储能科学与技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (3): 965-983.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0915
吉帅静1( ), 王军伟2, 杜宝帅3, 徐丽4, 楼平5, 管敏渊5, 汤舜2, 程时杰2, 曹元成2(
), 王军伟2, 杜宝帅3, 徐丽4, 楼平5, 管敏渊5, 汤舜2, 程时杰2, 曹元成2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-29
修回日期:2024-10-21
出版日期:2025-03-28
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
曹元成
E-mail:d202280483@hust.edu.cn;yccao@hust.edu.cn
作者简介:吉帅静(1996—),女,博士研究生,研究方向为退役动力电池综合利用与再生修复,E-mail:d202280483@hust.edu.cn;
基金资助:
Shuaijing JI1( ), Junwei WANG2, Baoshuai DU3, Li XU4, Ping LOU5, Minyuan GUAN5, Shun TAN2, Shijie CHENG2, Yuancheng CAO2(
), Junwei WANG2, Baoshuai DU3, Li XU4, Ping LOU5, Minyuan GUAN5, Shun TAN2, Shijie CHENG2, Yuancheng CAO2( )
)
Received:2024-09-29
Revised:2024-10-21
Online:2025-03-28
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Yuancheng CAO
E-mail:d202280483@hust.edu.cn;yccao@hust.edu.cn
摘要:
在锂离子电池于电动汽车及储能领域广泛应用的背景下,磷酸锰锂铁(LiFe x Mn1-x PO4,0<x<1)作为正极材料,因其卓越的高安全性和高工作电压特性而备受瞩目。然而,LiFe x Mn1-x PO4(LFMP)材料存在的导电性不足及循环稳定性较差等问题,成为制约其商业化应用的关键性障碍。针对这些问题,本文深入探讨了LFMPO4性能衰退的根源,包括Mn的Jahn-Teller畸变效应、迟缓的反应动力学以及锰基阴极材料中的歧化反应等核心问题,并深入分析了高温高压条件下产气产热的演变机制,以期揭示其失效机理。为提升LFMP的综合性能,本文总结了多种策略,如离子掺杂与碳包裹技术的结合使用、复合包覆技术以及电解质的改良等。这些策略着重于增强LFMP正极材料的电子导电性和Li+迁移率,稳定其相结构以抑制由Jahn-Teller效应引发的Mn溶解,减小界面应力,并提升材料的热稳定性和安全性。通过实施上述策略,不仅验证了失效机理分析的准确性,还展望了高性能锂离子电池LFMP正极材料的未来发展趋势。结合当前的研究成果,为实现高比容量、稳定的循环性能、出色的倍率性能以及高安全性,可能需要综合运用多种手段,如碳涂层、元素掺杂以及电解质优化等,以期开发出具有高能量密度、长循环寿命和热稳定性的全电池基LFMP正极材料。此外,本文还紧密结合当前的产业化研究进展,综述了不同合成工艺与Mn掺杂比例调控对LFMP材料结构和性能的具体影响,这不仅将推动LFMP基材料在高性能锂离子电池领域的广泛应用,也为其商业化进程奠定了坚实的基础。
中图分类号:
吉帅静, 王军伟, 杜宝帅, 徐丽, 楼平, 管敏渊, 汤舜, 程时杰, 曹元成. LiFe x Mn1–x PO4 (0<x<1)电池稳定性与安全性的提升路径:从失效机制到综合优化策略[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 965-983.
Shuaijing JI, Junwei WANG, Baoshuai DU, Li XU, Ping LOU, Minyuan GUAN, Shun TAN, Shijie CHENG, Yuancheng CAO. Improvement paths for the stability and safety of LiFe x Mn1–x PO4 (0 < x < 1) batteries: From failure mechanisms to comprehensive optimization strategies[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 965-983.

图2
LMFP-0、LMFP-/1、LMFP-2和LMFP-3的XRD谱图,LMFP-2中Pbnm相的晶体结构,LMFP-0、LMFP-/1、LMFP-2和LMFP-3的CV曲线,LMFP-0、LMFP-/1、LMFP-2和LMFP-3的循环性能和LMFP-0、LMFP-/1、LMFP-2和LMFP-3的充放电曲线 (a)[58];LFMP-0% Y和LFMP-1% Y的XPS全谱,LFMP-0% Y和LFMP-1% Y中Mn 2p的XPS光谱,LFMP-z%Y(z = 0、0.5、1、2和3)样品在25下以0.1 mV/s的扫描速率测试的循环伏安曲线,Fe2+/Fe3+ 和Mn2+/Mn3+ 氧化还原峰电位差与Y掺杂浓度之间的关系,以及在1 C下的循环性能(b)[60]"
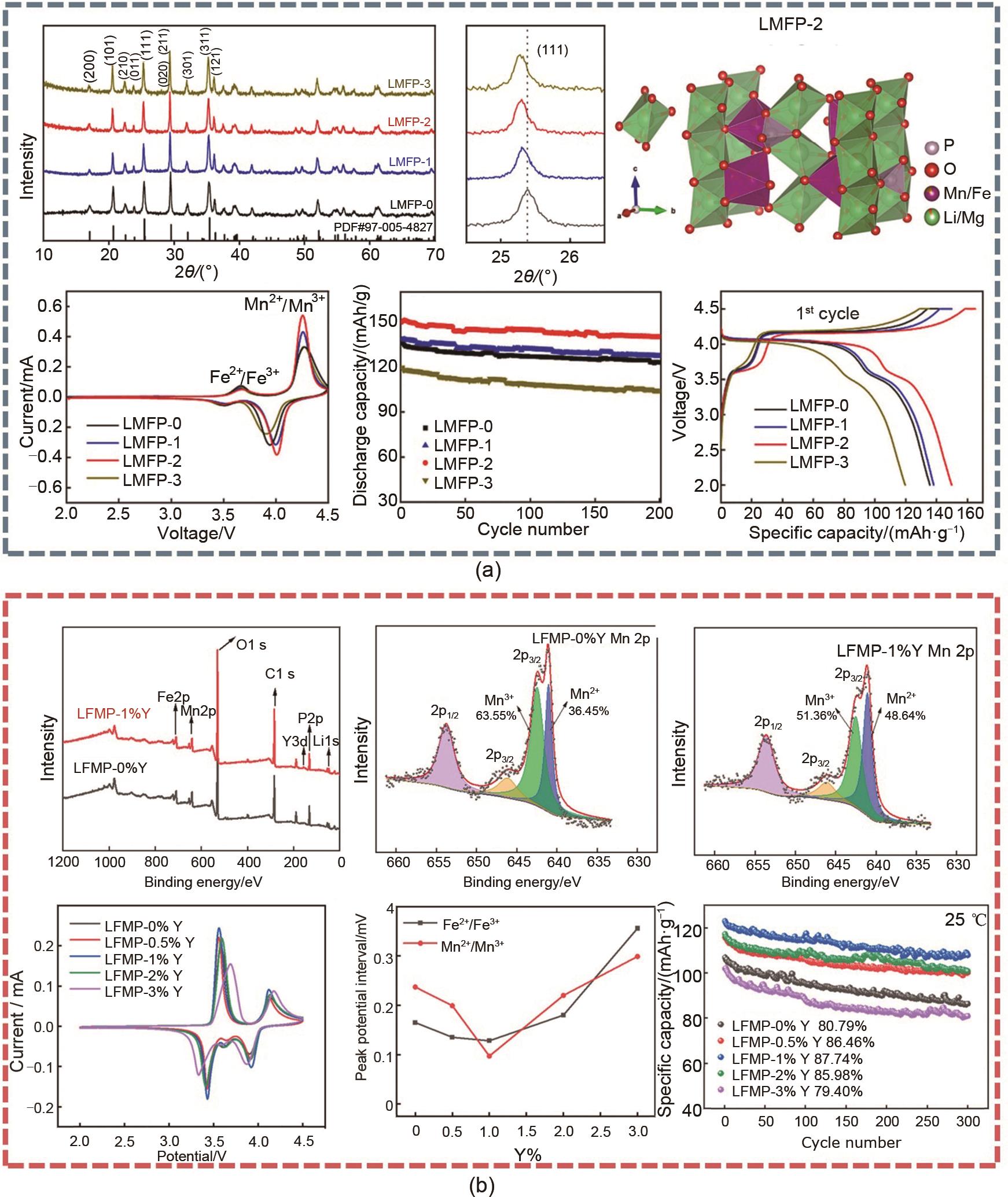
表1
掺杂LFMP材料的总结"
| 材料 | 合成方法 | 比容量(0.1 C)/ (mAh/g) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li(Mn0.85Fe0.15)0.92Ti0.08PO4/C | solid-state | 99.9% (after 50 cycles at 170 C) | [ |
| Li0.97Na0.03Mn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C | solvothermal | 96.65% (after 200 cycles at 85 C) | [ |
| Li(Mn0.9Fe0.1)0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | mechano-chemical liquid-phase activation | 98.6% (after 50 cycles at 163 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.7Mn0.25Mg0.05PO4/C | solvothermal | 91% (after 200 cycles at 162.6 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.47Mn0.5Ca0.03PO4/C | solid-state | 87.84% (after 300 cycles at 160 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.5Mn0.49Y0.01PO4/C | solid-state | 86.7% (after 500 cycles at 158.5 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.5Mn0.49In0.01PO3.97F0.03 | solvothermal | 100% (after 100 cycles at 170 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.39Mg0.01Mn0.6PO4/C | solid-state | 100% (after 100 cycles at 170 C) | [ |
| Li(Fe0.5Mn0.5)0.97Mo0.03PO4/C | solvothermal approach | 91.2% (after 200 cycles at 153 C) | [ |
表2
关于LFMP不同的Mn/Fe比总结"
| Mn/Fe比 | 含碳量(质量分数)/% | 合成方法 | 比容量/(mAh/g) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1∶0.9 | 0 | solvothermal | 130.6(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.1∶0.9 | 5 | solid state | 149(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.15∶0.85 | 3.95 | HEBM | 156.5(at 0.1C) | [ |
| 0.2∶0.8 | 2-3 | co-precipitation + solid state | 151.1(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.2∶0.8 | 33 | sol-gel | 160(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.2∶0.8 | 2.95 | spray dry | 151(at 0.1 C) | |
| 0.3∶0.7 | 12.2 | HEBM + solid-state reaction | 164(at 0.05 C) | [ |
| 0.3∶0.7 | 3.2 | hydrothermal | 156.3(at 0.05) | |
| 0.4∶0.6 | 5 nm | two-step sol-gel method | 150(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.4∶0.6 | 8.5 | ball-milling | 128(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.4∶0.6 | 10 | sol-gel | 152(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.5∶0.5 | 3.16 | ball-milling | 138(at 0.1 C) | [ |
| 0.6∶0.4 | solid-state | [ | ||
| 0.6∶0.4 | solid-state | 150(at 0.2 C) | [ | |
| 0.75∶0.25 | 5 | solid-state | [ | |
| 0.8∶0.2 | 3 | solvothermal | 133(at 0.05 C) | [ |
| 0.8∶0.2 | solid-state | 155(at 0.2 C) | [ |
| 1 | AMINE K, TUKAMOTO H, YASUDA H, et al. Preparation and electrochemical investigation of LiMn2- xMexO4 (Me: Ni, Fe, and x = 0.5, 1) cathode materials for secondary lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1997, 68(2): 604-608. DOI:10.1016/S0378-7753(96)02590-6. |
| 2 | KOPE¢ M, YAMADA A, KOBAYASHI G, et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Lix(MnyFe1 -y)PO4 electrode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 189(2): 1154-1163. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.12.096. |
| 3 | KUROSUMI S, HORIBA K, NAGAMURA N, et al. Resonant photoemission spectroscopy of the cathode material LixMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 for lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 226: 42-46. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.10.041. |
| 4 | MASQUELIER C, CROGUENNEC L. Polyanionic (phosphates, silicates, sulfates) frameworks as electrode materials for rechargeable Li (or Na) batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(8): 6552-6591. DOI:10.1021/cr3001862. |
| 5 | Ⅺ X, LI P, ZHAN Z. Process of preparing LiCoO2 as positive pole material for lithium ion cell: CN1810655-A; CN1319865-C[P]. |
| 6 | DING X, ZHANG Q, JIANG Z, et al. Anode material LiCoO2 of lithium ion cell and its preparation method: CN1808747-A[P]. |
| 7 | MOLENDA J, OJCZYK W, K Ś, et al. Diffusional mechanism of deintercalation in LiFe1– yMnyPO4 cathode material[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2006, 177(26/27/28/29/30/31/32): 2617-2624. DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2006.03.047. |
| 8 | MOSKON J, PIVKO M, JERMAN I, et al. Cycling stability and degradation mechanism of LiMnPO4 based electrodes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 303: 97-108. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2015.10.094. |
| 9 | PAOLELLA A, BERTONI G, DILENA E, et al. Redox centers evolution in phospho-olivine type (LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4) nanoplatelets with uniform cation distribution[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(3): 1477-1483. DOI:10.1021/nl4046697. |
| 10 | RAVNSBÆK D B, XIANG K, XING W, et al. Extended solid solutions and coherent transformations in nanoscale olivine cathodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(3): 1484-1491. DOI:10.1021/nl404679t. |
| 11 | CHANG H, LI Y, FANG Z K, et al. Construction of carbon-coated LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@Li0.33La0.56TiO3 nanorod composites for high-performance Li-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(28): 33102-33111. DOI:10.1021/acsami. 1c08373. |
| 12 | CHEN W Y, XU D H, CHEN Y C, et al. In situ electrospinning synthesis of N-doped C nanofibers with uniform embedding of Mn doped MFe1- xMnxPO4 (M = Li, Na) as a high performance cathode for lithium/sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2020, 7(19): 2000684. DOI:10.1002/admi.202000684. |
| 13 | CUI X L, TUO K Y, DONG H, et al. Modification of phosphorus-doped carbon coating enhances the electrochemical performance of LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4 cathode material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 885: 160946. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160946. |
| 14 | NORBERG N S, KOSTECKI R. The degradation mechanism of a composite LiMnPO4 cathode[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(9): A1431-A1434. DOI:10.1149/2.018209jes. |
| 15 | NEDOSEYKINA T, KIM M G, PARK S A, et al. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopic study for the electrochemical delithiation of a cathode LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4 material[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(28): 8876-8882. |
| 16 | DING D, MAEYOSHI Y, KUBOTA M, et al. Holey reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube/LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4 composite cathode for high-performance lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 449: 227553. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2019.227553. |
| 17 | LI X, LIU J D, HE J, et al. Hexafluoroisopropyl trifluoromethanesulfonate-driven easily Li+ desolvated electrolyte to afford Li||NCM811 cells with efficient anode/cathode electrolyte interphases[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(37): 2104395. DOI:10.1002/adfm.202104395. |
| 18 | HOU Y K, PAN G L, SUN Y Y, et al. LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/carbon Nanospheres@Graphene nanoribbons prepared by the biomineralization process as the cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(19): 16500-16510. DOI:10.1021/acsami.8b02736. |
| 19 | ZHU Y, CASSELMAN M D, LI Y, et al. Perfluoroalkyl-substituted ethylene carbonates: Novel electrolyte additives for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 246: 184-191. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.07.070. |
| 20 | ZHAO D Q, LI X F, TANG F J, et al. Compatibility between lithium bis(oxalate)borate-based electrolytes and a LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4/C cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Technology, 2017, 5(3): 406-413. DOI:10.1002/ente.201600307. |
| 21 | ZHANG Y Q, MA Q, WANG S L, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-assisted fabrication of hollow carbon spheres/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(5): 4824-4834. DOI:10.1021/acsnano.8b01549. |
| 22 | ZHANG J X, ZHAO N, ZHANG M, et al. Flexible and ion-conducting membrane electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Dispersion of garnet nanoparticles in insulating polyethylene oxide[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 28: 447-454. DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.09.002. |
| 23 | YANG C C, HUNG Y W, LUE S J. Improved electrochemical properties of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C composite materials via a surface coating process[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 325: 565-574. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.06.084. |
| 24 | DEKUN Q. Guoxuan Gaoke released Qichen battery without ternary materials can last 1000 km[N/OL]. May 21, 2023. https://company.cnstock.com/company/scp_gsxw/202305/5064140.htm |
| 25 | YU X F, LI Q W, LIU Q, et al. Rheological phase reaction method synthesis and characterizations of xLiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4– yLi3V2(PO4)3/C composites as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2020, 35(1): 2-11. DOI:10.1557/jmr.2019.326. |
| 26 | YU H, HAN J S, HWANG G C, et al. Optimization of high potential cathode materials and lithium conducting hybrid solid electrolyte for high-voltage all-solid-state batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 365: 137349. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta. 2020.137349. |
| 27 | YI H H, HU C L, FANG H S, et al. Optimized electrochemical performance of LiMn0.9Fe0.1- xMgxPO4/C for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(11): 4052-4057. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.01.121. |
| 28 | STARKE B, SEIDLMAYER S, SCHULZ M, et al. Gas evolution and capacity fading in LiFexMn1– xPO4/graphite cells studied by neutron imaging and neutron induced prompt gamma activation analysis[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(14): A3943-A3948. DOI:10.1149/2.0011802jes. |
| 29 | JALKANEN K, VUORILEHTO K. Entropy change characteristics of LiMn0.67Fe0.33PO4 and Li4Ti5O12 electrode materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 273: 351-359. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2014.09.091. |
| 30 | CHEN L, YUAN Y Q, FENG X, et al. Enhanced electrochemical properties of LiFe1- xMnxPO4/C composites synthesized from FePO4·2H2O nanocrystallites[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 214: 344-350. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.04.089. |
| 31 | HE W, GUO W B, WU H L, et al. Challenges and recent advances in high capacity Li-rich cathode materials for high energy density lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(50): 2005937. DOI:10.1002/adma.202005937. |
| 32 | ELDESOKY A, KOWALSKI N, NI H Q, et al. Studying the impact of electrolyte, Li excess, NMC blending, and cycling conditions on the lifetime and degradation of LMO/AG cells using UHPC cycling, XRF, and isothermal microcalorimetry[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2023, 170(9): 090530. DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/acf95e. |
| 33 | LIN X K, PARK J, LIU L, et al. A comprehensive capacity fade model and analysis for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(10): A1701-A1710. DOI:10.1149/2.040310jes. |
| 34 | KIM J K, VIJAYA R, ZHU L K, et al. Improving electrochemical properties of porous iron substituted lithium manganese phosphate in additive addition electrolyte[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 106-110. |
| 35 | WI S, PARK J, LEE S, et al. Synchrotron-based X-ray absorption spectroscopy for the electronic structure of LixMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 mesocrystal in Li+ batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 31: 495-503. DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.11.044. |
| 36 | WI S, PARK J, LEE S, et al. Insights on the delithiation/lithiation reactions of LixMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 mesocrystals in Li+ batteries by in situ techniques[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 39: 371-379. DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.07.016. |
| 37 | NEDOSEYKINA T, KIM M G, PARK S A, et al. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopic study for the electrochemical delithiation of a cathode LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4 material[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(28): 8876-8882. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.08.037. |
| 38 | OJCZYK W, MARZEC J, DYGAS J, et al. Structural and transport properties of LiFe0.45Mn0.55PO4 as a cathode material in Li-ion batteries[J]. Materials Science-Poland, 2006, 24(1): 103-113. |
| 39 | NIU J J, KUSHIMA A, QIAN X F, et al. In situ observation of random solid solution zone in LiFePO4 electrode[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(7): 4005-4010. DOI:10.1021/nl501415b. |
| 40 | ZHONG K F, CAI X H, WANG M. The mechanism of easier desorption of Fe atoms on the (100) surface of LiFePO4 and FePO4[J]. Chemical Physics, 2023, 570: 111891. DOI:10.1016/j.chemphys.2023.111891. |
| 41 | ZSOLDOS E S, ELDESOKY A, LOGAN E, et al. LiMn2O4/graphite cell degradation mechanisms studying how Mn deposition accelerates lithiated graphite reactivity with electrolyte[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2024, 171(7): 070504. DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/ad5910. |
| 42 | LUO C, JIANG Y, ZHANG X X, et al. Misfit strains inducing voltage decay in LiMnyFe1- yPO4/C[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 68: 206-212. DOI:10.1016/j.jechem. 2021.11.007. |
| 43 | LIU Y T, SUN Y, WEN X, et al. Li2ZrO3 coated LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C with enhanced cycling performance at elevated temperature for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 613: 234938. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2024.234938. |
| 44 | LESLIE K, HARLOW J, RATHORE D, et al. Correlating Mn dissolution and capacity fade in LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/graphite cells during cycling and storage at elevated temperature[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2024, 171(4): 040520. DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/ad3b77. |
| 45 | CHO I H, KIM S S, SHIN S C, et al. Effect of SEI on capacity losses of spinel lithium manganese oxide/graphite batteries stored at 60℃[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2010, 13(11): A168. DOI:10.1149/1.3481711. |
| 46 | LIU S, FANG H S, DAI E R, et al. Effect of carbon content on properties of LiMn0.8Fe0.19Mg0.01PO4/C composite cathode for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 116: 97-102. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.052. |
| 47 | KOSOVA N V, PODGORNOVA O A, GUTAKOVSKII A K. Different electrochemical responses of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 prepared by mechanochemical and solvothermal methods[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 742: 454-465. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2018.01.242. |
| 48 | HUANG Q Y, WU Z, SU J, et al. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Ti-Fe Co-doped LiMnPO4/C as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(9): 11348-11354. DOI:10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.057. |
| 49 | OUYANG C Y, SHI S Q, WANG Z X, et al. The effect of Cr doping on Li ion diffusion in LiFePO4 from first principles investigations and Monte Carlo simulations[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2004, 16(13): 2265-2272. DOI:10.1088/0953-8984/16/13/007. |
| 50 | ZHANG K, LI Z X, LI X, et al. Perspective on cycling stability of lithium-iron manganese phosphate for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Rare Metals, 2023, 42(3): 740-750. DOI:10.1007/s12598-022-02107-w. |
| 51 | ZHANG L S, GAO X L, LIU X H, et al. CHAIN: Unlocking informatics-aided design of Li metal anode from materials to applications[J]. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(5): 1477-1489. DOI:10.1007/s12598-021-01925-8. |
| 52 | LI Z F, REN X, TIAN W C, et al. LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/CA cathode materials with carbon aerogel as additive synthesized by wet ball-milling combined with spray drying[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(9): 090516. DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/ab819e. |
| 53 | OH S M, MYUNG P S, PARK J B, et al. Double-structured LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 coordinated with LiFePO4 for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(8): 1853-1856. DOI:10.1002/anie.201107394. |
| 54 | QI S H, WANG H P, HE J, et al. Electrolytes enriched by potassium perfluorinated sulfonates for lithium metal batteries[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(7): 685-693. DOI:10.1016/j.scib. 2020.09.018. |
| 55 | QIAO Y, ZHAO H P, SHEN Y L, et al. Recycling of graphite anode from spent lithium-ion batteries: Advances and perspectives[J]. EcoMat, 2023, 5(4): e12321. DOI:10.1002/eom2.12321. |
| 56 | SU P P, ZHANG H T, YANG L P, et al. Effects of conductive additives on the percolation networks and rheological properties of LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4 suspensions for lithium slurry battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133203. DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2021.133203. |
| 57 | LV Z, LI M L, LIN J X, et al. First-principles study on LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 doping to decrease the Jahn-Teller effect[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2024, 28(2): 577-587. DOI:10.1007/s10008-023-05705-5. |
| 58 | HU H, LI H, LEI Y, et al. Mg-doped LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nano-plate as a high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73: 109006. DOI:10.1016/j.est.2023.109006. |
| 59 | LIU Y Y, CHANG C K, ZHENG J N. Revealing the role of Mg doping in LiFe0.39Mg0.01Mn0.6PO4/C cathode: Enhanced electrochemical performance from improved electrical conductivity and promoted lithium diffusion kinetics[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 91: 112108. DOI:10.1016/j.est. 2024.112108. |
| 60 | PENG J, LI Z, YOU Y, et al. Contribution of Ti-doping to the cyclic stability of LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4/C[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(18): 8228-8238. DOI:10.1021/acs.iecr.4c00307. |
| 61 | ZHENG J W, YANG J W, WU J M, et al. Y3+ doping and electrochemical properties of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4@C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 960: 170610. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2023.170610. |
| 62 | SIN B C, SINGH L, LEE J, et al. Electrochemical performance of hybrid-structured LiFe(PO4)0.5(BO3)0.5 cathode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 823: 155-160. DOI:10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.06.010. |
| 63 | LI Z P, ZHU J H, XU M W, et al. Achieving long-lasting and high-capacity LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 cathodes with a synergistic F/In dual doping strategy[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2024, 48(15): 6857-6863. DOI:10.1039/D4NJ00255E. |
| 64 | LI R, FAN C L, ZHANG W H, et al. Structure and performance of Na+ and Fe2+ Co-doped Li1– xNaxMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nanocapsule synthesized by a simple solvothermal method for lithium ion batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 10501-10510. DOI:10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.02.112. |
| 65 | DUAN J G, HU G R, CAO Y B, et al. Synthesis of high-performance Fe-Mg-co-doped LiMnPO4/C via a mechano-chemical liquid-phase activation technique[J]. Ionics, 2016, 22(5): 609-619. DOI:10.1007/s11581-015-1582-0. |
| 66 | XIA K, LIANG R, LUO Y, et al. Solid-state preparation and electrochemical properties of Mg2+-doped LiFe0.7Mn0.3PO4/C as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2022, 17(12): 221273. DOI:10.20964/2022.12.72. |
| 67 | LIU W F, LIU X C, HAO R, et al. Contribution of calcium ion doping to the rate property for LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2023, 929: 117117. DOI:10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.117117. |
| 68 | KIM D, LEE S, CHOI W. Boosting both electronic and ionic conductivities via incorporation of molybdenum for LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 cathode in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 989: 174396. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2024. 174396. |
| 69 | FAN R Z, FAN C L, HU Z, et al. Construction of high performance N-doped carbon coated LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 nanocrystal cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 876: 160090. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160090. |
| 70 | LI J L, WANG Y, WU J H, et al. CNT-embedded LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C microsphere cathode with high rate capability and cycling stability for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 731: 864-872. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.338. |
| 71 | PODGORNOVA O A, VOLFKOVICH Y M, SOSENKIN V E, et al. Increasing the efficiency of carbon coating on olivine-structured cathodes by choosing a carbon precursor[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2022, 907: 116059. DOI:10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116059. |
| 72 | SONG Z Y, CHEN S L, DU S, et al. Construction of high-performance LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode by using quinoline soluble substance from coal pitch as carbon source for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 927: 166921. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166921. |
| 73 | THAHEEM I, KIM K J, LEE J J, et al. High performance Mn1.3Co1.3Cu0.4O4 spinel based composite cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(34): 19696-19703. DOI:10.1039/C9TA07069A. |
| 74 | YU M, LI J, NING X H. Improving electrochemical performance of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode by hybrid coating of Li3VO4 and carbon[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 368: 137597. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137597. |
| 75 | LIANG Y L, CHEN S L, FAN C L, et al. High-performance LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode prepared by using the toluene-soluble component of pitch as a carbon source[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(13): 19103-19119. DOI:10.1002/er.7092. |
| 76 | MARTHA S K, HAIK O, ZINIGRAD E, et al. On the thermal stability of olivine cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(10): A1115. DOI:10.1149/1.3622849. |
| 77 | YAO X, LI D, GUO L, et al. Carbon-coated LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathodes for high-rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2024, 7(2): 63. DOI:10.1007/s42114-024-00870-1. |
| 78 | LIU X C, OUYANG B X, HAO D R, et al. Li2SiO3 modification of C/LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 for high performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(16): e202200609. DOI:10.1002/celc. 202200609. |
| 79 | TUO K Y, MAO L P, DING H, et al. Boron and phosphorus dual-doped carbon coating improves electrochemical performances of LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4 cathode materials[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(8): 8003-8015. DOI:10.1021/acsaem.1c01318. |
| 80 | KIM J K, VIJAYA R, ZHU L K, et al. Improving electrochemical properties of porous iron substituted lithium manganese phosphate in additive addition electrolyte[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 106-110. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2014. 11.028. |
| 81 | ADACHI P G, IMANAKA D N, AONO D H. Fast Li+ conducting ceramic electrolytes[J]. Advanced Materials, 1996, 8(2): 127-135. DOI:10.1002/adma.19960080205. |
| 82 | CHENG L, WU C H, JARRY A, et al. Interrelationships among grain size, surface composition, air stability, and interfacial resistance of Al-substituted Li7La3Zr2O12 solid electrolytes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(32): 17649-17655. DOI:10.1021/acsami.5b02528. |
| 83 | DENG Z, RADHAKRISHNAN B, ONG S P. Rational composition optimization of the lithium-rich Li3OCl1– xBrx anti-perovskite superionic conductors[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(10): 3749-3755. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b00988. |
| 84 | DI LECCE D, FASCIANI C, SCROSATI B, et al. A gel-polymer Sn-C/LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 battery using a fluorine-free salt[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(38): 21198-21207. DOI:10.1021/acsami.5b05179. |
| 85 | YAO M, ZHANG H T, XING C X, et al. Rational design of biomimetic ant-nest solid polymer electrolyte for high-voltage Li-metal battery with robust mechanical and electrochemical performance[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 51-60. DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2021.05.049. |
| 86 | GOODENOUGH J B, SINGH P. Review—Solid electrolytes in rechargeable electrochemical cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(14): A2387-A2392. DOI:10.1149/2.0021514jes. |
| 87 | KNAUTH P. Inorganic solid Li ion conductors: An overview[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2009, 180(14/15/16): 911-916. DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2009.03.022. |
| 88 | ZHOU X, DENG Y, WAN L, et al. A surfactant-assisted synthesis route for scalable preparation of high performance of LiFe0.15Mn0.85PO4/C cathode using bimetallic precursor[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 265(1): 223-230. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.04.049. |
| 89 | GUO X P, WANG M, HUANG X L, et al. Direct evidence of antisite defects in LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 via atomic-level HAADF-EELS[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(31): 8775. DOI:10.1039/c3ta11564j. |
| 90 | WANG K, HOU M Y, YUAN S Y, et al. An additional discharge plateau of Mn3+ in LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 at high current rates[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2015, 55: 6-9. DOI:10.1016/j.elecom.2015.03.004. |
| 91 | SHAPOVALOV V V, GUDA A A, KOSOVA N V, et al. Laboratory operando Fe and Mn K-edges XANES and Mössbauer studies of the LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 cathode material[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2020, 175: 108065. DOI:10.1016/j.radphyschem. 2018.11.019. |
| 92 | KIM M S, JEGAL J P, ROH K C, et al. Synthesis of LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4/C microspheres using a microwave-assisted process with a complexing agent for high-rate lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(27): 10607-10613. DOI:10.1039/C4TA01197J. |
| 93 | KOSOVA N V, PODGORNOVA O A. The influence of synthesis method on structure, morphology and electrochemical properties of the LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 cathode material[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(11): 22806-22810. DOI:10.1016/j.matpr. 2018.07.094. |
| 94 | OH S M, MYUNG S T, CHOI Y S, et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of micro-sized spherical LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode material for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(48): 19368-19374. DOI:10.1039/C1JM13889H. |
| 95 | LIU W, GAO P, MI Y Y, et al. Fabrication of high tap density LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4/C microspheres by a double carbon coating-spray drying method for high rate lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(7): 2411-2417. DOI:10.1039/C2TA00939K. |
| 96 | YI Z H, MU Z J, YANG X, et al. A facile and reliable route to the synthesis of high-performance LiFe2/3Mn1/3PO4@C/graphene for lithium-ion power batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2024, 327: 129799. DOI:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2024.129799. |
| 97 | YAN S Y, WANG C Y, GU R M, et al. Synergetic Fe substitution and carbon connection in LiMn1- x FexPO4/C cathode materials for enhanced electrochemical performances[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 628: 471-479. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2014.12.182. |
| 98 | RAVNSBAEK D B, XIANG K, XING W, et al. Engineering the transformation strain in LiMnyFe1– yPO4 olivines for ultrahigh rate battery cathodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(4): 2375-2398. |
| 99 | YAMADA A, KUDO Y, LIU K Y. Reaction mechanism of the olivine-type Lix(Mn0.6Fe0.4)PO4 (0≤x≤1)[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(7): A747. DOI:10.1149/1.1375167. |
| 100 | CHEN L, YUAN Y Q, FENG X, et al. Enhanced electrochemical properties of LiFe1- xMnxPO4/C composites synthesized from FePO4·2H2O nanocrystallites[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 214: 344-350. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.04.089. |
| 101 | ARAVINDAN V, GNANARAJ J, LEE Y S, et al. LiMnPO4-A next generation cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(11): 3518-3539. DOI:10.1039/C2TA01393B. |
| 102 | YAMADA A, CHUNG S C. Crystal chemistry of the olivine-type Li(MnyFe1– y)PO4 and (MnyFe1– y)PO4 as possible 4 V cathode materials for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(8): A960. DOI:10.1149/1.1385377. |
| 103 | SARAVANAN K, RAMAR V, BALAYA P, et al. Li(MnxFe1- x)PO4/C (x = 0.5, 0.75 and 1) nanoplates for lithium storage application[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(38): 14925-14935. DOI:10.1039/C1JM11541C. |
| 104 | BHUVANESWARI D, GANGULIBABU, DOH C H, et al. Role of iron dopant and carbon additive in improving the ionic transport and electrochemical properties of LiFexMn1– xPO4 (x=0.25 and 0.75) solid solutions[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2011, 6(9): 3714-3728. DOI:10.1016/S1452-3981(23)18283-6. |
| 105 | WANG Z H, YUAN L X, ZHANG W X, et al. LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4/C cathode material with high energy density for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 532: 25-30. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.04.008. |
| 106 | MOLENDA J, OJCZYK W, MARZEC J. Electrical conductivity and reaction with lithium of LiFe1- yMnyPO4 olivine-type cathode materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 174(2): 689-694. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.06.238. |
| 107 | WANG D Y, OUYANG C Y, DRÉZEN T, et al. Improving the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4 via Mn-site substitution[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(2): A225. DOI:10.1149/1.3271112. |
| 108 | YE F P, WANG L, HE X M, et al. Solvothermal synthesis of nano LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4: Reaction mechanism and electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 253: 143-149. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.12.010. |
| 109 | ZHOU X, DENG Y F, WAN L N, et al. A surfactant-assisted synthesis route for scalable preparation of high performance of LiFe0.15Mn0.85PO4/C cathode using bimetallic precursor[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 265: 223-230. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2014.04.049. |
| 110 | DU K, ZHANG L H, CAO Y B, et al. Synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C by co-precipitation method and its electrochemical performances as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 136(2/3): 925-929. DOI:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.08.021. |
| 111 | LI B Z, WANG Y, XUE L, et al. Acetylene black-embedded LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C composite as cathode for lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 232: 12-16. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.019. |
| 112 | DING B, XIAO P F, JI G, et al. High-performance lithium-ion cathode LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/C and the mechanism of performance enhancements through Fe substitution[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(22): 12120-12126. DOI:10.1021/am403991f. |
| 113 | LIU J L, LIAO W J, YU A S. Electrochemical performance and stability of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C composite[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 587: 133-137. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom. 2013.10.154. |
| 114 | HUANG Y P, LI X, CHEN Z, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on electrochemical performance of LiFe0·4Mn0·6PO4/C cathode materials[J]. Materials Research Innovations, 2014, 18(sup4): S4-2-S4-5. DOI:10.1179/1432891714Z.000000000664. |
| 115 | ZHONG Y J, LI J T, WU Z G, et al. LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 solid solution materials synthesized by rheological phase reaction and their excellent electrochemical performances as cathode of lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 234: 217-222. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.184. |
| 116 | BRAMNIK N N, BRAMNIK K G, NIKOLOWSKI K, et al. Synchrotron diffraction study of lithium extraction from LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2005, 8(8): A379. DOI:10.1149/1.1940487. |
| 117 | RAVNSBÆK D B, XIANG K, XING W T, et al. Engineering the transformation strain in LiMnyFe1– yPO4 olivines for ultrahigh rate battery cathodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(4): 2375-2380. DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b05146. |
| 118 | PEREA A, SOUGRATI M T, IONICA-BOUSQUET C M, et al. operando 57Fe Mössbauer and XRD investigation of LixMnyFe1- yPO4/C composites (y = 0; 0.25)[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(5): 2080-2086. DOI:10.1039/C1RA00256B. |
| 119 | WI S, PARK J, LEE S, et al. Insights on the delithiation/lithiation reactions of LixMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 mesocrystals in Li+ batteries by in situ techniques[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 39: 371-379. DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.07.016. |
| 120 | Ravnsbæk D B, Xiang K, Xing W T, et al. Engineering the transformation strain in LiMnyFe1– yPO4 olivines for ultrahigh rate battery cathodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(4): 2375-2380. |
| 121 | WANG H L, YANG Y, LIANG Y Y, et al. LiMn1- xFexPO4 nanorods grown on graphene sheets for ultrahigh-rate-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(32): 7364-7368. DOI:10.1002/anie.201103163. |
| [1] | 周德清, 蔡艺嘉, 张子芩, 周丽萍, 胡思江, 黄有国, 王红强, 李庆余. MoS2 尖晶石包覆富锂锰基正极材料的电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 1087-1096. |
| [2] | 郝定邦, 栗永利. 高倍率和长循环稳定性钠离子电池正极材料Na0.85Ni0.3Fe0.2Mn0.5O1.95F0.05 @CuO的性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2489-2498. |
| [3] | 陈桢, 李贤傲, 徐艺维, 刘欣, 申泽骧, 陈明华. LATP、LAGP固态电解质材料合成改性路线研究现状及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(11): 3826-3855. |
| [4] | 赵争光, 陈振营, 翟光群, 张希, 庄小东. Sc/O掺杂硫化物固态电解质的制备及全固态电池性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(8): 2412-2423. |
| [5] | 郝增辉, 刘训良, 孟缘, 孟楠, 温治. 电极界面微观结构对固态锂离子电池性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(7): 2095-2104. |
| [6] | 王绍聪, 李伟, 黄瑞琴, 郭艺飞, 刘峥. 锰基钠离子电池正极材料Jahn-Teller效应抑制方法进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(1): 139-149. |
| [7] | 熊小琳, 岳金明, 周安行, 索鎏敏, 胡勇胜, 李泓, 黄学杰. 尖晶石锰酸锂正极在Water-in-salt电解液中的电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 375-384. |
| [8] | 孙兴伟, 王龙龙, 姜丰, 马君, 周新红, 崔光磊. 固态聚合物锂电池失效机制及其表征技术[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(6): 1024-1032. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
