Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (10): 3076-3089.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0028
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lifen LONG1( ), Xihua ZHANG1(
), Xihua ZHANG1( ), Peifan YAO1, Mingjie LI2, Jingwei WANG1
), Peifan YAO1, Mingjie LI2, Jingwei WANG1
Received:2022-01-14
Revised:2022-01-25
Online:2022-10-05
Published:2022-10-10
Contact:
Xihua ZHANG
E-mail:longlifen@njust.edu.cn;zhangxh@sspu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Lifen LONG, Xihua ZHANG, Peifan YAO, Mingjie LI, Jingwei WANG. Research advances on the utilization and disposal of graphite anode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(10): 3076-3089.
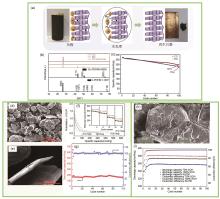
Fig. 5
(a) Hydrometallurgy using water leaching to recover graphite model, RG is the reclaimed graphite; (b)-(c) are the XRD and electrochemical performance characterizations of the reclaimed graphite after water leaching, respectively; (d)-(e) are respectively SEM images of waste cathode graphite of lithium ion battery and SEM images of reclaimed graphite obtained by hydrochloric acid leaching; (f)-(g) are electrochemical characterization diagrams of (e); (h) SEM images of reclaimed graphite obtained after heat treatment of electrolyte with subcritical carbon dioxide and acetonitrile; (i) Curve of the constant discharge capacity and coulomb efficiency of the reclaimed graphite recovered by (h) method[37, 40, 44]"
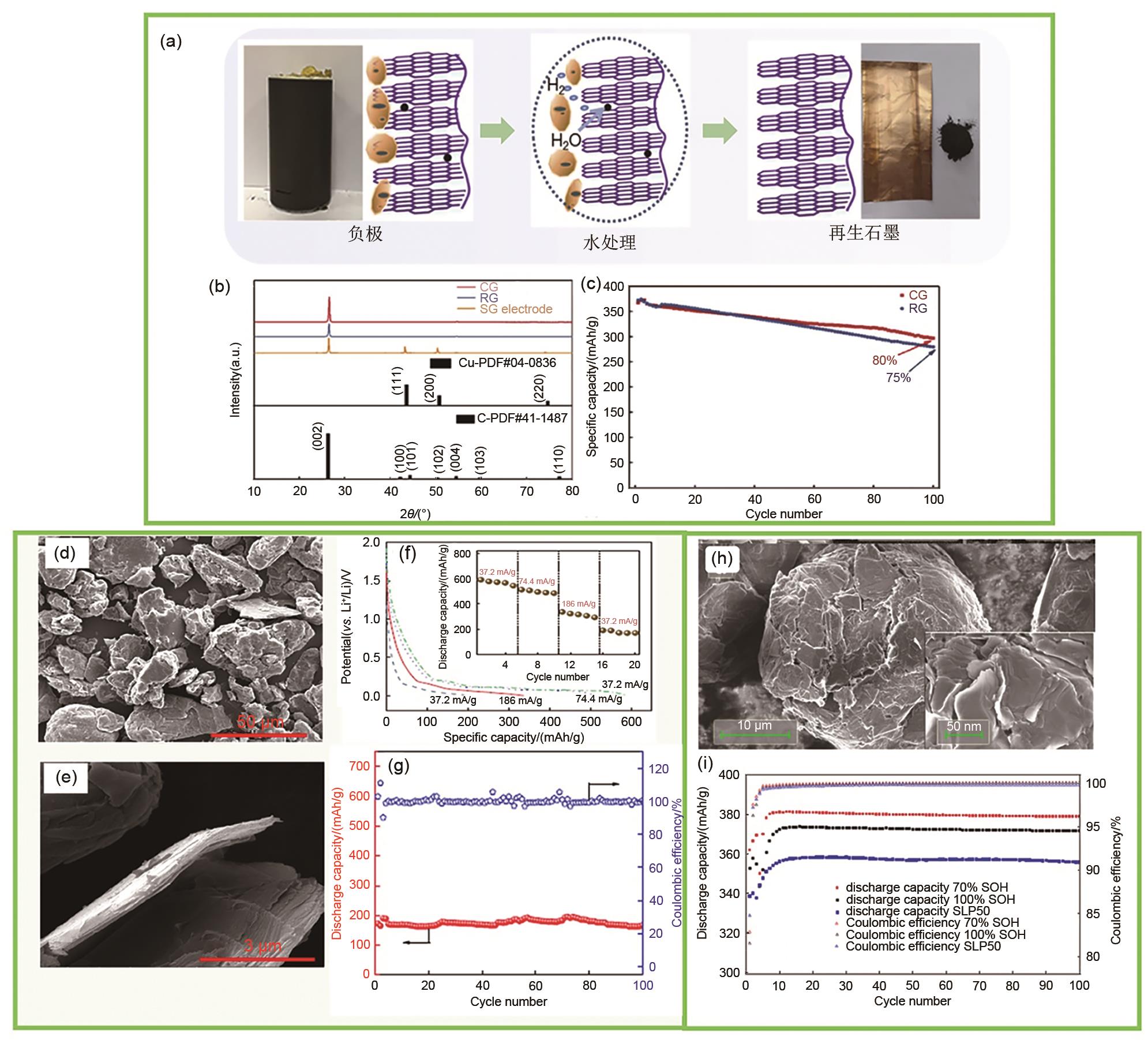
Fig. 8
(a) Schematic diagram of the preparation of graphene from the cathode graphite of the waste lithium-ion battery; (b) Exfoliated graphene; (c) Conductive ink conductivity test chart; Charge-discharge curve (d) and multiplier performance curve (e) of semi-battery prepared from recycled graphite; (f) Schematic diagram of a process for preparing phosphate adsorbent by modifying graphite with Mg(OH)2; (g) Adsorption isotherm data and modeling of phosphate on MG-MCMB (symbols represent experimental data, lines represent model results); (h) Schematic diagram of MB adsorption mechanism by go adsorbent; (i) Adsorption curve of go adsorbent on methylene blue dye; (j) Schematic diagram of REDOX reaction principle when waste lithium ion anode graphite material is used as reducing agent[46, 48, 62, 65, 71]"

| 1 | PETERSON S B, APT J, WHITACRE J F. Lithium-ion battery cell degradation resulting from realistic vehicle and vehicle-to-grid utilization[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(8): 2385-2392. |
| 2 | 陆浩, 刘柏男, 禇赓, 等. 锂离子电池负极材料产业化技术进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016(2):109-119. |
| LU H, LIU B N, ZHE G, et al. Technology review of anode materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2016(2):109-119. | |
| 3 | 高工锂电. 2021中国锂电材料产业大数据[EB/OL]. [2021-10-15]. https://www.gg-lb.com/art-43485.html |
| GGII. Big data of China lithium electric materials industry in 2021 [EB/OL]. [2021-10-15]. https://www.gg-lb.com/art-43485.html | |
| 4 | Prime Minister's Office of Japan. Resource assurance strategy [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.kantei.go.jp/jp/singi/package/dai15/sankou01.pdf |
| 5 | European Commission. On the 2017 list of critical raw materials for the EU [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52017DC0490 |
| 6 | United States Geological Survey (USGS). Interior releases 2018's final List of 35 minerals deemed critical to U.S. National Security and the Economy [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.usgs.gov/news/national-news-release/interior-releases-2018s-final-list-35-minerals-deemed-critical-us |
| 7 | Australian Government, Department of Industry, Innovation and Science, Australian Trade and Investment Commission. Australia's critical minerals strategy [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://minefreeglenaladale.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/australias-critical-minerals-strategy-2019.pdf. |
| 8 | 中国国家统计局.《战略性新兴产业分类(2018)》(国家统计局令第23号)[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjgz/tzgb/201811/t20181126_1635848.html |
| National Bureau of Statistics of China. Classification of strategic emerging industries (2018) (Order No. 23 of the National Bureau of Statistics)[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjgz/tzgb/201811/t20181126_1635848.html | |
| 9 | International Energy Agency. Global EV outlook 2021 [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2021 |
| 10 | 高工锂电. GGII:2018年负极材料出货量19.2万吨[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.gg-lb.com/asdisp2-65b095fb-36293-.html |
| GGII. GGII: 192,000 tons of anode materials were shipped in 2018 [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.gg-lb.com/asdisp2-65b095fb-36293-.html | |
| 11 | 高工锂电. GGII:2019年中国锂电负极材料出货26.5万吨 [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.gg-lb.com/art-40078.html |
| GGII. GGII: Shipments of anode materials in 2019 were 265,000 tons[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. https://www.gg-lb.com/art-40078.html | |
| 12 | 国务院. 国务院关于印发《中国制造2025》的通知(国发〔2015〕28号)[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01].http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2015-05/19/content_9784.htm |
| State Council. Notice of the State Council on the issue of made in China 2025 (No.28 Document in 2015 of the State Council) [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2015-05/19/content_9784.htm | |
| 13 | 工业和信息化部, 国家发展改革委, 科技部. 三部委关于印发《汽车产业中长期发展规划》的通知(工信部联装〔2017〕53号)[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n1146285/n1146352/n3054355/n7697926/n7697940/c7717739/content.html |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Science and Technology. Notice of the three ministries and commissions on the issuance of the mid and long-term development plan for the automobile industry (Joint Installation of Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (2017) No. 53) [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n1146285/n1146352/n3054355/n7697926/n7697940/c7717739/content.html | |
| 14 | 国务院办公厅. 国务院办公厅关于印发的通知《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035年)》(国办发〔2020〕39号)[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2020-11/02/content_5556716.htm. |
| General Office of the State Council. Circular of the General Office of the State Council on the development plan for new energy vehicle industry (2021-2035) (State Affairs and Development Administration (2020) No. 39) [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2020-11/02/content_5556716.htm | |
| 15 | SWAIN B. Recovery and recycling of lithium: A review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 172: 388-403. |
| 16 | ZHANG X X, LI L, FAN E S, et al. Toward sustainable and systematic recycling of spent rechargeable batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(19): 7239-7302. |
| 17 | WU F, XU S M, LI L Y, et al. Recovery of valuable metals from anode material of hydrogen-nickel battery[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(2): 468-473. |
| 18 | Syrah Resources. Syrah resources and graphite market [EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://www.syrahresources.com.au/investors/downloads/560 |
| 19 | United States Geological Survey (USGS). Graphite statistics and information [EB/OL]. [2021-07-02]. https://www.usgs.gov/centers/nmic/graphite-statistics-and-information |
| 20 | 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 中国矿产资源报告[R/OL]. [2021-07-02]. http://www.mnr.gov.cn/sj/sjfw/kc_19263/zgkczybg/201910/P020191022538918416752.pdf |
| Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC. China mineral resources report [R/OL]. [2021-07-02]. http://www.mnr.gov.cn/sj/sjfw/kc_19263/zgkczybg/201910/P020191022538918416752.pdf | |
| 21 | 中华人民共和国海关总署. 海关统计数据查询平台 [DB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://43.248.49.97/ |
| General Administration of Customs of the People's Republic of China. Customs statistical data query platform[DB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://43.248.49.97/ | |
| 22 | 中华人民共和国自然资源部.世界矿产资源年评,2015[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://geoglobal.mnr.gov.cn/np/2018np_598/fjskc/201903/P020190322552632757788.pdf |
| Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Annual review of world mineral resources,2015[EB/OL]. [2021-07-01]. http://geoglobal.mnr.gov.cn/np/2018np_598/fjskc/201903/P020190322552632757788.pdf | |
| 23 | 罗立群, 谭旭升, 田金星. 石墨提纯工艺研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(8): 2110-2116. |
| LUO L Q, TAN X S, TIAN J X. Research progress of graphite purification[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(8): 2110-2116. | |
| 24 | 中国地质调查局. 中国地质调查百项成果: 中国石墨资源调查报告[R/OL]. [2021-07-02]. http://www.cgs.gov.cn/ddztt/cgs100/bxcg/fwgj/201611/P020161128419087798555.pdf |
| China Geological Survey. Hundred achievements of China geological survey: China graphite resources survey report[R/OL]. [2021-07-02]. http://www.cgs.gov.cn/ddztt/cgs100/bxcg/fwgj/201611/P020161128419087798555.pdf | |
| 25 | CHOUBEY P, CHUNG K, KIM M S, et al. Advance review on the exploitation of the prominent energy-storage element Lithium. Part II: From sea water and spent lithium ion batteries (LIBs)[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 110: 104-121. |
| 26 | NIE H H, XU L, SONG D W, et al. LiCoO2: Recycling from spent batteries and regeneration with solid state synthesis[J]. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(2): 1276-1280. |
| 27 | ZHANG T, HE Y Q, GE L H, et al. Characteristics of wet and dry crushing methods in the recycling process of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 240: 766-771. |
| 28 | YU J D, HE Y Q, QU L L, et al. Exploring the critical role of grinding modification on the flotation recovery of electrode materials from spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 274: doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123066. |
| 29 | YU J D, HE Y Q, GE Z Z, et al. A promising physical method for recovery of LiCoO2 and graphite from spent lithium-ion batteries: Grinding flotation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 190: 45-52. |
| 30 | LIU J S, WANG H F, HU T T, et al. Recovery of LiCoO2 and graphite from spent lithium-ion batteries by cryogenic grinding and froth flotation[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 148: doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106223. |
| 31 | WAKAMATSU T, NUMATA Y. Flotation of graphite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 1991, 4(7/8/9/10/11): 975-982. |
| 32 | HE Y Q, ZHANG T, WANG F F, et al. Recovery of LiCoO2 and graphite from spent lithium-ion batteries by Fenton reagent-assisted flotation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 143: 319-325. |
| 33 | JIANG Y J, DENG Y C, BU W G. Pyrometallurgical extraction of valuable elements in Ni-metal hydride battery electrode materials[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2015, 46(5): 2153-2157. |
| 34 | MAROUFI S, NEKOUEI R K, HOSSAIN R, et al. Recovery of rare earth (i.e., La, Ce, Nd, and Pr) oxides from end-of-life Ni-MH battery via thermal isolation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(9): 11811-11818. |
| 35 | HE S C, WILSON B P, LUNDSTRÖM M, et al. Clean and efficient recovery of spent LiCoO2 cathode material: Water-leaching characteristics and low-temperature ammonium sulfate calcination mechanisms[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 268: doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122299. |
| 36 | DIVYA M L, NATARAJAN S, LEE Y S, et al. Achieving high-energy dual carbon Li-ion capacitors with unique low-and high-temperature performance from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(9): 4950-4959. |
| 37 | YANG Y, SONG S L, LEI S Y, et al. A process for combination of recycling lithium and regenerating graphite from spent lithium-ion battery[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 85: 529-537. |
| 38 | KIM T H, JEON E K, KO Y, et al. Enlarging the d-spacing of graphite and polarizing its surface charge for driving lithium ions fast[J]. J Mater Chem A, 2014, 2(20): 7600-7605. |
| 39 | WANG F F, ZHANG T, HE Y Q, et al. Recovery of valuable materials from spent lithium-ion batteries by mechanical separation and thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 185: 646-652. |
| 40 | ROTHERMEL S, EVERTZ M, KASNATSCHEEW J, et al. Graphite recycling from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(24): 3473-3484. |
| 41 | GAO Y, WANG C Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Graphite recycling from the spent lithium-ion batteries by sulfuric acid curing-leaching combined with high-temperature calcination[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(25): 9447-9455. |
| 42 | 贺理珀, 孙淑英, 于建国. 退役锂离子电池中有价金属回收研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 327-340. |
| HE L P, SUN S Y, YU J G. Review on processes and technologies for recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 327-340. | |
| 43 | NATARAJAN S, BORICHA A B, BAJAJ H C. Recovery of value-added products from cathode and anode material of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2018, 77: 455-465. |
| 44 | WANG H R, HUANG Y S, HUANG C F, et al. Reclaiming graphite from spent lithium ion batteries ecologically and economically[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 313: 423-431. |
| 45 | SABISCH J E C, ANAPOLSKY A, LIU G, et al. Evaluation of using pre-lithiated graphite from recycled Li-ion batteries for new LiB anodes[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018, 129: 129-134. |
| 46 | NATARAJAN S, BAJAJ H C. Recovered materials from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) as adsorbents for dye removal: Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(4): 4631-4643. |
| 47 | TANONG K, COUDERT L, MERCIER G, et al. Recovery of metals from a mixture of various spent batteries by a hydrometallurgical process[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 181: 95-107. |
| 48 | MA X T, CHEN M Y, CHEN B, et al. High-performance graphite recovered from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(24): 19732-19738. |
| 49 | CAO N, ZHANG Y L, CHEN L L, et al. An innovative approach to recover anode from spent lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 483: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229163. |
| 50 | ZHANG G W, HE Y Q, FENG Y, et al. Pyrolysis-ultrasonic-assisted flotation technology for recovering graphite and LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(8): 10896-10904. |
| 51 | ZHANG G W, HE Y Q, WANG H F, et al. Application of mechanical crushing combined with pyrolysis-enhanced flotation technology to recover graphite and LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 231: 1418-1427. |
| 52 | ZHANG G W, HE Y Q, WANG H F, et al. Removal of organics by pyrolysis for enhancing liberation and flotation behavior of electrode materials derived from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 2205-2214. |
| 53 | ZHAN R T, YANG Z Z, BLOOM I, et al. Significance of a solid electrolyte interphase on separation of anode and cathode materials from spent Li-ion batteries by froth flotation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(1): 531-540. |
| 54 | ZHANG G W, DU Z X, HE Y Q, et al. A sustainable process for the recovery of anode and cathode materials derived from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(8): 2363. |
| 55 | 王玥, 郑晓洪, 陶天一, 刘秀庆, 李丽, 孙峙. 废锂离子电池正极材料中锂元素选择性回收的研究进展[J/OL].化工进展, 2021. [2022-02-01]. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-1904. |
| WANG Y, ZHENG X H, TAO T Y, LIU X Q, LI L, SUN Z. Review on selective recovery of lithium from cathode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries[J/OL]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021. [2022-02-01]. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-1904. | |
| 56 | MA Z, ZHUANG Y C, DENG Y M, et al. From spent graphite to amorphous sp2+sp3 carbon-coated sp2 graphite for high-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 376: 91-99. |
| 57 | YI C X, YANG Y, ZHANG T, et al. A green and facile approach for regeneration of graphite from spent lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 277: doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123585. |
| 58 | ZHANG J, LI X L, SONG D W, et al. Effective regeneration of anode material recycled from scrapped Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 390: 38-44. |
| 59 | LIU K, YANG S L, LUO L Q, et al. From spent graphite to recycle graphite anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries and sodium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 356: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136856. |
| 60 | RUAN D S, WANG F M, WU L, et al. A high-performance regenerated graphite extracted from discarded lithium-ion batteries[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(3): 1535-1540. |
| 61 | XIAO J F, LI J, XU Z M. Recycling metals from lithium ion battery by mechanical separation and vacuum metallurgy[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 124-131. |
| 62 | HUANG Z, ZHU J, QIU R J, et al. A cleaner and energy-saving technology of vacuum step-by-step reduction for recovering cobalt and nickel from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 229: 1148-1157. |
| 63 | HAO J, MENG X Q, FANG S, et al. MnO2-functionalized amorphous carbon sorbents from spent lithium-ion batteries for highly efficient removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(21): 10210-10220. |
| 64 | ZHAO T, YAO Y, WANG M L, et al. Preparation of MnO2-modified graphite sorbents from spent Li-ion batteries for the treatment of water contaminated by lead, cadmium, and silver[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(30): 25369-25376. |
| 65 | ZHANG Y, GUO X M, WU F, et al. Mesocarbon microbead carbon-supported magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles: Turning spent Li-ion battery anode into a highly efficient phosphate adsorbent for wastewater treatment[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(33): 21315-21325. |
| 66 | YU J D, LIN M S, TAN Q Y, et al. High-value utilization of graphite electrodes in spent lithium-ion batteries: From 3D waste graphite to 2D graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123715. |
| 67 | YE L, WANG C H, CAO L, et al. Effective regeneration of high-performance anode material recycled from the whole electrodes in spent lithium-ion batteries via a simplified approach[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2021, 6(5): 725-733. |
| 68 | RIBEIRO J S, FREITAS M B J G, FREITAS J C C. Recycling of graphite and metals from spent Li-ion batteries aiming the production of graphene/CoO-based electrochemical sensors[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(1): doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104689. |
| 69 | ZHAO L L, LIU X Y, WAN C Y, et al. Soluble graphene nanosheets from recycled graphite of spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(2): 875-880. |
| 70 | YANG L, YANG L, XU G R, et al. Separation and recovery of carbon powder in anodes from spent lithium-ion batteries to synthesize graphene[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 9823. |
| 71 | CHEN X, ZHU Y, PENG W, LI Y, ZHANG G, ZHANG F, FAN X. Direct exfoliation of the anode graphite of used Li-ion batteries into few-layer graphene sheets: A green and high yield route to high-quality graphene preparation[J]. J Mater Chem A, 2017, 5(12): 5880. |
| [1] | Linwang DENG, Tianyu FENG, Shiwei SHU, Zifeng ZHANG, Bin GUO. Review of a fast-charging strategy and technology for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2879-2890. |
| [2] | Zhizhan LI, Jinlei QIN, Jianing LIANG, Zhengrong LI, Rui WANG, Deli WANG. High-nickel ternary layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries: Research progress, challenges and improvement strategies [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2900-2920. |
| [3] | Xiaoyu CHEN, Mengmeng GENG, Qiankun WANG, Jiani SHEN, Yijun HE, Zifeng MA. Electrochemical impedance feature selection and gaussian process regression based on the state-of-health estimation method for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2995-3002. |
| [4] | Tao SUN, Tengteng SHEN, Xin LIU, Dongsheng REN, Jinhai LIU, Yuejiu ZHENG, Luyan WANG, Languang LU, Minggao OUYANG. Application of titration gas chromatography technology in the quantitative detection of lithium plating in Li-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2564-2573. |
| [5] | Yang WANG, Xu LU, Yuxin ZHANG, Long LIU. Thermal runaway exhaust strategy of power battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2480-2487. |
| [6] | Qingsong ZHANG, Yang ZHAO, Tiantian LIU. Effects of state of charge and battery layout on thermal runaway propagation in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2519-2525. |
| [7] | Yong MA, Xiaohan LI, Lei SUN, Dongliang GUO, Jinggang YANG, Jianjun LIU, Peng XIAO, Guangjun QIAN. Parameter design of lithium-ion batteries based on a three-dimensional electrochemical thermal coupling lithium precipitation model [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2600-2611. |
| [8] | Liang TANG, Xiaobo YIN, Houfu WU, Pengjie LIU, Qingsong WANG. Demand for safety standards in the development of the electrochemical energy storage industry [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2645-2652. |
| [9] | Liping HUO, Weiling LUAN, Zixian ZHUANG. Development trend of lithium-ion battery safety technology for energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2671-2680. |
| [10] | Zhicheng CAO, Kaiyun ZHOU, Jiali ZHU, Gaoming LIU, Min YAN, Shun TANG, Yuancheng CAO, Shijie CHENG, Weixin ZHANG. Patent analysis of fire-protection technology of lithium-ion energy storage system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2664-2670. |
| [11] | Yue ZHANG, Depeng KONG, Ping PING. Performance and design optimization of a cold plate for inhibiting thermal runaway propagation of lithium-ion battery packs [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2432-2441. |
| [12] | Chengshan XU, Borui LU, Mengqi ZHANG, Huaibin WANG, Changyong JIN, Minggao OUYANG, Xuning FENG. Study on thermal runaway gas evolution in the lithium-ion battery energy storage cabin [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2418-2431. |
| [13] | Wei KONG, Jingtao JIN, Xipo LU, Yang SUN. Study on cooling performance of lithium ion batteries with symmetrical serpentine channel [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2258-2265. |
| [14] | Shunmin YI, Linbo XIE, Li PENG. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on VF-DW-DFN [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2305-2315. |
| [15] | Qingwei ZHU, Xiaoli YU, Qichao WU, Yidan XU, Fenfang CHEN, Rui HUANG. Semi-empirical degradation model of lithium-ion battery with high energy density [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2324-2331. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
