储能科学与技术 ›› 2022, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (2): 697-703.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0450
收稿日期:2021-08-30
修回日期:2021-10-13
出版日期:2022-02-05
发布日期:2022-02-08
通讯作者:
李建林
E-mail:dkyljl@163.com
Received:2021-08-30
Revised:2021-10-13
Online:2022-02-05
Published:2022-02-08
Contact:
Jianlin LI
E-mail:dkyljl@163.com
摘要:
简述了我国用于大规模储能的锂离子电池建模技术的最新研究进展。由于储能技术可以起到平抑波动、提高电能质量的作用,所以近年来电网对于储能的需求也逐年增大。大规模储能系统由锂电池组、双向逆变器和电池能量管理系统组成,在双向逆变器和电池能量管理系统有现成可用模型的前提下,建立精确、可靠的锂离子电池模型便成了实现大规模储能工程应用的重点。本文阐述了目前流行的电池建模方法:通过对电池电化学反应过程的模拟形成了电化学模型,虽然精度较高,但是模型复杂,使用时应当对其做适当简化,一般用于电池原理分析;通过对电池外特性不同程度的模拟形成了不同的等效电路模型,虽然不注重对原理的仿真,但是比较适合在工程实践中应用;通过对电池输入输出关系的研究形成了神经网络模型,但是其精度对于数据的数量和质量要求较高;最后总结指出为了更好地实现在电力系统中的应用,应当更加深入地研究锂离子电池反应原理并对其进行方程量化描述,提升模型在不同场景下的应用能力。
中图分类号:
李建林, 肖珩. 锂离子电池建模现状综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(2): 697-703.
Jianlin LI, Heng XIAO. Review on modeling of lithium-ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(2): 697-703.
表1
常用锂电池模型比较"
| 基本电路模型 | 电路结构 | 描述方程 | 参数 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rint | 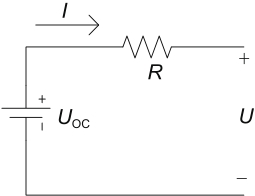 | 结构简单,参数容易计算 | 无法描述动态过程,电流过大时精度较差,对电池特性模拟情况差 | ||
| Thevenin | 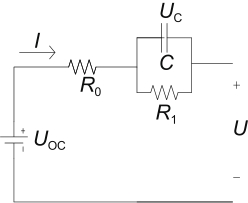 | 考虑了电池的极化效应,对电池特性有较好模拟,在实际工程应用中较多 | 电池老化、温度变化情况对模型精度有较大影响 | ||
| PNGV | 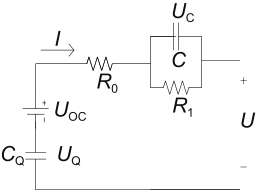 | 模型容易考虑温度影响,对电池各种工况适用性好,精确度较好 | 串联电容的累积误差会降低模型精确度,且仍不能较好反应极化现象 | ||
| 二阶RC | 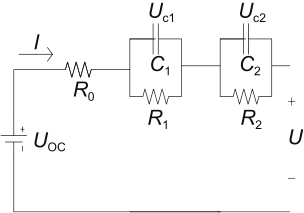 | 计算量适中,模型精度高,更接近真实电池特性 | 结构、参数计算较为复杂 | ||
| GNL |  | 考虑自放电影响,仿真精度高 | 模型复杂,参数整定困难,计算复杂 |
| 1 | 习近平. 继往开来,开启全球应对气候变化新征程——在气候雄心峰会上的讲话[J]. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 2020(35): 7. |
| 2 | 新华社. 习近平主持召开中央财经委员会第九次会议[J]. 预算管理与会计, 2021(4): 4-5. |
| 3 | 张超. 新能源发电并网对电网电能质量的分析研究[J]. 中国设备工程, 2019(19): 230-231. |
| 4 | 李建林, 袁晓冬, 郁正纲, 等. 利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(8): 15-24. |
| LI J L, YUAN X D, YU Z G, et al. Comments on power quality enhancement research for power grid by energy storage system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(8): 15-24. | |
| 5 | 袁世斐, 吴红杰, 殷承良. 锂离子电池简化电化学模型: 浓度分布估计[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2017, 51(3): 478-486. |
| YUAN S F, WU H J, YIN C L. Simplified electrochemical model for Li-ion battery: Lithium concentration estimation[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2017, 51(3): 478-486. | |
| 6 | 李云. 锂电池的建模与仿真[D]. 北京: 北方工业大学, 2018. |
| LI Y. The modeling and simulation of the lithium-ion battery[D]. Beijing: North China University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 7 | 陈旭. 温度影响下动力锂电池建模与均衡管理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2018. |
| CHEN X. Research on modeling and equalization management of power lithium battery under the influence of temperature[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2018. | |
| 8 | 康鑫, 时玮, 陈洪涛. 基于锂离子电池简化电化学模型的参数辨识[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(3): 969-978. |
| KANG X, SHI W, CHEN H T. Parameter identification based on simplified electrochemical model of lithium ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 969-978. | |
| 9 | 陈洪涛. 锂电池电化学模型参数辨识研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019. |
| CHEN H T. Study on parameters identification of electrochemical model for lithium ion battery[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 10 | JAGUEMONT J, BOULON L, DUBÉ Y. A comprehensive review of lithium-ion batteries used in hybrid and electric vehicles at cold temperatures[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 164: 99-114. |
| 11 | HARLOW J E, GLAZIER S L, LI J, et al. Use of asymmetric average charge- and average discharge- voltages as an indicator of the onset of unwanted lithium deposition in lithium-ion cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(16): A3595-A3601. |
| 12 | WANG D F, HUANG H Q, TANG Z H, et al. A lithium-ion battery electrochemical-thermal model for a wide temperature range applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 362: 137118. |
| 13 | 皇甫海文, 韩艾呈. 锂电池等效模型建立与参数辨识方法研究[J]. 电气开关, 2020, 58(3): 37-41. |
| HUANGPU Haiwen, HAN Aicheng. Research on lithium-ion battery models and model parameter identification methods[J]. Electric Switchgear, 2020, 58(3): 37-41. | |
| 14 | THAKKAR R R, RAO Y S, R SAWANT R. Performance analysis of electrical equivalent circuit models of lithium-ion battery[C]//2020 IEEE Pune Section International Conference (PuneCon). December 16-18, 2020, Pune, India. IEEE, 2020: 103-107. |
| 15 | 何耀, 刘兴涛, 张陈斌, 等. 基于动力电池组内阻模型的绝缘检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(5): 1165-1170. |
| HE Y, LIU X T, ZHANG C B, et al. Insulation detection algorithm for high-power battery system based on internal resistance model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(5): 1165-1170. | |
| 16 | 杨杰, 王婷, 杜春雨, 等. 锂离子电池模型研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(1): 58-64. |
| YANG J, WANG T, DU C Y, et al. Overview of the modeling of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 58-64. | |
| 17 | 魏克新, 陈峭岩. 基于多模型自适应卡尔曼滤波器的电动汽车电池荷电状态估计[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(31): 19-26,214. |
| WEI K X, CHEN Q Y. Electric vehicle battery SOC estimation based on multiple-model adaptive Kalman filter[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32(31): 19-26, 214. | |
| 18 | HUANG K F, WANG Y, FENG J Q. Research on equivalent circuit Model of Lithium-ion battery for electric vehicles[C]//2020 3rd World Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Manufacturing (WCMEIM). December 4-6, 2020, Shanghai, China. IEEE, 2020: 492-496. |
| 19 | 张宾, 郭连兑, 李宏义, 等. 电动汽车用磷酸铁锂离子电池的PNGV模型分析[J]. 电源技术, 2009, 33(5): 417-421. |
| ZHANG B, GUO L D, LI H Y, et al. PNGV model analysis of LiFePO4 Li-ion battery for electric vehicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 33(5): 417-421. | |
| 20 | CHEN S J, ZHAO Z D. Modeling and simulation of a new ternary lithium battery based on the 2th-order equivalent circuit model[C]//2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Automation and Systems (ICICAS). December 6-8, 2019, Chongqing, China. IEEE, 2019: 402-405. |
| 21 | HE D W, ZHANG W, LUO X Y. Overview of power lithium battery modeling and soc estimation[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 461(1): 012032. |
| 22 | 吴小慧, 张兴敢. 锂电池二阶RC等效电路模型参数辨识[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2020, 56(5): 754-761. |
| WU X H, ZHANG X G. Parameters identification of second order RC equivalent circuit model for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2020, 56(5): 754-761. | |
| 23 | 林成涛, 仇斌, 陈全世. 电动汽车电池功率输入等效电路模型的比较研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2006, 28(3): 229-234. |
| LIN C T, QIU B, CHEN Q S. A comparative study on power input equivalent circuit model for electric vehicle battery[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2006, 28(3): 229-234. | |
| 24 | RAHIMI EICHI H, CHOW M Y. Modeling and analysis of battery hysteresis effects[C]//2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE). September 15-20, 2012, Raleigh, NC, USA. IEEE, 2012: 4479-4486. |
| 25 | 李建杰. 电动汽车动力锂电池建模、仿真及均衡控制研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2020. |
| LI J J. Research on modeling, simulation and equalization control for power lithium battery of electric vehicle[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2020. | |
| 26 | 黄凯, 郭永芳, 李志刚. 考虑迟滞效应影响的动力锂离子电池特性建模[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41(8): 2695-2702. |
| HUANG K, GUO Y F, LI Z G. Modeling of power lithium-ion battery behavior considering hysteresis effect[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41(8): 2695-2702. | |
| 27 | KIM T, QIAO W, QU L. Hysteresis modeling for model-based condition monitoring of lithium-ion batteries[C]//2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE). September 20-24, 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada. IEEE, 2015: 5068-5073. |
| 28 | 宋凯, 陈旭, 成艾国. 考虑温度影响和滞回效应的锂电池特性建模[J]. 汽车工程, 2019, 41(3): 334-339. |
| SONG K, CHEN X, CHENG A G. Modeling of lithium battery characteristics considering the influence of temperature and hysteresis effect[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2019, 41(3): 334-339. | |
| 29 | 户龙辉, 李欣然, 黄际元, 等. 考虑多因素的磷酸铁锂电池综合建模研究[J]. 电源技术, 2016, 40(3): 514-518. |
| HU L H, LI X R, HUANG J Y, et al. Various factors LiFePO4 battery modeling study consideration[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 40(3): 514-518. | |
| 30 | KHARISMA M D, RIDWAN M, ILMIAWAN A F, et al. Modeling and simulation of lithium-ion battery pack using modified battery cell model[C]//2019 6th International Conference on Electric Vehicular Technology (ICEVT). November 18-21, 2019, Bali, Indonesia. IEEE, 2019: 25-30. |
| 31 | 宋旬. 电动汽车串并联动力电池组建模与性能分析研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019. |
| SONG X. Study on modeling and performance analysis of series-parallel connected battery pack for electric vehicles[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2019. | |
| 32 | 李建林, 屈树慷, 黄孟阳, 等. 锂离子电池建模现状研究综述[J]. 热力发电, 2021, 50(7): 1-7. |
| LI J L, QU S K, HUANG M Y, et al. A review of current research on lithium-ion battery modeling[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2021, 50(7): 1-7. | |
| 33 | 张加林. 动力电池主动均衡系统关键技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG J L. Research on key technologies of active battery balance system[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. | |
| 34 | 杜浩. 电动汽车电池组的均衡管理系统设计[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2017. |
| DU H. The design of the equalization management system of electric vehicle battery[D]. Xinxiang, China: Henan Normal University, 2017. | |
| 35 | 李腾, 林成涛, 陈全世. 磷酸铁锂电池组成组过程的不一致性分析[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 52(7): 1001-1006. |
| LI T, LIN C T, CHEN Q S. Inconsistency analysis of LiFePO4 battery packing[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2012, 52(7): 1001-1006. | |
| 36 | 张维戈, 时玮, 姜久春, 等. 动力锂离子电池串并联仿真技术研究[J]. 电网技术, 2012, 36(10): 70-75. |
| ZHANG W G, SHI W, JIANG J C, et al. Numerical simulation technique of series-parallel power lithium ion battery[J]. Power System Technology, 2012, 36(10): 70-75. | |
| 37 | 张言茹. 动力锂离子电池并联衰退机理分析[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015. |
| ZHANG Y R. Analysis of fading mechanisms for parallel-connected power lithium-ion batteries[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2015. | |
| 38 | 范刘洋, 汪可友, 张宝群, 等. 考虑电池组不一致性的储能系统建模及仿真[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(3): 110-115. |
| FAN L Y, WANG K Y, ZHANG B Q, et al. Modeling and simulation of battery energy storage system considering intrinsic inconsistency[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(3): 110-115. | |
| 39 | 苏振浩, 李晓杰, 秦晋, 等. 基于BP人工神经网络的动力电池SOC估算方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(5): 868-873. |
| SU Z H, LI X J, QIN J, et al. SOC estimation method of power battery based on BP artificial neural network[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(5): 868-873. | |
| 40 | WANG P, FAN J, OU Y, et al. A comparative study of machine learning based modeling methods for Lithium-ion battery[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 546(5): 052045. |
| 41 | WEI Y, LING L Y. State of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery based on artificial neural network[C]//2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC). March 12-14, 2021, Chongqing, China. IEEE, 2021: 2454-2458. |
| 42 | 黄妙华, 严永刚, 朱立明. 改进BP神经网络的磷酸铁锂电池SOC估算[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(信息与管理工程版), 2014, 36(6): 790-793. |
| HUANG M H, YAN Y G, ZHU L M. SOC estimation of lithium iron phosphate battery based on improved BP neural network[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Information & Management Engineering), 2014, 36(6): 790-793. | |
| 43 | 胡晓松, 唐小林. 电动车辆锂离子动力电池建模方法综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(16): 20-31. |
| HU X S, TANG X L. Review of modeling techniques for lithium-ion traction batteries in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(16): 20-31. | |
| 44 | 杨云龙. 基于改进型神经网络动力电池SOC估计研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019. |
| YANG Y L. Research on SOC estimation of power battery based on improved neural network[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. | |
| 45 | 徐峰. 基于改进神经网络模型的锂电池SOC预测方法研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆邮电大学, 2018. |
| XU F. Research on the prediction of lithium battery SOC based on improved artificial neural network model[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018. |
| [1] | 李海涛, 孔令丽, 张欣, 余传军, 王纪威, 徐琳. N/P设计对高镍NCM/Gr电芯性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2040-2045. |
| [2] | 曾伟, 熊俊杰, 李建林, 马速良, 武亦文. 基于权重自适应鲸鱼优化算法的多能系统储能电站最优配置[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2241-2249. |
| [3] | 姚祯, 张琦, 王锐, 刘庆华, 王保国, 缪平. 生物质衍生碳材料在全钒液流电池电极方面的应用[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2083-2091. |
| [4] | 时雨, 张忠, 杨晶莹, 钱薇, 李昊, 赵祥, 杨欣桐. 储能电池系统提供AGC调频的机会成本建模与市场策略[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2366-2373. |
| [5] | 陈龙, 夏权, 任羿, 曹高萍, 邱景义, 张浩. 多物理场耦合下锂离子电池组可靠性研究现状与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2316-2323. |
| [6] | 韩健民, 薛飞宇, 梁双印, 乔天舒. 模糊控制优化下的混合储能系统辅助燃煤机组调频仿真[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2188-2196. |
| [7] | 鲁志颖, 江杉, 李全龙, 马可心, 傅腾, 郑志刚, 刘志成, 李淼, 梁永胜, 董知非. 全钒液流电池在充电结束搁置阶段的开路电压变化[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2046-2050. |
| [8] | 易顺民, 谢林柏, 彭力. 基于VF-DW-DFN的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2305-2315. |
| [9] | 冯国会, 王天雨, 王刚. 封装方式对相变水箱蓄放热性能影响模拟分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2161-2176. |
| [10] | 董树锋, 刘灵冲, 唐坤杰, 赵海祺, 徐成司, 林立亨. 基于Simulink和低代码控制器的储能控制实验教学方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2386-2397. |
| [11] | 祝庆伟, 俞小莉, 吴启超, 徐一丹, 陈芬放, 黄瑞. 高能量密度锂离子电池老化半经验模型[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2324-2331. |
| [12] | 刘显茜, 孙安梁, 田川. 基于仿生翅脉流道冷板的锂离子电池组液冷散热[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2266-2273. |
| [13] | 王宇作, 王瑨, 卢颖莉, 阮殿波. 孔结构对软碳负极储锂性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2023-2029. |
| [14] | 郭雨涵, 郁丹, 杨鹏, 王子绩, 王金涛. 基于贪婪算法的分布式储能系统容量优化配置方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2295-2304. |
| [15] | 袁性忠, 胡斌, 郭凡, 严欢, 贾宏刚, 苏舟. 欧盟储能政策和市场规则及对我国的启示[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2344-2353. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

