储能科学与技术 ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (1): 278-298.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0436
袁紫微1( ), 林楚园1, 袁紫嫣1, 孙晓丽1, 钱庆荣1,2, 陈庆华1,2, 曾令兴1,2(
), 林楚园1, 袁紫嫣1, 孙晓丽1, 钱庆荣1,2, 陈庆华1,2, 曾令兴1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-02
修回日期:2022-08-26
出版日期:2023-01-05
发布日期:2023-02-08
通讯作者:
曾令兴
E-mail:ziweiyuan2001@163.com;lingxing@fjnu.edu.cn
作者简介:袁紫微(2001—),女,本科,研究方向为宽温域水系电池,E-mail:ziweiyuan2001@163.com;
基金资助:
Ziwei YUAN1( ), Chuyuan LIN1, Ziyan YUAN1, Xiaoli SUN1, Qingrong QIAN1,2, Qinghua CHEN1,2, Lingxing ZENG1,2(
), Chuyuan LIN1, Ziyan YUAN1, Xiaoli SUN1, Qingrong QIAN1,2, Qinghua CHEN1,2, Lingxing ZENG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-08-02
Revised:2022-08-26
Online:2023-01-05
Published:2023-02-08
Contact:
Lingxing ZENG
E-mail:ziweiyuan2001@163.com;lingxing@fjnu.edu.cn
摘要:
新兴的可充电锌离子电池具有高安全性、环境友好、低成本、操作简单等优势,因此成为极具应用前景的下一代储能设备之一。然而,其在低温条件下展现出较低的放电容量以及功率密度,有时甚至无法正常运行,严重制约可充电锌离子电池的实用性。因此,本文对近期相关文献进行探讨,从电极材料的设计、优化电解质以及改进其他组件三个方面综述了提高锌离子电池低温性能的策略,着重介绍了晶体工程和组分设计在提高电极材料低温离子传导率方面的作用机制。对于电解质优化策略,重点分析了水系高浓度电解质、有机电解质、准固态/固态电解质、电解质添加剂、共晶电解质五种方法对降低电解质凝固点和提升锌离子电池低温电化学性能的机理。此外,简要阐述了高亲水性黏结剂以及高电导率隔膜等改进方法。综合分析表明,通过晶体工程、准固态/固态电解质和电解质添加剂等多种策略的协同耦合,有望实现研制具有高比容量、长循环稳定性和大倍率性能的低温锌离子电池。
中图分类号:
袁紫微, 林楚园, 袁紫嫣, 孙晓丽, 钱庆荣, 陈庆华, 曾令兴. 锌离子电池低温性能研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(1): 278-298.
Ziwei YUAN, Chuyuan LIN, Ziyan YUAN, Xiaoli SUN, Qingrong QIAN, Qinghua CHEN, Lingxing ZENG. The research process on low temperature performance of zinc ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 278-298.
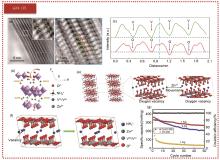
图2
(a) NH4V4O10-x ·nH2O正极材料ABF-STEM图像;(b)沿[100]轴方向的NVOH原子分辨率图像,绿色球为V原子,蓝色球为NH4+ 离子,红色球为O原子,黄色圆圈代表氧空位;(c) (b)图中相应列的强度线轮廓。(d) NH4V4O10-x ·nH2O正极材料的Zn2+ (脱)插层示意图;(e) Zn2+ 在NH4V4O10-x ·nH2O中的扩散示意图,末端位点上有氧空位,红色球为O原子,蓝色球为N原子(NH4+ 离子),绿色球为Zn2+ 离子,灰色球为V原子[35];(f) Zn2+ 在带有NH4+ 空位的Zn0.3(NH4)0.3V4O10·0.91H2O中的扩散示意图,黑色虚线圈表示NH4+ 空位[10];(g) 在1 A/g电流密度下,VO-300与CuVO-300容量对比图[37]"
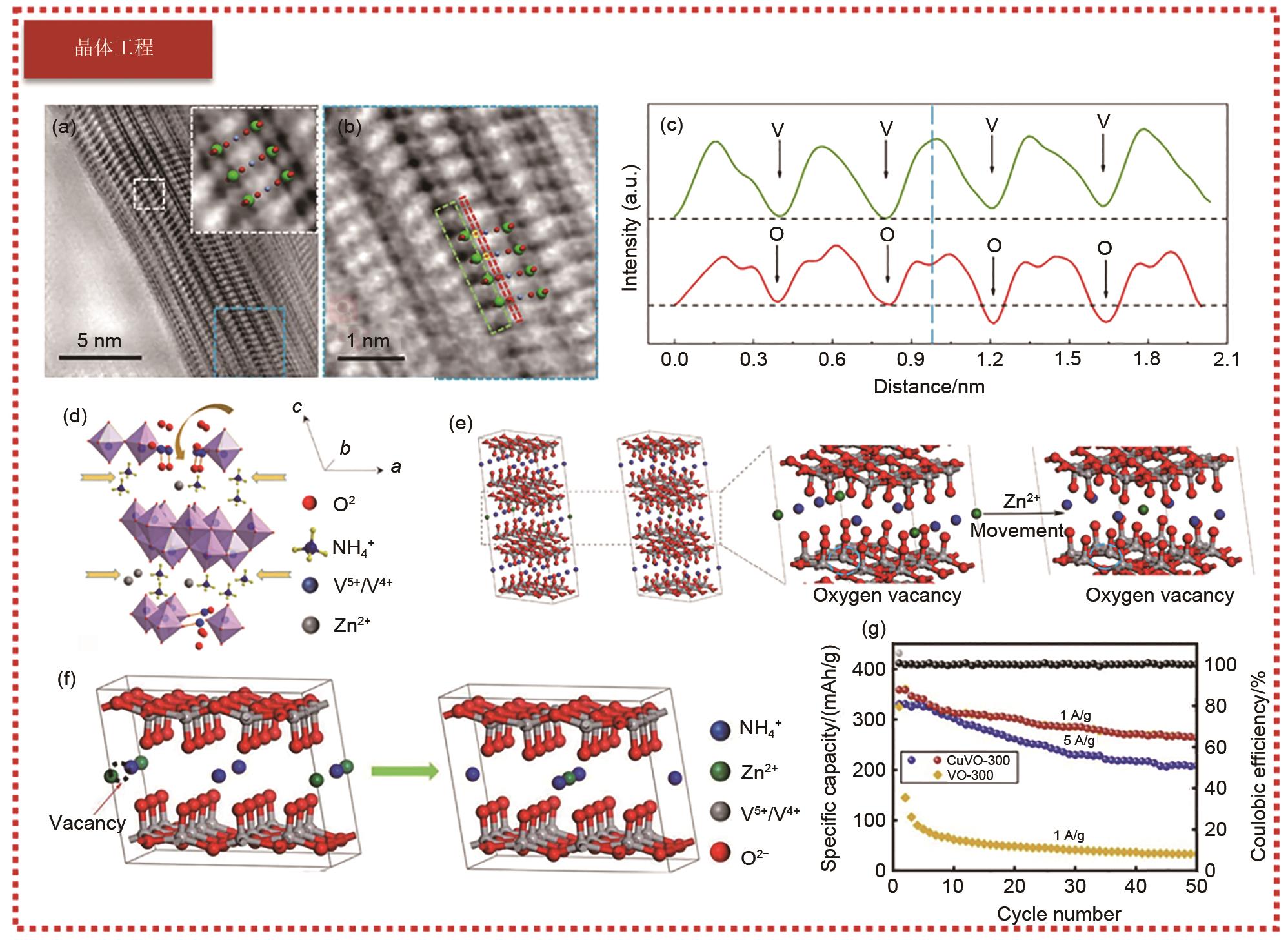
图4
(a) 水和电解质的结构演化示意图和低凝固点溶液的设计。由氢键连接的水网络在0 ℃时很容易转化为冰网络。加入氯化锌后,离子与水之间的强相互作用破坏了氢键网络,而离子的相互作用增强。通过平衡氢键和离子相互作用用于调节凝固点,在临界CZnCl2下的电解质能够在极低的温度下工作;(b) Zn||PANI电池的结构及氧化还原机理;(c) 离子与水之间的相互作用能,以及形成Zn2+ 溶剂化构型的能量;(d) 现有电池的工作温度窗口[11];(e) 4 mol/L Zn(BF4)2 电解质溶液的差示扫描量热法(DSC)曲线;(f) 4 mol/L Zn(BF4)2 电解质溶液随温度变化的电导率曲线;(g)分子动力学(MD)模拟中从快照中获得的不同类型的O—H…F氢键;(h)不同浓度的Zn(BF4)2 电解质溶液在140 ns模拟时间后的平均氢键数;(i) 不同浓度的Zn(BF4)2 电解质溶液中不同氢键的比例[49]"

图5
(a) 阴离子SO42-、NO3-、Cl-、I-、CF3SO3-的负静电势映射;(b)通过DFT计算,得到了SO42--H2O、NO3--H2O、Cl--H2O、I--H2O和CF3SO3--H2O配合物的构型和结合能;(c)采用DFT计算得到了Zn2+-SO42-、 Zn2+-NO3-、Zn2+-Cl-、Zn2+-I-和Zn2+-CF3SO3-配合物的构型和结合能;(d) Zn|2 mol/L Zn(CF3SO3)2|V2O5 电池与报道的低温水系电池的容量比较[51]。在DFT-MD模拟过程中(e) 4 mol/L ZnSO4 和(f) 4 mol/L Zn(TFSI)2 电解质的快照(红色代表氧,灰色代表锌,黄色代表硫,白色代表氢,蓝色代表氮,紫色代表氟);(g)在4 mol/L ZnSO4 、Zn(TFSI)2 和水中,水分子之间的平均氢键数;(h) 在不同的库仑速率(2~30 C)和不同的温度(25~-35 ℃)下放电容量随循环次数的变化曲线[54]"

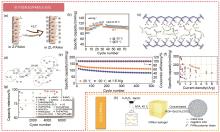
图8
(a) Z-PAAm和ZL-PAAm的界面反应性示意图(Z代表Zn2+,L代表Li+ );(b) Zn||LiFePO4 在-20和25 ℃下的速率性能[70];(c) 海藻酸、EG和水分子之间形成多样的氢键;(d) 海藻酸盐、EG和水分子之间形成不同的氢键相互作用;(e) Zn||MnO2 电池在1.6 A/g、25 ℃和-20 ℃下的循环性能[44]。Zn||[EMIM]PF6-PEDOT:PSS|Bi2S3 电池与其他报道的水溶液ZIBs相比的(f)比容量和(g)循环稳定性[45];(h) 水凝胶电解质的合成路线示意图。电解质通过将丙烯酸钠与过硫酸铵(APS)引发剂聚合,然后浸泡在6 mol/L KOH和0.2 mol/L Zn(CH3COO)2 的混合溶液中合成[75]"
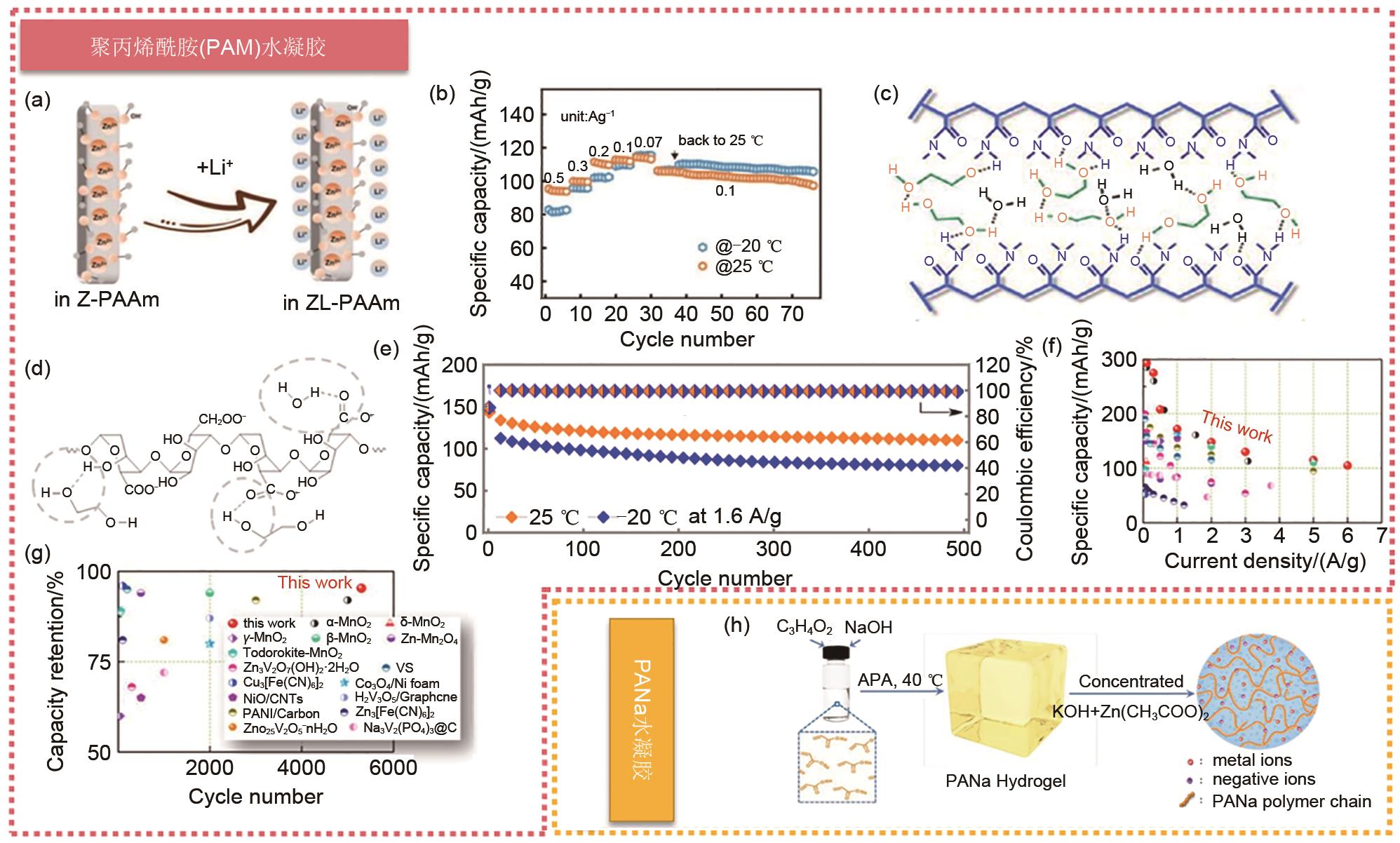

图10
(a) 使用EG和无EG的ZnCF||PANI电池在不同温度下的容量的比较;(b)在-20 ℃的固态光纤形ZnCF||PANI电池在1.0 A/g下的循环性能[87];(c)用未改性电解质和(d) EG&Et2O改性电解质进行500次循环后的锌箔表面的照片和扫描电镜图像;(e) -10 ℃、电流密度为3 A/g时,未加添加剂以及加1%的Et2O和不同含量EG添加剂的电解液的Zn||MnO2 电池的循环特性[88];(f) GG/SA和GG/SA/EG水凝胶电解质的制备示意图;(g) 含GG、GG/SA和GG/SA/EG水凝胶电解质在25、0和-20 ℃下的放电容量[90];(h) CT3G30水凝胶电解质的合成示意图;(i) 冻干的CT3G30的SEM图像。不同温度下,使用CT3G30水凝胶Zn||MnO2 电池与之前报道电池相比较的(j)面积能量密度和(k)体积能量密度图[91]"
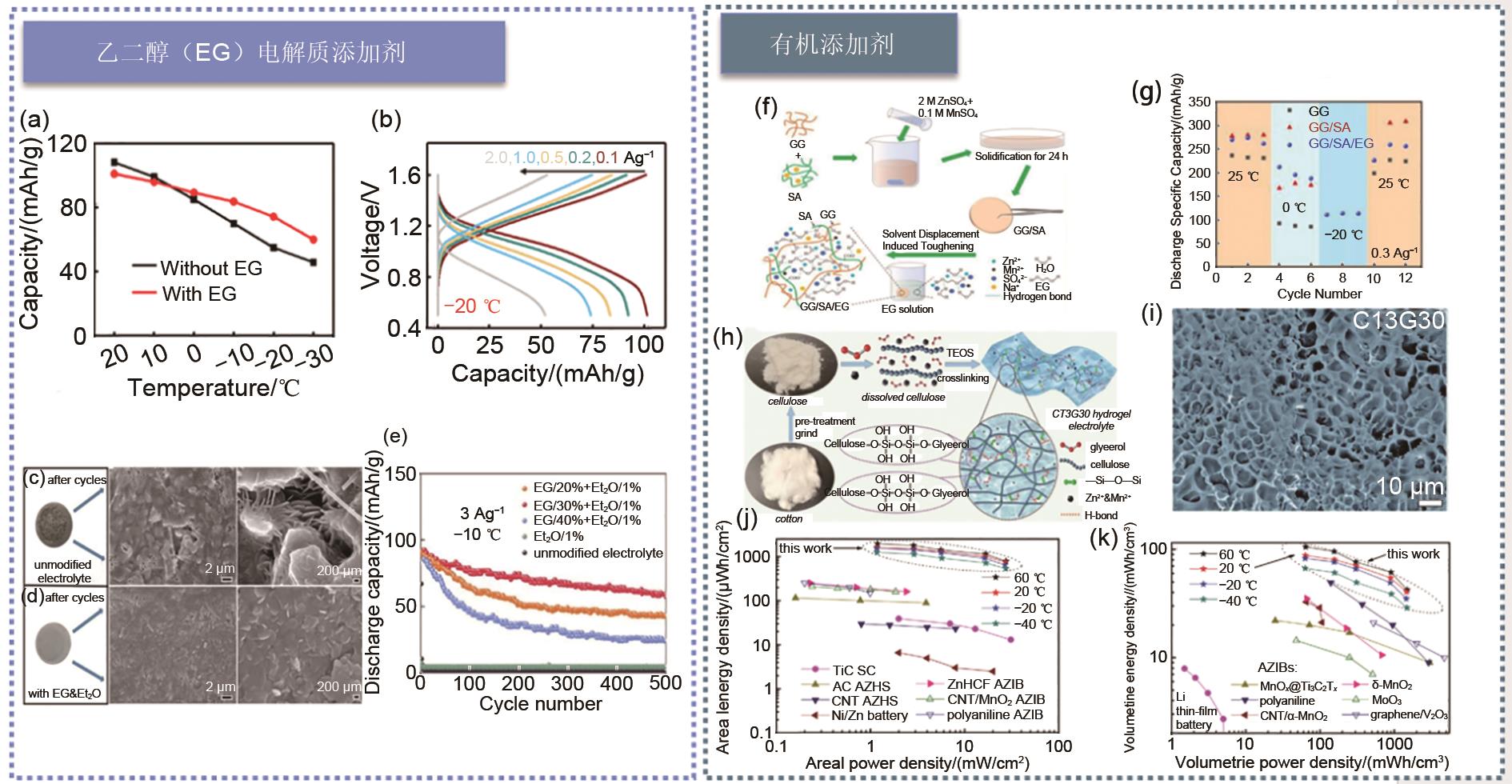
表1
低温锌离子电池物理化学性能以及电化学性能对比表"
| 电解质 | 分类 | 正极材料 | 负极材料 | 离子电导率/[(mS/cm)/℃] | 运行温度范围/℃ | 凝固点/℃ | 容量/[(mAh/g)/(A/g)] | 年份 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 mol/L ZnCl2 | 高浓度 电解质 | 聚苯胺(PANI) | Zn | 1.79/-60 | -90~60 | -114 | -90 ℃:50.6/0.01 | 2020[ |
| 4 mol/L Zn(BF4)2 | 高浓度 电解质 | 四氯苯醌(TCBQ) | Zn | 1.47/-70 | -95~25 | -122 | -95 ℃:63.5/0.022 | 2021[ |
| 2 mol/L Zn(CF3SO3)2 | 高浓度 电解质 | V2O5 | Zn | 4.47/-30 | -30~25 | -34.1 | -30 ℃:194.1/1 | 2021[ |
| 4 mol/L Zn(TFSI)2 | 高浓度 电解质 | 聚(邻苯二酚)氧化还原共聚物 | Zn | 90/25 | -35~ 25 | -38 | -35 ℃:178/2C | 2021[ |
| ZnOTf2-DMF | 有机电解质 | 菲醌大环三聚体(PQ-MCT) | Zn | 18.9/25 | -70~150 | -70.8 | -70 ℃:31.3/0.2 | 2020[ |
| PVA/G | 凝胶电解质 | δ-MgVO | Zn | 10.7/-30 | -30~60 | -30 | -30 ℃:136.7/5 | 2020[ |
| PVA-B-G | 凝胶电解质 | MnO2 | Zn | 10.1/-30 | -35~25 | -60 | -35 ℃:133.8/0.5 | 2020[ |
| 21 mol/L LiTFSI+3 mol/L ZnOTf2+PVA | 高浓度凝胶电解质 | V2O5/GO | Zn | 2.1/20 | 0~40 | — | 0 ℃:325/0.02 | 2020[ |
| 2 mol/L ZnSO4+4 mol/L LiCl+PAM | 高浓度凝胶电解质 | LiFePO4 | Zn | — | -20~25 | -45 | -20 ℃:104/0.1 | 2019[ |
| 海藻酸锌/PAM | 水凝胶电解质 | MnO2 | Zn | 14.1/-20 | -20~80 | -30~-20 | -20 ℃:165/0.2 | 2019[ |
1 mol/L Zn(TFSI)2+ 21 mol/L LiTFSI +PAM | 高浓度凝胶电解质 | [EMIM]PF6-PEDOT:PSS/Bi2S3 | Zn | — | — | — | 0 ℃:73/1 | 2019[ |
| 6 mol/L OH-/ PANa | 高浓度凝胶电解质 | NiCo | Zn | 5.7/-20 | -20~50 | — | -20 ℃:172/1.9C | 2018[ |
| PAMPS-K/ MC | 双网络水凝胶电解质 | 空气 | Zn | 18.1/-20 | -20~25 | -30 | -20 ℃:754.2/824.6 mWh/g | 2020[ |
| EG-waPUA+PAM | 双交联水凝胶电解质 | α-MnO2/CNT | Zn | 14.6/-20 | -20~20 | -24 | -20 ℃:196/0.3 | 2019[ |
| EG+PVA | 电解质添加剂 | PANI | Zn | 2.89/-30 | -30~20 | — | -20 ℃:101.2/0.1 | 2021[ |
| Et2O+EG+2 mol/L ZnSO4+0.2 mol/L MnSO4 | 电解质添加剂 | MnO2 | Zn | 0.42/-10 | -10~25 | — | -10 ℃:65.1/3 | 2020[ |
| 2 mol/L ZnSO4 +0.1 mol/L MnSO4 +GG/SA/EG | 电解质添加剂 | MnO2 | Zn | 6.19/-20 | -20~25 | — | -20 ℃:181.5/0.1 | 2020[ |
| 2 mol/L ZnSO4/0.2 mol/L MnSO4/甘油 /纤维素/ TEOS (CT3G30) | 电解质添加剂 | rGO/MnO2 | Zn | 19.4/-40 | -40~60 | -64.6 | -20 ℃:181.5/0.1 | 2021[ |
| ZnSO4:CH3COONH4 | 电解质添加剂 | Zn | Zn | — | -10~25 | — | — | 2022[ |
| 0.05 mol/L SnCl2-7.5 mol/L ZnCl2 | 共晶电解质 | VOPO4 | Zn | 0.8/-70 | -70~ 20 | — | -70 ℃:48.7/— | 2021[ |
| 1 | 陈海生, 李泓, 马文涛, 等. 2021年中国储能技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(3): 1052-1076. |
| CHEN H S, LI H, MA W T, et al. Research progress of energy storage technology in China in 2021[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 1052-1076. | |
| 2 | 张强, 李泓. 乘势而上, 奋发有为 努力推动化工与储能高质量发展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1682. |
| ZHANG Q, LI H. Riding on the trend and striving to be promising_Strive to promote the high-quality development of chemical industry and energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1682. | |
| 3 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 4 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. |
| 5 | LUO F, FENG X, ZENG L, et al. In situ simultaneous encapsulation of defective MoS2 nanolayers and sulfur nanodots into SPAN fibers for high rate sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126430. |
| 6 | SUN Y, GUO S H, ZHOU H S. Exploration of advanced electrode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(23): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201800212. |
| 7 | XU Q, SUN J K, LI J Y, et al. Scalable synthesis of spherical Si/C granules with 3D conducting networks as ultrahigh loading anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 12: 54-60. |
| 8 | ZENG L X, FANG Y X, XU L H, et al. Rational design of few-layer MoSe2 confined within ZnSe-C hollow porous spheres for high-performance lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(14): 6766-6775. |
| 9 | LIU Z X, LUO X, QIN L, et al. Progress and prospect of low-temperature zinc metal batteries[J]. Advanced Powder Materials, 2022, 1(2): doi: 10.1016/j.apmate.2021.10.002. |
| 10 | TAMTÖGL A, BAHN E, SACCHI M, et al. Motion of water monomers reveals a kinetic barrier to ice nucleation on graphene[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3120. |
| 11 | ZHANG Q, MA Y L, LU Y, et al. Modulating electrolyte structure for ultralow temperature aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4463. |
| 12 | MATSUMOTO M, SAITO S, OHMINE I. Molecular dynamics simulation of the ice nucleation and growth process leading to water freezing[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6879): 409-413. |
| 13 | DENG T, ZHANG W, ZHANG H B, et al. Anti-freezing aqueous electrolyte for high-performance co(OH)2 supercapacitors at -30 ℃[J]. Energy Technology, 2018, 6(4): 605-612. |
| 14 | ZHENG J X, BOCK D C, TANG T, et al. Regulating electrodeposition morphology in high-capacity aluminium and zinc battery anodes using interfacial metal-substrate bonding[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6(4): 398-406. |
| 15 | HAO J N, LI X L, ZENG X H, et al. Deeply understanding the Zn anode behaviour and corresponding improvement strategies in different aqueous Zn-based batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(11): 3917-3949. |
| 16 | ZHENG J X, YIN J F, ZHANG D H, et al. Spontaneous and field-induced crystallographic reorientation of metal electrodeposits at battery anodes[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(25): eabb1122. |
| 17 | SU J R, YIN X X, ZHAO H N, et al. Temperature-dependent nucleation and electrochemical performance of Zn metal anodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(4): 1549-1556. |
| 18 | LI F Y, HU X L. Zinc metal energy storage devices under extreme conditions of low temperatures[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2021, 4(3): 389-406. |
| 19 | NIAN Q S, SUN T, LIU S, et al. Issues and opportunities on low-temperature aqueous batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 423: do: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130253. |
| 20 | RAMANUJAPURAM A, YUSHIN G. Understanding the exceptional performance of lithium-ion battery cathodes in aqueous electrolytes at subzero temperatures[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(35): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201802624. |
| 21 | XU L H, CHEN X C, GUO W T, et al. Co-construction of sulfur vacancies and carbon confinement in V5S8/CNFs to induce an ultra-stable performance for half/full sodium-ion and potassium-ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(9): 5033-5044. |
| 22 | XU L, GUO W, ZENG L, et al. V3Se4 embedded within N/P co-doped carbon fibers for sodium/potassium ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 419: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129607. |
| 23 | WANG Y Y, CHEN X, CHEN X C, et al. Stabilizing intermediate phases via the efficient confinement effects of the SnS2-SPAN fibre composite for ultra-stable half/full sodium/potassium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(21): 11449-11457. |
| 24 | WANG Y, LIU J, CHEN X, et al. Structural engineering of tin sulfides anchored on nitrogen/phosphorus dual-doped carbon nanofibres in sodium/potassium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2022, 189: 46-56. |
| 25 | GUO Z W, HUANG J H, DONG X L, et al. An organic/inorganic electrode-based hydronium-ion battery[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 959. |
| 26 | RUFFO R, LA MANTIA F, WESSELLS C, et al. Electrochemical characterization of LiCoO2 as rechargeable electrode in aqueous LiNO3 electrolyte[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2011, 192(1): 289-292. |
| 27 | ZHANG Y, XU J, LI Z, et al. All-climate aqueous Na-ion batteries using "water-in-salt" electrolyte[J]. Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(2): 161-170. |
| 28 | LIU S L, ZHANG R Z, MAO J F, et al. From room temperature to harsh temperature applications: Fundamentals and perspectives on electrolytes in zinc metal batteries[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(12): doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn5097. |
| 29 | WU X Y, QIU S, XU Y K, et al. Hydrous nickel-iron turnbull's blue as a high-rate and low-temperature proton electrode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(8): 9201-9208. |
| 30 | YAN L, HUANG J H, GUO Z W, et al. Solid-state proton battery operated at ultralow temperature[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(2): 685-691. |
| 31 | WEI T T, PENG Y Q, MO L E, et al. Modulated bonding interaction in propanediol electrolytes toward stable aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Science China Materials, 2022, 65(5): 1156-1164. |
| 32 | CHEN S, ZHANG Y, GENG H, et al. Zinc ions pillared vanadate cathodes by chemical pre-intercalation towards long cycling life and low-temperature zinc ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 441: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227192. |
| 33 | YANG Y Q, TANG Y, FANG G Z, et al. Li+ intercalated V2O5 · nH2O with enlarged layer spacing and fast ion diffusion as an aqueous zinc-ion battery cathode[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(11): 3157-3162. |
| 34 | MO F N, LIANG G J, MENG Q Q, et al. A flexible rechargeable aqueous zinc manganese-dioxide battery working at -20 ℃[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(2): 706-715. |
| 35 | HE T, YE YS, LI H, et al. Oxygen-deficient ammonium vanadate for flexible aqueous zinc batteries with high energy density and rate capability at -30 ℃[J]. Materials Today, 2021, 43: 53-61. |
| 36 | HE T. Cation-deficient Zn0.3(NH4)0.3V4O101·0.91H2O for rechargeable aqueous zinc battery with superior low- temperature performance[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 38: 389-396. |
| 37 | YANG Y, TANG Y, LIANG S, et al.Transition metal ion-preintercalated V2O5 as high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery cathode with broad temperature adaptability[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 61: 617-625. |
| 38 | CHUAI M, YANG J, WANG M, et al. High-performance Zn battery with transition metal ions co-regulated electrolytic MnO2[J]. eScience, 2021, 1(2): 178-185. |
| 39 | 熊小琳, 岳金明, 周安行, 等. 尖晶石锰酸锂正极在Water-in-salt电解液中的电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 375-384. |
| XIONG X L, YUE J M, ZHOU A X, et al. Electrochemical performance of spinel LiMn2O4 in water-in-salt aqueous electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 375-384. | |
| 40 | ZHENG S B, SHI D J, YAN D, et al. Orthoquinone-based covalent organic frameworks with ordered channel structures for ultrahigh performance aqueous zinc-organic batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(12): doi: 10.1002/anie. 202117511. |
| 41 | LIANG Y L, JING Y, GHEYTANI S, et al. Universal quinone electrodes for long cycle life aqueous rechargeable batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(8): 841-848. |
| 42 | MA L T, LI N, LONG C B, et al. Achieving both high voltage and high capacity in aqueous zinc-ion battery for record high energy density[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(46): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201906142. |
| 43 | ZHANG H, LIU X, LI H H, et al. High-voltage operation of a V2O5 cathode in a concentrated gel polymer electrolyte for high-energy aqueous zinc batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(13): 15305-15312. |
| 44 | MO F N, LIANG G J, WANG D H, et al. Biomimetic organohydrogel electrolytes for high-environmental adaptive energy storage devices[J]. EcoMat, 2019, 1(1): e12008. |
| 45 | ZHAO Y W, MA L T, ZHU Y B, et al. Inhibiting grain pulverization and sulfur dissolution of bismuth sulfide by ionic liquid enhanced poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly(styrenesulfonate) for high-performance zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(6): 7270-7280. |
| 46 | LUKATSKAYA M R, FELDBLYUM J I, MACKANIC D G, et al. Concentrated mixed cation acetate "water-in-salt" solutions as green and low-cost high voltage electrolytes for aqueous batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(10): 2876-2883. |
| 47 | HU P, YAN M Y, ZHU T, et al. Zn/V2O5 aqueous hybrid-ion battery with high voltage platform and long cycle life[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(49): 42717-42722. |
| 48 | HUANG Y, LI Z, PEI Z X, et al. Solid-state rechargeable Zn||NiCo and Zn-air batteries with ultralong lifetime and high capacity: The role of a sodium polyacrylate hydrogel electrolyte[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(31): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201802288. |
| 49 | SUN T J, YUAN X M, WANG K, et al. An ultralow-temperature aqueous zinc-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(11): 7042-7047. |
| 50 | ZHANG Y J, CREMER P S. Interactions between macromolecules and ions: The hofmeister series[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2006, 10(6): 658-663. |
| 51 | ZHANG Q, XIA K X, MA Y L, et al. Chaotropic anion and fast-kinetics cathode enabling low-temperature aqueous Zn batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(8): 2704-2712. |
| 52 | GUAN C, HU F, YU X, et al. High performance of HNaV6O16 ·4H2O nanobelts for aqueous zinc-ion batteries with in situ phase transformation by Zn(CF3SO3)2 electrolyte[J]. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(2): 448-456. |
| 53 | ZHANG N, CHENG F Y, LIU Y C, et al. Cation-deficient spinel ZnMn2O4 cathode in Zn(CF3SO3)2 electrolyte for rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion battery[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(39): 12894-12901. |
| 54 | PATIL N, DE LA CRUZ C, CIURDUC D, et al. An ultrahigh performance zinc-organic battery using poly(catechol) cathode in Zn(TFSI)2-based concentrated aqueous electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(26): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202100939. |
| 55 | ZHANG Y, ZHAO L, LIANG Y, et al. Effect of electrolyte anions on the cycle life of a polymer electrode in aqueous batteries[J]. eScience, 2022, 2(1): 110-115. |
| 56 | BANIK S J, AKOLKAR R. Suppressing dendrite growth during zinc electrodeposition by PEG-200 additive[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(11): D519-D523. |
| 57 | ZHAO Z M, ZHAO J W, HU Z L, et al. Long-life and deeply rechargeable aqueous Zn anodes enabled by a multifunctional brightener-inspired interphase[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(6): 1938-1949. |
| 58 | MORÓN L E. Electrodeposition and corrosion behavior of Zn coatings formed using as brighteners arene additives of different structure[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 205(21/22): 4985-4992. |
| 59 | WANG N, DONG X L, WANG B L, et al. Zinc-organic battery with a wide operation-temperature window from -70 to 150 ℃[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(34): 14577-14583. |
| 60 | RODRIGUES M T F, BABU G, GULLAPALLI H, et al. A materials perspective on Li-ion batteries at extreme temperatures[J]. Nature Energy, 2017, 2: 17108. |
| 61 | YUE F, TIE Z W, DENG S Z, et al. An ultralow temperature aqueous battery with proton chemistry[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(25): 13882-13886. |
| 62 | JIANG H, SHIN W, MA L, et al. A high-rate aqueous proton battery delivering power below -78 ℃ via an unfrozen phosphoric acid[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(28): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202000968. |
| 63 | HUANG S, WAN F, BI S S, et al. A self-healing integrated all-in-one zinc-ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(13): 4313-4317. |
| 64 | LIU Z, WANG D, TANG Z, et al. A mechanically durable and device-level tough Zn-MnO2 battery with high flexibility[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 23: 636-645. |
| 65 | LI C, LI P, YANG S, et al. Recently advances in flexible zinc ion batteries[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(10): doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/10/101603. |
| 66 | LIANG G J, WANG Y L, HUANG Z D, et al. Initiating hexagonal MoO3 for superb-stable and fast NH4 + storage based on hydrogen bond chemistry[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(14): doi: 10.1002/adma.201907802. |
| 67 | PEI Z X, YUAN Z W, WANG C J, et al. A flexible rechargeable zinc-air battery with excellent low-temperature adaptability[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(12): 4793-4799. |
| 68 | ZHOU W J, CHEN J Z, CHEN M F, et al. An environmentally adaptive quasi-solid-state zinc-ion battery based on magnesium vanadate hydrate with commercial-level mass loading and anti-freezing gel electrolyte[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(17): 8397-8409. |
| 69 | CHEN M F, ZHOU W J, WANG A R, et al. Anti-freezing flexible aqueous Zn-MnO2 batteries working at -35 ℃ enabled by a borax-crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol/glycerol gel electrolyte[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(14): 6828-6841. |
| 70 | ZHU M S, WANG X J, TANG H M, et al. Antifreezing hydrogel with high zinc reversibility for flexible and durable aqueous batteries by cooperative hydrated cations[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(6): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201907218. |
| 71 | LIAO H, GUO X L, WAN P B, et al. Conductive MXene nanocomposite organohydrogel for flexible, healable, low-temperature tolerant strain sensors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(39): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201904507. |
| 72 | ZHANG S, ZHANG Y H, LI B, et al. One-Step preparation of a highly stretchable, conductive, and transparent poly(vinyl alcohol)-phytic acid hydrogel for casual writing circuits[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(35): 32441-32448. |
| 73 | FANG L Y, CAI Z F, DING Z Q, et al. Skin-inspired surface-microstructured tough hydrogel electrolytes for stretchable supercapacitors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(24): 21895-21903. |
| 74 | ZHOU D, CHEN F, HANDSCHUH-WANG S, et al. Biomimetic extreme-temperature- and environment-adaptable hydrogels[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2019, 20(17): 2139-2154. |
| 75 | WANG H, LIU J, WANG J Q, et al. Concentrated hydrogel electrolyte-enabled aqueous rechargeable NiCo// Zn battery working from -20 to 50 ℃[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(1): 49-55. |
| 76 | APPEL E A, DEL BARRIO J, LOH X J, et al. Supramolecular polymeric hydrogels[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41: 6195-6214. |
| 77 | DENG Y, HUANG M, SUN D, et al. Dual physically cross-linked κ-carrageenan-based double network hydrogels with superior self-healing performance for biomedical application[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(43): 37544-37554. |
| 78 | GONG J P, KATSUYAMA Y, KUROKAWA T, et al. Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength[J]. Advanced Materials, 2003, 15(14): 1155-1158. |
| 79 | SUN N, LU F, YU Y, et al. Alkaline double-network hydrogels with high conductivities, superior mechanical performances, and antifreezing properties for solid-state zinc-air batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(10): 11778-11788. |
| 80 | NIAN Q S, WANG J Y, LIU S, et al. Aqueous batteries operated at -50 ℃[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2019, 131(47): 17150-17155. |
| 81 | LIU S, LI G R, GAO X P. Lanthanum nitrate as electrolyte additive to stabilize the surface morphology of lithium anode for lithium-sulfur battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(12): 7783-7789. |
| 82 | ZHENG J M, ENGELHARD M H, MEI D H, et al. Electrolyte additive enabled fast charging and stable cycling lithium metal batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2017, 2: 17012. |
| 83 | WANG R, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Electrochemical analysis graphite/electrolyte interface in lithium-ion batteries: P-Toluenesulfonyl isocyanate as electrolyte additive[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 34: 131-140. |
| 84 | SUN P, MA L, ZHOU W H, et al. Simultaneous regulation on solvation shell and electrode interface for dendrite-free Zn ion batteries achieved by a low-cost glucose additive[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(33): 18247-18255. |
| 85 | CAO L S, LI D, HU E Y, et al. Solvation structure design for aqueous Zn metal batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(51): 21404-21409. |
| 86 | CHANG N N, LI T Y, LI R, et al. An aqueous hybrid electrolyte for low-temperature zinc-based energy storage devices[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(10): 3527-3535. |
| 87 | CONG Z F, GUO W B, ZHANG P P, et al. Wearable antifreezing fiber-shaped Zn|PANI batteries with suppressed Zn dendrites and operation in sweat electrolytes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(15): 17608-17617. |
| 88 | WANG A, ZHOU W, HUANG A, et al. Developing improved electrolytes for aqueous zinc-ion batteries to achieve excellent cyclability and antifreezing ability[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 586: 362-370. |
| 89 | DING Y Y, ZHONG X, YUAN C M, et al. Sodium alginate binders for bivalency aqueous batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(17): 20681-20688. |
| 90 | WANG J, HUANG Y, LIU B, et al. Flexible and anti-freezing zinc-ion batteries using a guar-gum/sodium-alginate/ethylene-glycol hydrogel electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 599-605. |
| 91 | CHEN M F, CHEN J Z, ZHOU W J, et al. Realizing an all-round hydrogel electrolyte toward environmentally adaptive dendrite-free aqueous Zn-MnO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(9): doi: 10.1002/adma.202007559. |
| 92 | HUANG C, ZHAO X, HAO Y S, et al. Highly reversible zinc metal anodes enabled by protonated melamine[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(12): 6636-6640. |
| 93 | ZENG X H, MAO J F, HAO J N, et al. Electrolyte design for in situ construction of highly Zn2+-conductive solid electrolyte interphase to enable high-performance aqueous Zn-ion batteries under practical conditions[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(11): doi: 10.1002/adma.202007416. |
| 94 | YANG Q, LI L, HUSSAIN T, et al. Stabilizing interface pH by N-modified graphdiyne for dendrite-free and high-rate aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(6): doi: 10.1002/anie.202112304. |
| 95 | HAN D L, WANG Z X, LU H T, et al. A self-regulated interface toward highly reversible aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(9): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202102982. |
| 96 | LIN C Y, YANG X H, XIONG P X, et al. High-rate, large capacity, and long life dendrite-free Zn metal anode enabled by trifunctional electrolyte additive with a wide temperature range[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(21): doi: 10.1002/advs.202201433. |
| 97 | CAO L S, LI D, DENG T, et al. Hydrophobic organic-electrolyte-protected zinc anodes for aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(43): 19292-19296. |
| 98 | YANG H J, QIAO Y, CHANG Z, et al. Reducing water activity by zeolite molecular sieve membrane for long-life rechargeable zinc battery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(38): doi: 10.1002/adma. 202102415. |
| 99 | XIE X S, LIANG S Q, GAO J W, et al. Manipulating the ion-transfer kinetics and interface stability for high-performance zinc metal anodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(2): 503-510. |
| 100 | ZENG Y X, ZHANG X Y, MENG Y, et al. Achieving ultrahigh energy density and long durability in a flexible rechargeable quasi-solid-state Zn-MnO2 battery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(26): doi: 10.1002/adma.201700274. |
| 101 | AH-LUNG G, FLAMME B, GHAMOUSS F, et al. Guidelines for designing highly concentrated electrolytes for low temperature applications[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2020, 56(68): 9830-9833. |
| 102 | CAO L S, LI D, SOTO F A, et al. Highly reversible aqueous zinc batteries enabled by zincophilic-zincophobic interfacial layers and interrupted hydrogen-bond electrolytes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(34): 18845-18851. |
| 103 | WANG D D, LV D, PENG H L, et al. Site-selective adsorption on ZnF2/Ag coated Zn for advanced aqueous zinc-metal batteries at low temperature[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(4): 1750-1758. |
| 104 | SONG C L, GONG Z S, BAI C, et al. High performance Zn-I2 battery with acetonitrile electrolyte working at low temperature[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(4): 3170-3177. |
| 105 | MA Z, CHEN J, VATAMANU J, et al. Expanding the low-temperature and high-voltage limits of aqueous lithium-ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 45: 903-910. |
| [1] | 裴英伟, 张红, 王星辉. 可充电锌离子电池电解质的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2075-2082. |
| [2] | 王心怡, 李维杰, 韩朝, 刘化鹍, 窦世学. 水系锌离子电池金属负极的挑战与优化策略[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(4): 1211-1225. |
| [3] | 吴渺, 赵贵青, 仇中柱, 王保峰. 一种新型水系锌离子电池正极材料NiCo2O4 的制备和电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(3): 1019-1025. |
| [4] | 张冬冬, 文华, 欧阳宏伟. 基于电化学-热耦合模型的电池低温脉冲加热[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(12): 3957-3964. |
| [5] | 衡永丽, 谷振一, 郭晋芝, 吴兴隆. Na3V2(PO4)3@C用作水系锌离子电池正极材料的研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(3): 938-944. |
| [6] | 高蕾, 孟玉凤, 颜琪斌, 杨慧. 铜箔对动力锂离子电池性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(S1): 1-6. |
| [7] | 徐志彬, 吴国强, 黄伟国, 陈理, 张雄, 周志学, 刘孝伟. 正交实验设计法优化铅炭负极配方[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(S1): 85-89. |
| [8] | 王绥军, 傅凯, 官亦标, 刘曙光, 徐彬, 范茂松. 软包磷酸铁锂电池低温热安全性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5(2): 204-209. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
