储能科学与技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (8): 3122-3137.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0289
• 储能材料与器件 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-03-27
修回日期:2025-04-18
出版日期:2025-08-28
发布日期:2025-08-18
通讯作者:
李晶晶
E-mail:jjli@ipezz.ac.cn
作者简介:李晶晶(1986—),女,硕士,工程师,研究方向为电池回收和材料制备,E-mail:jjli@ipezz.ac.cn。
基金资助:
Jingjing LI1( ), Danfeng JIANG2, Jiaxin LI2, Jie YAN2, Changjie SHEN3
), Danfeng JIANG2, Jiaxin LI2, Jie YAN2, Changjie SHEN3
Received:2025-03-27
Revised:2025-04-18
Online:2025-08-28
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
Jingjing LI
E-mail:jjli@ipezz.ac.cn
摘要:
富锂层状氧化物材料因其高比容量和低成本优势,被视为突破锂离子电池能量密度低瓶颈的下一代正极材料。传统多晶团聚体形貌的富锂材料在长循环过程中面临结构重构引发的颗粒粉化、晶格氧不可逆析出等本征缺陷,导致电极/电解质界面持续恶化与容量衰减。单晶化通过消除晶界应力效应,被证实是缓解上述衰退机制的有效途径。本文回顾了高镍单晶材料在结构和电化学性能方面的独特优势,系统对比了富锂单晶与多晶材料在关键性能指标的差异,重点构建了首次库仑效率、结构稳定性、循环后形貌演变及界面副反应诱导的产气行为等多维度评估体系,围绕高温固相法、熔融盐辅助法、水热/溶剂热法等主流合成技术,阐述了其合成工艺中关键参数对晶体形貌的影响。此外,本文进一步总结了富锂单晶材料的改性策略及研究进展,元素掺杂、表面包覆、结构构筑等优化策略均可显著提高富锂单晶材料的结构稳定性和电化学性能。最后,对富锂单晶材料未来的发展方向进行了总结和展望,为高能量密度锂离子电池的开发与应用提供了理论依据和技术支持。
中图分类号:
李晶晶, 蒋丹枫, 李嘉鑫, 闫婕, 申长洁. 高比容量富锂单晶材料的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(8): 3122-3137.
Jingjing LI, Danfeng JIANG, Jiaxin LI, Jie YAN, Changjie SHEN. Research progress on high specific-capacity lithium-rich single crystal materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(8): 3122-3137.
表1
不同合成方法制备的富锂单晶样品及其电化学性能"
| 材料组成 | 合成方法 | 煅烧工艺 | 形貌 | 电压范围/V | 容量/(mAh/g) | 循环保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | 高温固相法 | 800*12 | 片状 | 2.0~4.8 | 254.5 | 71.9(1000) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | 高温固相法 | 450*6+900*10 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 291.4 | 89.8(100) | [ |
| Li1.1Na0.1Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 | 高温固相法 | 450*5+850*12 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 278.5 | 87(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | 高温固相法 | 500*2+800*12 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 270 | 89(400) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | 高温固相法 | 450*5+900*12 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 290.4 | 100(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 | 高温固相法 | 450*5+925*14 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 290.3 | 81.9(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.56Ni0.12Co0.12O2 | 溶剂热法 | 450*6+900*12 | 片状 | 2.0~4.8 | 306.9 | — | [ |
| 0.5Li2MnO3·0.5LiMn0.4Ni0.3Co0.3O2 | 溶剂热法 | 450*6+900*12 | 片状 | 2.0~4.8 | 300.1 | 93.5(50) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.56Co0.12Ni0.12O2 | 溶剂热法 | 900*12 | 纳米棒 | 2.0~4.8 | 264.6 | 91(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 | 高温固相法 | 550*5+900*10+500*5 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 286.3 | 89(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 | 高温固相法 | 500*5+850*15 | 片状 | 2.0~4.8 | 296 | 83.2(160) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.48Ni0.16Co0.16O2 | 高温固相法 | 940*2+760*10 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 259 | 84.9(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.533Ni0.267O2 | 熔融盐辅助法 | 500*5+900*20 | 细长状 | 2.0~4.8 | 240 | 84.06(200) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.56Ni0.16Co0.08O2 | 熔融盐辅助法 | 900*15 | 多边形 | 2.0~4.7 | 263.1 | 82.7(200) | [ |
| Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 | 熔融盐辅助法 | 900*10 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 258 | 97.3(250) | [ |
| 0.5Li2MnO3· 0.5LiMn1/3Ni1/3Co1/3O2 | 熔融盐辅助法 | 900*12 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 268 | 82(100) | [ |
| Li1.2Mn0.533Ni0.267O2 | 熔融盐辅助法 | 500*5+900*20 | 不规则 | 2.0~4.8 | 210.8 | 84.06(200) | [ |
| Li1.2Ni0.13Mn0.54Co0.13O2 | 熔融盐辅助法 | 850*8 | 不规则 | 2.5~4.6 | 277 | — | [ |
| Li[Li0.2Ni0.2Mn0.6]O2 | 高温固相法 | 900*12 | 片状 | 2.0~4.8 | 253 | 85(200) | [ |
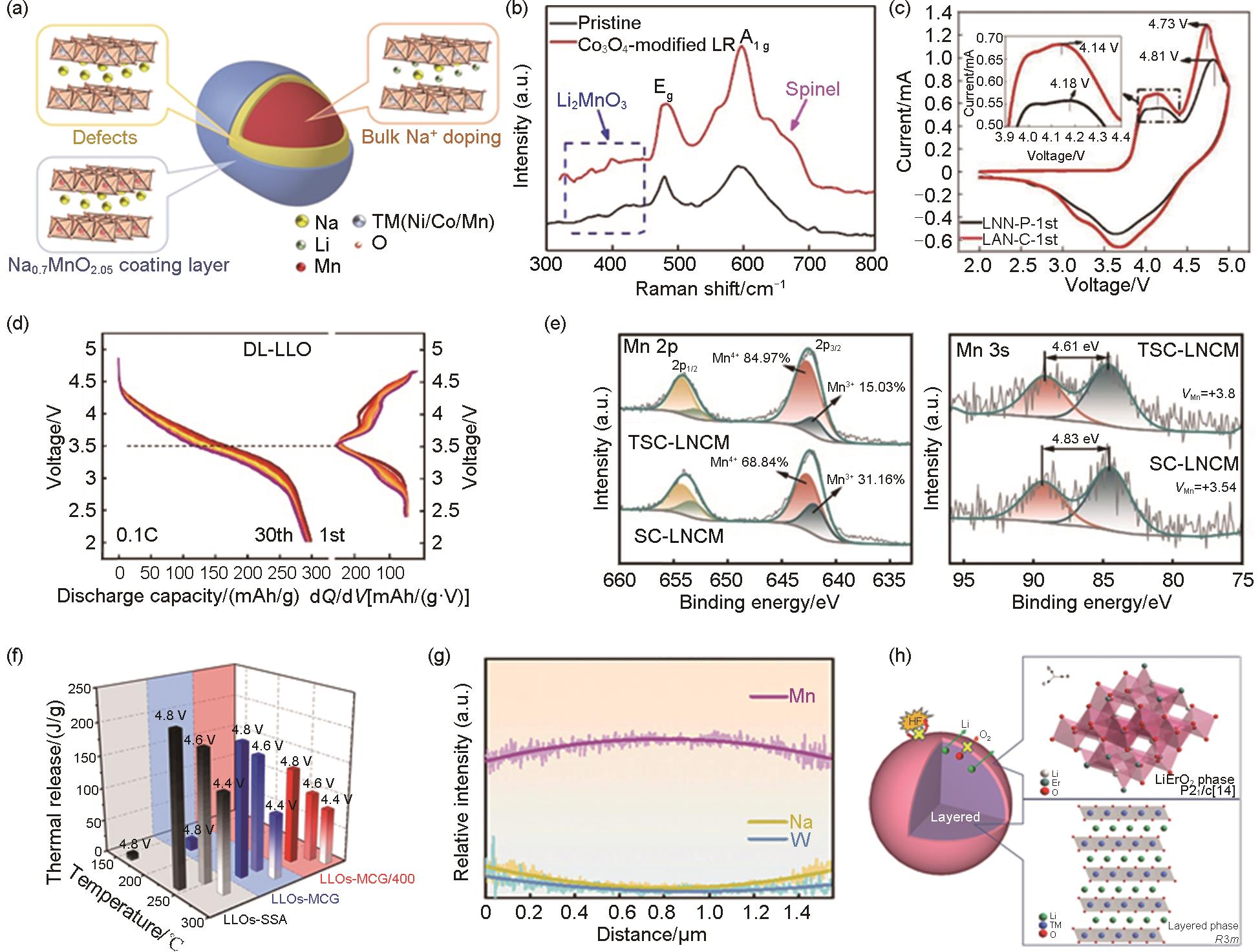
图7
(a) 钠掺杂的结构图[28];(b) Co3O4 包覆LR样品的拉曼光谱[34];(c) 未包覆的富锂氧化物 (LMN-P) 和CeO2 包覆的不含Co的富锂氧化物 (LMN-C) 第1周伏安图[63];(d) DL-LLO循环30次的放电曲线及对应dQ/dV[45];(e) SC-LNCM和TSC-LNCM的X射线光电子能谱 (XPS)[64];(f) 呈球形二次团聚体颗粒的富锂氧化物 (LLOs-SSA)、LLOs-MCG和LLOs-MCG/400在4.4 V、4.6 V和4.8 V状态下的差示扫描量热 (DSC) 图[50];(g) 元素曲线[35];(h) LiErO2 包覆晶体结构[65]"
| [1] | CUI S L, GAO M Y, LI G R, et al. Insights into Li-rich Mn-based cathode materials with high capacity: From dimension to lattice to atom[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(4): 2003885. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202003885. |
| [2] | SHI J L, XIAO D D, GE M Y, et al. High-capacity cathode material with high voltage for Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(9): 1705575. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201705575. |
| [3] | LEE Y, LEE J, LEE K Y, et al. Facile formation of a Li3PO4 coating layer during the synthesis of a lithium-rich layered oxide for high-capacity lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 315: 284-293. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.03.024. |
| [4] | SHI J L, ZHANG J N, HE M, et al. Mitigating voltage decay of Li-rich cathode material via increasing Ni content for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(31): 20138-20146. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b06733. |
| [5] | ZHANG X D, HAO J J, WU L C, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of perovskite LaNiO3 coating on Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 283: 1203-1212. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018. 07.057. |
| [6] | ZHANG L J, LI N, WU B R, et al. Sphere-shaped hierarchical cathode with enhanced growth of nanocrystal planes for high-rate and cycling-stable li-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(1): 656-661. DOI: 10.1021/nl5041594. |
| [7] | YANG Y L, GAO C, LUO T, et al. Unlocking the potential of Li-rich Mn-based oxides for high-rate rechargeable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(52): 2307138. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202307138. |
| [8] | LIU K L, ZHANG Q F, LU Z, et al. Molten-salt-assisted strategy enables high-rate micron-sized single-crystal Li-rich, Mn-based layered oxide cathode materials[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(12): 14902-14911. DOI: 10.1021/acsami. 4c00291. |
| [9] | SU Y F, WANG M, ZHANG M X, et al. The positive role of the single crystal morphology in improving the electrochemical performance of Li-rich cathode materials[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 905: 164204. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022. 164204. |
| [10] | FAN X M, HU G R, ZHANG B, et al. Crack-free single-crystalline Ni-rich layered NCM cathode enable superior cycling performance of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 70: 104450×6522: 1313-1317. DOI: 10.1126/science.abc3167. |
| [12] | LIU Y L, HARLOW J, DAHN J. Microstructural observations of "single crystal" positive electrode materials before and after long term cycling by cross-section scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(2): 020512. DOI: 10.1149/1945-7111/ab6288. |
| [13] | SUN J M, CAO X, YANG H J, et al. The origin of high-voltage stability in single-crystal layered Ni-rich cathode materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(40): e2022 07225. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202207225. |
| [14] | LENG J, WANG J P, PENG W J, et al. Highly-dispersed submicrometer single-crystal nickel-rich layered cathode: Spray synthesis and accelerated lithium-ion transport[J]. Small, 2021, 17(14): 2006869. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202006869. |
| [15] | HU J T, LI L Z, BI Y J, et al. Locking oxygen in lattice: A quantifiable comparison of gas generation in polycrystalline and single crystal Ni-rich cathodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 47: 195-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2022.02.025. |
| [16] | LOGAN E R, HEBECKER H, MA X W, et al. A comparison of the performance of different morphologies of LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 using isothermal microcalorimetry, ultra-high precision coulometry, and long-term cycling[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(6): 060530. DOI: 10.1149/1945-7111/ab8620. |
| [17] | HU J T, WANG H B, XIAO B W, et al. Challenges and approaches of single-crystal Ni-rich layered cathodes in lithium batteries[J]. National Science Review, 2023, 10(12): nwad252. DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwad252. |
| [18] | CHA H, KIM J, LEE H, et al. Boosting reaction homogeneity in high-energy lithium-ion battery cathode materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(39): 2003040. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202003040. |
| [19] | ZHAO X W, CAO X, SHENG C C, et al. Perspective on high-stability single-crystal Li-rich cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(19): 24147-24161. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c05206. |
| [20] | LI L T, CHEN Y F, LIU Y C, et al. Synthesis of high-performance single-crystal Li-rich cathode by self-combustion method[J]. Rare Metals, 2023, 42(3): 830-837. DOI: 10.1007/s12598-022-02158-z. |
| [21] | SUN J M, SHENG C C, CAO X, et al. Restraining oxygen release and suppressing structure distortion in single-crystal Li-rich layered cathode materials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(10): 2110295. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202110295. |
| [22] | HAO Z K, GOU X X, MA H Y, et al. Boosting the cycle and rate performance of Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 via single-crystal structure design[J]. Science China Materials, 2023, 66(9): 3424-3432. DOI: 10.1007/s40843-023-2494-1. |
| [23] | YANG X X, WANG S N, HAN D Z, et al. Structural origin of suppressed voltage decay in single-crystalline Li-rich layered Li [Li0.2Ni0.2Mn0.6]O2 cathodes[J]. Small, 2022, 18(25): 2201522. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202201522. |
| [24] | YOON M S, DONG Y H, HUANG Y M, et al. Eutectic salt-assisted planetary centrifugal deagglomeration for single-crystalline cathode synthesis[J]. Nature Energy, 2023: 482-491. |
| [25] | XIE Y, MENG S, CHEN X, et al. Synergetic effect of high Ni ratio and low oxygen defect interface zone of single crystals on the capacity retention of lithium rich layered oxides[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 594: 485-492. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.038. |
| [26] | HE W X, LIU J G, SUN W, et al. Coprecipitation-gel synthesis and degradation mechanism of octahedral Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 as high-performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(27): 23018-23028. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b04023. |
| [27] | XU C Y, LI J L, SUN J, et al. Li-rich layered oxide single crystal with Na doping as a high-performance cathode for Li ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 895: 162613. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162613. |
| [28] | LIU Q, XIE T, XIE Q S, et al. Multiscale deficiency integration by Na-rich engineering for high-stability Li-rich layered oxide cathodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(7): 8239-8248. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c19040. |
| [29] | LIN S Z, WANG Z, LU T X, et al. One-step preparation of homogeneous single crystal Li-rich cathode materials with encouraging electrochemical performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 822: 153638. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom. 2020.153638. |
| [30] | 缪胤宝, 张文华, 刘伟昊, 等. 富锂正极材料Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2的制备及性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(5): 1427-1434. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0850. |
| [31] | FU F, HUANG Y Y, WU P, et al. Controlled synthesis of lithium-rich layered Li1.2Mn0.56Ni0.12Co0.12O2 oxide with tunable morphology and structure as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries by solvo/hydrothermal methods[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 618: 673-678. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.191 |
| [32] | FU F, DENG Y P, SHEN C H, et al. A hierarchical micro/nanostructured 0.5Li2MnO3·0.5LiMn0.4Ni0.3Co0.3O2 material synthesized by solvothermal route as high rate cathode of lithium ion battery[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2014, 44: 54-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2014.04.013. |
| [33] | FU F, YAO Y Z, WANG H Y, et al. Structure dependent electrochemical performance of Li-rich layered oxides in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 35: 370-378. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.04.005. |
| [34] | XIN Y, LAN X W, CHANG P, et al. Conformal spinel/layered heterostructures of Co3O4 shells grown on single-crystal Li-rich nanoplates for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 447: 829-836. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc. 2018.04.070. |
| [35] | DUAN J D, WANG F Q, HUANG M J, et al. High-performance single-crystal lithium-rich layered oxides cathode materials via Na2WO4-assisted sintering[J]. Small, 2024, 20(15): 2307998. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202307998. |
| [36] | SUN J M, CAO X, YANG W H, et al. Impact of particle size on the kinetics and structure stability of single-crystal Li-rich cathode materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(26): 13956-13964. DOI: 10.1039/D3TA01624B. |
| [37] | ZHONG X X, CHEN M, ZHU Y M, et al. Layered lithium-rich oxide nanoparticles: Low-temperature synthesis in mixed molten salt and excellent performance as cathode of lithium-ion battery[J]. Ionics, 2017, 23(8): 1955-1966. DOI: 10.1007/s11581-017-2039-4. |
| [38] | KUPPAN S, SHUKLA A K, MEMBRENO D, et al. Revealing anisotropic spinel formation on pristine Li- and Mn-rich layered oxide surface and its impact on cathode performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(11): 1602010. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201602010. |
| [39] | JIAO C M, WANG M, HUANG B, et al. Surface modification single crystal Li-rich Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 as high performance cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 937: 168389. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022. 168389. |
| [40] | LI J, LI H Y, STONE W, et al. Synthesis of single crystal LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2 for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(14): A3529-A3537. DOI: 10. 1149/2.0401714jes. |
| [41] | ZHANG B D, ZHANG Y M, WU H C, et al. Does single-crystallization a feasible direction for designing Li-rich layered cathodes [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 62: 102926. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2023.102926. |
| [42] | ZHAO X W, SHENG C C, CHANG Z, et al. Solid-state exfoliation growth mechanism of single-crystal Li-rich layered cathode materials[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2025, 75: 104093. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2025.104093. |
| [43] | YAN L Y, GAO Y, CHEN M M, et al. Preparation of single-crystal Li-rich Mn-based layered oxides with excellent electrochemical performance via simple stepwise high-temperature sintering[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(44): 60166-60179. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c11204. |
| [44] | ZHAO Z Y, HUANG B, WANG M, et al. Facile synthesis of fluorine doped single crystal Ni-rich cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2019, 342: 115065. DOI: 10. 1016/j.ssi.2019.115065. |
| [45] | ZENG W H, LIU F, YANG J L, et al. Single-crystal Li-rich layered cathodes with suppressed voltage decay by double-layer interface engineering[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 54: 651-660. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2022.11.016. |
| [46] | LIU T C, LIU J J, LI L X, et al. Origin of structural degradation in Li-rich layered oxide cathode[J]. Nature, 2022, 606(7913): 305-312. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04689-y. |
| [47] | HE H C, LI H, MOU L S, et al. Achieving long cycle life and single-crystal of Li-rich Mn-based cathodes by reheating with sintering additives[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2023, 2539(1): 012040. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/2539/1/012040. |
| [48] | WU T H, ZHANG X, WANG Y Z, et al. Gradient "single-crystal" Li-rich cathode materials for high-stable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(4): 2210154. DOI: 10. 1002/adfm.202210154. |
| [49] | WANG L, XU L, XUE W R, et al. Synergistic enhancement of Li-rich manganese-based cathode materials through single crystallization and in situ spinel coating[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 121: 109241. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.109241. |
| [50] | WANG Y Z, WANG L, GUO X W, et al. Thermal stability enhancement through structure modification on the microsized crystalline grain surface of lithium-rich layered oxides[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(7): 8306-8315. DOI: 10. 1021/acsami.9b21303. |
| [51] | ZUO P, WANG F X, CHEN G Y, et al. Facet-dependent Ni segregation in a micron-sized single-crystal Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024. DOI: 10. 1021/acsami.4c02885. |
| [52] | PENG H, ZHAO S X, HUANG C, et al. In situ construction of spinel coating on the surface of a lithium-rich manganese-based single crystal for inhibiting voltage fade[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(10): 11579-11588. DOI: 10.1021/acsami. 9b21271. |
| [53] | LI S F, QIAN G N, HE X M, et al. Thermal-healing of lattice defects for high-energy single-crystalline battery cathodes[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 704. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28325-5. |
| [54] | LI X Q, ZHOU L M, WANG H, et al. Dopants modulate crystal growth in molten salts enabled by surface energy tuning[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(35): 19675-19680. DOI: 10.1039/D1TA02351A. |
| [55] | CHEN G Y, HAI B, SHUKLA A K, et al. Impact of initial Li content on kinetics and stabilities of layered Li1+ x(Ni0.33Mn0.33Co0.33)1+ xO2[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(9): A1543-A1550. DOI: 10.1149/2.038209jes. |
| [56] | MIAO X W, YAN Y, WANG C G, et al. Optimal microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nanosized xLi2MnO3·(1-x)LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials for lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 247: 219-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.08.097. |
| [57] | HU S J, LI Y, CHEN Y H, et al. Insight of a phase compatible surface coating for long-durable Li-rich layered oxide cathode[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(34): 1901795. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201901795. |
| [58] | WEI Y R, CHENG J, LI D P, et al. A structure self-healing Li-rich cathode achieved by lithium supplement of Li-rich LLZO coating[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(22): 2214775. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202214775. |
| [59] | SHAO Q N, GAO P Y, YAN C H, et al. A redox couple strategy enables long-cycling Li- and Mn-rich layered oxide cathodes by suppressing oxygen release[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(14): 2108543. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202108543. |
| [60] | YU R Z, WANG C H, DUAN H, et al. Manipulating charge-transfer kinetics of lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes in halide all-solid-state batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(5): 2207234. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202207234. |
| [61] | LI J L, LIN H Y, TANG C J, et al. Na doping into Li-rich layered single crystal nanoparticles for high-performance lithium-ion batteries cathodes[J]. Nanotechnology, 2022, 33(6): 065705. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac353c. |
| [62] | YALÇıN A, DEMIR M, GÜLER M O, et al. Synthesis of Sn-doped Li-rich NMC as a cathode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 440: 141743. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta. 2022.141743. |
| [63] | LIU Y L, LI B, CHEN M, et al. Low-temperature-aged synthesis of CeO2-coated Li-rich oxide as cathode for low-cost high-energy density Li-ion batteries[J]. Batteries, 2023, 9(6): 330. DOI: 10. 3390/batteries9060330. |
| [64] | DUAN J D, WANG F Q, LI S M, et al. Stable surface lattice for prolonged cycle life of single-crystal lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 489: 151257. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.151257. |
| [65] | WEI Z C, ZHANG D, ZHONG J J, et al. Enhanced cycling stability of lithium-rich cathode materials achieved by in situ formation of LiErO2 coating[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2023, 6(4): e202200568. DOI: 10.1002/batt.202200568. |
| [66] | ZHU Z, YU D W, YANG Y, et al. Gradient Li-rich oxide cathode particles immunized against oxygen release by a molten salt treatment[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(12): 1049-1058. DOI: 10. 1038/s41560-019-0508-x. |
| [67] | CAI Z F, WANG S, ZHU H K, et al. Improvement of stability and capacity of co-free, Li-rich layered oxide Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 cathode material through defect control[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 630(Pt B): 281-289. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022. 10.105. |
| [68] | CELESTE A, TUCCILLO M, SANTONI A, et al. Exploring a co-free, Li-rich layered oxide with low content of nickel as a positive electrode for Li-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(10): 11290-11297. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.1c02133. |
| [1] | 曾州岚, 尚雷, 胡志金, 王宗凡, 辛小超, 刘瑛. 高容量锂离子电池正极补锂材料Li5FeO4@C的性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1875-1883. |
| [2] | 吉帅静, 王军伟, 杜宝帅, 徐丽, 楼平, 管敏渊, 汤舜, 程时杰, 曹元成. LiFe x Mn1–x PO4 (0<x<1)电池稳定性与安全性的提升路径:从失效机制到综合优化策略[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 965-983. |
| [3] | 周德清, 蔡艺嘉, 张子芩, 周丽萍, 胡思江, 黄有国, 王红强, 李庆余. MoS2 尖晶石包覆富锂锰基正极材料的电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 1087-1096. |
| [4] | 王志勇, 蔡君瑶, 佘英奇, 钟树林, 潘康华. 氮杂环导电高分子改性锂离子电池石墨负极材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2511-2518. |
| [5] | 郝定邦, 栗永利. 高倍率和长循环稳定性钠离子电池正极材料Na0.85Ni0.3Fe0.2Mn0.5O1.95F0.05 @CuO的性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2489-2498. |
| [6] | 林炜琦, 卢巧瑜, 陈宇鸿, 邱麟媛, 季钰榕, 管联玉, 丁翔. 低温钠离子电池正极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2348-2360. |
| [7] | 肖鹏飞, 梅琳, 陈立宝. 多元包覆石墨复合负极材料的低温电化学储锂性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2116-2123. |
| [8] | 赵晨阳, 于晓琨, 陶于兵. 改性氧化铜/正十八烷复合相变材料制备及性能表征研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(6): 1786-1793. |
| [9] | 刘博宇, 庞青, 王腾飞, 望红玉. 高镍三元正极材料LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 在高压下的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(11): 3784-3795. |
| [10] | 陈桢, 李贤傲, 徐艺维, 刘欣, 申泽骧, 陈明华. LATP、LAGP固态电解质材料合成改性路线研究现状及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(11): 3826-3855. |
| [11] | 方泽平, 邱报, 刘兆平. 富锂层状氧化物正极材料“可逆高氧活性”的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 240-251. |
| [12] | 廖雅贇, 周峰, 张颖曦, 吕途安, 何阳, 陈晓燕, 霍开富. 锂离子电池快充石墨负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 130-142. |
| [13] | 张吉禄, 董育辰, 宋强, 袁思鸣, 郭孝东. 多晶及单晶高镍三元材料LiNi0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 的可控制备及其电化学储锂特性[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(8): 2382-2389. |
| [14] | 赵争光, 陈振营, 翟光群, 张希, 庄小东. Sc/O掺杂硫化物固态电解质的制备及全固态电池性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(8): 2412-2423. |
| [15] | 张琦, 李银雷, 栗艳芳, 宋俊, 吴学红, 刘重阳, 张雪龄. 膨胀石墨/多壁碳纳米管基共晶盐复合相变材料的制备及热特性[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(8): 2435-2443. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
