Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (3): 822-834.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0699
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Longjin JIANG1( ), Shun ZHANG1, Yu QIAO2, Chenzhen LIU2, Zhonghao RAO2(
), Shun ZHANG1, Yu QIAO2, Chenzhen LIU2, Zhonghao RAO2( )
)
Received:2022-11-28
Revised:2022-12-18
Online:2023-03-05
Published:2023-04-14
Contact:
Zhonghao RAO
E-mail:jianglongjin@ah-cy.cn;2021101@hebut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Longjin JIANG, Shun ZHANG, Yu QIAO, Chenzhen LIU, Zhonghao RAO. A review of failure mechanisms and anode graphite recycling from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 822-834.
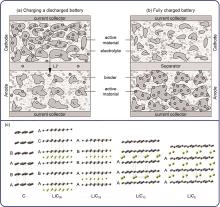
Fig. 3
Schematic of a charging process of a Li-ion battery, consisting of current collectors, anode, cathode, and separator (a) Onset of charging in the discharged state[40]; (b) Fully charged state[40]; (c) Illustration of the structural transformations in lithiated graphite (The gray and green spheres represent carbon and lithium, respectively)[41]"
| 1 | LI M, LU J, CHEN Z W, et al. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(33): doi: 10.1002/adma.201800561. |
| 2 | XIE J, LU Y C. A retrospective on lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-4. |
| 3 | 黄艳阳. 中国锂电池行业市场需求预测与投资战略规划分析报告[R]. 北京: 前瞻产业研究院, 2021. |
| HUANG Y Y. Report of market demand forecast and investment strategy planning on China lithium batteries industry[R]. Beijing: Qianzhan Industry Research Institute, 2021. | |
| 4 | ZHENG X H, ZHU Z W, LIN X, et al. A mini-review on metal recycling from spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Engineering, 2018, 4(3): 361-370. |
| 5 | ARSENAULT R, RENATA A. Battery recycling overview[R]. Europe: MPSC Battery Recycling Symposium, 2021. |
| 6 | SCHWARZER S. UNEP/GRID-Geneva. Challenges for the growth of the electric vehicle market[R]. Kenya: the United Nations Environment Programme, 2020. |
| 7 | NATARAJAN S, ARAVINDAN V. An urgent call to spent LIB recycling: Whys and wherefores for graphite recovery[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(37): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202002238. |
| 8 | HUANG W S, FENG X N, HAN X B, et al. Questions and answers relating to lithium-ion battery safety issues[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2021, 2(1): doi: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2020.100285. |
| 9 | SARKAR A, NLEBEDIM I C, SHROTRIYA P. Performance degradation due to anodic failure mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 502: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229145. |
| 10 | CHUNG J. A micro-/ macroscopic safety mechanism study for Li ion battery[J]. ECS Transactions, 2014, 62(1): 203-213. |
| 11 | MENG X Q, XU Y L, CAO H B, et al. Internal failure of anode materials for lithium batteries—a critical review[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2020, 5(1): 22-36. |
| 12 | HORSTMANN B, SINGLE F, LATZ A. Review on multi-scale models of solid-electrolyte interphase formation[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2019, 13: 61-69. |
| 13 | BIRKL C R, ROBERTS M R, MCTURK E, et al. Degradation diagnostics for lithium ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 341: 373-386. |
| 14 | AHMAD Z, VENTURI V, HAFIZ H, et al. Interfaces in solid electrolyte interphase: Implications for lithium-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(21): 11301-11309. |
| 15 | ZHENG T, GOZDZ A S, AMATUCCI G G. Reactivity of the solid electrolyte interface on carbon electrodes at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1999, 146(11): 4014-4018. |
| 16 | SATOH A, TAKAMI N, OHSAKI T. Electrochemical intercalation of lithium into graphitized carbons[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1995, 80(3/4): 291-298. |
| 17 | HEISKANEN S K, KIM J, LUCHT B L. Generation and evolution of the solid electrolyte interphase of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(10): 2322-2333. |
| 18 | HERSTEDT M, ABRAHAM D P, KERR J B, et al. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of negative electrodes from high-power lithium-ion cells showing various levels of power fade[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49(28): 5097-5110. |
| 19 | HOU C, HAN J H, LIU P, et al. Operando observations of SEI film evolution by mass-sensitive scanning transmission electron microscopy[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(45): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201902675. |
| 20 | KIM J, KIM H, RYU J H, et al. Communication—lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) as a promising salt to suppress solid electrolyte interphase degradation at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(8): doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ab8fd5. |
| 21 | LARESGOITI I, KÄBITZ S, ECKER M, et al. Modeling mechanical degradation in lithium ion batteries during cycling: Solid electrolyte interphase fracture[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 300: 112-122. |
| 22 | VETTER J, NOVÁK P, WAGNER M R, et al. Ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 147(1/2): 269-281. |
| 23 | HUANG W, ATTIA P M, WANG H S, et al. Evolution of the solid-electrolyte interphase on carbonaceous anodes visualized by atomic-resolution cryogenic electron microscopy[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(8): 5140-5148. |
| 24 | KONG L X, XING Y J, PECHT M G. In-situ observations of lithium dendrite growth[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 8387-8393. |
| 25 | CHENG X B, ZHANG R, ZHAO C Z, et al. Toward safe lithium metal anode in rechargeable batteries: A review[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(15): 10403-10473. |
| 26 | ARORA P, WHITE R E, DOYLE M. Capacity fade mechanisms and side reactions in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(10): 3647-3667. |
| 27 | ELY D R, GARCÍA R E. Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of lithium electrodeposits on negative electrodes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(4): doi: 10.1149/1.057304jes. |
| 28 | PERSSON K, SETHURAMAN V A, HARDWICK L J, et al. Lithium diffusion in graphitic carbon[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(8): 1176-1180. |
| 29 | HARRIS S J, RAHANI E K, SHENOY V B. Direct in situ observation and numerical simulations of non-shrinking-core behavior in an MCMB graphite composite electrode[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(9): doi: 10.1149/2.055209jes. |
| 30 | MONROE C, NEWMAN J. Dendrite growth in lithium/polymer systems[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150(10): doi: 10.1149/1.1606686. |
| 31 | AKOLKAR R. Modeling dendrite growth during lithium electrodeposition atsub-ambient temperature[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 246: 84-89. |
| 32 | JIN Y, ZHENG Z K, WEI D H, et al. Detection of micro-scale Li dendrite via H2 gas capture for early safety warning[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(8): 1714-1729. |
| 33 | PENG C X, YANG L, FANG S H, et al. Electrochemical behavior of copper current collector in imidazolium-based ionic liquid electrolytes[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2010, 40(3): 653-662. |
| 34 | SHU J, SHUI M, HUANG F T, et al. Comparative study on surface behaviors of copper current collector in electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(8): 3006-3014. |
| 35 | LIN N, JIA Z, WANG Z H, et al. Understanding the crack formation of graphite particles in cycled commercial lithium-ion batteries by focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 365: 235-239. |
| 36 | LI J, MURPHY E, WINNICK J, et al. Studies on the cycle life of commercial lithium ion batteries during rapid charge-discharge cycling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 102(1/2): 294-301. |
| 37 | HARRIS S J, DESHPANDE R D, QI Y, et al. Mesopores inside electrode particles can change the Li-ion transport mechanism and diffusion-induced stress[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 25(8): 1433-1440. |
| 38 | AURBACH D, ZINIGRAD E, COHEN Y, et al. A short review of failure mechanisms of lithium metal and lithiated graphite anodes in liquid electrolyte solutions[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148(3/4): 405-416. |
| 39 | LIU X, YIN L, REN D S, et al. In situ observation of thermal-driven degradation and safety concerns of lithiated graphite anode[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1-11. |
| 40 | MIEHE C, DAL H, SCHÄNZEL L M, et al. A phase-field model for chemo-mechanical induced fracture in lithium-ion battery electrode particles[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2016, 106(9): 683-711. |
| 41 | ANDERSEN H L, DJUANDHI L, MITTAL U, et al. Strategies for the analysis of graphite electrode function[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(48): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202102693. |
| 42 | LIANG H J, HOU B H, LI W H, et al. Staging Na/K-ion de-/ intercalation of graphite retrieved from spent Li-ion batteries: in operando X-ray diffraction studies and an advanced anode material for Na/K-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(12): 3575-3584. |
| 43 | ANDERSEN H L, DJUANDHI L, MITTAL U, et al. Strategies for the analysis of graphite electrode function[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(48): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202102693. |
| 44 | CHEN X F, ZHU Y Z, PENG W C, et al. Direct exfoliation of the anode graphite of used Li-ion batteries into few-layer graphene sheets: A green and high yield route to high-quality graphene preparation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(12): 5880-5885. |
| 45 | WANG H R, HUANG Y S, HUANG C F, et al. Reclaiming graphite from spent lithium ion batteries ecologically and economically[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 313: 423-431. |
| 46 | XIAO H G, JI G J, YE L, et al. Efficient regeneration and reutilization of degraded graphite as advanced anode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 888: doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161593. |
| 47 | LIU K, YANG S L, LUO L Q, et al. From spent graphite to recycle graphite anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries and sodium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 356: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136856. |
| 48 | YANG Y, SONG S L, LEI S Y, et al. A process for combination of recycling lithium and regenerating graphite from spent lithium-ion battery[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 85: 529-537. |
| 49 | BI H J, ZHU H B, ZU L, et al. Combined mechanical process recycling technology for recovering copper and aluminium components of spent lithium-iron phosphate batteries[J]. Waste Management & Research: the Journal of the International Solid Wastes and Public Cleansing Association, ISWA, 2019, 37(8): 767-780. |
| 50 | WANG F F, ZHANG T, HE Y Q, et al. Recovery of valuable materials from spent lithium-ion batteries by mechanical separation and thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 185: 646-652. |
| 51 | ZHANG G W, HE Y Q, FENG Y, et al. Enhancement in liberation of electrode materials derived from spent lithium-ion battery by pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 199: 62-68. |
| 52 | 杨生龙, 杨凯雲, 范小萍, 等. 废旧锂离子电池负极片的硫酸浸出回收研究[J]. 电源技术, 2020, 44(3): 364-366, 376. |
| YANG S L, YANG K Y, FAN X P, et al. Recycling of negative electrode sheets of spent lithium ion batteries by sulfuric acid leaching[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 44(3): 364-366, 376. | |
| 53 | 詹剑虹, 杜志威, 张思维, 等. 废旧锂离子电池负极石墨闭环回收的基础研究[J]. 电源技术, 2020, 44(2): 173-175, 252. |
| ZHAN J H, DU Z W, ZHANG S W, et al. Research on closed-loop recovery of graphite in cathode for spent lithium batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 44(2): 173-175, 252. | |
| 54 | CAO N, ZHANG Y L, CHEN L L, et al. An innovative approach to recover anode from spent lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 483: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229163. |
| 55 | ZHANG J, LI X L, SONG D W, et al. Effective regeneration of anode material recycled from scrapped Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 390: 38-44. |
| 56 | NATARAJAN S, SHANTHANA LAKSHMI D, BAJAJ H C, et al. Recovery and utilization of graphite and polymer materials from spent lithium-ion batteries for synthesizing polymer-graphite nanocomposite thin films[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3(4): 2538-2545. |
| 57 | YU H J, DAI H L, ZHU Y, et al. Mechanistic insights into the lattice reconfiguration of the anode graphite recycled from spent high-power lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 481: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229159. |
| 58 | MARKEY B, ZHANG M H, ROBB I, et al. Effective upcycling of graphite anode: Healing and doping enabled direct regeneration[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(16): doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abcc2f. |
| 59 | NATARAJAN S, RAO EDE S, BAJAJ H C, et al. Environmental benign synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) graphite and its application in supercapacitor[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 543: 98-108. |
| 60 | XU Q, WANG Y, SHI X Y, et al. The direct application of spent graphite as a functional interlayer with enhanced polysulfide trapping and catalytic performance for Li-S batteries[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(2): 942-950. |
| 61 | DU K D, MENG Y F, ZHAO X X, et al. A unique co-recovery strategy of cathode and anode from spent LiFePO4 battery[J]. Science China Materials, 2022, 65(3): 637-645. |
| 62 | DIVYA M L, NATARAJAN S, LEE Y S, et al. Achieving high-energy dual carbon Li-ion capacitors with unique low- and high-temperature performance from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(9): 4950-4959. |
| 63 | WANG Y X, CAO H B, CHEN L L, et al. Tailored synthesis of active reduced graphene oxides from waste graphite: Structural defects and pollutant-dependent reactive radicals in aqueous organics decontamination[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 229: 71-80. |
| 64 | RUAN D S, ZHANG Z H, WU X F, et al. Synthesizing high-quality graphene from spent anode graphite and further functionalization applying in ORR electrocatalyst[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2021, 6(1): 90-95. |
| 65 | ZHANG W X, LIU Z P, XIA J, et al. Preparing graphene from anode graphite of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2017, 11(5): doi: 10.1007/s11783-017-0993-8. |
| 66 | LI B S, WU C B, XU J D, et al. One-pot redox synthesis of graphene from waste graphite of spent lithium ion batteries with peracetic acid assistance[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 241: doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122397. |
| 67 | ZHAO L L, LIU X Y, WAN C Y, et al. Soluble graphene nanosheets from recycled graphite of spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(2): 875-880. |
| 68 | KANG S H, YU T, LIU T T, et al. Eco-friendly preparation of large-sized graphene via short-circuit discharge of lithium primary battery[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 512: 489-496. |
| 69 | ZHANG Y, GUO X M, WU F, et al. Mesocarbon microbead carbon-supported magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles: Turning spent Li-ion battery anode into a highly efficient phosphate adsorbent for wastewater treatment[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(33): 21315-21325. |
| 70 | ZHAO T, YAO Y, WANG M L, et al. Preparation of MnO2-modified graphite sorbents from spent Li-ion batteries for the treatment of water contaminated by lead, cadmium, and silver[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(30): 25369-25376. |
| 71 | RUISMÄKI R, RINNE T, DAŃCZAK A, et al. Integrating flotation and pyrometallurgy for recovering graphite and valuable metals from battery scrap[J]. Metals, 2020, 10(5): doi: 10.3390/met10050680. |
| 72 | QIAO Y, SHENG W, HE C, et al. A facile freeze-thaw ultrasonic assisted circulation method of graphite flakes prepared by anode graphite from spent lithium-ion batteries for application in nanofluids[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2021, 5(19): 4882-4894. |
| [1] | Guojing LIU, Bingjie LI, Xiaoyan HU, Fen YUE, Jiqiang XU. Australia policy mechanisms and business models for energy storage and their applications to china [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2332-2343. |
| [2] | YAN Qiaoyi, WU Feng, CHEN Renjie, LI Li. Recovery and resource recycling of graphite anode materials for spent lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1760-1771. |
| [3] | Jian YAO, Zhaoyang LIU, Hai WANG, Jiadong WANG, Xuanwen GAO, Jianzhong LI, Zhaomeng LIU, Yuchun ZHAI, Wenbin LUO. Exploration of mixed positive and negative electrodes of spent lithium iron phosphate batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(12): 3759-3767. |
| [4] | Lifen LONG, Xihua ZHANG, Peifan YAO, Mingjie LI, Jingwei WANG. Research advances on the utilization and disposal of graphite anode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(10): 3076-3089. |
| [5] | Hong LI, Jiangwei CHU, Shufa SUN, Honggang LI. Characteristics of vehicle-mounted electromagnetic coupling flywheel energy storage system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(5): 1687-1693. |
| [6] | Baohong ZHU, Guangjun LI, Shusheng LI, Yadong CUI. Power compensation and energy saving application of oil well generator based on energy storage flywheel [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 1088-1094. |
| [7] | Mingjun DU, Jiaqiang JING, Zhigui ZHANG, Jinshuai LI, Ran YIN. Study on key technologies of solar energy photothermal conversion for heavy oil thermal recovery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(S1): 62-69. |
| [8] | SUN Shoubin, YAO Hua, LIU Changpeng, HUANG Yun, MA Guangyu, ZHANG Tianfu, WANG Xiangfeng. Characteristics analysis of the phase change thermal storage equipment for medium and low temperature flue gas from steel industry [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 730-734. |
| [9] | CHEN Yongzhen, LI Hualing, SONG Wenji, TU Xiaolin, FENG Ziping. A review on recycling technology of spent lithium iron phosphate battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(2): 237-247. |
| [10] | WANG Dajie, CHEN Ying, TANG Yingwei, LI Shengfei, ZHAO Sifeng. Application and research of flywheel energy storage system in electrified railway [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(5): 853-860. |
| [11] | LI Dongliang, SHI Haimin, LIANG Deqing. Thermal storage in an air conditioning system with dual energy storage unit [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2014, 3(5): 480-485. |
| [12] | ZHAO Liang, WANG Haiyang, FANG Xiangchen, WANG Gang, XU Hong. Modification of fly ash as a carrier of paraffin wax based phase change energy storage material for waste heat recovery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2013, 2(6): 598-602. |
| [13] | DENG Guangyi, GUO Zuogang, CHEN Guangming. Design and thermodynamic analysis of compressed air energy storage system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2013, 2(6): 615-619. |
| [14] | ZHANG Guocai 1,2,3,XU Zhe1,CHEN Yunfa2,LI Jianqiang1. Progress in metal-based phase change materials for thermal energy storage applications [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2012, 1(1): 74-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
