Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (10): 3062-3075.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0160
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Weixiang CHENG1( ), Xingwen HUANG1, Yuezhu LI1, Junqi HU1, Songyi LIAO2(
), Xingwen HUANG1, Yuezhu LI1, Junqi HU1, Songyi LIAO2( ), Yonggang MIN1,2,3(
), Yonggang MIN1,2,3( )
)
Received:2022-03-28
Revised:2022-04-27
Online:2022-10-05
Published:2022-10-10
Contact:
Songyi LIAO, Yonggang MIN
E-mail:weixiangcheng2021@126.com;songyiliao@gdut.edu.cn;ygmin@gdut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Weixiang CHENG, Xingwen HUANG, Yuezhu LI, Junqi HU, Songyi LIAO, Yonggang MIN. Advances in layered metal disulfide as anode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(10): 3062-3075.
Table1
Electrochemical performance of common NIBs"
| 材料种类 | 材料名称 | 电化学性能 |
|---|---|---|
| TMDs | MoS2 | 56 mAh/g(20 A/g) 394 mAh/g(1 A/g循环350圈)[ |
| SnS2 | 343 mAh/g(5 A/g) 396 mAh/g(1 A/g循环500圈)[ | |
| WS2 | 194 mAh/g(5 A/g) 182 mAh/g(5 A/g循环6000圈)[ | |
| VS2 | 117 mAh/g(20 A/g) 176 mAh/g(10 A/g循环5000圈)[ | |
| 金属氧化物 | MoO3 | 127 mAh/g(5 A/g) 105 mAh/g(5 A/g循环1200圈)[ |
| SnO2 | 203 mAh/g(0.15 A/g) 488 mAh/g(0.02 A/g循环70圈)[ | |
| WO3 | 204.6 mAh/g(5 A/g) 306.5 mAh/g(2 A/g循环3000圈)[ | |
| 金属磷化物 | MoP | 133 mAh/g(4.1 A/g) 307 mAh/g(0.06 A/g循环100圈)[ |
| Sn4P3 | 853 mAh/g(0.1 A/g) 718 mAh/g(0.1 A/g循环100圈)[ | |
| V4P7 | 90 mAh/g(0.8 A/g) 122 mAh/g(0.2 A/g循环500圈)[ | |
| WP | 56 mAh/g(2 A/g) 50 mAh/g(2 A/g循环1000圈)[ |
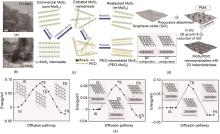
Fig. 4
(a) HRTEM images of FG-MoS2[62]; (b) HRTEM images of CG-MoS2[62]; (c) Schematic diagram of synthesis of restacked MoS2 (re-MoS2) and PEO-MoS2via exfoliation-restacking process[63]; (d) Schematic illustration for the preparation of MoS2/RGO heterostructures[64]; (e) Different energetically possible sites for Na adsorption in MoS2 and its heterostructure[64]"
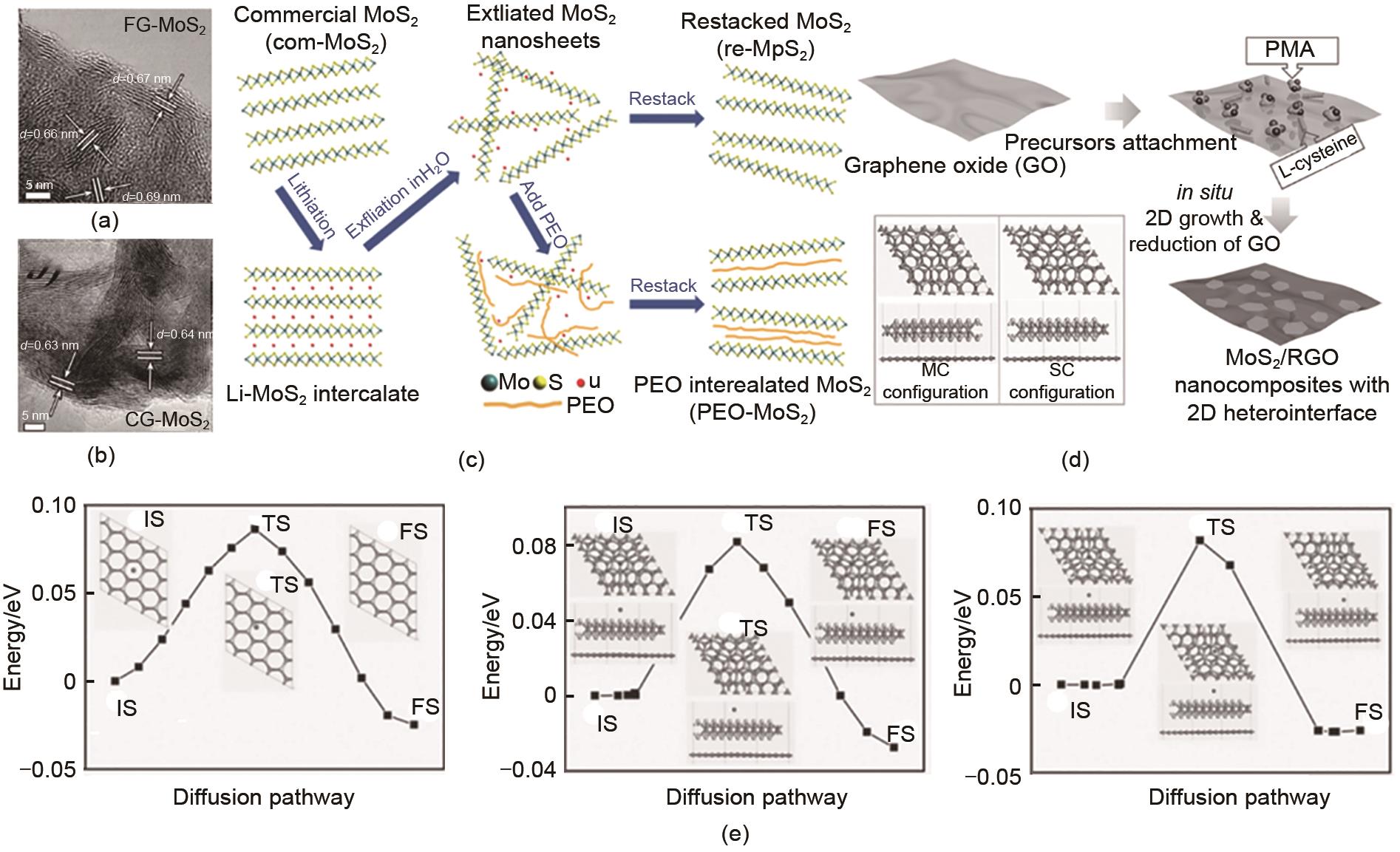
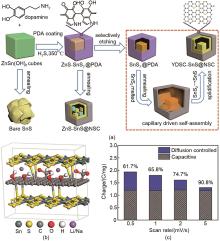
Fig. 5
(a) Schematic of synthesis of YDSC-SnS@NSC by the self-templated and selective etching method as well as a heat-and capillary-induced self-assembly[75]; (b) The supercell model of SnS2-GO-SnS2 composite containing Li+/Na+[76]; (c) Pseudo-capacitance contribution of SnS2/CNT as anode of NIBs at different scan rates[77]"
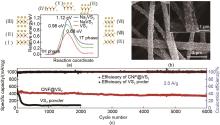
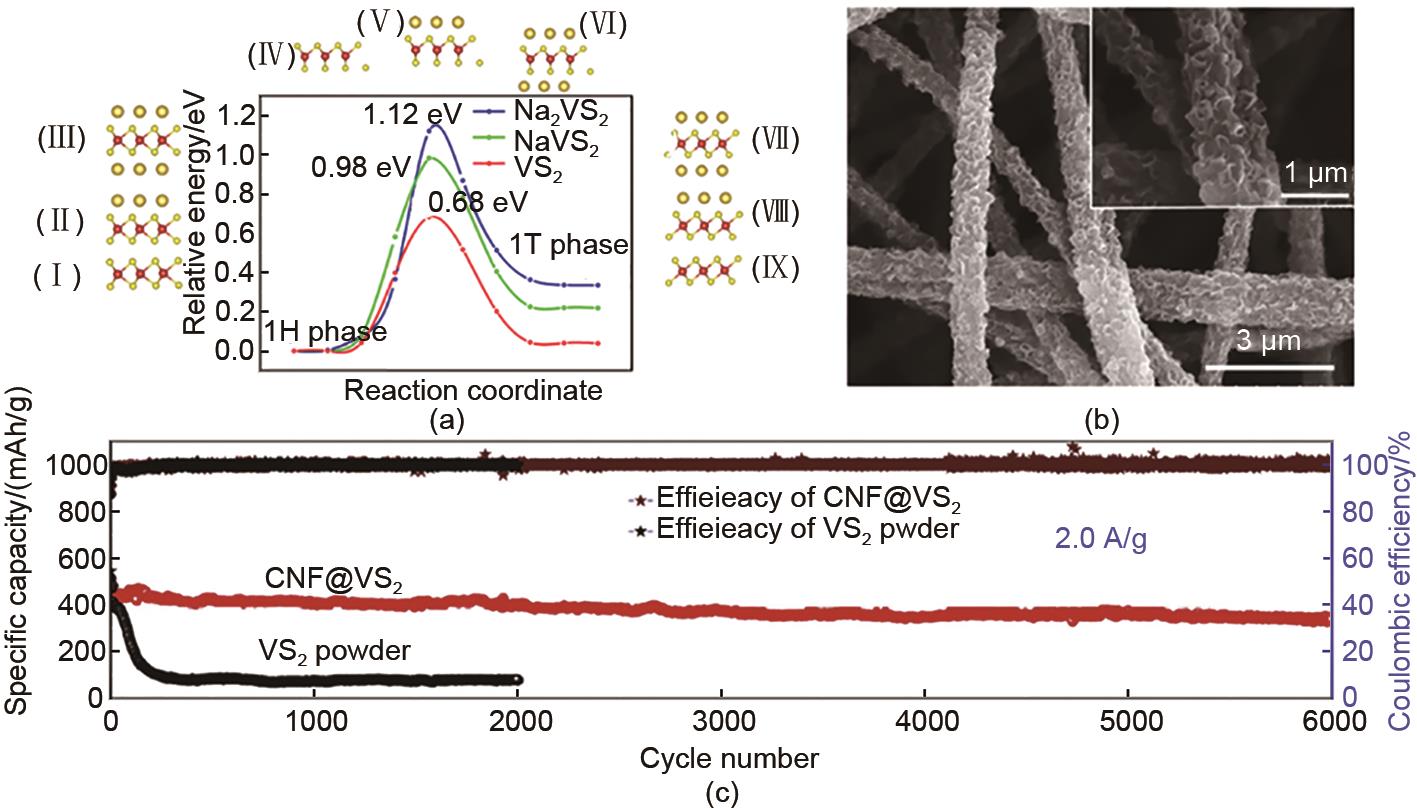
Fig. 7
(a) 1H-to-1T structural phase transition of VS2 monolayer. Also shown are the corresponding configurations of the initial structures (Ⅰ, Ⅱ, and Ⅲ), transition-state structures (Ⅳ, Ⅴ, and Ⅵ), andfinal structures (Ⅶ, Ⅷ, and Ⅸ)[87]; (b) SEM images after 6000 cycles of the CNF@VS2 electrode[88]; (c) Long-term cycling life for 6000 cycles at a high current density of 2 A/g[89]"
| 1 | TANG Y J, ZHENG S S, XU Y X, et al. Advanced batteries based on manganese dioxide and its composites[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 12: 284-309. |
| 2 | 曹余良. 钠离子电池机遇与挑战[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(3): 757-761. |
| CAO Y L. The opportunities and challenges of sodium ion battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 757-761. | |
| 3 | 王跃生, 容晓晖, 徐淑银, 等. 室温钠离子储能电池电极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5(3): 268-284. |
| WANG Y S, RONG X H, XU S Y, et al. Recent progress of electrode materials for room-temperature sodium-ion stationary batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2016, 5(3): 268-284. | |
| 4 | 容晓晖, 陆雅翔, 戚兴国, 等. 钠离子电池:从基础研究到工程化探索[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 515-522. |
| RONG X H, LU Y X, QI X G, et al. Na-ion batteries: From fundamental research to engineering exploration[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 515-522. | |
| 5 | PRAMUDITA J C, SEHRAWAT D, GOONETILLEKE D, et al. An initial review of the status of electrode materials for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(24): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201602911. |
| 6 | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: Present and future[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529-3614. |
| 7 | 田丽媛, 鞠小霞, 向枫, 等. 钠离子电池金属化合物负极材料的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2018, 7(6): 1211-1216. |
| TIAN L Y, JU X X, XIANG F, et al. Recent research progress of metal compounds as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(6): 1211-1216. | |
| 8 | LÜ J J, ZHENG J N, WANG Y Y, et al. A simple one-pot strategy to platinum-palladium@palladium core-shell nanostructures with high electrocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 265: 231-238. |
| 9 | LUO B, HU Y X, ZHU X B, et al. Controllable growth of SnS2 nanostructures on nanocarbon surfaces for lithium-ion and sodium-ion storage with high rate capability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(4): 1462-1472. |
| 10 | WANG G, ZHANG J, YANG S, et al. Vertically aligned MoS2 nanosheets patterned on electrochemically exfoliated graphene for high-performance lithium and sodium storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(8): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201702254. |
| 11 | WANG B, ANG E H, YANG Y, et al. Interlayer engineering of molybdenum trioxide toward high-capacity and stable sodium ion half/full batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(28): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202001708. |
| 12 | BISWAL R, NAYAK D, JANAKIRAMAN S, et al. Revisiting and enhancing electrochemical properties of SnO2 as anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2021, 25(2): 561-573. |
| 13 | ZENG F Y, CHENG W T, PAN Y, et al. Mono-faceted WO3– x nanorods in situ hybridized in carbon nanosheets for ultra-fast/stable sodium-ion storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(45): 23919-23929. |
| 14 | ALI G, ANJUM M A R, MEHBOOB S, et al. Sulfur-doped molybdenum phosphide as fast dis/charging anode for Li-ion and Na-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(6): 8452-8463. |
| 15 | KIM Y, KIM Y, CHOI A, et al. Tin phosphide as a promising anode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(24): 4139-4144. |
| 16 | KIM K H, CHOI J, HONG S H. Superior electrochemical sodium storage of V4P7 nanoparticles as an anode for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(22): 3207-3210. |
| 17 | PAN Q, CHEN H, WU Z G, et al. Nanowire of WP as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemistry, 2019, 25(4): 971-975. |
| 18 | WANG P P, SUN H Y, JI Y J, et al. Three-dimensional assembly of single-layered MoS2[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(6): 964-969. |
| 19 | YANG Y, WANG S T, ZHANG J C, et al. Nanosheet-assembled MoSe2 and S-doped MoSe2– x nanostructures for superior lithium storage properties and hydrogen evolution reactions[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2015, 2(10): 931-937. |
| 20 | ZHANG L, WU H B, YAN Y, et al. Hierarchical MoS2 microboxes constructed by nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium storage and water splitting[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(10): 3302-3306. |
| 21 | SUN P L, ZHANG W X, HU X L, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical MoS2 and its electrochemical performance as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(10): 3498-3504. |
| 22 | ZHANG S P, CHOWDARI B V R, WEN Z Y, et al. Constructing highly oriented configuration by few-layer MoS2: Toward high-performance lithium-ion batteries and hydrogen evolution reactions[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(12): 12464-12472. |
| 23 | ZHOU J, WANG L, YANG M, et al. Hierarchical VS2 nanosheet assemblies: A universal host material for the reversible storage of alkali metalions[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(35): doi: 10.1002/adma.201702061. |
| 24 | LANE C, CAO D X, LI H Y, et al. Understanding phase stability of metallic 1T-MoS2 anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Condensed Matter, 2019, 4(2): 53. |
| 25 | WANG M, LI G D, XU H Y, et al. Enhanced lithium storage performances of hierarchical hollow MoS2 nanoparticles assembled from nanosheets[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(3): 1003-1008. |
| 26 | ZENG L, ZHANG L P, LIU X G, et al. Three-dimensional porous graphene supported MoS2 nanoflower prepared by a facile solvothermal method with excellent rate performance and sodium-ion storage[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(9): 2134. |
| 27 | HAO X Q, JIANG Z Q, SHANG X N, et al. Understanding the role of graphene intercalation layers on both sides of sandwich structured graphene@MoS2@porous graphene anode in promoting sodium storage performance and stability[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 845: doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155336. |
| 28 | LI Y F, MAO H J, ZHENG C, et al. Compositing reduced graphene oxide with interlayer spacing enlarged MoS2 for performance enhanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2020, 136: doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.109163. |
| 29 | NIE W, LIU X L, ZHOU Y T, et al. Graphene-induced three-dimensional network structure to MoS2/graphene composite as an excellent anode for sodium ion batteries[J]. Functional Materials Letters, 2020, 13(1): doi: 10.1142/s1793604719510068. |
| 30 | ZHANG R, WANG J K, LI C, et al. Facile synthesis of hybrid MoS2/graphene nanosheets as high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(2): 711-717. |
| 31 | REDDY B, PREMASUDHA M, OH K M, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of MoS2/rGO composite as sulfur hosts for room temperature sodium-sulfur batteries and its electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 39: doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.102660. |
| 32 | YU X L, CHEN C M, LI R X, et al. Construction of SnS2@MoS2@rGO heterojunction anode and their half/full sodium ion storage performances[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 896: doi: 10.1016/j.jalløcom.2022.162784. |
| 33 | YUVARAJ S, VEERASUBRAMANI G K, PARK M S, et al. Facile synthesis of FeS2/MoS2 composite intertwined on rGO nanosheets as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 821: doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.162784. |
| 34 | CUI L S, TAN C L, LI Y, et al. Hierarchical Fe2O3@MoS2/C nanorods as anode materials for sodium ion batteries with high cycle stability[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(4): 3757-3765. |
| 35 | XIONG K Z, GUO J Z, SHEN K E, et al. Few-layered MoS2 with expanded interplanar spacing strongly encapsulated inside compact carbon spheres by C-S interaction as ultra-stable sodium-ion batteries anode[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 858: doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.157675. |
| 36 | FAN H L, MAO P C, LAN G X, et al. Ultrathin metallic-phase molybdenum disulfide nanosheets stabilized on functionalized carbon nanotubes via covalent interface interaction for sodium-and lithium-ion storage[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(9): 9440-9449. |
| 37 | WANG J L, SUN L, GONG Y, et al. A CNT/MoS2@PPy composite with double electron channels and boosting charge transport for high-rate lithium storage[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 566: doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150693. |
| 38 | JI Q Q, LI C, WANG J L, et al. Metallic vanadium disulfide nanosheets as a platform material for multifunctional electrode applications[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(8): 4908-4916. |
| 39 | CHOUDHARY N, LI C, CHUNG H S, et al. High-performance one-body core/shell nanowire supercapacitor enabled by conformal growth of capacitive 2D WS2 layers[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12): 10726-10735. |
| 40 | SOON J M, LOH K P. Electrochemical double-layer capacitance of MoS2 nanowall films[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2007, 10(11): A250. |
| 41 | YANG Y, FEI H L, RUAN G D, et al. Edge-oriented MoS2 nanoporous films as flexible electrodes for hydrogen evolution reactions and supercapacitor devices[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(48): 8163-8168. |
| 42 | LIU B, LUO T, MU G Y, et al. Rechargeable Mg-ion batteries based on WSe2 nanowire cathodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(9): 8051-8058. |
| 43 | HE J J, ZHANG C J, DU H P, et al. Engineering vertical aligned MoS2 on graphene sheet towards thin film lithium ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 178: 476-483. |
| 44 | ZHANG Q, TAN S J, MENDES R G, et al. Extremely weak van der Waals coupling in vertical ReS2 nanowalls for high-current-density lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(13): 2616-2623. |
| 45 | ZHANG Z J, ZHAO H L, TENG Y Q, et al. Lithium-ion batteries: Carbon-sheathed MoS2 nanothorns epitaxially grown on CNTs: Electrochemical application for highly stable and ultrafast lithium storage (adv. energy mater. 7/2018)[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(7): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201870029. |
| 46 | COLEMAN J N, LOTYA M, O'NEILL A, et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials[J]. Science, 2011, 331(6017): 568-571. |
| 47 | FENG J, SUN X, WU C Z, et al. Metallic few-layered VS2 ultrathin nanosheets: High two-dimensional conductivity for in-plane supercapacitors[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(44): 17832-17838. |
| 48 | ZHANG X, LAI Z C, TAN C L, et al. Solution-processed two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets: Preparation, hybridization, and applications[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(31): 8816-8838. |
| 49 | ACERCE M, VOIRY D, CHHOWALLA M. Metallic 1T phase MoS2 nanosheets as supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(4): 313-318. |
| 50 | EDA G, FUJITA T, YAMAGUCHI H, et al. Coherent atomic and electronic heterostructures of single-layer MoS2[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(8): 7311-7317. |
| 51 | EDA G, YAMAGUCHI H, VOIRY D, et al. Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2[J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(12): 5111-5116. |
| 52 | JING Y, ORTIZ-QUILES E O, CABRERA C R, et al. Layer-by-layer hybrids of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 147: 392-400. |
| 53 | JEONG J M, LEE K G, CHANG S J, et al. Ultrathin sandwich-like MoS2@N-doped carbon nanosheets for anodes of lithium ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(1): 324-329. |
| 54 | LIU Y, WANG W, WANG Y W, et al. Homogeneously assembling like-charged WS2 and GO nanosheets lamellar composite films by filtration for highly efficient lithium ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2014, 7: 25-32. |
| 55 | WANG W W, GUO S Z, ZHANG P L, et al. Polypyrrole-wrapped SnS2 vertical nanosheet arrays grown on three-dimensional nitrogen-doped porous graphene for high-performance lithium and sodium storage[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(10): 11101-11111. |
| 56 | LIU Y C, ZHANG N, KANG H Y, et al. WS2 nanowires as a high-performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemistry, 2015, 21(33): 11878-11884. |
| 57 | ZHAO Y Y, YANG D, HE T Q, et al. Vacancy engineering in VS2 nanosheets for ultrafast pseudocapacitive sodium ion storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129715. |
| 58 | STEPHENSON T, LI Z, OLSEN B, et al. Lithium ion battery applications of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanocomposites[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(1): 209-231. |
| 59 | WANG X F, SHEN X, WANG Z X, et al. Atomic-scale clarification of structural transition of MoS2 upon sodium intercalation[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(11): 11394-11400. |
| 60 | CHOI S H, KO Y N, LEE J K, et al. 3D MoS2-graphene microspheres consisting of multiple nanospheres with superior sodium ion storage properties[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(12): 1780-1788. |
| 61 | LU Y Y, ZHAO Q, ZHANG N, et al. Facile spraying synthesis and high-performance sodium storage of mesoporous MoS2/C microspheres[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(6): 911-918. |
| 62 | HU Z, WANG L X, ZHANG K, et al. MoS2 nanoflowers with expanded interlayers as high-performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(47): 12794-12798. |
| 63 | LI Y F, LIANG Y L, ROBLES HERNANDEZ F C, et al. Enhancing sodium-ion battery performance with interlayer-expanded MoS2-PEO nanocomposites[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 15: 453-461. |
| 64 | XIE X Q, AO Z M, SU D W, et al. MoS2/graphene composite anodes with enhanced performance for sodium-ion batteries: The role of the two-dimensional heterointerface[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(9): 1393-1403. |
| 65 | PAN Q C, ZHANG Q B, ZHENG F H, et al. Construction of MoS2/C hierarchical tubular heterostructures for high-performance sodium ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(12): 12578-12586. |
| 66 | LI P, JEONG J Y, JIN B J, et al. Vertically oriented MoS2 with spatially controlled geometry on nitrogenous graphene sheets for high-performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(19): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201703300. |
| 67 | REN W N, ZHANG H F, GUAN C, et al. Ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets@metal organic framework-derived N-doped carbon nanowall arrays as sodium ion battery anode with superior cycling life and rate capability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(32): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201702116. |
| 68 | LI J H, TAO H C, ZHANG Y K, et al. Molybdenum disulfide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite with expanded interlayer spacing for sodium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166(15): A3685-A3692. |
| 69 | GONZÁLEZ J R, ALCÁNTARA R, TIRADO J L, et al. Electrochemical interaction of few-layer molybdenum disulfide composites vs sodium: New insights on the reaction mechanism[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(14): 5886-5895. |
| 70 | CHEN D Y, JI G, DING B, et al. Double transition-metal chalcogenide as a high-performance lithium-ion battery anode material[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(46): 17901-17908. |
| 71 | LIU Y C, KANG H Y, JIAO L F, et al. Exfoliated-SnS2 restacked on graphene as a high-capacity, high-rate, and long-cycle life anode for sodium ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(4): 1325-1332. |
| 72 | WANG J W, LIU X H, MAO S X, et al. Microstructural evolution of tin nanoparticles during in situ sodium insertion and extraction[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(11): 5897-5902. |
| 73 | QU B H, MA C Z, JI G, et al. Layered SnS2-reduced graphene oxide composite—A high-capacity, high-rate, and long-cycle life sodium-ion battery anode material[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(23): 3854-3859. |
| 74 | SUN W P, RUI X H, YANG D, et al. Two-dimensional tin disulfide nanosheets for enhanced sodium storage[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11371-11381. |
| 75 | CHEN M L, ZHANG Z Y, SI L P, et al. Engineering of yolk-double shell cube-like SnS@N-S codoped carbon as a high-performance anode for Li-and Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(38): 35050-35059. |
| 76 | JIANG Y, SONG D Y, WU J, et al. Sandwich-like SnS2/graphene/SnS2 with expanded interlayer distance as high-rate lithium/sodium-ion battery anode materials[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(8): 9100-9111. |
| 77 | CUI J, YAO S S, LU Z H, et al. Revealing pseudocapacitive mechanisms of metal dichalcogenide SnS2/graphene-CNT aerogels for high-energy Na hybrid capacitors[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(10): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201702488. |
| 78 | LIU Y H, YU X Y, FANG Y J, et al. Confining SnS2 ultrathin nanosheets in hollow carbon nanostructures for efficient capacitive sodium storage[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(4): 725-735. |
| 79 | WANG Y, KONG D Z, SHI W H, et al. Ice templated free-standing hierarchically WS2/CNT-rGO aerogel for high-performance rechargeable lithium and sodium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(21): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201601057 |
| 80 | NANDI D K, YEO S, ANSARI M Z, et al. Thickness-dependent electrochemical response of plasma enhanced atomic layer deposited WS2 anodes in Na-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 322: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.134766. |
| 81 | MO L L, GAO M Y, ZHOU G Y, et al. Low-crystallinity tungsten disulfide construction by in situ confinement effect enables ultrastable sodium-ion storage[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 900: doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163518. |
| 82 | LI X, SUN Y G, XU X, et al. Lotus rhizome-like S/N-C with embedded WS2 for superior sodium storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(45): 25932-25943. |
| 83 | CHOI S H, KANG Y C. Sodium ion storage properties of WS2-decorated three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide microspheres[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(9): 3965-3970. |
| 84 | KAN M, WANG B, LEE Y H, et al. A density functional theory study of the tunable structure, magnetism and metal-insulator phase transition in VS2 monolayers induced by in-plane biaxial strain[J]. Nano Research, 2015, 8(4): 1348-1356. |
| 85 | MIKHALEVA N S, VISOTIN M A, KUZUBOV A A, et al. VS2/graphene heterostructures as promising anode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(43): 24179-24184. |
| 86 | LI W B, KHEIMEH SARI H M, LI X F. Emerging layered metallic vanadium disulfide for rechargeable metal-ion batteries: Progress and opportunities[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(6): 1172-1202. |
| 87 | PUTUNGAN D B, LIN S H, KUO J L. Metallic VS2 monolayer polytypes as potential sodium-ion battery anode via ab initio random structure searching[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(29): 18754-18762. |
| 88 | SUN R M, WEI Q L, SHENG J Z, et al. Novel layer-by-layer stacked VS2 nanosheets with intercalation pseudocapacitance for high-rate sodium ion charge storage[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 35: 396-404. |
| 89 | XU D M, WANG H W, QIU R Y, et al. Coupling of bowl-like VS2 nanosheet arrays and carbon nanofiber enables ultrafast Na+-storage and robust flexibility for sodium-ion hybrid capacitors[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 28: 91-100. |
| [1] | Shuya GONG, Yue WANG, Meng LI, Jingyi QIU, Hong WANG, Yuehua WEN, Bin XU. Research progress on TiNb2O7 anodes for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2921-2932. |
| [2] | Qiannan LIU, Weiping HU, Zhe HU. Research progress of phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1201-1210. |
| [3] | Dewang SUN, Bizhi JIANG, Tao YUAN, Shiyou ZHENG. Research progress of titanium niobium oxide used as anode of lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2127-2143. |
| [4] | Qiang CHEN, Min LI, Jingfa LI. Application of Prussian blue analogs and their derivatives in potassium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 1002-1015. |
| [5] | Tenghui WANG, Guo CHEN, Xuelin YANG. Review of preparations of amorphous nanostructured silicon powder [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 440-447. |
| [6] | Guangling WEI, Ying JIANG, Jiahui ZHOU, Ziheng WANG, Yongxin HUANG, Man XIE, Feng WU. Research progress on metal oxides/sulfides/selenides anode materials of sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1318-1326. |
| [7] | MA Tengfei, MA Chao, SUN Rui, JI Hongmei, YANG Gang. Freeze-drying assisted synthesis of mno/reduced graphene composite and the improved rate cyclic performance for lithium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 1044-1051. |
| [8] | ZHOU Junhua, LUO Fei, CHU Geng, LIU Bonan, LU Hao, ZHENG Jieyun, LI Hong, HUANG Xuejie, CHEN Liquan. Research progress on nano silicon-carbon anode materials for lithium ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 569-582. |
| [9] | LI Zhendong, WANG Zhenhua, ZHANG Shilong, FU Chunlin. Research progress of MOFs and its derivatives as electrode materials for lithium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(1): 18-24. |
| [10] | LIU Xingwen, HE Jinxin, WANG Hailin, JIN Chengyou, MIAO Yonghua, XUE Chi. Preparation and electrochemical performance of F-doped SiO@C composite material [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(S1): 56-59. |
| [11] | SHEN Jinran, GUO Cuijing, CHEN He, ZHOU Shuqin, XU Bin, GUAN Yibiao. Synthesis and lithium storage property of high-performance N-doped reduced graphene oxide [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(6): 1137-1144. |
| [12] | XU Hui, YANG Liuqing, YIN Fan, YANG Gang. Preparation and electrochemical performance of amorphous carbon coated tin-based anode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(4): 732-737. |
| [13] | FENG Guofei, WU Jianguo, LIU Wei, XU Shenghua, LIN Zhizhu. Carbonization process of artifcial graphite coated with asphalt [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(3): 580-582. |
| [14] | GAO Xiang, ZHU Zirui. Applications of atomic force microscopy in lithium ion batteries research [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 75-82. |
| [15] | ZHOU Junhua, ZHU Geng, LU Hao, LIU Bonan, LUO Fei, ZHENG Jieyun, CHEN Shimou, GUO Yuguo, LI Hong. Interpretation of anode material standards for lithium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 215-223. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
