithium iron phosphate based traction batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 638-644. | |
| 3 | DAI Y, XU Z D, HUA D, et al. Theoretical-molar Fe3+ recovering lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries: An acid-free, efficient, and selective process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 396: 122707. |
| 4 | 田柳文, 于华, 章文峰. 锂离子电池的明星材料磷酸铁锂: 基本性能、优化改性及未来展望[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(11): 3561-3579. |
| TIAN L W, YU H, ZHANG W F. The star material of Lithium ion batteries, LiFePO4 optimized modification and future prospects[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(11): 3561-3579. | |
| 5 | 范茂松, 金翼, 杨凯, 等. 退役LiFePO4电池性能测评及储能应用[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(2): 408-414. |
| FAN M S, JIN Y, YANG K, et al. Testing of the performance and energy-storage applied for retired LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(2): 408-414. | |
| 6 | 李雨, 赵慧春, 白莹, 等. 高能量密度层状富锂锰基正极材料的改性研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2018, 7(3): 395-403. |
| LI Y, ZHAO H C, BAI Y, et al. Progress in the modification of lithium-rich manganese-based layered cathode materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(2): 408-414. | |
| 7 | 王栋, 邓莉莉, 杜光超, 等. 锂离子电池正极材料掺杂和表面包覆研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(1): 43-48. |
| WANG D, DEN L L, DU G C, et al. Review of doping and surface coating of cathode materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 43-48. | |
| 8 | HUANG Y Y, ZHU Y C, FU H Y, et al. Mg-pillared LiCoO2: Towards stable cycling at 4.6 V[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Ed in English, 2021, 60(9): 4682-4688. |
| 9 | KOYAMA Y, UYAMA T, ORIKASA Y, et al. Hidden two-step phase transition and competing reaction pathways in LiFePO4[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(7): 2855-2863. |
| 10 | WANG T Z, WU X G, XU S B, et al. Performance of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle under low temperature condition and economy analysis of battery pre-heating[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 401(8): 245-254. |
| 11 | NITTA N, WU F X, LEE J T, et al. Li-ion battery materials: Present and future[J]. Materials Today, 2015, 18(5): 252-264. |
| 12 | JI Y, ZHANG Y C, WANG C Y. Li-ion cell operation at low temperatures[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(4): A636-A649. |
| 13 | MA S, JIANG M D, TAO P, et al. Temperature effect and thermal impact in lithium-ion batteries: A review[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2018, 28(6): 653-666. |
| 14 | YAN M Y, ZHANG G B, WEI Q L, et al. In operando observation of temperature-dependent phase evolution in lithium-incorporation olivine cathode[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 22(1): 406-413. |
| 15 | WU G, LIU N, GAO X G, et al. A hydrothermally synthesized LiFePO4/C composite with superior low-temperature performance and cycle life[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 435(11): 1329-1336. |
| 16 | CHUNG S Y, BLOKING J T, CHIANG Y M. Electronically conductive phospho-olivines as lithium storage electrodes[J]. Nature Materials, 2002, 1(2): 123-128. |
| 17 | LIU Y, QIN W C, ZHANG D K, et al. Effect of Na+ in situ doping on LiFePO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2021, 31(1): 14-18. |
| 18 | JOHNSON I D, BLAGOVIDOVA E, DINGWALL P A, et al. High power Nb-doped LiFePO4 Li-ion battery cathodes; pilot-scale synthesis and electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 326(6): 476-481. |
| 19 | KULKA A, BRAUN A, HUANG T W, et al. Evidence for Al doping in lithium sublattice of LiFePO4[J]. Solid State Ion, 2015, 270(12): 33-38. |
| 20 | SŁAWIŃSKI W A, PLAYFORD H Y, HULL S, et al. Neutron pair distribution function study of FePO4 and LiFePO4[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(14): 5024-5034. |
| 21 | GOONETILLEKE D, FAULKNER T, PETERSON V K, et al. Structural evidence for Mg-doped LiFePO4 electrode polarisation in commercial Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 394(5): 1-8. |
| 22 | LEE H, KIM S, PARMAR N S, et al. Carbon-free Mn-doped LiFePO4 cathode for highly transparent thin-film batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 434(10): 1-8. |
| 23 | GUO X P, WANG M, HUANG X L, et al. Direct evidence of antisite defects in LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4via atomic-level HAADF-EELS[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(31): 8775-8781. |
| 24 | ZHANG Y, SHAO Z C, ZHANG Y. Preparation of Mo-doping LiFePO4/C by carbon reduction method[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 36(4): 419-425. |
| 25 | JOHNSON I D, LÜBKE M, WU O Y, et al. Pilot-scale continuous synthesis of a vanadium-doped LiFePO4/C nanocomposite high-rate cathodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 302(10): 410-418. |
| 26 | KIM S, MATHEW V, KANG J, et al. High rate capability of LiFePO4 cathodes doped with a high amount of Ti[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(6): 7230-7236. |
| 27 | OKADA K, KIMURA I, MACHIDA K. High rate capability by sulfur-doping into LiFePO4 matrix[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(11): 5848-5853. |
| 28 | LIU H, LUO S H, YAN S X, et al. A novel and low-cost iron source for synthesizing Cl-doped LiFePO4/C cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2019, 850: 113434. |
| 29 | GAO C, ZHOU J, LIU G Z, et al. Synthesis of F-doped LiFePO4/C cathode materials for high performance lithium-ion batteries using co-precipitation method with hydrofluoric acid source[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 727(8): 501-513. |
| 30 | TU J G, WU K, TANG H, et al. Mg-Ti co-doping behavior of porous LiFePO4 microspheres for high-rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(32): 17021-17028. |
| 31 | GAO L B, XU Z R, ZHANG S. The Co-doping effects of Zr and Co on structure and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4 cathode materials[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 739: 529-535. |
| 32 | YUAN H, WANG X Y, WU Q, et al. Effects of Ni and Mn doping on physicochemical and electrochemical performances of LiFePO4/C[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 675: 187-194. |
| 33 | LI X T, YU L N, CUI Y H, et al. Enhanced properties of LiFePO4/C cathode materials Co-doped with V and F ions via high-temperature ball milling route[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(50): 27204-27213. |
| 34 | WANG H Q, LAI A J, HUANG D Q, et al. Y-F co-doping behavior of LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for high-rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(12): 5695-5703. |
| 35 | LIU W M, HUANG Q Z, HU G R. A novel preparation route for multi-doped LiFePO4/C from spent electroless nickel plating solution[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 632: 185-189. |
| 36 | ZHANG Z F, WU Z J, SU S H, et al. Sustainable preparation of Li(FeM)PO4/C from converter sludge and its electrochemical performance as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 574: 136-141. |
| 37 | MENG Y S, LI Y Z, XIA J, et al. F-doped LiFePO4@N/B/F-doped carbon as high performance cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 476: 761-768. |
| 38 | LIU Y L, WANG J J, LIU J, et al. Origin of phase inhomogeneity in lithium iron phosphate during carbon coating[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 45: 52-60. |
| 39 | SONG J J, SUN B, LIU H, et al. Enhancement of the rate capability of LiFePO4 by a new highly graphitic carbon coating method[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(24): 15225-15231. |
| 40 | PARK S, OH J, KIM J M, et al. Facile preparation of cellulose nanofiber derived carbon and reduced graphene oxide co-supported LiFePO4 nanocomposite as enhanced cathode material for lithium-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 354: 136707. |
| 41 | WANG P, ZHANG G, LI Z C, et al. Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4@N-doped carbon nanocomposites using polybenzoxazine as nitrogen and carbon sources[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(40): 26908-26915. |
| 42 | WANG X F, FENG Z J, HOU X L, et al. Fluorine doped carbon coating of LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122371. |
| 43 | LI F, TAO R, TAN X Y, et al. Graphite-embedded lithium iron phosphate for high-power-energy cathodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(6): 2572-2579. |
| 44 | LUO W-B, CHOU S-L, ZHAI Y-C, et al. Self-assembled graphene and LiFePO4 composites with superior high rate capability for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(14): 4927-4931. |
| 45 | WANG B, AL ABDULLA W, WANG D, et al. A three-dimensional porous LiFePO4 cathode material modified with a nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel for high-power lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(3): 869-875. |
| 46 | XU L T, LÜ W, SHI K, et al. Holey graphenes as the conductive additives for LiFePO4 batteries with an excellent rate performance[J]. Carbon, 2019, 149: 257-262. |
| 47 | FAN J M, CHEN J J, CHEN Y X, et al. Hierarchical structure LiFePO4@C synthesized by oleylamine-mediated method for low temperature applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(14): 4870-4873. |
| 48 | WU X L, GUO Y G, SU J, et al. Carbon-nanotube-decorated nano-LiFePO4@C cathode material with superior high-rate and low-temperature performances for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3(9): 1155-1160. |
| 49 | LU Z G, CHENG H, LO M F, et al. Pulsed laser deposition and electrochemical characterization of LiFePO4-Ag composite thin films[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2007, 17(18): 3885-3896. |
| 50 | ZHU M Y, CHENG L F, LIU Y, et al. LiFePO4/(C+Cu) composite with excellent cycling stability as lithium ion battery cathodes synthesized via a modified carbothermal reduction method[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(11): 12106-12111. |
| 51 | LIN Y B, LIN Y, ZHOU T, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performances of LiFePO4/C by surface modification with Sn nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 226: 20-26. |
| 52 | ZIOLKOWSKA D, KORONA K P, HAMANKIEWICZ B, et al. The role of SnO2 surface coating on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 108: 532-539. |
| 53 | LIU S X, YIN H B, WANG H B, et al. Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical performances of MoO2 and carbon co-coated LiFePO4 cathode materials[J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(2): 3325-3331. |
| 54 | LIU S X, WANG H B. WO2 modified LiFePO4/C cathode materials with improved electrochemical performance synthesized by in-situ synthesis method[J]. Materials Letters, 2014, 122: 151-154. |
| 55 | ZHANG M, GARCIA-ARAEZ N, HECTOR A L, et al. A sol-gel route to titanium nitride conductive coatings on battery materials and performance of TiN-coated LiFePO4[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(5): 2251-2260. |
| 56 | LU J, PENG Q, WANG W Y, et al. Nanoscale coating of LiMO2 (M =Ni, Co, Mn) nanobelts with Li+-conductive Li2TiO3: Toward better rate capabilities for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(5): 1649-1652. |
| 57 | TANG H, XU J. Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 coated with Li0.34La0.51TiO2.94 by rheological phase reaction method[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2013, 178(20): 1503-1508. |
| 58 | PARK K Y, PARK I, KIM H, et al. Lithium-excess olivine electrode for lithium rechargeable batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(9): 2902-2915. |
| 59 | CHIEN W C, JHANG J S, WU S H, et al. Preparation of LiFePO4/Li3V2(PO4)3/C composite cathode materials and their electrochemical performance analysis[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 847: 156447. |
| 60 | GUO Y, HUANG Y D, JIA D Z, et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of high-capacity LiFePO4-Li3V2(PO4)3/C composite for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 246: 912-917. |
| 61 | ZHANG X P, GUO H J, LI X H, et al. Studies of fast-ion conducting Li3V2(PO4)3 coated LiFePO4via sol-gel method[J]. Solid State Ion, 2012, 212: 106-111. |
| 62 | ZHENG J C, LI X H, WANG Z X, et al. Novel synthesis of LiFePO4-Li3V2(PO4)3 composite cathode material by aqueous precipitation and lithiation[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(9): 2935-2938. |
| 63 | ZHONG S K, WU L, LIU J Q. Sol-gel synthesis and electrochemical properties of 9LiFePO4·Li3V2(PO4)3/C composite cathode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 74: 8-15. |
| 64 | LIANG S Q, CAO X X, WANG Y P, et al. Uniform 8LiFePO4·Li3V2(PO4)3/C nanoflakes for high-performance Li-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 22: 48-58. |
| 65 | IM J, HEO K, KANG S-W, et al. LiFePO4 synthesis using refined Li3PO4 from wastewater in Li-ion battery recycling process[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166(15): A3861-A3868. |
| 66 | WANG X, WANG X Y, ZHANG R, et al. Hydrothermal preparation and performance of LiFePO4 by using Li3PO4 recovered from spent cathode scraps as Li source[J]. Waste Managment, 2018, 78: 208-216. |
| 67 | ZHAO S X, DING H, WANG Y C, et al. Improving rate performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials by hybrid coating of nano-Li3PO4 and carbon[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 566: 206-211. |
| 68 | SHU H B, CHEN M F, WEN F, et al. Li fast ion conductive La0.56Li0.33TiO3 inlaid LiFePO4/C microspheres with enhanced high-rate performance as cathode materials[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 152: 368-377. |
| 69 | SHU H B, CHEN M F, FU Y Q, et al. Improvement of electrochemical performance for spherical LiFePO4via hybrid coated with electron conductive carbon and fast Li ion conductive La0.56Li0.33TiO3[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 252: 73-78. |
| 70 | 赵鹤, 韩策, 程小露. 采用阳极预锂化技术的锂离子电池高倍率老化容量衰减机理研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(2): 454-461. |
| ZHAO H, HAN C, CHEN X L. Research on the capacity fading mechanism of high rate aged lithium-ion batteries with anode prelithiation treatment[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 454-461. | |
| 71 | DIAZ-LOPEZ M, CHATER P A, BORDET P, et al. Li2O: Li-Mn-O disordered rock-Salt nanocomposites as cathode prelithiation additives for high-energy density Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(7): 1902788. |
| 72 | SUN Y M, LEE H-W, SEH Z W, et al. High-capacity battery cathode prelithiation to offset initial lithium loss[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 15008. |
| 73 | SUN Y, LEE H W, ZHENG G, et al. In situ chemical synthesis of lithium fluoride/metal nanocomposite for high capacity prelithiation of cathodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(2): 1497-1501. |
| 74 | DU J M, WANG W Y, ENG A Y S, et al. Metal/LiF/Li2O nanocomposite for battery cathode prelithiation: trade-off between capacity and stability[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(1): 546-552. |
| 75 | SUN Y M, LI Y B, SUN J, et al. Stabilized Li3N for efficient battery cathode prelithiation[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2017, 6: 119-124. |
| 76 | ZHAN Y J, YU H L, BEN L B, et al. Using Li2S to compensate for the loss of active lithium in Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 255(9): 212-219. |
| [1] | 李海涛, 孔令丽, 张欣, 余传军, 王纪威, 徐琳. N/P设计对高镍NCM/Gr电芯性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2040-2045. |
| [2] | 刘显茜, 孙安梁, 田川. 基于仿生翅脉流道冷板的锂离子电池组液冷散热[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2266-2273. |
| [3] | 陈龙, 夏权, 任羿, 曹高萍, 邱景义, 张浩. 多物理场耦合下锂离子电池组可靠性研究现状与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2316-2323. |
| [4] | 易顺民, 谢林柏, 彭力. 基于VF-DW-DFN的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2305-2315. |
| [5] | 张肖洒, 王宏源, 李振彪, 夏志美. 废旧磷酸铁锂电池电极材料的硫酸化焙烧-水浸新工艺[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2066-2074. |
| [6] | 祝庆伟, 俞小莉, 吴启超, 徐一丹, 陈芬放, 黄瑞. 高能量密度锂离子电池老化半经验模型[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2324-2331. |
| [7] | 王宇作, 王瑨, 卢颖莉, 阮殿波. 孔结构对软碳负极储锂性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2023-2029. |
| [8] | 孔为, 金劲涛, 陆西坡, 孙洋. 对称蛇形流道锂离子电池冷却性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2258-2265. |
| [9] | 霍思达, 薛文东, 李新丽, 李勇. 基于CiteSpace知识图谱的锂电池复合电解质可视化分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2103-2113. |
| [10] | 邓健想, 赵金良, 黄成德. 高能量锂离子电池硅基负极黏结剂研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2092-2102. |
| [11] | 欧宇, 侯文会, 刘凯. 锂离子电池中的智能安全电解液研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1772-1787. |
| [12] | 韩俊伟, 肖菁, 陶莹, 孔德斌, 吕伟, 杨全红. 致密储能:基于石墨烯的方法学和应用实例[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1865-1873. |
| [13] | 辛耀达, 李娜, 杨乐, 宋维力, 孙磊, 陈浩森, 方岱宁. 锂离子电池植入传感技术[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1834-1846. |
| [14] | 燕乔一, 吴锋, 陈人杰, 李丽. 锂离子电池负极石墨回收处理及资源循环[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1760-1771. |
| [15] | 沈秀, 曾月劲, 李睿洋, 李佳霖, 李伟, 张鹏, 赵金保. γ射线辐照交联原位固态化阻燃锂离子电池[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1816-1821. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
