储能科学与技术 ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (5): 1364-1379.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0258
• 喜迎东北大学建校百年-储能电池关键材料与循环技术专刊 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-04-23
修回日期:2023-05-06
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-05-29
通讯作者:
高宣雯
E-mail:2171581@stu.neu.edu.cn;gaoxuanwen@smm.neu.edu.cn
作者简介:韩文哲(1999—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为电池正极材料,E-mail:2171581@stu.neu.edu.cn;
基金资助:
Wenzhe HAN( ), Qingsong LAI, Xuanwen GAO(
), Qingsong LAI, Xuanwen GAO( ), Wenbin LUO
), Wenbin LUO
Received:2023-04-23
Revised:2023-05-06
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-05-29
Contact:
Xuanwen GAO
E-mail:2171581@stu.neu.edu.cn;gaoxuanwen@smm.neu.edu.cn
摘要:
可再生能源替代传统化石燃料的研究推动了电能存储系统的发展。随着对规模储能的需求不断增加,钾离子电池(PIBs)因其成本低廉、元素丰度高、理论工作电压高以及电解液中K+卓越的传输动力学,在未来将成为商用锂离子电池的补充或替代品。电极材料的发展深刻影响电池的电化学性能。石墨作为钾离子电池负极展现出了优异的循环稳定性,然而,找到具有快速的传输动力学和稳定的框架结构来嵌入/脱嵌大尺寸K+的正极材料是钾离子电池面临的主要挑战。层状过渡金属氧化物因其结构稳定、合成过程简单及价格低廉等优点而具有广阔的应用前景。本文介绍了钾含量和合成温度等对过渡金属层状氧化物晶体结构的影响,并说明了各种晶体结构在脱钾过程中的结构演变和容量损失机理;在此基础上,提出了针对不同晶体结构的锰基过渡金属层状氧化物的改性方法以提高其电化学性能;最后,对新型过渡金属层状氧化物正极的主要研究方向和研究热点进行了预测,以指导未来钾离子电池正极材料的发展。
中图分类号:
韩文哲, 赖青松, 高宣雯, 骆文彬. 钾离子电池锰基层状氧化物正极的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1364-1379.
Wenzhe HAN, Qingsong LAI, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Advances toward manganese-based layered oxide cathodes for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1364-1379.
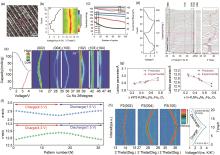
图3
(a) K0.77MnO2 ?H2O0.23 的HRTEM放大图[26];(b) K0.77MnO2 ?H2O0.23 电极在电流密度为20 mA/g时的充放电曲线及其在10.5°~15.5°区域的原位XRD谱图[26];(c) 电流密度为100 mA/g,循环100次时电极的循环性能和相应的库仑效率[26];(d) K0.77MnO2 ?H2O0.23 电极充放电时的原位XRD表征[43];(e) P2-K0.75[Ni1/3Mn2/3]O2 电极的XRD结果[44];(f) 相应的计算晶格参数[44];(g) 由实验计算的数据和第一性原理计算预测的数据[13];(h) P2-K0.75MNFO2 在1.5~3.9 V(K/K+)电压范围内充放电过程的XRD图谱[13]"

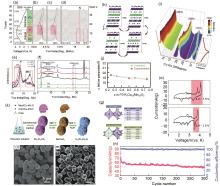
图4
(a) P3型K0.5MnO2 在电流密度为2 mA/g时的充放电曲线;(b)~(d) #1、#7和#14的原位XRD图;(e) P3-K0.5MnO2 的XRD峰比较;(f) O3和P3结构的XRD模拟图谱比较[48];(g) P3-K0.75MnO2 和P3-K0.75[Co0.5Mn0.5]O2 的晶体结构示意图;(h) P3-K x [Co0.5Mn0.5]O2(0.25≤ x ≤0.75)的结构变化;(i) P3-K x [Co0.5Mn0.5]O2 的XRD谱图;(j) 通过DFT计算和XRD数据得到的P3-K x [Co0.5Mn0.5]O2 的晶格参数的对比图[57];(k) 花生状P3型K0.45Mn0.5Co0.5O2 微粒的合成示意图[59];(l)、(m) P3型K0.45Mn0.5Co0.5O2 的SEM图像[59];(n) P3型K0.45Mn0.5Co0.5O2 在300 mA/g电流密度下的长期循环性能[59];(o) K0.5MnO2 的循环伏安图"

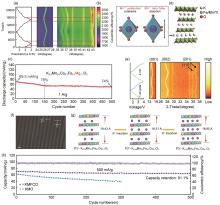
图5
(a) P3型K0.5Mn0.6Co0.2Fe0.1Mg0.1O2 电极的XRD谱图;(b) 姜-泰勒效应的可视化结构变化示意图;(c) K0.5Mn0.6Co0.2Fe0.1Mg0.1O2 在1 A/g下的长循环性能;(d) 沿 b 轴观察P3-K0.4Fe0.1Mn0.8Ti0.1O2 的结构示意图;(e) K0.35Mn0.8Fe0.1Cu0.1O2 的原位XRD图[66];(f) K0.35Mn0.8Fe0.1Cu0.1O2 的HRTEM图[66];(g) K0.35Mn0.8Fe0.1Cu0.1O2 在K+ 嵌入过程中的结构变化示意图[66];(h) K0.35Mn0.8Fe0.1Cu0.1O2 在500 mA/g时的循环性能[66]"
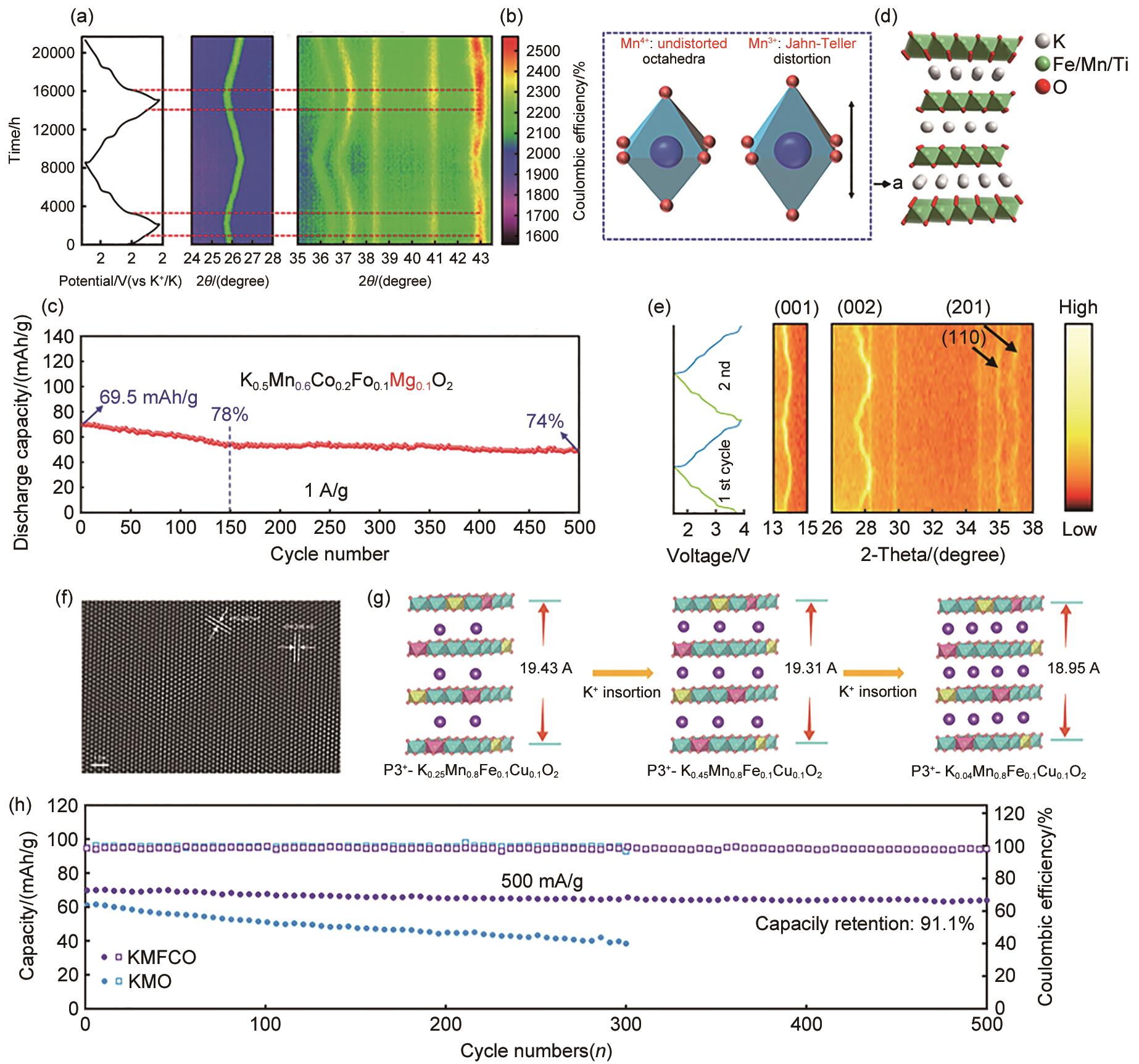
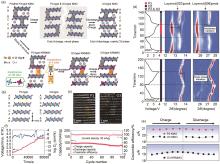
图6
(a) Rb和Mg元素取代对晶体结构影响的示意图;(b) P3型和O3型层状结构沿TM层 c 轴方向的结构示意图;(c) K0.45Rb0.05Mn0.85Mg0.15O2 粉末以及用其组装电池但未开始循环时的HRTEM图;(d) K0.45MnO2 和K0.45Rb0.05Mn0.85Mg0.15O2 在1.5~3.9 V电压范围、70 mA/g电流密度下的电压曲线及对应的原位XRD图谱;(e) 通过原位XRD图谱计算的K0.45MnO2 和K0.45Rb0.05Mn0.85Mg0.15O2 的晶格参数;(f) K0.45Rb0.05Mn0.85Mg0.15O2 在20 mA/g下的GITT结果,以及相应的 DK+;(g) K0.45Rb0.05Mn0.85Mg0.15O2 在200 mA/g下的循环性能[69]"

| 1 | KANG B, CEDER G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7235): 190-193. |
| 2 | MANTHIRAM A. A reflection on lithium-ion battery cathode chemistry[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-9. |
| 3 | PRAMUDITA J C, SEHRAWAT D, GOONETILLEKE D, et al. An initial review of the status of electrode materials for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(24): 1602911. |
| 4 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7(1): 19-29. |
| 5 | XU Y S, DUAN S Y, SUN Y G, et al. Recent developments in electrode materials for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(9): 4334-4352. |
| 6 | KUBOTA K, DAHBI M, HOSAKA T, et al. Towards K-ion and Na-ion batteries as "beyond Li-ion"[J]. The Chemical Record, 2018, 18(4): 459-479. |
| 7 | LUO W, WAN J Y, OZDEMIR B, et al. Potassium ion batteries with graphitic materials[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(11): 7671-7677. |
| 8 | WANG J, LIU Z M, ZHOU J, et al. Insights into metal/metalloid-based alloying anodes for potassium ion batteries[J]. ACS Materials Letters, 2021, 3(11): 1572-1598. |
| 9 | XUE L G, GAO H C, LI Y T, et al. Cathode dependence of liquid-alloy Na-K anodes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(9): 3292-3298. |
| 10 | HAN K, MENG J S, HONG X F, et al. Three-dimensional graphene-supported nickel disulfide nanoparticles promise stable and fast potassium storage[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(15): 8255-8261. |
| 11 | WANG X P, XIAO Z T, HAN K, et al. Advances in fine structure optimizations of layered transition-metal oxide cathodes for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(2): 2202861. |
| 12 | LI J Y, MANTHIRAM A. A comprehensive analysis of the interphasial and structural evolution over long-term cycling of ultrahigh-nickel cathodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(45): 1902731. |
| 13 | HWANG J Y, KIM J, YU T Y, et al. A new P2-type layered oxide cathode with superior full-cell performances for K-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(37): 21362-21370. |
| 14 | XU Y S, ZHANG Q H, WANG D, et al. Enabling reversible phase transition on K5/9Mn7/9Ti2/9O2 for high-performance potassium-ion batteries cathodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 31: 20-26. |
| 15 | ZHANG L, ZHANG B W, WANG C R, et al. Constructing the best symmetric full K-ion battery with the NASICON-type K3V2(PO4)3[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 60: 432-439. |
| 16 | CHONG S K, WU Y F, GUO S W, et al. Potassium nickel hexacyanoferrate as cathode for high voltage and ultralong life potassium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 22: 120-127. |
| 17 | KAPAEV R R, ZHIDKOV I S, KURMAEV E Z, et al. Hexaazatriphenylene-based polymer cathode for fast and stable lithium-, sodium- and potassium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(39): 22596-22603. |
| 18 | KIM U H, JUN D W, PARK K J, et al. Pushing the limit of layered transition metal oxide cathodes for high-energy density rechargeable Li ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(5): 1271-1279. |
| 19 | ZHANG H Y, XI K Y, JIANG K Z, et al. Enhanced K-ion kinetics in a layered cathode for potassium ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(55): 7910-7913. |
| 20 | ZHANG H, WANG L, HE X M. Trends in a study on thermal runaway mechanism of lithium-ion battery with LiNixMnyCo1- x- yO2 cathode materials[J]. Battery Energy, 2022, 1(1): 20210011. |
| 21 | VAALMA C, GIFFIN G A, BUCHHOLZ D, et al. Non-aqueous K-ion battery based on layered K0.3MnO2 and hard carbon/carbon black[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(7): A1295-A1299. |
| 22 | LIU C L, LUO S H, HUANG H B, et al. Layered potassium-deficient P2- and P3-type cathode materials KxMnO2 for K-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356: 53-59. |
| 23 | PATOUX S, DOLLÉ M, DOEFF M M. Layered Manganese oxide intergrowth electrodes for rechargeable lithium batteries. 2. substitution with Al[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2005, 17(5): 1044-1054. |
| 24 | HUANG Z X, GU Z Y, HENG Y L, et al. Advanced layered oxide cathodes for sodium/potassium-ion batteries: Development, challenges and prospects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139438. |
| 25 | SUN R, DONG S Y, XU F, et al. Co-intercalation strategy of constructing partial cation substitution of ammonium vanadate {(NH4)2V6O16} for stable zinc ion storage[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(19): 7607-7612. |
| 26 | LIN B W, ZHU X H, FANG L Z, et al. Birnessite nanosheet arrays with high K content as a high-capacity and ultrastable cathode for K-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(24): 1900060. |
| 27 | KUMAKURA S, TAHARA Y, SATO S, et al. P'2-Na2/3Mn0.9Me0.1O2 (Me=Mg, Ti, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn): Correlation between orthorhombic distortion and electrochemical property[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(21): 8958-8962. |
| 28 | BILLAUD J, SINGH G, ARMSTRONG A R, et al. Na0.67Mn1- xMgxO2 (0≤x≤0.2): A high capacity cathode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(4): 1387-1391. |
| 29 | YABUUCHI N, KUBOTA K, DAHBI M, et al. Research development on sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11636-11682. |
| 30 | NAM K W, KIM S, YANG E, et al. Critical role of crystal water for a layered cathode material in sodium ion batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(10): 3721-3725. |
| 31 | JO J H, CHOI J U, KONAROV A, et al. Sodium-ion batteries: Building effective layered cathode materials with long-term cycling by modifying the surface via sodium phosphate[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(14): 1705968. |
| 32 | LIU Z M, WANG J, JIA X X, et al. Graphene armored with a crystal carbon shell for ultrahigh-performance potassium ion batteries and aluminum batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9): 10631-10642. |
| 33 | BAO S, LUO S H, LU J L. Preparation and optimization of ZrO2 modified P2-type Na2/3Ni1/6Co1/6Mn2/3O2 with enhanced electrochemical performance as cathode for sodium ion batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10): 16080-16087. |
| 34 | YU Y, KONG W J, LI Q Y, et al. Understanding the multiple effects of TiO2 coating on NaMn0.33Fe0.33Ni0.33O2 cathode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(1): 933-942. |
| 35 | ZHANG Y, LIU L, JAMIL S, et al. Al2O3 coated Na0.44MnO2 as high-voltage cathode for sodium ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 494: 1156-1165. |
| 36 | SUN H H, HWANG J Y, YOON C S, et al. Capacity degradation mechanism and cycling stability enhancement of AlF3-coated nanorod gradient Na[Ni0.65Co0.08Mn0.27]O2 cathode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(12): 12912-12922. |
| 37 | 戚兴国, 王伟刚, 胡勇胜, 等. 钠离子电池层状氧化物正极材料的表面修饰研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(5)1396-1401 |
| QI X G, WANG W G, HU Y S, et al. Surface modification research of layered oxide materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5)1396-1401 | |
| 38 | ZHENG J M, GU M, XIAO J, et al. Functioning mechanism of AlF3 coating on the Li- and Mn-rich cathode materials[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(22): 6320-6327. |
| 39 | ZHAO S Q, YAN K, MUNROE P, et al. Construction of hierarchical K1.39Mn3O6 spheres via AlF3 coating for high-performance potassium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(10): 1803757. |
| 40 | TAPIA-RUIZ N, DOSE W M, SHARMA N, et al. High voltage structural evolution and enhanced Na-ion diffusion in P2-Na2/3Ni1/3- xMgxMn2/3O2 (0≤x≤0.2) cathodes from diffraction, electrochemical and ab initio studies[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(6): 1470-1479. |
| 41 | PIAO J Y, GU L, WEI Z X, et al. Phase control on surface for the stabilization of high energy cathode materials of lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(12): 4900-4907. |
| 42 | WANG Q C, MENG J K, YUE X Y, et al. Tuning P2-structured cathode material by Na-site Mg substitution for Na-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(2): 840-848. |
| 43 | GAO A, LI M, GUO N N, et al. K-birnessite electrode obtained by ion exchange for potassium-ion batteries: Insight into the concerted ionic diffusion and K storage mechanism[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(1): 1802739. |
| 44 | JO J H, CHOI J U, PARK Y J, et al. P2-K0.75[Ni1/3Mn2/3]O2 cathode material for high power and long life potassium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(7): 1903605. |
| 45 | WANG S H, SUN C L, WANG N, et al. Ni- and/or Mn-based layered transition metal oxides as cathode materials for sodium ion batteries: Status, challenges and countermeasures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(17): 10138-10158. |
| 46 | MA C Z, ALVARADO J, XU J, et al. Exploring oxygen activity in the high energy P2-type Na0.78Ni0.23Mn0.69O2 cathode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(13): 4835-4845. |
| 47 | 刘欢庆, 高旭, 陈军, 等. 钠离子电池层状氧化物正极: 层间滑移, 相变与性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(5): 1327-1339 |
| LIU H Q, GAO X, CHEN J, et al. Layered oxide cathode for sodium ion batteries: Interlayer glide, phase transition and performance[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1327-1339 | |
| 48 | KIM H, SEO D H, KIM J C, et al. Investigation of potassium storage in layered P3-type K0.5MnO2 cathode[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(37): 1702480. |
| 49 | BO S H, LI X, TOUMAR A J, et al. Layered-to-rock-salt transformation in desodiated NaxCrO2 (x=0.4)[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(5): 1419-1429. |
| 50 | BEZZA I, KAUS M, HEINZMANN R, et al. Mechanism of the delithiation/lithiation process in LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4: in situ and ex situ investigations on long-range and local structures[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(17): 9016-9024. |
| 51 | CHOI J U, YOON C S, ZHANG Q, et al. Understanding on the structural and electrochemical performance of orthorhombic sodium Manganese oxides[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(1): 202-211. |
| 52 | WANG X P, XU X M, NIU C J, et al. Earth abundant Fe/Mn-based layered oxide interconnected nanowires for advanced K-ion full batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(1): 544-550. |
| 53 | CHO M K, JO J H, CHOI J U, et al. Cycling stability of layered potassium Manganese oxide in nonaqueous potassium cells[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(31): 27770-27779. |
| 54 | SADA K, BARPANDA P. P3-type layered K0.48Mn0.4Co0.6O2: A novel cathode material for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(15): 2272-2275. |
| 55 | WENG J Y, DUAN J, SUN C L, et al. Construction of hierarchical K0.7Mn0.7Mg0.3O2 microparticles as high capacity & long cycle life cathode materials for low-cost potassium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123649. |
| 56 | RAMASAMY H V, SENTHILKUMAR B, BARPANDA P, et al. Superior potassium-ion hybrid capacitor based on novel P3-type layered K0.45Mn0.5Co0.5O2 as high capacity cathode[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 368: 235-243. |
| 57 | CHOI J U, KIM J, HWANG J Y, et al. K0.54[Co0.5Mn0.5]O2: New cathode with high power capability for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 61: 284-294. |
| 58 | LIU Z M, WANG J, LU B G. Plum pudding model inspired KVPO4F@3DC as high-voltage and hyperstable cathode for potassium ion batteries[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(15): 1242-1251. |
| 59 | ZHANG Z Z, SUN J L, DUAN L P, et al. Self-templated construction of peanut-like P3-type K0.45Mn0.5Co0.5O2 for highly reversible potassium storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(2): 554-560. |
| 60 | BAI P L, JIANG K Z, ZHANG X P, et al. Ni-doped layered Manganese oxide as a stable cathode for potassium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(9): 10490-10495. |
| 61 | XIAO Z T, XIA F J, XU L H, et al. Suppressing the jahn-teller effect in Mn-based layered oxide cathode toward long-life potassium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(14): 2108244. |
| 62 | LIU W, LI X F, XIONG D B, et al. Significantly improving cycling performance of cathodes in lithium ion batteries: The effect of Al2O3 and LiAlO2 coatings on LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 44: 111-120. |
| 63 | CHOI J U, KIM J, JO J H, et al. Facile migration of potassium ions in a ternary P3-type K0.5[Mn0.8Fe0.1Ni0.1]O2 cathode in rechargeable potassium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 25: 714-723. |
| 64 | XU Y S, ZHOU Y N, ZHANG Q H, et al. Layered oxides with solid-solution reaction for high voltage potassium-ion batteries cathode[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 412: 128735. |
| 65 | ZHANG X Y, YU D X, WEI Z X, et al. Layered P3-type K0.4Fe0.1Mn0.8Ti0.1O2 as a low-cost and zero-strain electrode material for both potassium and sodium storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(16): 18897-18904. |
| 66 | LV J R, WANG B, HAO J X, et al. Single-crystalline Mn-based oxide as a high-rate and long-life cathode material for potassium-ion battery[J]. eScience, 2023, 3(1): 100081. |
| 67 | WANG P F, XIN H S, ZUO T T, et al. An abnormal 3.7 Volt O3 -Type sodium-ion battery cathode[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(27): 8178-8183. |
| 68 | DENG J Q, LUO W B, LU X, et al. High energy density sodium-ion battery with industrially feasible and air-stable O3 -Type layered oxide cathode[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(5): 1701610. |
| 69 | CAIXIANG Z M, HAO J X, ZHOU J, et al. Interlayer-engineering and surface-substituting Manganese-based self-evolution for high-performance potassium cathode[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(1): 2203126. |
| 70 | KIM H, SEO D H, URBAN A, et al. Stoichiometric layered potassium transition metal oxide for rechargeable potassium batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(18): 6532-6539. |
| 71 | JIANG X Y, LIU X W, ZENG Z Q, et al. A nonflammable Na+-based dual-carbon battery with low-cost, high voltage, and long cycle life[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(36): 1802176. |
| 72 | 黄永浩, 藏国景, 朱霨亚, 等. LiF添加剂改善含锂陶瓷隔膜与4.35 V LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2正极的界面稳定性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0128. |
| HUANG Yonghao, ZANG Guojing, ZHU WeiYa, et al. Improvement in interfacial stability between lithium-containing ceramic separator and 4.35 V LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode by LiF additives[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239. 2023.0128. | |
| 73 | HU Z, HAO J X, SHEN D Y, et al. Electro-spraying/spinning: A novel battery manufacturing technology[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.gee.2022.05.004. |
| [1] | 张言, 王海, 刘朝孟, 张德柳, 王佳东, 李建中, 高宣雯, 骆文彬. 锂离子电池富镍三元正极材料NCM的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1693-1705. |
| [2] | 冯晓晗, 孙杰, 何健豪, 魏义华, 周成冈, 孙睿敏. 磷酸铁锂正极材料改性研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(2): 467-486. |
| [3] | 王继贤, 彭思侃, 南文争, 陈翔, 王晨, 燕绍九, 戴圣龙. 喷雾干燥法制备石墨烯包覆富锂锰基材料Li1.22Mn0.52Ni0.26O2及其电化学性质[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(1): 111-117. |
| [4] | 王 灿, 马 盼, 祝国梁, 马永超, 季鹏程, 魏水淼, 赵 健, 于治水. 锂离子电池长寿命石墨电极研究现状与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(1): 59-67. |
| [5] | 古月圆, 韦聚才, 李金东, 王路阳, 吴旭. 电化学还原二氧化碳电解器相关研究概述及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(6): 1691-1701. |
| [6] | 任思佳, 田雷武, 邵钦君, 陈剑. 助熔剂法制备单晶LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2正极材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(6): 1702-1713. |
| [7] | 刘兴稳, 贺劲鑫, 王海林, 靳承铀, 缪永华, 薛驰. 氟元素掺杂的硅碳复合材料的制备和电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(S1): 56-59. |
| [8] | 王栋, 郑莉莉, 杜光超, 张志超, 冯燕, 戴作强. 锂离子电池正极材料掺杂和表面包覆研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(S1): 43-48. |
| [9] | 梁大宇, 包婷婷, 高田慧, 张健. 高比能NMC811/SiO-C软包电池循环失效分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2018, 7(3): 459-464. |
| [10] | 吴敏昌1,喻宁波1,乔永民1,孙方静2,张 洁1. 硬碳包覆人造石墨作为锂离子电池负极材料的快充性能评价[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2017, 6(S1): 15-. |
| [11] | 谢佳, 彭文, 杨续来. 尖晶石镍锰酸锂全电池常温循环寿命分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2014, 3(6): 624-628. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
