Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2021, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (6): 2156-2168.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0115
• New Energy Storage Technologies • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dajin LIU1,2( ), Qiang WU1,2, Renjie HE1,2, Chuang YU1, Jia XIE1(
), Qiang WU1,2, Renjie HE1,2, Chuang YU1, Jia XIE1( ), Shijie CHENG1
), Shijie CHENG1
Received:2021-03-19
Revised:2021-04-13
Online:2021-11-05
Published:2021-11-03
CLC Number:
Dajin LIU, Qiang WU, Renjie HE, Chuang YU, Jia XIE, Shijie CHENG. Research progress of biopolymers in Si anodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2156-2168.
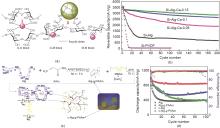
Fig. 1
(a) Schematic representation of coordinate bonds between alginate chains and calcium cations (region Ⅰ) and strong hydrogen bonding between hydroxylated Si surface and free alginate carboxylic groups (region Ⅱ); (b) Cycling performance of anodes prepared with different binders[37]; (c) Synthesis of Alg-g-PAAm and c-Alg-g-PAAm; (d) Cycling performance of Si/C anode with different binders[38]"
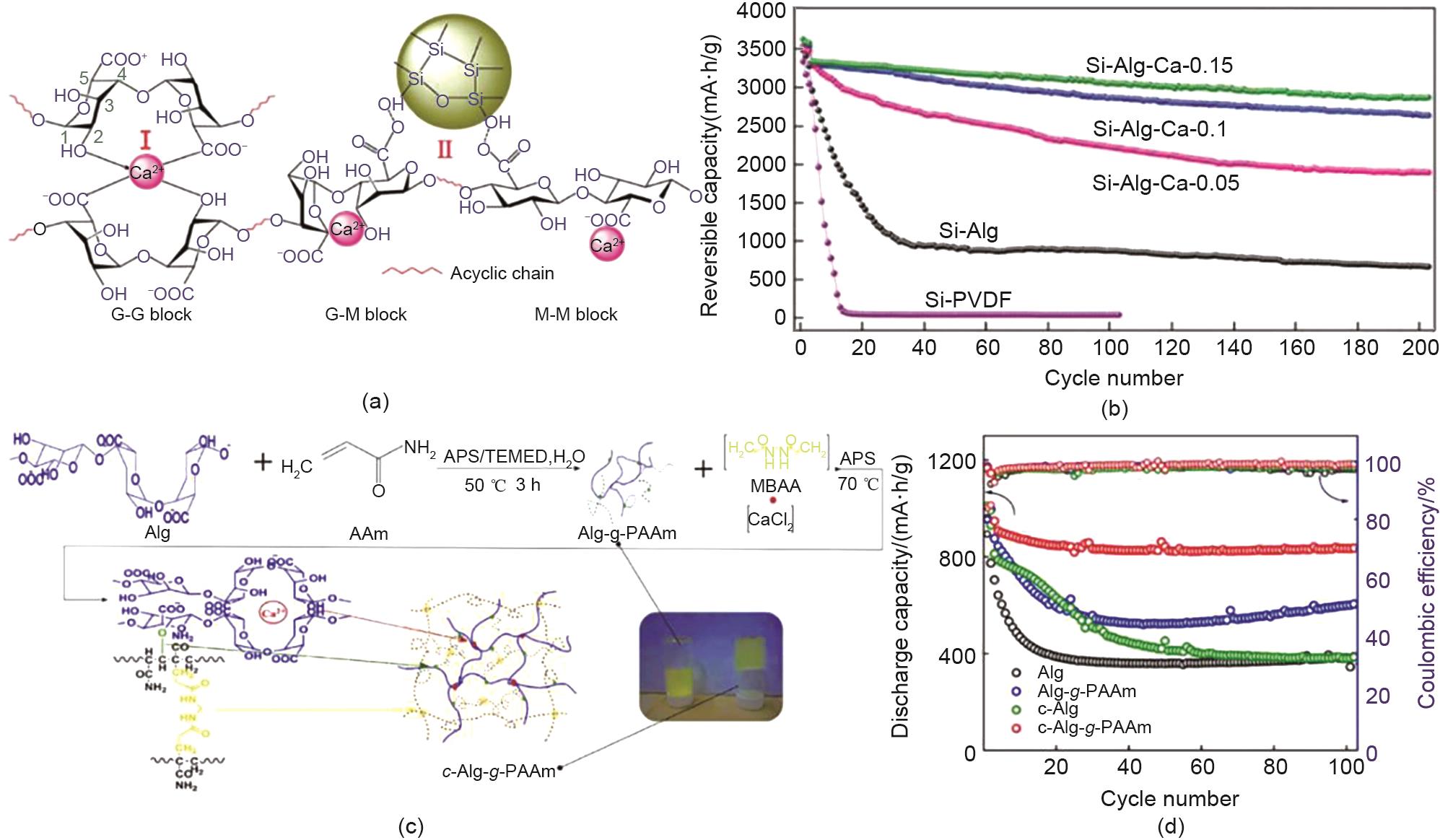
Table 1
Summary of Si anode binders based on biopolymers"
| 生物高分子黏结剂 | 循环圈数 | 容量保持/(mA·h/g) | 极片中黏结剂含量/% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS-g-PANI-0.5 | 200 (1 C) | 1091 | 20 | [ |
| ppSA-ppCMC | 150 (0.5 A/g) | 1863 | 10 | [ |
| guar gum | 300 (2.1 A/g) | 1561 | 15 | [ |
| Alg-Ca-0.15 | 200 (0.42 A/g) | 2837.5 | 15 | [ |
| c-Alg-g-PAAm | 100 (1 C) | 836 | 15 | [ |
| SA-250 | 150 (1.39 A/g) | 934 | 10 | [ |
| CE55 | 1600 (8 A/g) | 1350 | 15 | [ |
| CS-CG10%+6%GA | 100 | 2144 | 20 | [ |
| AP | 100 (0.1 C) | 1517.9 | 20 | [ |
| SSC4SA | 100 (1 A/g) | 2874 | 20 | [ |
| starch/PEG | 300 (0.5 A/g) | ~1100 | 20 | [ |
| cross-linked corn starch | 200 (0.5 C) | 2106 | 20 | [ |
| c-XG-PAM | 1000 (2 A/g) | 1104 | 10 | [ |
| PEC/PAA (10) | 100 (0.2 C) | 2386 | 20 | [ |
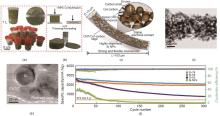
Fig. 4
(a) Digital photographs of of a Si@CNT/cellulose mixed solution; (b) Synthetic illustration of press/annealing procedure of free-standing Si@CNT/C electrode; (c) Structural illustration of one Si@CNT/C microscroll; (d, e) TEM images of Si@CNT/C; (f) Cyclability of Si@CNT/C electrode (Si-74, 85, and 92) at 0.2 A/g[30]"
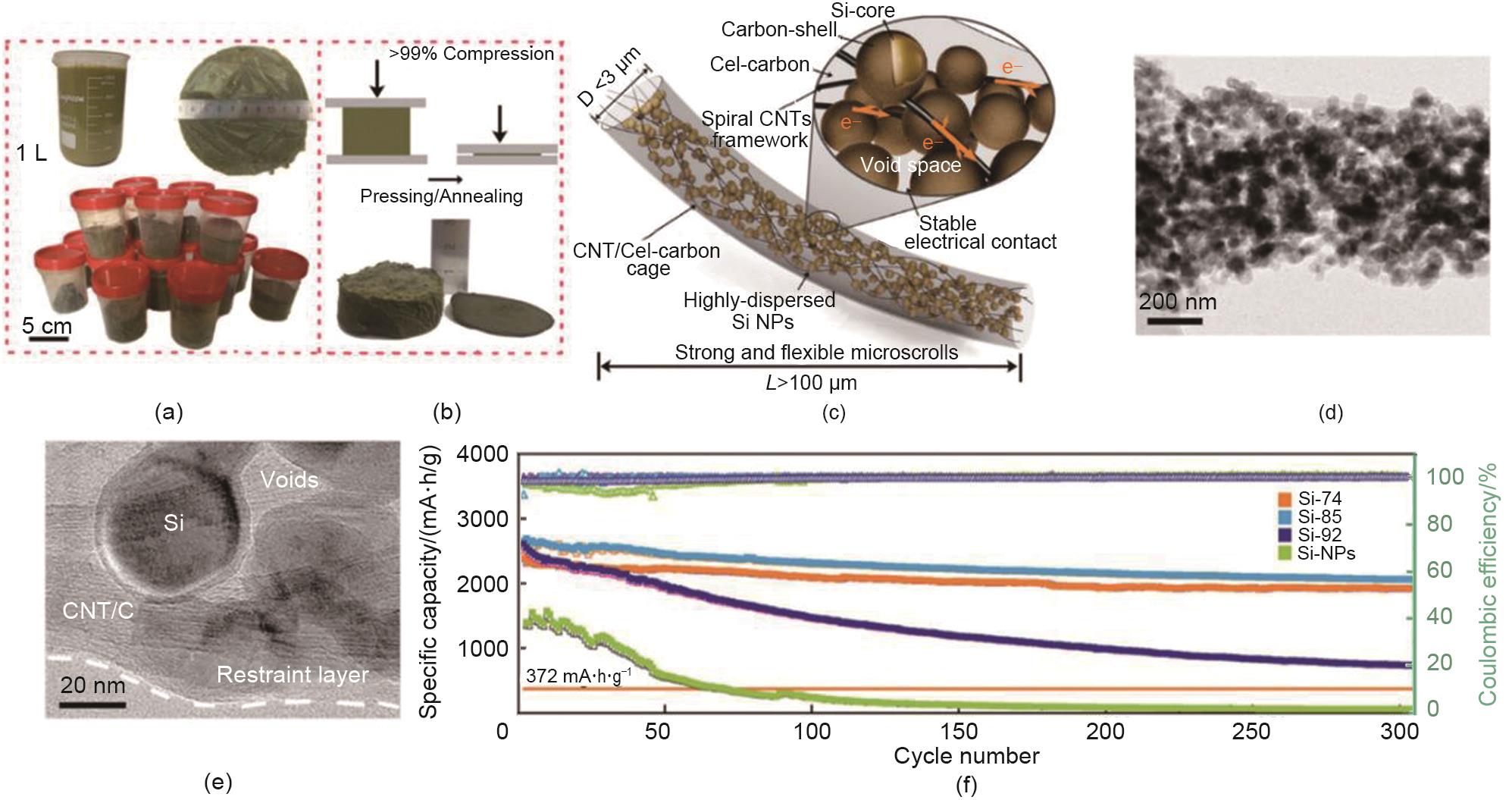
Table 2
Summary of Si/C composites prepared using biopolymers as carbon source"
| 生物高分子制备的硅碳复合材料 | 循环圈数 | 容量保持/(mA·h/g) | 硅含量/% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si-85 | 300 (0.2 A/g) | 2056 | 84.5 | [ |
| PG/Si/Ni | 2000 (1 A/g) | 604.3 | 37.4 | [ |
| Si/HC | 100 (0.2 C) | ~490 | ~15 | [ |
| Si@SiO2@C | 200 (0.42 A/g) | 1071 | ~76 | [ |
| PSC-30% Si-C | 100 (0.2 A/g) | 850 | 30.0 | [ |
| SN-MCB | 500 (0.2 C) | 1440 | 44.0 | [ |
| GCSi | 100 (0.2 A/g) | 676 | 25.0 | [ |
| rGO/C@Si | 150 (0.42 A/g) | 1115.8 | 72.7 | [ |
| Si@CTSC | 300 (1 A/g) | 1324 | 83.2 | [ |
| Porous Si/C | 200 (0.5 C) | 782.1 | 65.0 | [ |
| Si@C-AL-azo-NO2 | 150 (0.2 A/g) | 882 | 65 | [ |
| Si/C composite | 200 (0.2 A/g) | 584.1 | ~30 | [ |
| 1 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 2 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. |
| 3 | THACKERAY M M, WOLVERTON C, ISAACS E D. Electrical energy storage for transportation—Approaching the limits of, and going beyond, lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(7): 7854-7863. |
| 4 | CHOI J W, AURBACH D. Promise and reality of post-lithium-ion batteries with high energy densities[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1(4): 1-16. |
| 5 | JIANG Z P, JIN L, HAN Z L, et al. Facile generation of polymer-alloy hybrid layers for dendrite-free lithium-metal anodes with improved moisture stability[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(33): 11374-11378. |
| 6 | JIN Y, ZHU B, LU Z D, et al. Challenges and recent progress in the development of Si anodes for lithium-ion battery[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(23): 1700715. |
| 7 | CHAE S, KO M, KIM K, et al. Confronting issues of the practical implementation of Si anode in high-energy lithium-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2017, 1(1): 47-60. |
| 8 | JIAO X X, YIN J Q, XU X Y, et al. Highly energy-dissipative, fast self-healing binder for stable Si anode in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(3): 2005699. |
| 9 | CHEN Z, ZHANG H R, DONG T T, et al. Uncovering the chemistry of cross-linked polymer binders via chemical bonds for silicon-based electrodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(42): 47164-47180. |
| 10 | CHEN J, FAN X L, LI Q, et al. Electrolyte design for LiF-rich solid-electrolyte interfaces to enable high-performance microsized alloy anodes for batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2020, 5(5): 386-397. |
| 11 | 周军华, 罗飞, 褚赓, 等. 锂离子电池纳米硅碳负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 569-582. |
| ZHOU J H, LUO F, CHU G, et al. Research progress on nano silicon-carbon anode materials for lithium ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 569-582. | |
| 12 | XU Q, LI J Y, SUN J K, et al. Watermelon-inspired Si/C microspheres with hierarchical buffer structures for densely compacted lithium-ion battery anodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(3): 1601481. |
| 13 | JIN Y, LI S, KUSHIMA A, et al. Self-healing SEI enables full-cell cycling of a silicon-majority anode with a coulombic efficiency exceeding 99.9%[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(2): 580-592. |
| 14 | JIA H P, ZOU L F, GAO P Y, et al. High-performance silicon anodes enabled by nonflammable localized high-concentration electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(31): 1900784. |
| 15 | LI Z H, ZHANG Y P, LIU T F, et al. Silicon anode with high initial coulombic efficiency by modulated trifunctional binder for high-areal-capacity lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(20): 1903110. |
| 16 | LIU N, LU Z D, ZHAO J, et al. A pomegranate-inspired nanoscale design for large-volume-change lithium battery anodes[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(3): 187-192. |
| 17 | FROMM O, HECKMANN A, RODEHORST U C, et al. Carbons from biomass precursors as anode materials for lithium ion batteries: New insights into carbonization and graphitization behavior and into their correlation to electrochemical performance[J]. Carbon, 2018, 128: 147-163. |
| 18 | ZOU K X, GUAN Z X, DENG Y F, et al. Nitrogen-rich porous carbon in ultra-high yield derived from activation of biomass waste by a novel eutectic salt for high performance Li-ion capacitors[J]. Carbon, 2020, 161: 25-35. |
| 19 | CHEN M F, JIANG S X, HUANG C, et al. Honeycomb-like nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped hierarchical porous biomass-derived carbon for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(8): 1803-1812. |
| 20 | CHEN C J, WANG Z G, ZHANG B, et al. Nitrogen-rich hard carbon as a highly durable anode for high-power potassium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2017, 8: 161-168. |
| 21 | XU D F, CHEN C J, XIE J, et al. A hierarchical N/S-codoped carbon anode fabricated facilely from cellulose/polyaniline microspheres for high-performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(6): 1501929. |
| 22 | MA J Q, GAO L F, LI S P, et al. Dual play of chitin-derived N-doped carbon nanosheets enabling high-performance Na-SeS2 half/full cells[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2020, 3(2): 165-173. |
| 23 | LIU D J, JIANG Z P, ZHANG W, et al. Micron-sized SiOx/N-doped carbon composite spheres fabricated with biomass chitosan for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(63): 38524-38531. |
| 24 | GAO L F, MA J Q, LI S P, et al. 2D ultrathin carbon nanosheets with rich N/O content constructed by stripping bulk chitin for high-performance sodium ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(26): 12626-12636. |
| 25 | SU A Y, LI J, DONG J J, et al. An amorphous/crystalline incorporated Si/SiOx anode material derived from biomass corn leaves for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2020, 16(24): 2001714. |
| 26 | HE Y Y, XU G, WANG C S, et al. Horsetail-derived Si@N-doped carbon as low-cost and long cycle life anode for Li-ion half/full cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 264: 173-182. |
| 27 | LIU J, KOPOLD P, VAN AKEN P A, et al. Energy storage materials from nature through nanotechnology: A sustainable route from reed plants to a silicon anode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 127(33): 9768-9772. |
| 28 | DEVIC T, LESTRIEZ B, ROUÉ L. Silicon electrodes for Li-ion batteries. addressing the challenges through coordination chemistry[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(2): 550-557. |
| 29 | RAJEEV K K, KIM E, NAM J, et al. Chitosan-grafted-polyaniline copolymer as an electrically conductive and mechanically stable binder for high-performance Si anodes in Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 333: 135532. |
| 30 | WANG H W, FU J Z, WANG C, et al. A binder-free high silicon content flexible anode for Li-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(3): 848-858. |
| 31 | SU W M, WAN R C, LIANG Y, et al. A novel 3D porous pseudographite/Si/Ni composite anode material fabricated by a facile method[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2020, 49(21): 7166-7173. |
| 32 | GUO R N, ZHANG S L, YING H J, et al. Preparation of an amorphous cross-linked binder for silicon anodes[J]. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(21): 4838-4845. |
| 33 | PREMAN A N, LEE H, YOO J, et al. Progress of 3D network binders in silicon anodes for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(48): 25548-25570. |
| 34 | KOVALENKO I, ZDYRKO B, MAGASINSKI A, et al. A major constituent of brown algae for use in high-capacity Li-ion batteries[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6052): 75-79. |
| 35 | LIU J, ZHANG Q, ZHANG T, et al. A robust ion-conductive biopolymer as a binder for Si anodes of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(23): 3599-3605. |
| 36 | HU J Z, WANG Y K, LI D W, et al. Effects of adhesion and cohesion on the electrochemical performance and durability of silicon composite electrodes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 397: 223-230. |
| 37 | ZHANG L, ZHANG L Y, CHAI L L, et al. A coordinatively cross-linked polymeric network as a functional binder for high-performance silicon submicro-particle anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(44): 19036-19045. |
| 38 | GENDENSUREN B, OH E-S. Dual-crosslinked network binder of alginate with polyacrylamide for silicon/graphite anodes of lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 384: 379-386. |
| 39 | LI Z H, JI J P, WU Q, et al. A new battery process technology inspired by partially carbonized polymer binders[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 67: 104234. |
| 40 | CHAI L L, QU Q T, ZHANG L F, et al. Chitosan, a new and environmental benign electrode binder for use with graphite anode in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 105: 378-383. |
| 41 | LEE S H, LEE J H, NAM D H, et al. Epoxidized natural rubber/chitosan network binder for silicon anode in lithium-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(19): 16449-16457. |
| 42 | CAO P-F, YANG G, LI B, et al. Rational design of a multifunctional binder for high-capacity silicon-based anodes[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(5): 1171-1180. |
| 43 | LING H Y, WANG C R, SU Z, et al. Amylopectin from glutinous rice as a sustainable binder for high-performance silicon anodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2021, 4(2): 263-268. |
| 44 | JIN B Y, WANG D Y, SONG L N, et al. Biomass-derived fluorinated corn starch emulsion as binder for silicon and silicon oxide based anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 365: 137359. |
| 45 | HAPUARACHCHI S N S, WASALATHILAKE K C, NERKAR J Y, et al. Mechanically robust tapioca starch composite binder with improved ionic conductivity for sustainable lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(26): 9857-9865. |
| 46 | ROHAN R, KUO T C, CHIOU C Y, et al. Low-cost and sustainable corn starch as a high-performance aqueous binder in silicon anodes via in situ cross-linking[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 396: 459-466. |
| 47 | ZHANG L, JIAO X X, FENG Z H, et al. A nature-inspired binder with three-dimensional cross-linked networks for silicon-based anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 484: 229198. |
| 48 | WANG J T, WAN C C, HONG J L. Polymer blends of pectin/poly(acrylic acid) as efficient binders for silicon anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(14): 3106-3115. |
| 49 | LING M, XU Y N, ZHAO H, et al. Dual-functional gum arabic binder for silicon anodes in lithium ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 12: 178-185. |
| 50 | HUANG L H, LI C C. Effects of interactions between binders and different-sized silicons on dispersion homogeneity of anodes and electrochemistry of lithium-silicon batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 409: 38-47. |
| 51 | HWANG G, KIM J M, HONG D, et al. Multifunctional natural agarose as an alternative material for high-performance rechargeable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(9): 2710-2716. |
| 52 | SHI Q T, ZHOU J H, ULLAH S, et al. A review of recent developments in Si/C composite materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 34: 735-754. |
| 53 | SHEN T, YAO Z J, XIA X H, et al. Rationally designed silicon nanostructures as anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 20(1): 15. |
| 54 | ZHANG H, ZHANG X F, JIN H, et al. A robust hierarchical 3D Si/CNTs composite with void and carbon shell as Li-ion battery anodes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 360: 974-981. |
| 55 | XU Q, SUN J K, YU Z L, et al. SiOx encapsulated in graphene bubble film: an ultrastable Li-ion battery anode[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(25): e1707430. |
| 56 | HUANG G, HAN J H, LU Z, et al. Ultrastable silicon anode by three-dimensional nanoarchitecture design[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(4): 4374-4382. |
| 57 | SONG J J, GUO S W, REN D Z, et al. Rice husk-derived SiOx@carbon nanocomposites as a high-performance bifunctional electrode for rechargeable batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8B): 11570-11576. |
| 58 | WANG Y, WANG X L, JIN H, et al. The synergetic effects of a multifunctional citric acid and rice husk derived honeycomb carbon matrix on a silicon anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2020, 4(5): 2583-2592. |
| 59 | REHMAN W U, WANG H F, MANJ R Z A, et al. When silicon materials meet natural sources: opportunities and challenges for low-cost lithium storage[J]. Small, 2021, 17(9): e1904508. |
| 60 | WANG L, GAO B, PENG C J, et al. Bamboo leaf derived ultrafine Si nanoparticles and Si/C nanocomposites for high-performance Li-ion battery anodes[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(33): 13840-13847. |
| 61 | WONG D P, SURIYAPRABHA R, YUVAKUMAR R, et al. Binder-free rice husk-based silicon-graphene composite as energy efficient Li-ion battery anodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(33): 13437-13441. |
| 62 | LIU N A, HUO K F, MCDOWELL M T, et al. Rice husks as a sustainable source of nanostructured silicon for high performance Li-ion battery anodes[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3(1): 1919. |
| 63 | MOHANTY A K, VIVEKANANDHAN S, PIN J M, et al. Composites from renewable and sustainable resources: Challenges and innovations[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6414): 536-542. |
| 64 | MIYASHIRO D, HAMANO R, UMEMURA K. A review of applications using mixed materials of cellulose, nanocellulose and carbon nanotubes[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(2): 186. |
| 65 | SHEN D Z, HUANG C F, GAN L H, et al. Rational design of Si@SiO2/C composites using sustainable cellulose as a carbon resource for anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(9): 7946-7954. |
| 66 | WEI R H, XU R H, ZHANG K Y, et al. Biological enzyme treatment of starch-based lithium-ion battery silicon-carbon composite[J]. Nanotechnology, 2020, 32(4): 045605. |
| 67 | KWON H J, HWANG J Y, SHIN H J, et al. Nano/microstructured silicon-carbon hybrid composite particles fabricated with corn starch biowaste as anode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(1): 625-635. |
| 68 | PAREKH M H, SEDIAKO A D, NASERI A, et al. In situ mechanistic elucidation of superior Si-C-graphite Li-ion battery anode formation with thermal safety aspects[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(2): 1902799. |
| 69 | YU L B, LIU J, HE S S, et al. N-doped rGO/C@Si composites using sustainable chitosan as the carbon source for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 501: 144136. |
| 70 | LI L, FANG C, WEI W F, et al. Nano-ordered structure regulation in delithiated Si anode triggered by homogeneous and stable Li-ion diffusion at the interface[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 72: 104651. |
| 71 | JIN H L, ZHU M S Q, LIU J, et al. Alkaline chitosan solution as etching phase to design Si@SiO2@N-carbon anode for lithium-ion battery[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 541: 148436. |
| 72 | QIAO M, MEYSAMI S S, FERRERO G A, et al. Low-cost chitosan-derived N-doped carbons boost electrocatalytic activity of multiwall carbon nanotubes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(16): 7. |
| 73 | HAMMI N, CHEN S, DUMEIGNIL F, et al. Chitosan as a sustainable precursor for nitrogen-containing carbon nanomaterials: Synthesis and uses[J]. Materials Today Sustainability, 2020: 100053. |
| 74 | SHAO R, ZHU F, CAO Z J, et al. Heteroatom-doped carbon networks enabling robust and flexible silicon anodes for high energy Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(35): 18338-18347. |
| 75 | ZHAO T T, ZHU D L, LI W R, et al. Novel design and synthesis of carbon-coated porous silicon particles as high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 439: 227027. |
| 76 | WANG H L, PU Y Q, RAGAUSKAS A, et al. From lignin to valuable products-strategies, challenges, and prospects[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 271: 449-461. |
| 77 | ZHANG L L, CHEN K L, PENG L C. Comparative research about wheat straw lignin from the black liquor after soda-oxygen and soda-AQ pulping: Structural changes and pyrolysis behavior[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(10): 10916-10923. |
| 78 | FENG Z Q, CHEN H L, LI H Q, et al. Preparation, characterization, and application of magnetic activated carbon for treatment of biologically treated papermaking wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 713: 136423. |
| 79 | XI Y B, HUANG S, YANG D J, et al. Hierarchical porous carbon derived from the gas-exfoliation activation of lignin for high-energy lithium-ion batteries[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(13): 4321-4330. |
| 80 | NIRMALE T C, KALE B B, VARMA A J. A review on cellulose and lignin based binders and electrodes: small steps towards a sustainable lithium ion battery[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 103: 1032-1043. |
| 81 | TENHAEFF W E, RIOS O, MORE K, et al. Highly robust lithium ion battery anodes from lignin: An abundant, renewable, and low-cost material[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(1): 86-94. |
| 82 | NIU X Y, ZHOU J Q, QIAN T, et al. Confined silicon nanospheres by biomass lignin for stable lithium ion battery[J]. Nanotechnology, 2017, 28(40): 405401. |
| 83 | DU L L, WU W, LUO C, et al. Lignin derived Si@C composite as a high performance anode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2018, 319: 77-82. |
| 84 | CHEN T, HU J Z, ZHANG L, et al. High performance binder-free SiOx/C composite LIB electrode made of SiOx and lignin[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 362: 236-42. |
| 85 | CHEN T, ZHANG Q L, PAN J, et al. Low-temperature treated lignin as both binder and conductive additive for silicon nanoparticle composite electrodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(47): 32341-32348. |
| 86 | LIU W W, LIU J, ZHU M H, et al. Recycling of lignin and Si waste for advanced Si/C battery anodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(51): 57055-57063. |
| [1] | Xianxi LIU, Anliang SUN, Chuan TIAN. Research on liquid cooling and heat dissipation of lithium-ion battery pack based on bionic wings vein channel cold plate [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2266-2273. |
| [2] | Jianxiang DENG, Jinliang ZHAO, Chengde HUANG. High energy density lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2092-2102. |
| [3] | OU Yu, HOU Wenhui, LIU Kai. Research progress of smart safety electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1772-1787. |
| [4] | HAN Junwei, XIAO Jing, TAO Ying, KONG Debin, LV Wei, YANG Quanhong. Compact energy storage: Methodology with graphenes and the applications [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1865-1873. |
| [5] | Lei LI, Zhao LI, Dan JI, Huichang NIU. Overcharge induced thermal runaway behaviors of pouch-type lithium-ion batteries with LFP and NCM cathodes: the differences and reasons [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1419-1427. |
| [6] | Ce ZHANG, Siwu LI, Jia XIE. Research progress on the prelithiation technology of alloy-type anodes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1383-1400. |
| [7] | Nan LIN, Ulrike KREWER, Jochen ZAUSCH, Konrad STEINER, Haibo LIN, Shouhua FENG. Development and application of multiphysics models for electrochemical energy storage and conversion systems [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1149-1164. |
| [8] | Hongzhang ZHU, Chuanping WU, Tiannian ZHOU, Jie DENG. Thermal runaway characteristics of LiFePO4 and ternary lithium batteries with external overheating [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 201-210. |
| [9] | Lianbing LI, Sijia LI, Jie LI, Kun SUN, Zhengping WANG, Haiyue YANG, Bing GAO, Shaobo YANG. RUL prediction of lithium-ion battery based on differential voltage and Elman neural network [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2373-2384. |
| [10] | Mengyu TIAN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Xuejie HUANG. Replenishment technology of the lithium ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 800-812. |
| [11] | Zuhao ZHANG, Xiaokai DING, Dong LUO, Jiaxiang CUI, Huixian XIE, Chenyu LIU, Zhan LIN. Challenges and solutions of lithium-rich manganese-based layered oxide cathode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 408-424. |
| [12] | Ran XIONG, Shunli WANG, Chunmei YU, Lili XIA. An estimation method for lithium-ion battery SOC of special robots based on Thevenin model and improved extended Kalman [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 695-704. |
| [13] | Zhendong ZHU, Huanhuan WU, Zheng ZHANG, Wen PENG, Lijuan LI. Analysis of lithium plating-stripping process in lithium-ion batteries by three-electrode measurements [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 448-453. |
| [14] | Jin WANG, Jianquan WANG, Dianbo RUAN, Jiao XIE, Bin YANG. Preparation and electrochemical performances of Si/activated carbon composites [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 104-110. |
| [15] | Zheng CHEN, Guangda ZHAO, Shiquan SHEN, Xing SHU, Jiangwei SHEN. SOC estimation of aging lithium-ion battery based on a migration model [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 326-334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
