Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (9): 3134-3149.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0713
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhenwei ZHU1( ), Jiawei MIAO2, Xiayu ZHU1, Xiaoxu WANG2, Jingyi QIU1, Hao ZHANG1(
), Jiawei MIAO2, Xiayu ZHU1, Xiaoxu WANG2, Jingyi QIU1, Hao ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-07-31
Revised:2024-08-29
Online:2024-09-28
Published:2024-09-20
Contact:
Hao ZHANG
E-mail:zhenweizhu1@outlook.com;dr.h.zhang@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Zhenwei ZHU, Jiawei MIAO, Xiayu ZHU, Xiaoxu WANG, Jingyi QIU, Hao ZHANG. Research progress in lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction based on machine learning[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3134-3149.
Fig. 3
(a) The basic structure of RNN, where x represents the input layer, h represents the hidden layer, y represents the output layer, and W represents the weight matrix. (b) The basic structure of ESN, where W represents the weight matrix. (c) The basic structure of LSTM, where x, h, C represent the input, output, and cell state respectively, and Sigmoid refers to the activation function. (d) The basic structure of CNN. (e) Transition from regular convolution to dilated convolution, where x is the input and y is the output"
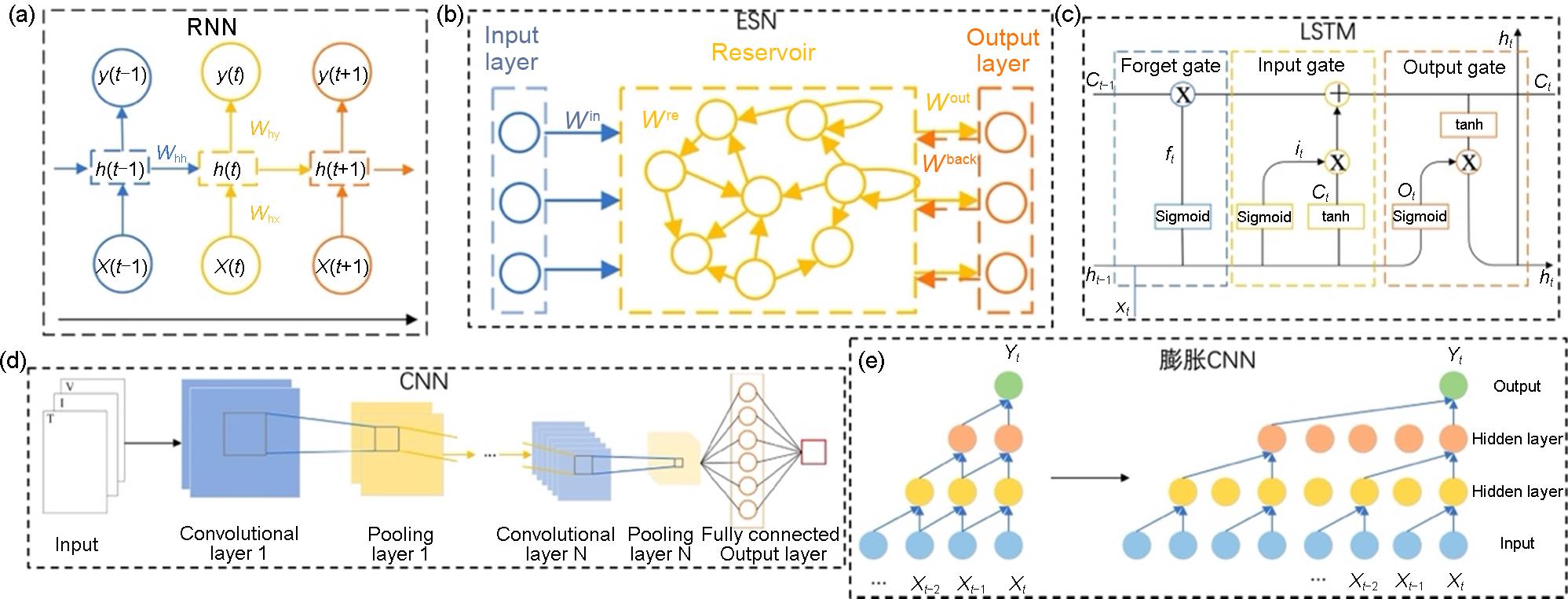
Table 1
Performance of different ML methods in RUL prediction"
| 年份 | 机器学习方法 | 参考文献 | 预测性能 | 电池类型 | 精度 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | RNN | [ | 容量 | LCO/石墨(NASA 5#) | 0.0030 RMSE | 较好的泛化性能 |
| 2021 | ESN | [ | 容量 | LCO/石墨(NASA 5#) | 3周 | 预测精度高,稳定 |
| 2021 | LSTM | [ | SOH | CALCE CS2-34# | 0.0017 RMSE(1周) | 不同电池不同工况下误差小,精度高 |
| 2021 | GRU | [ | 容量 | LCO/石墨(NASA 5#) | 0.0156 RMSE | 效率和精度都较高 |
| 2022 | SVR-PSO | [ | 电压对时间的积分 | LCO/石墨(NASA 5#) | 0.0133 RMSE | 高精度在线预测 |
| 2022 | CNN | [ | 自定义 | LFP/石墨(MIT) | 6.46%MAPE | 只需要一圈循环数据即可以实现预测 |
| 2022 | CTC-ELM | [ | 容量 | LCO/石墨(NASA,Oxford) | 0.000036MES(NASA),0.000001MES(Oxford) | 高精度预测 |
| 2021 | RVM | [ | 容量 | LCO/graphite (NASA 5#) | 0.0105 RMSE | 具有长预测能力,预测稳定性高 |
| 2021 | GPR | [ | 峰位置、峰高、峰面积 | CALCE CS2-35# | 5周 | 高精度,适配不同电池,预测实际变化曲线表现良好 |
| 1 | SAMANTA A, CHOWDHURI S, WILLIAMSON S S. Machine learning-based data-driven fault detection/diagnosis of lithium-ion battery: A critical review[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(11): 1309. DOI: 10.3390/electronics10111309. |
| 2 | ALKHEDHER M, AL TAHHAN A B, YOUSAF J, et al. Electrochemical and thermal modeling of lithium-ion batteries: A review of coupled approaches for improved thermal performance and safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 86: 111172. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2024.111172. |
| 3 | CHANG W Y. The state of charge estimating methods for battery: A review[J]. ISRN Applied Mathematics, 2013, 2013: 953792. DOI: 10.1155/2013/953792. |
| 4 | NDECHE K C, EZEONU S O. Implementation of coulomb counting method for estimating the state of charge of lithium-ion battery[J]. Physical Science International Journal, 2021: 1-8. DOI: 10.9734/psij/2021/v25i330244. |
| 5 | HOW D N T, HANNAN M A, HOSSAIN LIPU M S, et al. State of charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries using model-based and data-driven methods: A review[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 136116-136136. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2942213. |
| 6 | LI Y, LIU K L, FOLEY A M, et al. Data-driven health estimation and lifetime prediction of lithium-ion batteries: A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 113: 109254. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109254. |
| 7 | MENG H X, LI Y F. A review on prognostics and health management (PHM) methods of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 116: 109405. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.109405. |
| 8 | ZHANG Q S, YANG L, GUO W C, et al. A deep learning method for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction based on sparse segment data via cloud computing system[J]. Energy, 2022, 241: 122716. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.122716. |
| 9 | HASHEMZADEH P, DÉSILETS M, LACROIX M, et al. Investigation of the P2D and of the modified single-particle models for predicting the nonlinear behavior of Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 52: 104909. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2022.104909. |
| 10 | LIN X Y, TANG Y L, REN J, et al. State of charge estimation with the adaptive unscented Kalman filter based on an accurate equivalent circuit model[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 41: 102840. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.102840. |
| 11 | ZHANG Y, TU L, XUE Z W, et al. Weight optimized unscented Kalman filter for degradation trend prediction of lithium-ion battery with error compensation strategy[J]. Energy, 2022, 251: 123890. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.123890. |
| 12 | LI Y Y, STROE D I, CHENG Y H, et al. On the feature selection for battery state of health estimation based on charging-discharging profiles[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 33: 102122. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2020.102122. |
| 13 | JIANG B, ZHU J G, WANG X Y, et al. A comparative study of different features extracted from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in state of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 322: 119502. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119502. |
| 14 | LI X J, YU D, SØREN BYG V, et al. The development of machine learning-based remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 82: 103-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2023.03.026. |
| 15 | GASPER P, SCHIEK A, SMITH K, et al. Predicting battery capacity from impedance at varying temperature and state of charge using machine learning[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2022, 3(12): 101184. DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.101184. |
| 16 | FARAJI-NIRI M, RASHID M, SANSOM J, et al. Accelerated state of health estimation of second life lithium-ion batteries via electrochemical impedance spectroscopy tests and machine learning techniques[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 58: 106295. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2022.106295. |
| 17 | SEVERSON K A, ATTIA P M, JIN N, et al. Data-driven prediction of battery cycle life before capacity degradation[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4: 383-391. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-019-0356-8. |
| 18 | FAN J M, FAN J P, LIU F, et al. A novel machine learning method based approach for Li-ion battery prognostic and health management[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 160043-160061. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947843. |
| 19 | WANG Y J, PAN R, YANG D, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery based on discrete wavelet transform[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 2053-2058. DOI: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.582. |
| 20 | HAN X J, WANG Z R, WEI Z X. A novel approach for health management online-monitoring of lithium-ion batteries based on model-data fusion[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 302: 117511. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117511. |
| 21 | CHEN L, DING Y H, LIU B H, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery using a novel particle filter framework with grey neural network[J]. Energy, 2022, 244: 122581. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.122581. |
| 22 | KWON S J, HAN D, CHOI J H, et al. Remaining-useful-life prediction via multiple linear regression and recurrent neural network reflecting degradation information of 20 Ah LiNixMnyCo1- x- yO2 pouch cell[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 858: 113729. DOI: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113729. |
| 23 | ANSARI S, AYOB A, HOSSAIN LIPU M S, et al. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion battery storage system: A comprehensive review of methods, key factors, issues and future outlook[J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8: 12153-12185. DOI: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.09.043. |
| 24 | CHEN J C, CHEN T L, LIU W J, et al. Combining empirical mode decomposition and deep recurrent neural networks for predictive maintenance of lithium-ion battery[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2021, 50: 101405. DOI: 10.1016/j.aei.2021.101405. |
| 25 | ZHANG Y Z, XIONG R, HE H W, et al. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 5695-5705. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2805189. |
| 26 | TONG Z M, MIAO J Z, TONG S G, et al. Early prediction of remaining useful life for Lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid machine learning method[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 317: 128265. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128265. |
| 27 | CHENG G, WANG X Z, HE Y R. Remaining useful life and state of health prediction for lithium batteries based on empirical mode decomposition and a long and short memory neural network[J]. Energy, 2021, 232: 121022. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.121022. |
| 28 | PARK K, CHOI Y, CHOI W J, et al. LSTM-based battery remaining useful life prediction with multi-channel charging profiles[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 20786-20798. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968939. |
| 29 | ZHANG M, WU L F, PENG Z. The early prediction of lithium-ion battery remaining useful life using a novel long short-term memory network[C]// 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA). IEEE, 2021: 1364-1371[2024-09-01]. DOI: 10.1109/ICIEA51954.2021.9516254. |
| 30 | WANG Z Q, LIU N, GUO Y M. Adaptive sliding window LSTM NN based RUL prediction for lithium-ion batteries integrating LTSA feature reconstruction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 466: 178-189. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.09.025. |
| 31 | LIU Y F, ZHAO G Q, PENG X Y. Deep learning prognostics for lithium-ion battery based on ensembled long short-term memory networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 155130-155142. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937798. |
| 32 | WANG F K, HUANG C Y, MAMO T. Ensemble model based on stacked long short-term memory model for cycle life prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(10): 3549. DOI: 10.3390/app10103549. |
| 33 | PAN D W, LI H F, WANG S J. Transfer learning-based hybrid remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries under different stresses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 3501810. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3142757. |
| 34 | SONG Y C, LI L, PENG Y, et al. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction based on GRU-RNN[C]// 2018 12th International Conference on Reliability, Maintainability, and Safety (ICRMS). IEEE, 2018: 317-322[2024-09-01]. DOI: 10.1109/ICRMS.2018.00067. |
| 35 | WEI M, GU H R, YE M, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on Monte Carlo Dropout and gated recurrent unit[J]. Energy Reports, 2021, 7: 2862-2871. DOI: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.05.019. |
| 36 | TANG T, YUAN H M. A hybrid approach based on decomposition algorithm and neural network for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 217: 108082. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2021.108082. |
| 37 | CHE Y H, DENG Z W, LIN X K, et al. Predictive battery health management with transfer learning and online model correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(2): 1269-1277. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3055811. |
| 38 | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N M, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All you Need[J/OL]. Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017[2024-07-31]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762 |
| 39 | CHEN D Q, HONG W C, ZHOU X Z. Transformer network for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. IEEE Access, 1975, 10: 19621-19628. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3151975. |
| 40 | YU J S, YANG J, WU Y, et al. Online state-of-health prediction of lithium-ion batteries with limited labeled data[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(14): 11345-11360. DOI: 10.1002/er.5750. |
| 41 | ZHAO Q, QIN X L, ZHAO H B, et al. A novel prediction method based on the support vector regression for the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2018, 85: 99-108. DOI: 10.1016/j.microrel.2018.04.007. |
| 42 | LI X, MA Y, ZHU J J. An online dual filters RUL prediction method of lithium-ion battery based on unscented particle filter and least squares support vector machine[J]. Measurement, 2021, 184: 109935. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109935. |
| 43 | DONG H C. Prediction of the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries based on Dempster-Shafer theory and the support vector regression-particle filter[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 165490-165503. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3136131. |
| 44 | WANG F K, AMOGNE Z E, TSENG C, et al. A hybrid method for online cycle life prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(7): 9080-9096. DOI: 10.1002/er.7785. |
| 45 | NUHIC A, TERZIMEHIC T, SOCZKA-GUTH T, et al. Health diagnosis and remaining useful life prognostics of lithium-ion batteries using data-driven methods[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 239: 680-688. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.11.146. |
| 46 | VILSEN S B, SUI X, STROE D I. A time-varying log-linear model for predicting the resistance of lithium-ion batteries[C]// 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia). IEEE, 2020: 1659-1666. DOI: 10.1109/IPEMC-ECCEAsia48364.2020.9367839. |
| 47 | LONG B, XIAN W M, JIANG L, et al. An improved autoregressive model by particle swarm optimization for prognostics of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2013, 53(6): 821-831. DOI: 10.1016/j.microrel.2013.01.006. |
| 48 | LIU D T, LUO Y, LIU J, et al. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation based on fusion nonlinear degradation AR model and RPF algorithm[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2014, 25(3): 557-572. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-013-1520-x. |
| 49 | GUO L M, PANG J Y, LIU D T, et al. Data-driven framework for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation based on improved nonlinear degradation factor[C]// 2013 IEEE 11th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments. IEEE, 2013, 2: 1014-1020[2024-09-01]. DOI: 10.1109/ICEMI.2013.6743205. |
| 50 | SONG Y C, LIU D T, YANG C, et al. Data-driven hybrid remaining useful life estimation approach for spacecraft lithium-ion battery[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2017, 75: 142-153. DOI: 10.1016/j.microrel.2017.06.045. |
| 51 | LIN J, WEI M H. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery based on auto-regression and particle filter[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics, 2021, 14(2): 218-237. DOI: 10.1108/ijicc-09-2020-0131. |
| 52 | LIN C P, CABRERA J, YANG F F, et al. Battery state of health modeling and remaining useful life prediction through time series model[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 275: 115338. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115338. |
| 53 | ZHOU B T, CHENG C, MA G J, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery based on attention mechanism with positional encoding[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 895(1): 012006. DOI: 10.1088/1757-899x/895/1/012006. |
| 54 | HSU C W, XIONG R, CHEN N Y, et al. Deep neural network battery life and voltage prediction by using data of one cycle only[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 306: 118134. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy. 2021.118134. |
| 55 | XIONG R, TIAN J P, SHEN W X, et al. Semi-supervised estimation of capacity degradation for lithium ion batteries with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 76: 404-413. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.09.045. |
| 56 | KONG D P, WANG S H, PING P. State-of-health estimation and remaining useful life for lithium-ion battery based on deep learning with Bayesian hyperparameter optimization[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(5): 6081-6098. DOI: 10.1002/er.7548. |
| 57 | REN L, DONG J B, WANG X K, et al. A data-driven auto-CNN-LSTM prediction model for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(5): 3478-3487. DOI: 10.1109/TII.2020.3008223. |
| 58 | ZHANG X W, QIN Y, YUEN C, et al. Time-series regeneration with convolutional recurrent generative adversarial network for remaining useful life estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(10): 6820-6831. DOI: 10.1109/TII.2020.3046036. |
| 59 | YANG H, WANG P L, AN Y B, et al. Remaining useful life prediction based on denoising technique and deep neural network for lithium-ion capacitors[J]. eTransportation, 2020, 5: 100078. DOI: 10.1016/j.etran.2020.100078. |
| 60 | HONG J, LEE D, JEONG E R, et al. Towards the swift prediction of the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries with end-to-end deep learning[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 278: 115646. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115646. |
| 61 | ZHOU D H, LI Z Y, ZHU J L, et al. State of health monitoring and remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on temporal convolutional network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 53307-53320. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981261. |
| 62 | SHEN S, SADOUGHI M, LI M, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks with ensemble learning and transfer learning for capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 260: 114296. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114296. |
| 63 | RAZAVI-FAR R, CHAKRABARTI S, SAIF M, et al. An integrated imputation-prediction scheme for prognostics of battery data with missing observations[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 115: 709-723. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.033. |
| 64 | CHEN X W, LIU Z, WANG J Y, et al. An adaptive prediction model for the remaining life of an Li-ion battery based on the fusion of the two-phase Wiener process and an extreme learning machine[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(5): 540. DOI: 10.3390/electronics10050540. |
| 65 | SUN T F, XIA B Z, LIU Y F, et al. A novel hybrid prognostic approach for remaining useful life estimation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(19): 3678. DOI: 10.3390/en12193678. |
| 66 | YANG J, PENG Z, WANG H M, et al. The remaining useful life estimation of lithium-ion battery based on improved extreme learning machine algorithm[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2018, 13(5): 4991-5004. DOI: 10.20964/2018.05.84. |
| 67 | TANG T, YUAN H M. The capacity prediction of Li-ion batteries based on a new feature extraction technique and an improved extreme learning machine algorithm[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 514: 230572. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2021.230572. |
| 68 | ZHANG M, KANG G Q, WU L F, et al. A method for capacity prediction of lithium-ion batteries under small sample conditions[J]. Energy, 2022, 238: 122094. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.122094. |
| 69 | MA Y Y, WU L F, GUAN Y, et al. The capacity estimation and cycle life prediction of lithium-ion batteries using a new broad extreme learning machine approach[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 476: 228581. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2020.228581. |
| 70 | FENG H L, SONG D D. A health indicator extraction based on surface temperature for lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 34: 102118. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2020.102118. |
| 71 | ZHANG Y Z, XIONG R, HE H W, et al. Validation and verification of a hybrid method for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 212: 240-249. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.041. |
| 72 | JIA S, MA B, GUO W, et al. A sample entropy based prognostics method for lithium-ion batteries using relevance vector machine[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 61: 773-781. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.03.019. |
| 73 | WANG R R, FENG H L. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery using a novel health indicator[J]. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2021, 37(3): 1232-1243. DOI: 10.1002/qre.2792. |
| 74 | ZHENG X J, FANG H J. An integrated unscented Kalman filter and relevance vector regression approach for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life and short-term capacity prediction[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 144: 74-82. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2015.07.013. |
| 75 | CHANG Y, FANG H J, ZHANG Y. A new hybrid method for the prediction of the remaining useful life of a lithium-ion battery[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 206: 1564-1578. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.106. |
| 76 | CHEN Z W, SHI N, JI Y F, et al. Lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction based on BLS-RVM[J]. Energy, 2021, 234: 121269. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.121269. |
| 77 | CAI Y S, YANG L, DENG Z W, et al. Prediction of lithium-ion battery remaining useful life based on hybrid data-driven method with optimized parameter[C]// 2017 2nd International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE). IEEE, 2017: 1-6. DOI: 10.1109/ICPRE.2017.8390489. |
| 78 | ZHOU Y, GU H H, SU T, et al. Remaining useful life prediction with probability distribution for lithium-ion batteries based on edge and cloud collaborative computation[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 44: 103342. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103342. |
| 79 | ZHANG C L, HE Y G, YUAN L F, et al. Capacity prognostics of lithium-ion batteries using EMD denoising and multiple kernel RVM[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 12061-12070. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2716353. |
| 80 | SUN X F, ZHONG K, HAN M. A hybrid prognostic strategy with unscented particle filter and optimized multiple kernel relevance vector machine for lithium-ion battery[J]. Measurement, 2021, 170: 108679. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108679. |
| 81 | LIU D T, ZHOU J B, PAN D W, et al. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation with an optimized relevance vector machine algorithm with incremental learning[J]. Measurement, 2015, 63: 143-151. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2014.11.031. |
| 82 | SONG Y C, LIU D T, HOU Y D, et al. Satellite lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation with an iterative updated RVM fused with the KF algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2018, 31(1): 31-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.cja.2017.11.010. |
| 83 | ZHAO L, WANG Y P, CHENG J H. A hybrid method for remaining useful life estimation of lithium-ion battery with regeneration phenomena[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): 1890. DOI: 10.3390/app9091890. |
| 84 | WANG S J, LIU D T, ZHOU J B, et al. A run-time dynamic reconfigurable computing system for lithium-ion battery prognosis[J]. Energies, 2016, 9(8): 572. DOI: 10.3390/en9080572. |
| 85 | DONG G Z, XU Y, WEI Z B. A hierarchical approach for finite-time H-∞ state-of-charge observer and probabilistic lifetime prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2022, 37(1): 718-728. DOI: 10.1109/TEC.2021.3109896. |
| 86 | LI X Y, YUAN C G, WANG Z P. Multi-time-scale framework for prognostic health condition of lithium battery using modified Gaussian process regression and nonlinear regression[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 467: 228358. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228358. |
| 87 | PAN W J, LUO X S, ZHU M T, et al. A health indicator extraction and optimization for capacity estimation of Li-ion battery using incremental capacity curves[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 42: 103072. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103072. |
| 88 | KONG J Z, YANG F F, ZHANG X, et al. Voltage-temperature health feature extraction to improve prognostics and health management of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy, 2021, 223: 120114. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.120114. |
| 89 | ZHANG Y W, TANG Q C, ZHANG Y, et al. Identifying degradation patterns of lithium ion batteries from impedance spectroscopy using machine learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1706. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15235-7. |
| 90 | LIU K L, HU X S, WEI Z B, et al. Modified Gaussian process regression models for cyclic capacity prediction of lithium-ion batteries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2019, 5(4): 1225-1236. DOI: 10.1109/TTE.2019.2944802. |
| 91 | LIU J, CHEN Z Q. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on health indicator and Gaussian process regression model[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39474-39484. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905740. |
| 92 | ZHANG C L, ZHAO S S, HE Y G. An integrated method of the future capacity and RUL prediction for lithium-ion battery pack[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 2601-2613. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3138959. |
| 93 | LI M, SADOUGHI M, SHEN S, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries using multi-model Gaussian process[C]// 2019 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management (ICPHM). IEEE, 2019[2024-09-01]. DOI: 10.1109/ICPHM.2019.8819384. |
| 94 | ANSARI S, AYOB A, HOSSAIN LIPU M S, et al. Data-driven remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries using multi-charging profile framework: A recurrent neural network approach[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(23): 13333. DOI: 10.3390/su132313333. |
| 95 | JI Y F, CHEN Z W, SHEN Y, et al. An RUL prediction approach for lithium-ion battery based on SADE-MESN[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 104: 107195. DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107195. |
| 96 | ROUHI ARDESHIRI R, MA C B. Multivariate gated recurrent unit for battery remaining useful life prediction: A deep learning approach[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(11): 16633-16648. DOI: 10.1002/er.6910. |
| 97 | ZOU L, WEN B Y, WEI Y Y, et al. Online prediction of remaining useful life for Li-ion batteries based on discharge voltage data[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(6): 2237. DOI: 10.3390/en15062237. |
| 98 | PAN H P, CHEN C T, GU M M. A method for predicting the remaining useful life of lithium batteries considering capacity regeneration and random fluctuations[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(7): 2498. DOI: 10.3390/en15072498. |
| 99 | STRANDBERG J. Pulse charging of Li-ion batteries for enhanced life performance[D]. KTH Royal Institute of Technology, 2023. |
| 100 | GUO J, XU Y L, EXNER M, et al. Unravelling the mechanism of pulse current charging for enhancing the stability of commercial LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2/graphite lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(22): 2400190. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202400190. |
| 101 | ZHANG W B, SAYAVONG P, XIAO X, et al. Recovery of isolated lithium through discharged state calendar ageing[J]. Nature, 2024, 626: 306-312. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06992-8. |
| 102 | WU Y, HUANG Z W, LIAO H T, et al. Adaptive power allocation using artificial potential field with compensator for hybrid energy storage systems in electric vehicles[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 257: 113983. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113983. |
| 103 | HUANG X R, LIU W J, MENG J H, et al. Lifetime extension of lithium-ion batteries with low-frequency pulsed current charging[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2023, 11(1): 57-66. DOI: 10.1109/JESTPE. 2021.3130424. |
| 104 | LEE C H, WU Z Y, HSU S H, et al. Cycle life study of Li-ion batteries with an aging-level-based charging method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2020, 35(3): 1475-1484. DOI: 10.1109/TEC.2020.2984799. |
| 105 | MAIA L K K, DRÜNERT L, LA MANTIA F, et al. Expanding the lifetime of Li-ion batteries through optimization of charging profiles[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 225: 928-938. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.031. |
| 106 | LI Y Q, GUO J, PEDERSEN K, et al. Investigation of multi-step fast charging protocol and aging mechanism for commercial NMC/graphite lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 80: 237-246. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem. 2023.01.016. |
| 107 | ATTIA P M, GROVER A, JIN N, et al. Closed-loop optimization of fast-charging protocols for batteries with machine learning[J]. Nature, 2020, 578: 397-402. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-1994-5. |
| 108 | GUO J, LI Y Q, MENG J H, et al. Understanding the mechanism of capacity increase during early cycling of commercial NMC/graphite lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 74: 34-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.07.005. |
| 109 | NASCIMENTO R G, CORBETTA M, KULKARNI C S, et al. Hybrid physics-informed neural networks for lithium-ion battery modeling and prognosis[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 513: 230526. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230526. |
| 110 | GUO W D, SUN Z C, VILSEN S B, et al. Review of "grey box" lifetime modeling for lithium-ion battery: Combining physics and data-driven methods[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 56: 105992. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2022.105992. |
| [1] | Zhonglin SUN, Jiabo LI, Di TIAN, Zhixuan WANG, Xiaojing XING. Useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on COA-LSTM and VMD [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3254-3265. |
| [2] | Chengwen TIAN, Bingxiang SUN, Xinze ZHAO, Zhicheng FU, Shichang MA, Bo ZHAO, Xubo ZHANG. Accelerated life prediction of lithium-ion batteries using data-driven approaches [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3103-3111. |
| [3] | Yi ZHONG, Yan LENG, Sihui CHEN, Peiyi LI, Zhi ZOU, Yang LIU, Jiayu WAN. Accelerating battery research with retrieval-augmented large language models: Present and future [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3214-3225. |
| [4] | Nana FENG, Ming YANG, Zhouli HUI, Ruijie WANG, Hongyang NING. Prediction of the remaining useful life of lithium batteries based on Antlion optimization Gaussian process regression [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1643-1652. |
| [5] | Bingjin LI, Xiaoxia HAN, Wenjie ZHANG, Weiguo ZENG, Jinde WU. Review of the remaining useful life prediction methods for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1266-1276. |
| [6] | Qiquan ZENG, Maji LUO, Yinlong YANG, Qingze HUANG. Life prediction of fuel cells based on the LSTM-UPF hybrid method [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 963-970. |
| [7] | Minghu WU, Chengpeng YUE, Fan ZHANG, Junxiao LI, Wei HUANG, Sheng HU, Jing TANG. Combined GRU-MLR method for predicting the remaining useful life of lithium batteries via multiscale decomposition [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2220-2228. |
| [8] | Pengkai WANG, Xinyan ZHANG, Guanghao ZHANG. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on ResNet-Bi-LSTM-Attention model [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1215-1222. |
| [9] | Yuanchang DONG, Xiaoqiong PANG, Jianfang JIA, Yuanhao SHI, Jie WEN, Xiao LI, Xin ZHANG. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on SVD-SAE-GPR [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1257-1267. |
| [10] | Lianbing LI, Le ZHU, Ruixiong JING, Lanchao WANG, Qiqi HAN. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on the DESSA-DESN model and the NCA algorithm [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(10): 3191-3202. |
| [11] | Xinghai SONG, Xiaoqian ZHANG, Huishi LIANG, Zinan SHI, Miangang LI, Kui ZHOU, Xiaoxu GONG. Predicting the remaining service life of lithium batteries based on the SDAE-transformer-ECA network [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(10): 3181-3190. |
| [12] | Qiantong LIU, Yuanxiu XING. Remaining life prediction of lithium-ion battery based on VMD-PSO-GRU model [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 236-246. |
| [13] | Shunmin YI, Linbo XIE, Li PENG. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on VF-DW-DFN [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2305-2315. |
| [14] | Chunhui LIU, Hongbin REN. Research on active equalization of power batteries based on state of charge [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(2): 667-672. |
| [15] | Haoyi XIAO, Xiaoxia HE, Jiajia LIANG, Chunli LI. A lithium battery life-prediction method based on mode decomposition and machine learning [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(12): 3999-4009. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
