Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (3): 788-824.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0826
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chenxi LIANG1( ), Zhenbin WANG1,2, Mingjin ZHANG1,2(
), Zhenbin WANG1,2, Mingjin ZHANG1,2( ), Cunhua MA1,2(
), Cunhua MA1,2( ), Ning LIANG3,4
), Ning LIANG3,4
Received:2023-11-16
Revised:2023-12-07
Online:2024-03-28
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
Mingjin ZHANG, Cunhua MA
E-mail:1658548263@qq.com;zhangmingjin@qhnu.edu.cn;20211001@qhnu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Chenxi LIANG, Zhenbin WANG, Mingjin ZHANG, Cunhua MA, Ning LIANG. Research progress on magnesium-based solid hydrogen storage nanomaterials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 788-824.
Table 1
Comparison of gas, liquid and solid hydrogen storage methods"
| 储氢类型 | 气态储氢 | 液态储氢 | 固态储氢 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 储氢原理 | 通过压缩、吸附等方式将氢气储存于钢瓶中 | 将氢气冷却到20 K,进行液化储存 | 使用固体材料,通过物理或化学吸附实现吸氢 |
储氢密度 (质量分数) | 1%~5%(含气瓶) | 5.5%(含储罐) | 1.4%~20% |
| 优点 | 1. 吸放氢速度快 2. 能在零下几十度环境下工作 | 1. 液态氢密度高 2. 储氢量大 | 1. 储氢量大 2. 不易爆炸,安全性好 3. 储存、运输方便 4. 多数材料可循环使用 |
| 缺点 | 1. 易泄漏,危险系数高 2. 储氢量低 | 1. 液化过程氢的热值损耗20%~30% 2. 需要苛刻的绝热条件 | 1. 储氢量与吸放氢温度不能兼顾 2. 多数材料使用前需要进行循环活化 |

Fig.6
(a) DSC and (b) TPD curves of Mg80Ni20H x before and after exposure for 15 days, 4 and 10 months, isothermal (c) hydrogenation and (d) dehydrogenation curves of Mg80Ni20H x before and after air exposure for 4 months, (e) JMAK fitting plots and (f) Arrhenius plot of air-exposed Mg80Ni20H x for the dehydriding kinetics [53]"
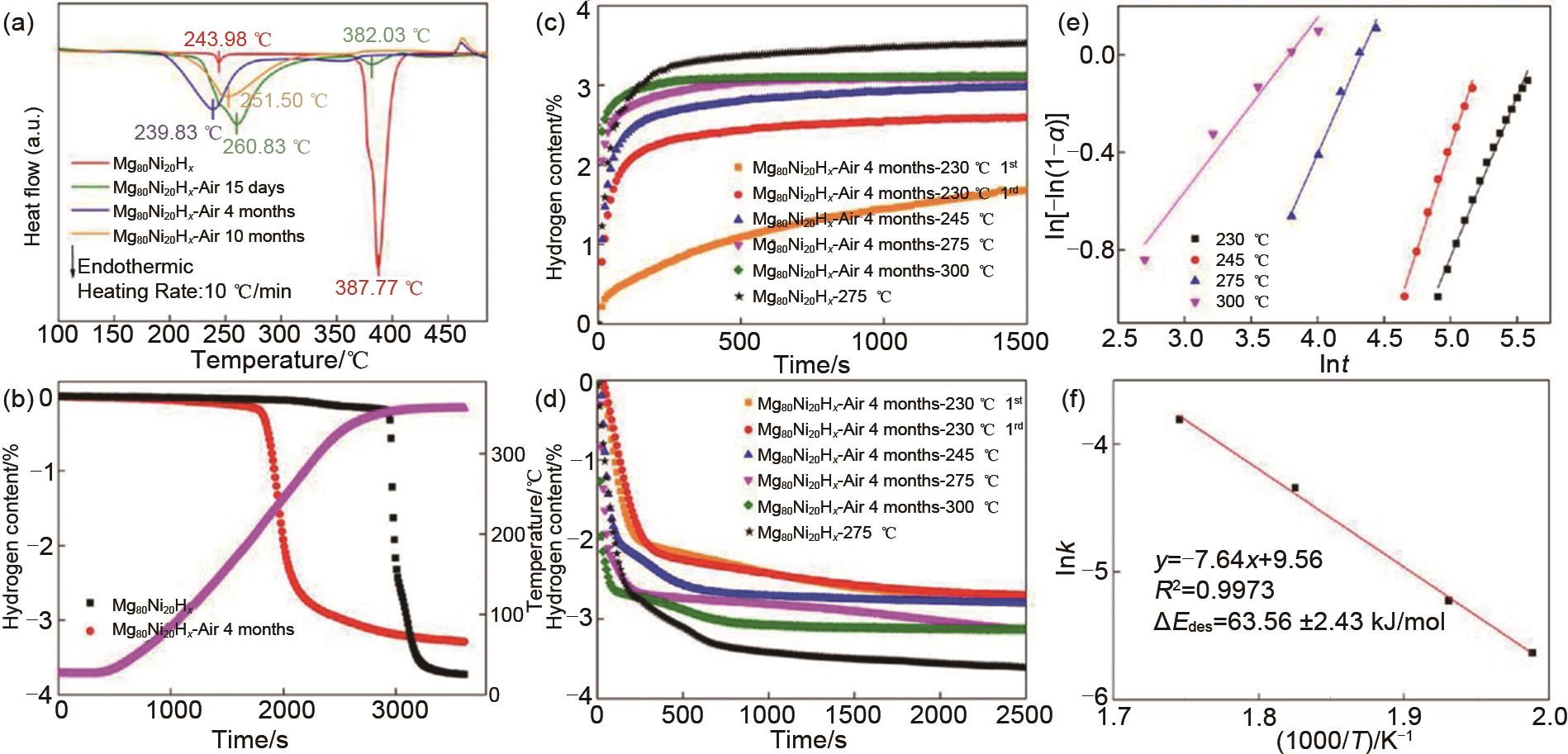
Table 3
Corresponding hydrogen storage parameters of some magnesium alloys"
| 合金 | 脱氢活化能Ea/(kJ/mol) | 初始脱氢温度T/℃ | 脱氢焓ΔH/(kJ/mol) | 脱氢量/%(质量分数) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gd5Mg80Ni15 | 75.07 | 280 | 75.1 | 4.87 | [ |
| Mg90Ce3Ni7 | 72.2 | 100 | 80.0 | 3.5 | [ |
| Mg98Ni1.67La0.33 | 107.26 | 175 | — | 5.59 | [ |
| Mg90Ce5Sm5 | 106 | 300 | 81.2 | 4.95 | [ |
| Mg96Y2Zn2 | 166.504 | 389 | — | 6.2 | [ |
| Mg80Ni10La64 | 70.30 | 278.4 | — | 4.7 | [ |
| Mg22Y3Ni9C | 66.13 | 235.1 | 64.29 | 2.8 | [ |
| AlMg2TiZn | 148 | 310 | 76 | 1.4 | [ |
Table 4
Performance differences and technical difficulties of MgH2 prepared by different methods"
| 材料 | 制备方法 | 尺寸/nm | 脱氢量 /%(质量分数) | 脱氢Ea/(kJ/mol) | 技术难点 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgH2 | 高能球磨 | — | 7 | — | 球磨时间过长,效率较低 | [ |
| MgH2 | 介质阻挡放电等离子体辅助球磨 | 2~6 | 6.5 | — | 设备要求过高 | [ |
| MgH2-MgC0.5Co3 | 氢化燃烧合成法 | — | 4.38 | 126.7±1.4 | 制备过程存在危险性 | [ |
| 胶体MgH2 | 化学还原法 | 5 | 7.6 | — | 材料的规模和形貌难以调控 | [ |
| Mg纳米线 | 气相沉积法 | 30~170 | 7.6 | — | 制备过程复杂 | [ |
| MgH2@Ni-MOF | 纳米限域 | 3 | 1.45 | 41.5±3.7 | 材料储氢性能较差 | [ |
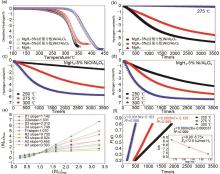
Fig. 26
(a)Temperature-programmed-desorption and (b) isothermal dehydrogenation curves at 275 ℃ of MgH2, MgH2-5%Ni/Al2O3 and MgH2-5%NiO/Al2O3 ; isothermal dehydrogenation curves of (c)MgH2-5%NiO/Al2O3 and (d)MgH2-5%Ni/Al2O3 at different temperatures of 250 ℃, 275 ℃ and 300 ℃; (e)the corresponding solid-state reaction mechanism model and rate-controlling step of MgH2-5%Ni/Al2O3; (f)time dependence of the kinetic modeling equation F(α)and the plot for the temperature-dependent rate constant k, obtained by the Arrhenius equation[128]"
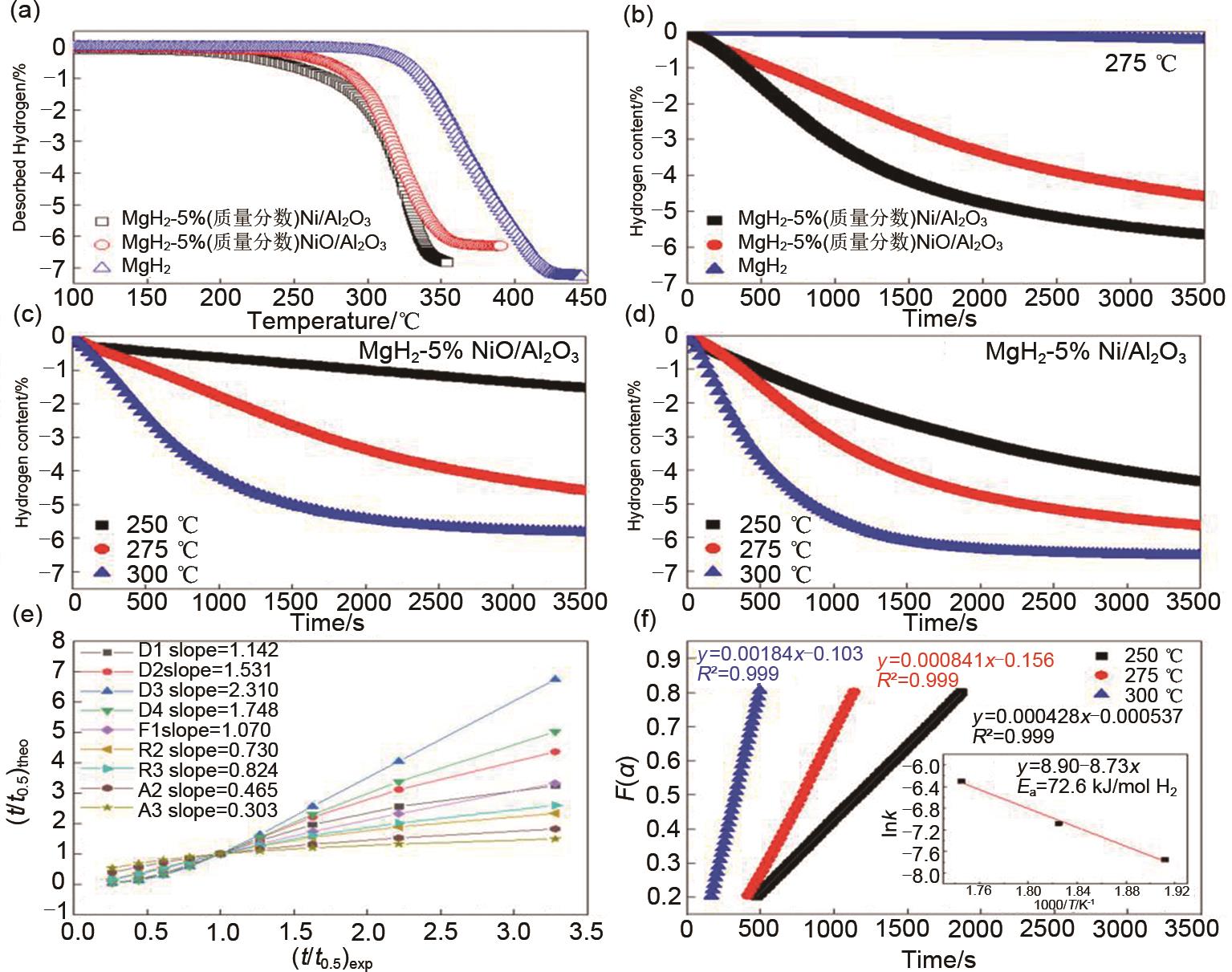

Fig. 29
(a)Isothermal dehydrogenation curves of MgH2-6 wt% MnCo2O4.5 and (c)as-milled MgH2; (b)isothermal hydrogenation curves of MgH2-6 wt% MnCo2O4.5 and (d)as-milled MgH2; (e)de/hydrogenation cycle curves of MgH2-6 wt% MnCo2O4.5 at 325 ℃, and (f)decay curves of hydrogen storage capacity[120]"
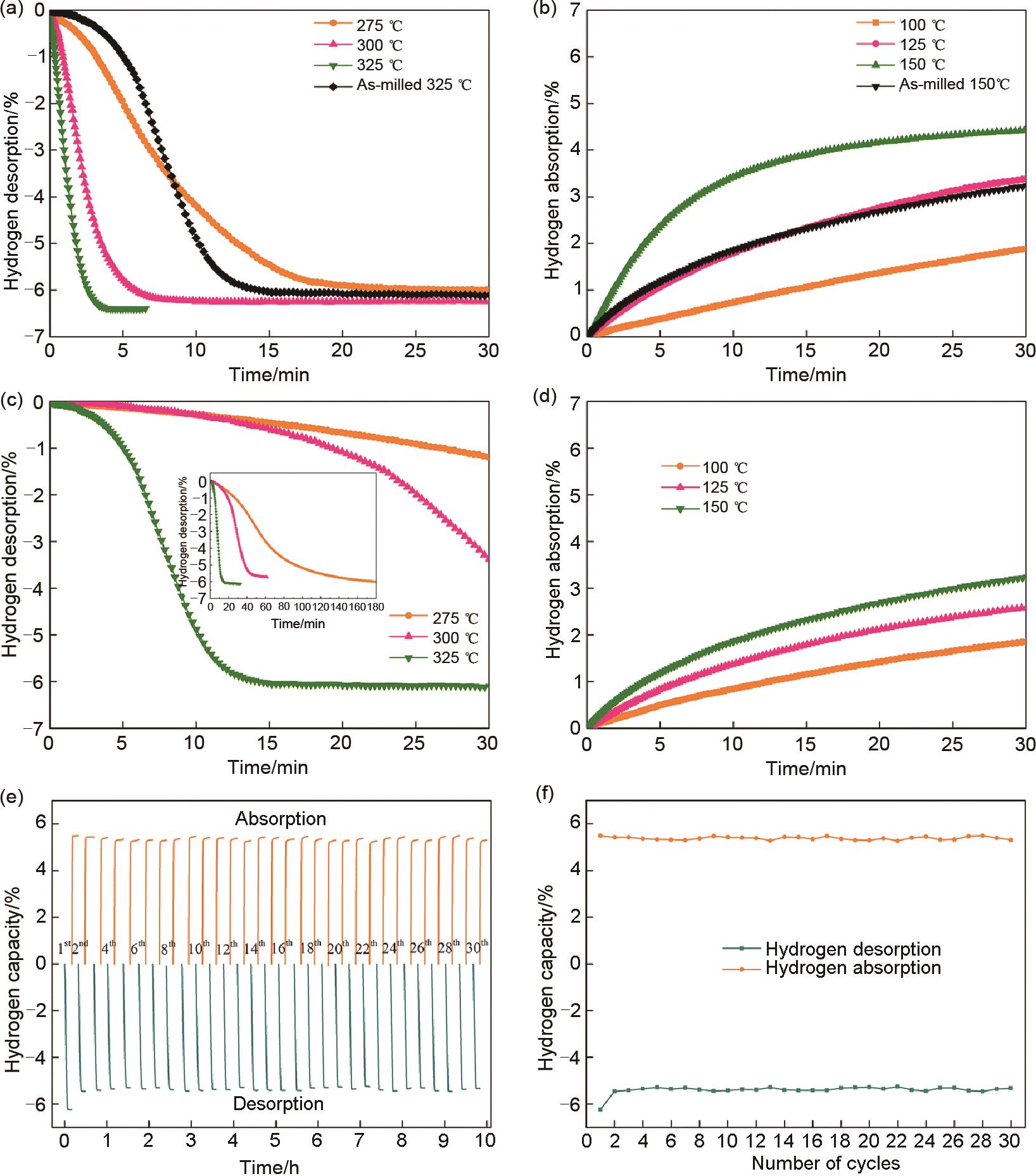
Table 5
Hydrogen storage properties of some MgH2- ternary transition metal oxides"
| 材料 | 初始脱氢T/℃ | 脱氢Ea/ (kJ/mol) | 脱氢量/%(质量分数) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgH2-BiVO4 | 265 | 84.33 | 1.1 | [ |
| MgH2-TiNb2O7 | 178 | 100.4±0.1 | 7.0 | [ |
| MgH2-MnV2O6 | 182.1 | 67±0.7 | 5.57 | [ |
| MgH2-NiTiO3 | 235 | 74±4 | 7.1 | [ |
| MgH2-TiVO3.5 | 197 | 62.4 | 5.0 | [ |
| MgH2-NiV2O6 | 227 | 75.32±4.2 | 5.3 | [ |
| MgH2-LiNbO3 | 228 | 79.2±0.5 | 5.45 | [ |
| MgH2-NaNbO3 | 251 | 73 | 6.5 | [ |
Table 6
Summary of hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 modified by some other metal compounds"
| 材料 | 初始脱氢T/℃ | 脱氢Ea/ (kJ/mol) | 脱氢量/%(质量分数) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-NiF2 | 362 | 139.21 | 3.85 | [ |
| MgH2-K2NiF6 | 260 | 111.0 | 4.9 | [ |
| MgH2-TiS2 | 204 | 50.8 | 5.9 | [ |
MgH2-FeNi2S4 Mg/ZIF-67 MgH2-Ni-MOF MgH2-Nb2O5@MOF | 267 275 292 181.9 | 65.5 161.73 107.8 75.57±4.16 | 1.92 3.7 5.7 6.2 | [ [ [ [ |
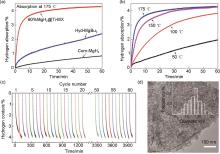
Fig. 43
(a) Isothermal hydrogenation curves of commercial MgH2, hyd-MgBu2, and 60% MgH2@Ti-MX at 175 ℃ and (b) isothermal hydrogenation curves of 60% MgH2@Ti-MX at different temperatures; (c) cycling dehydrogenation curves of 60% MgH2@Ti-MX at 200 ℃, and (d) typical TEM image of 60% MgH2@Ti-MX after 60 de/hydrogenation cycles at 200 ℃[173]"
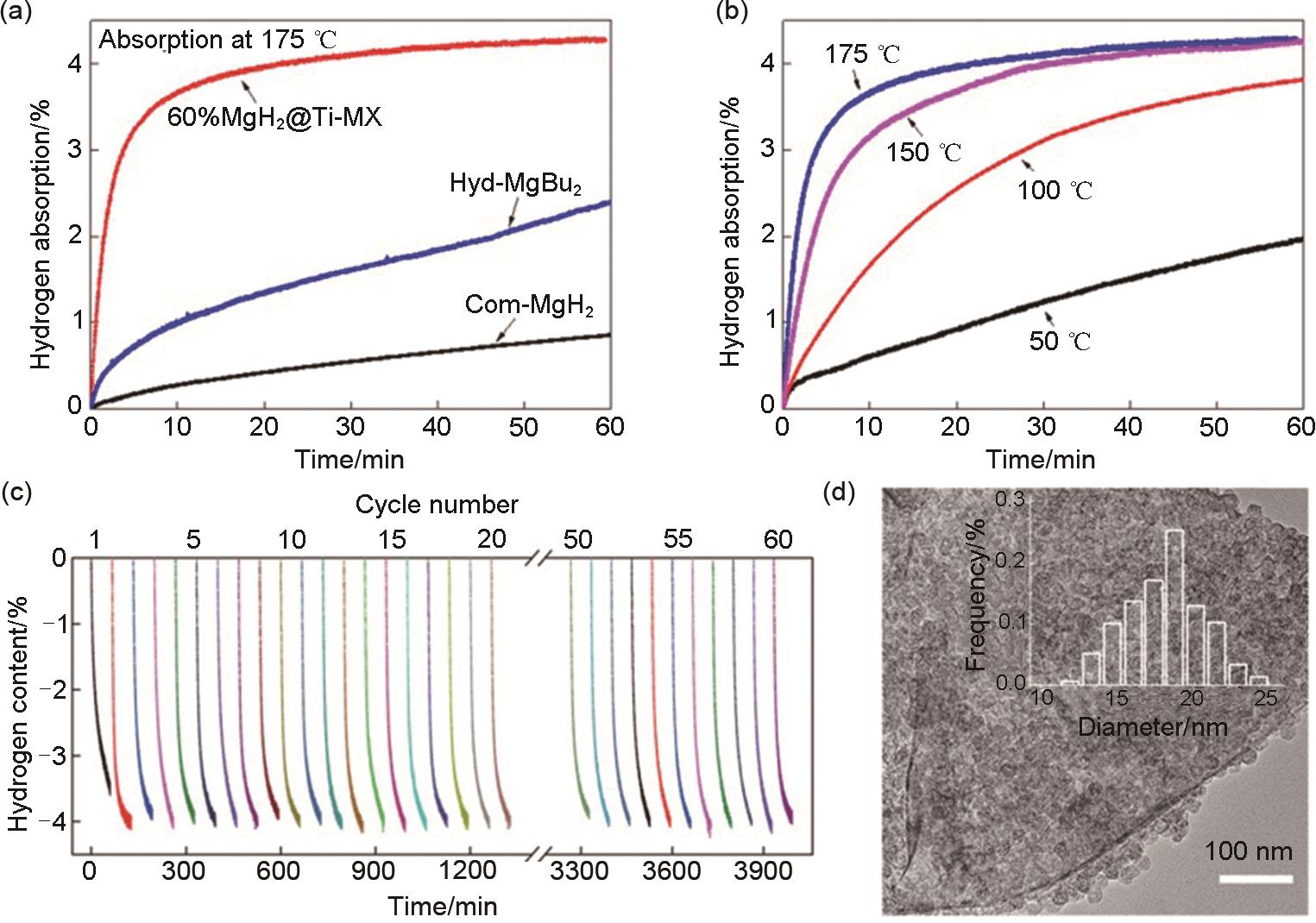
Table 7
Hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 modified by some metal and carbon based composite catalysts"
| 材料 | 脱氢Ea/(kJ/mol) | 初始脱氢T/℃ | 脱氢ΔH/(kJ/mol) | 脱氢量/%(质量分数) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MgH2-Co/Pd@BCNTs MgH2-Ni3ZnC0.7/CNT MgH2+Fe–Ni@3DG MgH2- CoNi@C | 76.66 84.22 83.8 78.5 | 198.9 110 — 173 | — 75.17 72.2 — | 6.35 5.36 5.13 5.83 | [ [ [ [ |
| MgH2-ML-Ti3C2 | 99 | 142 | — | 6.45 | [ |
| MgH2-NbTiC | 80 | 195 | — | 5.8 | [ |
| MgH2-PrF3/Ti3C2 | 78.11 | 180 | — | 7.0 | [ |
| MgH2-V2C | 87.6 | 190 | 73.6 | 6.4 | [ |
| 1 | TARHAN C, ALI ÇIL M. A study on hydrogen, the clean energy of the future: Hydrogen storage methods[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 40: 102676. |
| 2 | ISHAQ H, DINCER I, CRAWFORD C. A review on hydrogen production and utilization: Challenges and opportunities[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(62): 26238-26264. |
| 3 | SIMOES S G, CATARINO J, PICADO A, et al. Water availability and water usage solutions for electrolysis in hydrogen production[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 315: 128124. |
| 4 | AKANDE O, LEE B. Plasma steam methane reforming (PSMR) using a microwave torch for commercial-scale distributed hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(5): 2874-2884. |
| 5 | LEE J E, SHAFIQ I, HUSSAIN M, et al. A review on integrated thermochemical hydrogen production from water[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(7): 4346-4356. |
| 6 | KAMAT P V, SIVULA K. Celebrating 50 years of photocatalytic hydrogen generation[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(9): 3149-3150. |
| 7 | CUI P Z, YAO D, MA Z Y, et al. Life cycle water footprint comparison of biomass-to-hydrogen and coal-to-hydrogen processes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 773: 145056. |
| 8 | LIU J J, MA Y, YANG J G, et al. Recent advance of metal borohydrides for hydrogen storage[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 945208. |
| 9 | LI J Q, LI J C L, PARK K, et al. Investigation on the changes of pressure and temperature in high pressure filling of hydrogen storage tank[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2022, 37: 102143. |
| 10 | LAMB K E, WEBB C J. A quantitative review of slurries for hydrogen storage–Slush hydrogen, and metal and chemical hydrides in carrier liquids[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 906: 164235. |
| 11 | JIANG L J. Expediting the innovation and application of solid hydrogen storage technology[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(6): 731-733. |
| 12 | ZHONG H, WANG H, LIU J W, et al. Enhanced hydrolysis properties and energy efficiency of MgH2-base hydrides[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 680: 419-426. |
| 13 | ZHANG Y H, WEI X, ZHANG W, et al. Effect of milling duration on hydrogen storage thermodynamics and kinetics of Mg-based alloy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(58): 33832-33845. |
| 14 | LAI Q W, PASKEVICIUS M, SHEPPARD D A, et al. Hydrogen storage materials for mobile and stationary applications: Current state of the art[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(17): 2789-2825. |
| 15 | BARDHAN R, RUMINSKI A M, BRAND A, et al. Magnesium nanocrystal-polymer composites: A new platform for designer hydrogen storage materials[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(12): 4882-4895. |
| 16 | PARK J H, PARK S J. Expansion of effective pore size on hydrogen physisorption of porous carbons at low temperatures with high pressures[J]. Carbon, 2020, 158: 364-371. |
| 17 | GIZER G, CAO H J, PUSZKIEL J, et al. Enhancement effect of bimetallic amide K2Mn(NH2)4 and In-situ formed KH and Mn4N on the dehydrogenation/hydrogenation properties of Li-Mg-N-H system[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(14): 2779. |
| 18 | CHEN P, XIONG Z T, WU G T, et al. Metal-N-H systems for the hydrogen storage[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 56(10): 817-822. |
| 19 | LUO Y M, SUN L X, XU F, et al. Improved hydrogen storage of LiBH4 and NH3BH3 by catalysts[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(17): 7293-7309. |
| 20 | MANOHARAN K, PALANISWAMY V K, RAMAN K, et al. Investigation of solid state hydrogen storage performances of novel NaBH4/Ah-BN nanocomposite as hydrogen storage medium for fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 860: 158444. |
| 21 | WEI S, LIU J X, XIA Y P, et al. Remarkable catalysis of spinel ferrite XFe2O4 (X=Ni, Co, Mn, Cu, Zn) nanoparticles on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4: An experimental and theoretical study[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 111: 189-203. |
| 22 | ZHU J Y, MAO Y C, WANG H, et al. Reaction route optimized LiBH4 for high reversible capacity hydrogen storage by tunable surface-modified AlN[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(12): 11964-11973. |
| 23 | ETIEMBLE A, IDRISSI H, ROUÉ L. On the decrepitation mechanism of MgNi and LaNi5-based electrodes studied by in situ acoustic emission[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(11): 5168-5173. |
| 24 | KO W S, PARK K B, PARK H K. Density functional theory study on the role of ternary alloying elements in TiFe-based hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 92: 148-158. |
| 25 | LI Q, PENG X D, PAN F S. Magnesium-based materials for energy conversion and storage[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2021, 9(6): 2223-2224. |
| 26 | HUANG Y J, CHENG Y H, ZHANG J Y. A review of high density solid hydrogen storage materials by pyrolysis for promising mobile applications[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(7): 2737-2771. |
| 27 | CHEN X H, YANG H, PAN F S. A special editor's issue on Mg-based functional materials: Design and development[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2021, 9(6): 1835-1836. |
| 28 | LI Q, LU Y F, LUO Q, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of hydriding and dehydriding reactions in Mg-based hydrogen storage materials[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2021, 9(6): 1922-1941. |
| 29 | DUAN C W, TIAN Y T, WANG X Y, et al. Ni-CNTs as an efficient confining framework and catalyst for improving dehydriding/rehydriding properties of MgH2[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 187: 417-427. |
| 30 | ZHANG X, LIU Y F, REN Z H, et al. Realizing 6.7 wt% reversible storage of hydrogen at ambient temperature with non-confined ultrafine magnesium hydrides[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(4): 2302-2313. |
| 31 | LU Z Y, YU H J, LU X, et al. Two-dimensional vanadium nanosheets as a remarkably effective catalyst for hydrogen storage in MgH2[J]. Rare Metals, 2021, 40(11): 3195-3204. |
| 32 | DING X, CHEN R R, ZHANG J X, et al. Recent progress on enhancing the hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based materials via fabricating nanostructures: A critical review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 897: 163137. |
| 33 | LI Z Y, SUN Y J, ZHANG C C, et al. Optimizing hydrogen ad/desorption of Mg-based hydrides for energy-storage applications[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 141: 221-235. |
| 34 | ALMATROUK H S, CHIHAIA V, ALEXIEV V. Density functional study of the thermodynamic properties and phase diagram of the magnesium hydride[J]. Calphad, 2018, 60: 7-15. |
| 35 | LUIGGI A N J. Electronic, elastic, and topological behavior of MgH2, MgTiH4, and TiH2 under pressure[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 28: 102639. |
| 36 | EDALATI K, KITABAYASHI K, IKEDA Y, et al. Bulk nanocrystalline gamma magnesium hydride with low dehydrogenation temperature stabilized by plastic straining via high-pressure torsion[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 157: 54-57. |
| 37 | SHANG Y Y, PISTIDDA C, GIZER G, et al. Mg-based materials for hydrogen storage[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2021, 9(6): 1837-1860. |
| 38 | REN L, LI Y H, ZHANG N, et al. Nanostructuring of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: Recent advances for promoting key applications[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 93. |
| 39 | MARINELLI M, SANTARELLI M. Hydrogen storage alloys for stationary applications[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 32: 101864. |
| 40 | FLORIANO R, ZEPON G, EDALATI K, et al. Hydrogen storage properties of new A3B2-type TiZrNbCrFe high-entropy alloy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(46): 23757-23766. |
| 41 | CHEN X Y, XU J, ZHANG W R, et al. Effect of Mn on the long-term cycling performance of AB5-type hydrogen storage alloy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(42): 21973-21983. |
| 42 | LUO Q, GUO Y L, LIU B, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of phase transformation in rare earth–magnesium alloys: A critical review[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2020, 44: 171-190. |
| 43 | MARQUES F, BALCERZAK M, WINKELMANN F, et al. Review and outlook on high-entropy alloys for hydrogen storage[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(10): 5191-5227. |
| 44 | YONG H, WEI X, HU J F, et al. Influence of Fe@C composite catalyst on the hydrogen storage properties of Mg–Ce–Y based alloy[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 162: 2153-2165. |
| 45 | POZZO M, ALFÈ D. Hydrogen dissociation and diffusion on transition metal (=Ti, Zr, V, Fe, Ru, Co, Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu, Ag)-doped Mg(0001) surfaces[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(4): 1922-1930. |
| 46 | POLETAEV A A, DENYS R V, SOLBERG J K, et al. Microstructural optimization of LaMg12 alloy for hydrogen storage[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: S633-S639. |
| 47 | REILLY J J Jr, WISWALL R H Jr. Reaction of hydrogen with alloys of magnesium and copper[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1967, 6(12): 2220-2223. |
| 48 | REILLY J J Jr, WISWALL R H Jr. Reaction of hydrogen with alloys of magnesium and nickel and the formation of Mg2NiH4[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1968, 7(11): 2254-2256. |
| 49 | AKIYAMA T, ISOGAI H, YAGI J. Hydriding combustion synthesis for the production of hydrogen storage alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1997, 252(1/2): L1-L4. |
| 50 | LI L Q, AKIYAMA T, YAGI J I. Effect of hydrogen pressure on the combustion synthesis of Mg2NiH4[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(2): 201-205. |
| 51 | SHAO H Y, ASANO K, ENOKI H, et al. Preparation and hydrogen storage properties of nanostructured Mg-Ni BCC alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 477(1/2): 301-306. |
| 52 | TAN Y J, MAO Q F, SU W, et al. Remarkable hydrogen storage properties at low temperature of Mg-Ni composites prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis and mechanical milling[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(78): 63202-63208. |
| 53 | NI J L, ZHU Y F, ZHANG J G, et al. Air exposure improving hydrogen desorption behavior of Mg-Ni-based hydrides[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(58): 22183-22191. |
| 54 | ZHANG J G, YAO L L, LIU W Q, et al. An exciting synergistic effect: Realizing large-sized MgH2 dehydrogenation at lowered temperatures by locally assembling a heterophase composite[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2019, 14: 100345. |
| 55 | ANDREASEN A. Hydrogenation properties of Mg-Al alloys[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(24): 7489-7497. |
| 56 | CHEN X, ZOU J X, ZENG X Q, et al. Hydrogen storage in Mg2Fe(Ni)H6 nanowires synthesized from coarse-grained Mg and nano sized γ-Fe(Ni) precursors[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(33): 14795-14806. |
| 57 | VAJO J J, MERTENS F, AHN C C, et al. Altering hydrogen storage properties by hydride destabilization through alloy formation: LiH and MgH2 destabilized with Si[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(37): 13977-13983. |
| 58 | ZHONG H C, WANG H, LIU J W, et al. Altered desorption enthalpy of MgH2 by the reversible formation of Mg(In) solid solution[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65(4): 285-287. |
| 59 | OUYANG L Z, QIN F X, ZHU M. The hydrogen storage behavior of Mg3La and Mg3LaNi0.1[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 55(12): 1075-1078. |
| 60 | WANG Y Q, LÜ S X, ZHOU Z Y, et al. Effect of transition metal on the hydrogen storage properties of Mg-Al alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(5): 2392-2399. |
| 61 | WEI X, ZHANG W, SUN H F, et al. Investigation on the gaseous hydrogen storage properties of as-cast Mg95- xAl5Yx (x=0-5) alloys[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(25): 12653-12664. |
| 62 | OUYANG L Z, WANG H, CHUNG C Y, et al. MgNi/Pd multilayer hydrogen storage thin films prepared by dc magnetron sputtering[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 422(1/2): 58-61. |
| 63 | YU Y C, JI Y Q, ZHANG S H, et al. Microstructure characteristics, hydrogen storage thermodynamic and kinetic properties of Mg-Ni-Y based hydrogen storage alloys[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(63): 27059-27070. |
| 64 | XIE X B, HOU C X, CHEN C G, et al. First-principles studies in Mg-based hydrogen storage Materials: A review[J]. Energy, 2020, 211: 118959. |
| 65 | GUO F H, ZHANG T B, SHI L M, et al. Hydrogen absorption/desorption cycling performance of Mg-based alloys with in situ formed Mg2Ni and LaHx (x=2, 3) nanocrystallines[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2023, 11(4): 1180-1192. |
| 66 | BU W G, LIU Q H, PENG W L, et al. Hydrogen storage characteristics, kinetics and thermodynamics of Gd-Mg-Ni-based alloys[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(19): 7048-7057. |
| 67 | SONG F, YAO J W, YONG H, et al. Investigation of ball-milling process on microstructure, thermodynamics and kinetics of Ce-Mg-Ni-based hydrogen storage alloy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(30): 11274-11286. |
| 68 | DING X, CHEN R R, ZHANG J X, et al. Achieving superior hydrogen storage properties via in-situ formed nanostructures: A high-capacity Mg-Ni alloy with La microalloying[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(10): 6755-6766. |
| 69 | YONG H, GUO S H, YUAN Z M, et al. Phase evolution, hydrogen storage thermodynamics and kinetics of ternary Mg90Ce5Sm5 alloy[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(6): 633-641. |
| 70 | ZHANG J X, DING X, CHEN R R, et al. Comparative study of solid-solution treatment and hot-extrusion on hydrogen storage performance for Mg96Y2Zn2 alloy: The nonnegligible role of elements distribution[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 548: 232037. |
| 71 | ZHANG Y H, ZHANG W, GAO J L, et al. Improved hydrogen storage kinetics of Mg-based alloys by substituting La with Sm[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(41): 21588-21599. |
| 72 | ZHANG Y H, WEI X, YUAN Z M, et al. Hydrogen storage thermodynamics and dynamics of Mg-Y-Ni-Cu based alloys synthesized by melt spinning[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2020, 138: 109252. |
| 73 | CERMAK J, KRAL L, ROUPCOVA P. A new light-element multi-principal-elements alloy AlMg2TiZn and its potential for hydrogen storage[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 198: 1186-1192. |
| 74 | YEH J W, CHEN S K, LIN S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(5): 299-303. |
| 75 | 申炳泽, 樊建锋, 郭卉君. 含镁高熵合金MgxTiVNiAlCr储氢性能的研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2021, 42(7): 565-569. |
| SHEN B Z, FAN J F, GUO H J. Study on Hydrogen Storage Properties of High Entropy Alloy MgxTiVNiAlCr [J]. Casting technology, 2021, 42 (7) : 565-569. | |
| 76 | MONTERO J, EK G, SAHLBERG M, et al. Improving the hydrogen cycling properties by Mg addition in Ti-V-Zr-Nb refractory high entropy alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2021, 194: 113699. |
| 77 | KIM K C, DAI B, KARL JOHNSON J, et al. Assessing nanoparticle size effects on metal hydride thermodynamics using the Wulff construction[J]. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(20): 204001. |
| 78 | VAJEESTON P, RAVINDRAN P, FICHTNER M, et al. Influence of crystal structure of bulk phase on the stability of nanoscale phases: Investigation on MgH2 derived nanostructures[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(35): 18965-18972. |
| 79 | VAJEESTON P, SARTORI S, RAVINDRAN P, et al. MgH2 in carbon scaffolds: A combined experimental and theoretical investigation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(40): 21139-21147. |
| 80 | HOUSE S D, VAJO J J, REN C, et al. Effect of ball-milling duration and dehydrogenation on the morphology, microstructure and catalyst dispersion in Ni-catalyzed MgH2 hydrogen storage materials[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 86: 55-68. |
| 81 | BOLARIN J A, ZOU R, LI Z, et al. Recent path to ultrafine Mg/MgH2 synthesis for sustainable hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 52: 251-274. |
| 82 | CHEN M, HU M M, XIE X B, et al. High loading nanoconfinement of V-decorated Mg with 1 nm carbon shells: Hydrogen storage properties and catalytic mechanism[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(20): 10045-10055. |
| 83 | ZHANG P, XIONG J, QIAO N Q, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of protists in the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Water Biology and Security, 2022, 1(4): 100064. |
| 84 | SCHULZ R, HUOT J, LIANG G, et al. Recent developments in the applications of nanocrystalline materials to hydrogen technologies[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1999, 267(2): 240-245. |
| 85 | VARIN R A, CZUJKO T, WRONSKI Z. Particle size, grain size and γ-MgH2 effects on the desorption properties of nanocrystalline commercial magnesium hydride processed by controlled mechanical milling[J]. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(15): 3856-3865. |
| 86 | OUYANG L Z, CAO Z J, WANG H, et al. Application of dielectric barrier discharge plasma-assisted milling in energy storage materials–A review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 691: 422-435. |
| 87 | DAN L, WANG H, LIU J W, et al. H2 plasma reducing Ni nanoparticles for superior catalysis on hydrogen sorption of MgH2[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(4): 4976-4984. |
| 88 | LIU X F, ZHU Y F, LI L Q. Hydriding and dehydriding properties of nanostructured Mg2Ni alloy prepared by the process of hydriding combustion synthesis and subsequent mechanical grinding[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 425(1/2): 235-238. |
| 89 | FU Y K, DING Z M, ZHANG L, et al. Catalytic effect of a novel MgC0.5Co3 compound on the dehydrogenation of MgH2[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2021, 31(2): 264-269. |
| 90 | RIEKE R D, HUDNALL P M. Activated metals. I. Preparation of highly reactive magnesium metal[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1972, 94(20): 7178-7179. |
| 91 | SUN Y H, AGUEY-ZINSOU K F. Synthesis of magnesium nanofibers by electroless reduction and their hydrogen interaction properties[J]. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2017, 34(4): 1600276-1600284. |
| 92 | LIU W, AGUEY-ZINSOU K F. Size effects and hydrogen storage properties of Mg nanoparticles synthesised by an electroless reduction method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(25): 9718-9726. |
| 93 | RIEKE R D, LI P T J, BURNS T P, et al. Preparation of highly reactive metal powders. New procedure for the preparation of highly reactive zinc and magnesium metal powders[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1981, 46(21): 4323-4324. |
| 94 | SHEN C Q, AGUEY-ZINSOU K F. Can γ-MgH2 improve the hydrogen storage properties of magnesium?[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(18): 8644-8652. |
| 95 | JEON K J, MOON H R, RUMINSKI A M, et al. Air-stable magnesium nanocomposites provide rapid and high-capacity hydrogen storage without using heavy-metal catalysts[J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10: 286-290. |
| 96 | FRANCOIS A Z K, RAMÓN A F J. Synthesis of colloidal magnesium: A near room temperature store for hydrogen[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(2): 376-378. |
| 97 | NORBERG N S, ARTHUR T S, FREDRICK S J, et al. Size-dependent hydrogen storage properties of Mg nanocrystals prepared from solution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(28): 10679-10681. |
| 98 | MATSUMOTO I, AKIYAMA T, NAKAMURA Y, et al. Controlled shape of magnesium hydride synthesized by chemical vapor deposition[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 507(2): 502-507. |
| 99 | LI W Y, LI C S, MA H, et al. Magnesium nanowires: Enhanced kinetics for hydrogen absorption and desorption[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(21): 6710-6711. |
| 100 | LU C, MA Y L, LI F, et al. Visualization of fast "hydrogen pump" in core-shell nanostructured Mg@Pt through hydrogen-stabilized Mg3Pt[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(24): 14629-14637. |
| 101 | GREMAUD R, BROEDERSZ C P, BORSA D M, et al. Hydrogenography: An optical combinatorial method to find new light-weight hydrogen-storage materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(19): 2813-2817. |
| 102 | HIGUCHI K, YAMAMOTO K, KAJIOKA H, et al. Remarkable hydrogen storage properties in three-layered Pd/Mg/Pd thin films[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 330/331/332: 526-530. |
| 103 | ZHU C X, CHEN M, HU M M, et al. Hydrogen storage properties of Mg-Nb@C nanocomposite: Effects of Nb nanocatalyst and carbon nanoconfinement[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(14): 9443-9451. |
| 104 | LIU M J, ZHAO S C, XIAO X Z, et al. Novel 1D carbon nanotubes uniformly wrapped nanoscale MgH2 for efficient hydrogen storage cycling performances with extreme high gravimetric and volumetric capacities[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 61: 540-549. |
| 105 | XIA G L, TAN Y B, CHEN X W, et al. Monodisperse magnesium hydride nanoparticles uniformly self-assembled on graphene[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(39): 5981-5988. |
| 106 | RUMINSKI A M, BARDHAN R, BRAND A, et al. Synergistic enhancement of hydrogen storage and air stability via Mg nanocrystal-polymer interfacial interactions[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(11): 3267-3271. |
| 107 | LIM D W, YOON J W, RYU K Y, et al. Magnesium nanocrystals embedded in a metal-organic framework: Hybrid hydrogen storage with synergistic effect on physi-and chemisorption[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2012, 51(39): 9814-9817. |
| 108 | MA Z W, ZHANG Q Y, PANDA S, et al. In situ catalyzed and nanoconfined magnesium hydride nanocrystals in a Ni-MOF scaffold for hydrogen storage[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2020, 4(9): 4694-4703. |
| 109 | MA Z W, PANDA S, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Improving hydrogen sorption performances of MgH2 through nanoconfinement in a mesoporous CoS nano-boxes scaffold[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126790. |
| 110 | WEBB C J. A review of catalyst-enhanced magnesium hydride as a hydrogen storage material[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2015, 84: 96-106. |
| 111 | YANG X L, ZHANG J Q, HOU Q H, et al. Improvement of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials by metal catalysts: Review and summary[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2021, 6(33): 8809-8829. |
| 112 | LIANG G, HUOT J, BOILY S, et al. Catalytic effect of transition metals on hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline ball milled MgH2–Tm (Tm=Ti, V, Mn, Fe and Ni) systems[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1999, 292(1/2): 247-252. |
| 113 | PUKAZHSELVAN D, SANDHYA K S, RAMASAMY D, et al. Transformation of metallic Ti to TiH2 phase in the Ti/MgH2 composite and its influence on the hydrogen storage behavior of MgH2[J]. Chemphyschem: a European Journal of Chemical Physics and Physical Chemistry, 2020, 21(11): 1195-1201. |
| 114 | CHOI Y J, CHOI J W, SOHN H Y, et al. Chemical vapor synthesis of Mg-Ti nanopowder mixture as a hydrogen storage material[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(18): 7700-7706. |
| 115 | HANADA N, ICHIKAWA T, FUJII H. Catalytic effect of Ni nano-particle and Nb oxide on H-desorption properties in MgH2 prepared by ball milling[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 404/405/406: 716-719. |
| 116 | XIE L, LIU Y, ZHANG X Z, et al. Catalytic effect of Ni nanoparticles on the desorption kinetics of MgH2 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 482(1/2): 388-392. |
| 117 | YANG W N, SHANG C X, GUO Z X. Site density effect of Ni particles on hydrogen desorption of MgH2[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(10): 4534-4542. |
| 118 | BASSETTI A, BONETTI E, PASQUINI L, et al. Hydrogen desorption from ball milled MgH2 catalyzed with Fe[J]. The European Physical Journal B-Condensed Matter and Complex Systems, 2005, 43(1): 19-27. |
| 119 | CHEN H P, MA N N, LI J Q, et al. Effect of atomic iron on hydriding reaction of magnesium: Atomic-substitution and atomic-adsorption cases from a density functional theory study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 504: 144489. |
| 120 | ANTIQUEIRA F J, LEIVA D R, ZEPON G, et al. Fast hydrogen absorption/desorption kinetics in reactive milled Mg-8 mol% Fe nanocomposites[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(22): 12408-12418. |
| 121 | ZHANG L T, JI L, YAO Z D, et al. Facile synthesized Fe nanosheets as superior active catalyst for hydrogen storage in MgH2[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(39): 21955-21964. |
| 122 | ZHANG J, YAN S, QU H. Recent progress in magnesium hydride modified through catalysis and nanoconfinement[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(3): 1545-1565. |
| 123 | BARKHORDARIAN G, KLASSEN T, BORMANN R. Effect of Nb2O5 content on hydrogen reaction kinetics of Mg[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 364(1/2): 242-246. |
| 124 | TERZIEVA M, KHRUSSANOVA M, PESHEV P. Dehydriding kinetics of mechanically alloyed mixtures of magnesium with some 3d transition metal oxides[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1991, 16(4): 265-270. |
| 125 | OELERICH W, KLASSEN T, BORMANN R. Metal oxides as catalysts for improved hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline Mg-based materials[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 315(1/2): 237-242. |
| 126 | CHEN M, XIAO X Z, ZHANG M, et al. Insights into 2D graphene-like TiO2 (B) nanosheets as highly efficient catalyst for improved low-temperature hydrogen storage properties of MgH2[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2020, 16: 100411. |
| 127 | REN L, ZHU W, LI Y H, et al. Oxygen vacancy-rich 2D TiO2 nanosheets: A bridge toward high stability and rapid hydrogen storage kinetics of nano-confined MgH2[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 144. |
| 128 | LIU Z B, LIU J C, WU Z H, et al. Enhanced hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2 catalyzed by a novel layered Ni/Al2O3 hybrid[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 895: 162682. |
| 129 | LIU Y F, ZHONG K, LUO K, et al. Size-dependent kinetic enhancement in hydrogen absorption and desorption of the Li-Mg-N-H system[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(5): 1862-1870. |
| 130 | HUANG H X, YUAN J G, ZHANG B, et al. A noteworthy synergistic catalysis on hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2 with bimetallic oxide Sc2O3/TiO2[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 839: 155387. |
| 131 | SAZELEE N A, IDRIS N H, MD DIN M F, et al. Synthesis of BaFe12O19 by solid state method and its effect on hydrogen storage properties of MgH2[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(45): 20853-20860. |
| 132 | ZHANG Y, WU F Y, GUEMOU S, et al. Constructing Mg2Co-Mg2CoH5 nano hydrogen pumps from LiCoO2 nanosheets for boosting the hydrogen storage property of MgH2[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(42): 16195-16205. |
| 133 | ZHOU S M, WEI D, WAN H Y, et al. Efficient catalytic effect of the page-like MnCo2O4.5 catalyst on the hydrogen storage performance of MgH2[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2022, 9(21): 5495-5506. |
| 134 | XU G, SHEN N, CHEN L J, et al. Effect of BiVO4 additive on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2017, 89: 197-203. |
| 135 | XIAN K C, WU M H, GAO M X, et al. A unique nanoflake-shape bimetallic Ti-Nb oxide of superior catalytic effect for hydrogen storage of MgH2[J]. Small, 2022, 18(43): e2107013. |
| 136 | FU H F, HU J, LU Y F, et al. Synergistic effect of a facilely synthesized MnV2O6 catalyst on improving the low-temperature kinetic properties of MgH2[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(29): 33161-33172. |
| 137 | HUANG X, XIAO X Z, WANG X C, et al. Synergistic catalytic activity of porous rod-like TMTiO3 (TM = Ni and co) for reversible hydrogen storage of magnesium hydride[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(49): 27973-27982. |
| 138 | ZHANG X, SHEN Z Y, JIAN N, et al. A novel complex oxide TiVO3.5 as a highly active catalytic precursor for improving the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(52): 23327-23335. |
| 139 | LIANG H R, XIE Z Z, ZHAO R L, et al. Facile synthesis of nickel-vanadium bimetallic oxide and its catalytic effects on the hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(77): 32969-32980. |
| 140 | YANG X, WAN H Y, ZHOU S M, et al. Synergistic enhancement of hydrogen storage properties in MgH2 using LiNbO3 catalyst[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(71): 27726-27736. |
| 141 | RATHI B, AGARWAL S, SHRIVASTAVA K, et al. An insight into the catalytic mechanism of perovskite ternary oxide for enhancing the hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 970: 172616. |
| 142 | LIN H J, MATSUDA J, LI H W, et al. Enhanced hydrogen desorption property of MgH2 with the addition of cerium fluorides[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 645: S392-S396. |
| 143 | MAO J F, ZOU J X, LU C, et al. Hydrogen storage and hydrolysis properties of core-shell structured Mg-MFx(M=V, Ni, La and Ce) nano-composites prepared by arc plasma method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 366: 131-142. |
| 144 | SULAIMAN N N, JUAHIR N, MUSTAFA N S, et al. Improved hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 catalyzed with K2NiF6[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2016, 25(5): 832-839. |
| 145 | YAN C G, LU X, ZHENG J G, et al. Dual-cation K2TaF7 catalyst improves high-capacity hydrogen storage behavior of MgH2[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(15): 6023-6033. |
| 146 | WANG P, TIAN Z H, WANG Z X, et al. Improved hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 using transition metal sulfides as catalyst[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(53): 27107-27118. |
| 147 | FU Y K, ZHANG L, LI Y, et al. Effect of ternary transition metal sulfide FeNi2S4 on hydrogen storage performance of MgH2[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2023, 11(8): 2927-2938. |
| 148 | CHEN Z J, KIRLIKOVALI K O, IDREES K B, et al. Porous materials for hydrogen storage[J]. Chem, 2022, 8(3): 693-716. |
| 149 | HE H B, LI R, YANG Z H, et al. Preparation of MOFs and MOFs derived materials and their catalytic application in air pollution: A review[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 375: 10-29. |
| 150 | REGO R M, KURIYA G, KURKURI M D, et al. MOF based engineered materials in water remediation: Recent trends[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123605. |
| 151 | ZHOU H, HAN J J, CUAN J, et al. Responsive luminescent MOF materials for advanced anticounterfeiting[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 134170. |
| 152 | ROWSELL J L C, MILLWARD A R, PARK K S, et al. Hydrogen sorption in functionalized metal-organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(18): 5666-5667. |
| 153 | LIU M J, XIAO X Z, ZHAO S C, et al. ZIF-67 derived Co@CNTs nanoparticles: Remarkably improved hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 and synergetic catalysis mechanism[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(2): 1059-1069. |
| 154 | WANG Y Q, LAN Z Q, HUANG X, et al. Study on catalytic effect and mechanism of MOF (MOF=ZIF-8, ZIF-67, MOF-74) on hydrogen storage properties of magnesium[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(54): 28863-28873. |
| 155 | GAO H G, SHI R, SHAO Y T, et al. Catalysis derived from flower-like Ni MOF towards the hydrogen storage performance of magnesium hydride[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(15): 9346-9356. |
| 156 | WANG Y Q, LAN Z Q, FU H, et al. Synergistic catalytic effects of ZIF-67 and transition metals (Ni, Cu, Pd, and Nb) on hydrogen storage properties of magnesium[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(24): 13376-13386. |
| 157 | ZHANG L T, NYAHUMA F M, ZHANG H Y, et al. Metal organic framework supported niobium pentoxide nanoparticles with exceptional catalytic effect on hydrogen storage behavior of MgH2[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2023, 8(2): 589-600. |
| 158 | XU W C, TAKAHASHI K, MATSUO Y, et al. Investigation of hydrogen storage capacity of various carbon materials[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(13): 2504-2512. |
| 159 | ROSTAMI S, POUR A N, IZADYAR M. A review on modified carbon materials as promising agents for hydrogen storage[J]. Science Progress, 2018, 101(2): 171-191. |
| 160 | IIJIMA S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J]. Nature, 1991, 354: 56-58. |
| 161 | KAJIURA H, TSUTSUI S, KADONO K, et al. Hydrogen storage capacity of commercially available carbon materials at room temperature[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 82(7): 1105-1107. |
| 162 | RITSCHEL M, UHLEMANN M, GUTFLEISCH O, et al. Hydrogen storage in different carbon nanostructures[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 80(16): 2985. |
| 163 | MOSQUERA-VARGAS E, TAMAYO R, MOREL M, et al. Hydrogen storage in purified multi-walled carbon nanotubes: Gas hydrogenation cycles effect on the adsorption kinetics and their performance[J]. Heliyon, 2021, 7(12): e08494. |
| 164 | LIU M J, XIAO X Z, ZHAO S C, et al. Facile synthesis of Co/Pd supported by few-walled carbon nanotubes as an efficient bidirectional catalyst for improving the low temperature hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(10): 5277-5287. |
| 165 | ZHANG B, XIE X B, WANG Y K, et al. In situ formation of multiple catalysts for enhancing the hydrogen storage of MgH2 by adding porous Ni3ZnC0.7/Ni loaded carbon nanotubes microspheres[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2022 |
| 166 | ZHANG J, YU X F, MAO C, et al. Influences and mechanisms of graphene-doping on dehydrogenation properties of MgH2: Experimental and first-principles studies[J]. Energy, 2015, 89: 957-964. |
| 167 | ZHOU D M, CUI K X, ZHOU Z W, et al. Enhanced hydrogen-storage properties of MgH2 by Fe–Ni catalyst modified three-dimensional graphene[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(69): 34369-34380. |
| 168 | AMIRI A, CHEN Y J, BEE TENG C, et al. Porous nitrogen-doped MXene-based electrodes for capacitive deionization[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 25: 731-739. |
| 169 | WU Z T, SHANG T X, DENG Y Q, et al. The assembly of MXenes from 2D to 3D[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(7): 1903077. |
| 170 | BORYSIUK V N, MOCHALIN V N, GOGOTSI Y. Molecular dynamic study of the mechanical properties of two-dimensional titanium carbides Tin+1Cn (MXenes)[J]. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(26): 265705. |
| 171 | NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2[J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(37): 4248-4253. |
| 172 | TONTINI G, GREAVES M, GHOSH S, et al. MXene-based 3D porous macrostructures for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Journal of Physics: Materials, 2020, 3(2): 022001. |
| 173 | ZHU W, REN L, LU C, et al. Nanoconfined and in situ catalyzed MgH2 self-assembled on 3D Ti3C2 MXene folded nanosheets with enhanced hydrogen sorption performances[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(11): 18494-18504. |
| 174 | LIU H Z, LU C L, WANG X C, et al. Combinations of V2C and Ti3C2 MXenes for boosting the hydrogen storage performances of MgH2[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(11): 13235-13247. |
| 175 | ZHAO Y Y, ZHU Y F, LIU J C, et al. Enhancing hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 by core-shell CoNi@C[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 862: 158004. |
| 176 | WU Z J, FANG J H, LIU N, et al. The improvement in hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 enabled by multilayer Ti3C2[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(10): 1190. |
| 177 | WANG Z Y, ZHANG X L, REN Z H, et al. In situ formed ultrafine NbTi nanocrystals from a NbTiC solid-solution MXene for hydrogen storage in MgH2[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(23): 14244-14252. |
| 178 | WANG Y H, FAN G X, ZHANG D F, et al. Striking enhanced effect of PrF3 particles on Ti3C2 MXene for hydrogen storage properties of MgH2[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 914: 165291. |
| 179 | LU C L, LIU H Z, XU L, et al. Two-dimensional vanadium carbide for simultaneously tailoring the hydrogen sorption thermodynamics and kinetics of magnesium hydride[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2022, 10(4): 1051-1065. |
| 180 | WAN H Y, YANG X, ZHOU S M, et al. Enhancing hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 using FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy catalysts[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 149: 88-98. |
| 181 | ZHANG J X, LIU H, ZHOU C S, et al. TiVNb-based high entropy alloys as catalysts for enhanced hydrogen storage in nanostructured MgH2[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(9): 4789-4800. |
| 182 | VERMA S K, MISHRA S S, MUKHOPADHYAY N K, et al. Superior catalytic action of high-entropy alloy on hydrogen sorption properties of MgH2[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 50: 749-762. |
| [1] | Wenbiao LI, Haitao GENG, Yibo GAO, Zhaoshun GAO, Bao WANG. Cu-In/Bi alloys with lithiophilic sites induce uniform lithium nucleation for high-rate lithium-metal batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2735-2745. |
| [2] | Jin WANG, Shaofei ZHANG, Jinfeng SUN, Tiantian LI. Rapid oxidation of nanoporous alloys by self-combustion and their high-efficiency energy storage performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1480-1489. |
| [3] | WANG Peican, WAN Lei, XU Ziang, XU Qin, PANG Maobin, CHEN Jinxun, WANG Baoguo. Interface engineering of self-supported electrode for electrochemical water splitting [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1934-1946. |
| [4] | Weishu WANG, Xiangxin ZHANG, Zikun YAO, Juan ZHEN. Study on reaction rate characteristics of hydrogen storage in MgH2 reactor [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1543-1550. |
| [5] | Yezhou HU, Shuang WANG, Tao SHEN, Ye ZHU, Deli WANG. Recent progress in confined noble-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1264-1277. |
| [6] | Shenzhi ZHANG, Likai WANG, Yinggang SUN, Heng LÜ, Ziyin YANG, Leilei LI, Zhongfang LI. Construction of two dimensional carbon-supported Au4Pd2 catalysts and their electrocatalytic performances [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2028-2038. |
| [7] | Yuexia LI, Quanbing LIU. Application of MXene-based nanomaterials in electrocatalysis for oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1918-1930. |
| [8] | Feng HE, Jingjing ZHANG, Yijun CHEN, Jian ZHANG, Deli WANG. Recent progress on carbon-based catalysts for electrochemical synthesis of H2O2 via oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1963-1976. |
| [9] | Ziyue ZHU, Dongju FU, Jianjun CHEN, Bianrong ZENG. Research progress of non-precious metal bifunctional cathode electrocatalysts for zinc-air batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1489-1496. |
| [10] | LIANG Yaohua, KE Xi, LIU Jun, SHI Zhicong. Preparation and supercapacitive performance of MnO2@ nanoporous gold/Ni foam electrode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2017, 6(S1): 1-. |
| [11] | SHEN Dan, ZHAO Changying. Optimal analysis of the exothermic process of a Mg/MgH2 thermochemical heat storage system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2014, 3(1): 36-41. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
