Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (3): 857-869.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0703
• Energy Storage System and Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xing WANG( ), Jun SUN(
), Jun SUN( ), Ningfang CHEN, Li YAN
), Ningfang CHEN, Li YAN
Received:2022-11-25
Revised:2022-12-09
Online:2023-03-05
Published:2023-04-14
Contact:
Jun SUN
E-mail:287748240@qq.com;sunjun@whut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Xing WANG, Jun SUN, Ningfang CHEN, Li YAN. Modeling of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell cooling system based on the Simscape temperature control strategy[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 857-869.
Table 3
Basic parameter table of water pump, radiator and expansion tank"
| 模型符号 | 关键接口含义 | 参数名称 | 参数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
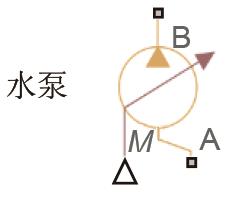 | M—质量流量控制信号kg/s | 管道横截面积/cm2 | 20 |
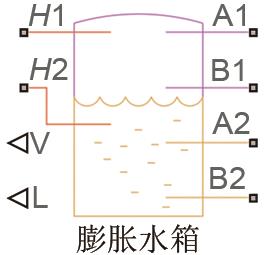 | A1、B1—气体出入口 A2、B2—热液体出入口 H1、H2—上下半部分壁温 | 水箱体积/L 水箱横截面积/m2 出入口横截面积/cm2 | 10 0.0625 4.9087 |
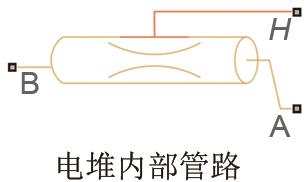 | H—管壁温度 | 管道长度/cm 管道横截面积/cm2 水力直径/cm | 200.7984 20 1 |
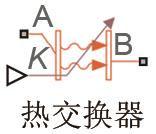 | K—传热系数控制信号 | 换热面积/m2 | 9.3169 |
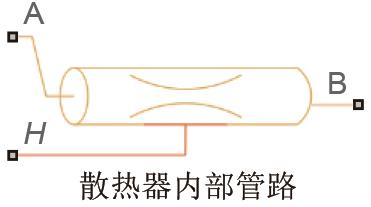 | H—管壁温度 | 管道长度/m 管道横截面积/cm2 水力直径/cm | 1 9.375 1 |
 | — | 质量/kg 比热容/[J/(kg·K)] | 3.4521 910 |
Table 4
Temperature data of simulation model and experiment under different working condition[5]"
| 输出功率/kW | 冷却液 流量/(kg/s) | 空气 流量/(kg/s) | 仿真电堆温度/K | 仿真冷却液 温差/K | 文献电堆 温度/K | 文献冷却液温差/K | 电堆温度 相对误差/% | 冷却液温差 相对误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 347.4 | 13.4 | 345.9 | 15.68 | 0.43 | -14.54 |
| 10 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 359.4 | 8.84 | 357.1 | 8.75 | 0.64 | 1.03 |
| 10 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 326.61 | 6.88 | 325.8 | 7.53 | 0.25 | -8.63 |
| 10 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 330.65 | 5.11 | 328.8 | 5.77 | 0.56 | -11.44 |
| 1 | 赵永志, 蒙波, 陈霖新, 等. 氢能源的利用现状分析[J]. 化工进展, 2015, 34(9): 3248-3255. |
| ZHAO Y Z, MENG B, CHEN L X, et al. Utilization status of hydrogen energy[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2015, 34(9): 3248-3255. | |
| 2 | TISS F, CHOUIKH R, GUIZANI A. Dynamic modeling of a PEM fuel cell with temperature effects[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(20): 8532-8541. |
| 3 | 李珊珊, 田禾青, 周俊杰, 等. 基于Simscape的汽车制冷系统建模及仿真[J]. 低温与超导, 2021, 49(9): 61-65. |
| LI S S, TIAN H Q, ZHOU J J, et al. Modeling and simulation of automobile refrigeration system based on Simscape[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2021, 49(9): 61-65. | |
| 4 | 牛茁. 水冷型质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统控制研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. |
| NIU Z. Study on thermal management system control of water-cooled PEMFC[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018. | |
| 5 | 杨孝才. 水冷型PEMFC冷却系统建模与控制研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2022. |
| YANG X C. Research on modeling and control of water-cooled PEMFC cooling system[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2022. | |
| 6 | VAISHAMPAYAN V, VANGARI A, SHAH J. Challenges and opportunities of affordable Fuel Cell for distributed generation[C]//2014 1st International Conference on Non Conventional Energy (ICONCE 2014). January 16-17, 2014, Kalyani, India. IEEE, 2014: 319-323. |
| 7 | ZHAO X Q, LI Y K, LIU Z X, et al. Thermal management system modeling of a water-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(7): 3048-3056. |
| 8 | 赵洪波, 刘杰, 马彪, 等. 水冷PEMFC热管理系统控制策略及仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2139-2150. |
| ZHAO H B, LIU J, MA B, et al. Control strategy and simulation research of water-cooled PEMFC thermal management system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2139-2150. | |
| 9 | LARMINIE J, DICKS A. Introduction[M]//Fuel cell systems explained. West Sussex, England: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2013: 1-24. |
| 10 | ZOU W J, KIM Y B. Temperature control for a 5 kW water-cooled PEM fuel cell system for a household application[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 144826-144835. |
| 11 | 周奕, 陈建利, 赵阳, 等. 燃料电池客车散热系统设计分析[J]. 上海汽车, 2010(1): 19-20, 48. |
| ZHOU Y, CHEN J L, ZHAO Y, et al. Design and analysis of the heat rejection system of fuel cell bus[J]. Shanghai Auto, 2010(1): 19-20, 48. | |
| 12 | 张宝斌, 刘佳鑫, 李建功, 等. 燃料电池冷却方法及热管理控制策略进展[J]. 电池, 2019, 49(2): 158-162. |
| ZHANG B B, LIU J X, LI J G, et al. Development of fuel cell cooling method and thermal management control strategy[J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2019, 49(2): 158-162. | |
| 13 | TISS F, CHOUIKH R, GUIZANI A. Dynamic modeling of a PEM fuel cell with temperature effects[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(20): 8532-8541. |
| 14 | HU P, CAO G Y, ZHU X J, et al. Coolant circuit modeling and temperature fuzzy control of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9110-9123. |
| 15 | 赵安. 质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统动态建模与控制策略研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022. |
| ZHAO A. Study of dynamic modeling and control strategy for proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. | |
| 16 | 吕雪. 氢燃料电池发动机冷却系统建模分析及控制策略研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2021. |
| LYU X. Modeling analysis and control strategy research of hydrogen fuel cell engine cooling system[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 17 | 朱斌. 自抗扰控制入门[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2017. |
| ZHU B. Introduction to active disturbance rejection control[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics Press, 2017. |
| [1] | Yezhou HU, Shuang WANG, Tao SHEN, Ye ZHU, Deli WANG. Recent progress in confined noble-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1264-1277. |
| [2] | Zhihao LI, Hao PENG, Yaqin CHEN. Neural network prediction model for temperature distribution of proton exchange membrane fuel cell membrane electrode assembly [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2053-2059. |
| [3] | Jing ZHANG, Yan LU, Sheng LI, Guangcai XIE, Zhongmin WAN. Modeling and simulation of domestic fuel cell cogenerated heat and power system based on fuzzy PID control [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 1117-1126. |
| [4] | Junxiang ZHAI, Guangli HE, Zhuang XU, Congmin LIU. Experimental study on system efficiency of air-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(6): 1885-1889. |
| [5] | ZHAI Junxiang, HE Guangli, XIONG Yalin. Experimental study on hydrogen utilization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 684-687. |
| [6] | ZHU Xiaozhou, CHEN Minwu, LIU Xiangdong, ZHAO Hangfei, HAN Ming. Experimental study on anode exhaust methods of air-cooled PEMFC [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(1): 118-. |
| [7] | ZHU Xiaozhou, CHEN Minwu, LIU Xiangdong, ZHAO Hangfei, HAN Ming. Design of single cell voltage monitor system based on LabVIEW for PEMFC [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(1): 123-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
