Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (7): 2259-2269.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0360
• Special Issue on Low Temperature Batteries • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haotian WANG( ), Yonggang WANG, Xiaoli DONG(
), Yonggang WANG, Xiaoli DONG( )
)
Received:2024-04-24
Revised:2024-05-08
Online:2024-07-28
Published:2024-07-23
Contact:
Xiaoli DONG
E-mail:23210220038@m.fudan.edu.cn;xldong@fudan.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Haotian WANG, Yonggang WANG, Xiaoli DONG. Advances in low-temperature organic batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2259-2269.
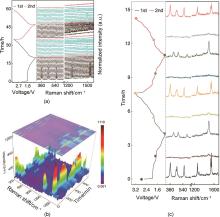
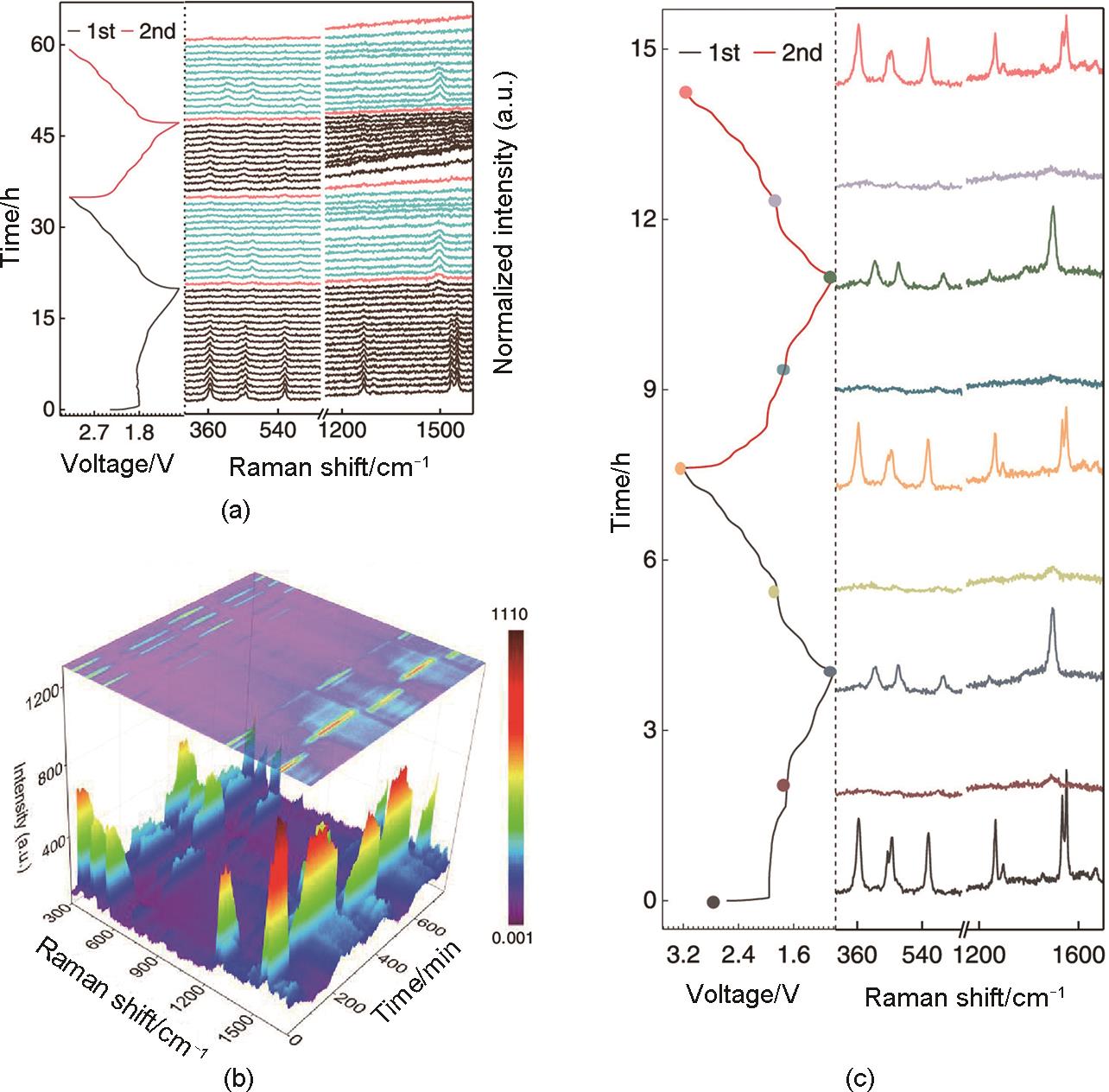
Fig. 4
Revealing solid-liquid-solid conversion reaction in nDSR and nDSR*π (a) Operando Raman spectra for nDSR and the corresponding discharge-charge profile for the initial two cycles; (b) Operando Raman 3D projection contour plot for nDSR*π cell; (c) Selected operando Raman spectra for nDSR*π electrode at differing discharge/charge states and corresponding discharge-charge profile[50]"
| 1 | KITTNER N, LILL F, KAMMEN D M. Energy storage deployment and innovation for the clean energy transition[J]. Nature Energy, 2017, 2(9): 17125. |
| 2 | XU K. A long journey of lithium: From the big Bang to our smartphones[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2019, 2(4): 229-233. |
| 3 | ALBERTUS P, BABINEC S, LITZELMAN S, et al. Status and challenges in enabling the lithium metal electrode for high-energy and low-cost rechargeable batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3: 16-21. |
| 4 | YANG Y, LI P L, WANG N, et al. Fluorinated carboxylate ester-based electrolyte for lithium ion batteries operated at low temperature[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(67): 9640-9643. |
| 5 | HOLOUBEK J, YIN Y J, LI M Q, et al. Exploiting mechanistic solvation kinetics for dual-graphite batteries with high power output at extremely low temperature[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2019, 58(52): 18892-18897. |
| 6 | FAN X L, JI X, CHEN L, et al. All-temperature batteries enabled by fluorinated electrolytes with non-polar solvents[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4: 882-890. |
| 7 | HOLOUBEK J, LIU H D, WU Z H, et al. Tailoring electrolyte solvation for Li metal batteries cycled at ultra-low temperature[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6: 303-313. |
| 8 | SUN T, SUN Q Q, YU Y, et al. Polypyrrole as an ultrafast organic cathode for dual-ion batteries[J]. eScience, 2021, 1(2): 186-193. |
| 9 | GU S, WU S F, CAO L J, et al. Tunable redox chemistry and stability of radical intermediates in 2D covalent organic frameworks for high performance sodium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(24): 9623-9628. |
| 10 | GAN X, YANG Z, SONG Z. Solid-state batteries based on organic cathode materials[J]. Batteries Supercaps, 2023, 6(6): 1-24. |
| 11 | POIZOT P, GAUBICHER J, RENAULT S, et al. Opportunities and challenges for organic electrodes in electrochemical energy storage[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(14): 6490-6557. |
| 12 | DONG X, GUO Z, GUO Z, et al. Organic batteries operated at -70 ℃[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(5): 902-913. |
| 13 | QIN J, LAN Q, LIU N, et al. A metal-free battery working at -80 ℃ [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 26: 585-592. |
| 14 | PAUDEL A, KUCHENA S F, WANG Y. A full metal-free battery operating under cold condition enabled by an antisolvent[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 469: 143227. |
| 15 | CHEN J W, PENG Y, YIN Y, et al. A desolvation-free sodium dual-ion chemistry for high power density and extremely low temperature[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(44): 23858-23862. |
| 16 | KIM D J, YOO D J, OTLEY M T, et al. Rechargeable aluminium organic batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4: 51-59. |
| 17 | LI M J, YANG J X, SHI Y Q, et al. Soluble organic cathodes enable long cycle life, high rate, and wide-temperature lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(5): e2107226. |
| 18 | WANG D D, PENG H L, ZHANG S J, et al. Localized anion-cation aggregated aqueous electrolytes with accelerated kinetics for low-temperature zinc metal batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2023, 62(50): e202315834. |
| 19 | GAN X T, SONG Z P. Small-molecule organic electrode materials for rechargeable batteries[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2023, 66(11): 3070-3104. |
| 20 | HONG Y H, MA Z, LI K X, et al. Research progress and perspectives on ultra-low temperature organic batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(15): 7898-7923. |
| 21 | SONG Z P, ZHOU H S. Towards sustainable and versatile energy storage devices: An overview of organic electrode materials[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(8): 2280-2301. |
| 22 | ZENG R H, XING L, QIU Y C, et al. Polycarbonyl(quinonyl) organic compounds as cathode materials for sustainable lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 146: 447-454. |
| 23 | HAN X Y, CHANG C X, YUAN L J, et al. Aromatic carbonyl derivative polymers as high-performance Li-ion storage materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(12): 1616-1621. |
| 24 | QIN K Q, HOLGUIN K, MOHAMMADIROUDBARI M, et al. A conjugated tetracarboxylate anode for stable and sustainable Na-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2021, 57(19): 2360-2363. |
| 25 | SAKAUSHI K, NICKERL G, WISSER F M, et al. An energy storage principle using bipolar porous polymeric frameworks[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2012, 51(31): 7850-7854. |
| 26 | WANG J D, LIU X L, JIA H, et al. A high-voltage organic framework for high-performance Na- and K-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(2): 668-674. |
| 27 | LÓPEZ-HERRAIZ M, CASTILLO-MARTÍNEZ E, CARRETERO-GONZÁLEZ J, et al. Oligomeric-Schiff bases as negative electrodes for sodium ion batteries: Unveiling the nature of their active redox centers[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(11): 3233-3241. |
| 28 | HANYU Y, HONMA I. Rechargeable quasi-solid state lithium battery with organic crystalline cathode[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 453. |
| 29 | LUO C, JI X, HOU S, et al. Azo compounds derived from electrochemical reduction of nitro compounds for high performance Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(23): e1706498. |
| 30 | LU Y, CAI Y C, ZHANG Q, et al. Insights into redox processes and correlated performance of organic carbonyl electrode materials in rechargeable batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(22): 2104150. |
| 31 | LIANG Y L, ZHANG P, YANG S Q, et al. Fused heteroaromatic organic compounds for high-power electrodes of rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3(5): 600-605. |
| 32 | SONG Z P, QIAN Y M, GORDIN M L, et al. Polyanthraquinone as a reliable organic electrode for stable and fast lithium storage[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2015, 54(47): 13947-13951. |
| 33 | NARAYAN R, BLAGOJEVIĆ A, MALI G, et al. Nanostructured poly(hydroquinonyl-benzoquinonyl sulfide)/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite cathodes: Improved synthesis and performance for rechargeable Li and Mg organic batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34 (14): 6378-6388. |
| 34 | LI M J, HICKS R P, CHEN Z F, et al. Electrolytes in organic batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00374. |
| 35 | SENOH H, YAO M, SAKAEBE H, et al. A two-compartment cell for using soluble benzoquinone derivatives as active materials in lithium secondary batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(27): 10145-10150. |
| 36 | SONG Z P, QIAN Y M, OTANI M, et al. Stable Li-organic batteries with nafion-based sandwich-type separators[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2016, 6(7): 1-7 |
| 37 | ZHENG Y W, JI H Q, LIU J, et al. Surpassing the redox potential limit of organic cathode materials via extended p-π conjugation of dioxin[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(8): 3473-3479. |
| 38 | YAO M, SENOH H, SAKAI T, et al. Redox active poly(N-vinylcarbazole) for use in rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 202: 364-368. |
| 39 | SAKAUSHI K, HOSONO E, NICKERL G, et al. Aromatic porous-honeycomb electrodes for a sodium-organic energy storage device[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1485. |
| 40 | WANG M, TANG Y B. Dual-ion batteries: A review on the features and progress of dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(19): doi:10.1002/aenm.201870088. |
| 41 | WANG H G, WANG Y, WU Q, et al. Recent developments in electrode materials for dual-ion batteries: potential alternatives to conventional batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2022, 52: 269-298. |
| 42 | HAGEMANN T, WINSBERG J, HÄUPLER B, et al. A bipolar nitronyl nitroxide small molecule for an all-organic symmetric redox-flow battery[J]. NPG Asia Materials, 2017, 9(1): e340. |
| 43 | NISHIDE H, IWASA S, PU Y J, et al. Organic radical battery: Nitroxide polymers as a cathode-active material[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 50(): 827-831. |
| 44 | NIGREY P J, MACINNES D, NAIRNS D P, et al. Lightweight rechargeable storage batteries using polyacetylene (CH) [sub X] as the cathode-active material[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1981, 128(8): 1651. |
| 45 | ZHU L M, LEI A W, CAO Y L, et al. An all-organic rechargeable battery using bipolar polyparaphenylene as a redox-active cathode and anode[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(6): 567-569. |
| 46 | DONG X L, LIN Y X, LI P L, et al. High-energy rechargeable metallic lithium battery at -70 ℃ enabled by a cosolvent electrolyte[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2019, doi: 10.1002/anie.201900266. |
| 47 | LI Y X, LIU L J, LU Y, et al. High-energy-density quinone-based electrodes with [Al(OTF)]2+ storage mechanism for rechargeable aqueous aluminum batteries[J]. Advanced functional materials, 2021(26): 31. |
| 48 | WANG N, DONG X L, WANG B L, et al. Zinc-organic battery with a wide operation-temperature window from -70 to 150 ℃[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(34): 14577-14583. |
| 49 | FAN X L, WANG F, JI X, et al. A universal organic cathode for ultrafast lithium and multivalent metal batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2018, 57(24): 7146-7150. |
| 50 | XU X, REN S Y, WU H, et al. Establishing exceptional durability in ultralow-temperature organic-sodium batteries via stabilized multiphase conversions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(2): 1619-1626. |
| 51 | LU Y, HOU X S, MIAO L C, et al. Cyclohexanehexone with ultrahigh capacity as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2019, 58(21): 7020-7024. |
| 52 | SUN T J, DU H H, ZHENG S B, et al. High power and energy density aqueous proton battery operated at -90 ℃[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(16): 2010127. |
| 53 | WANG Y R, WANG C X, WANG W, et al. Organic hydronium-ion battery with ultralong life[J]. Acs Energy Lett, 2023: 1390-1396. |
| 54 | YAN L, QI Y E, DONG X L, et al. Ammonium-ion batteries with a wide operating temperature window from -40 to 80 ℃[J]. eScience, 2021, 1(2): 212-218. |
| 55 | QUE L F, WU J H, LAN Z, et al. Potassium-based dual-ion batteries operating at -60 ℃ enabled by co‐intercalation anode chemistry[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, doi.org/10.1002/adma.202307592. |
| 56 | QIN J, LAN Q, LIU N, et al. A metal-free battery with pure ionic liquid electrolyte[J]. iScience, 2019, 15: 16-27. |
| 57 | SUN T J, DU H H, ZHENG S B, et al. Bipolar organic polymer for high performance symmetric aqueous proton battery[J]. Small Methods, 2021, 5(8): e2100367. |
| [1] | Qingyi LIU. Energy storage mechanism and performance enhancement strategies of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1871-1873. |
| [2] | Zan DUAN, Lingfang LI, Penghui LIU, Dongfang XIAO. Review on advanced preparation methods and energy storage mechanism of MXenes as energy storage materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 982-990. |
| [3] | XIANG Yu, CAO Gaoping. A review on the mechanism of the energy storage about the electrochemical double-layer capacitors #br# [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2016, 5(6): 816-827. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
