Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (2): 812-821.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0805
• Energy Storage Test: Methods and Evaluation • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xueru LI( ), Zhejie MA(
), Zhejie MA( ), Ping LI(
), Ping LI( )
)
Received:2024-09-02
Online:2025-02-28
Published:2025-03-18
Contact:
Zhejie MA, Ping LI
E-mail:y82220019@mail.ecust.edu.cn;y20190088@mail.ecust.edu.cn;lipingunilab@ecust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Xueru LI, Zhejie MA, Ping LI. Research progress on microstructure characterization of cathode catalyst layer in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 812-821.
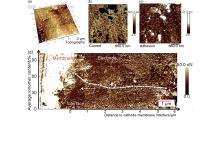
Fig. 8
Cross section of the electrode of a Nafion®-based MEA: (a) 3D topography image; (b) Current mapping at bias voltage U=2 V; (c) Adhesion mapping; (d) Adhesion image of a cross section of the catalyst layer of a Nafion®-based MEA, overlaid with a diagram where white dots indicate the average ionomer content of an area of 1 μm2 with 1 μm step width[31]"
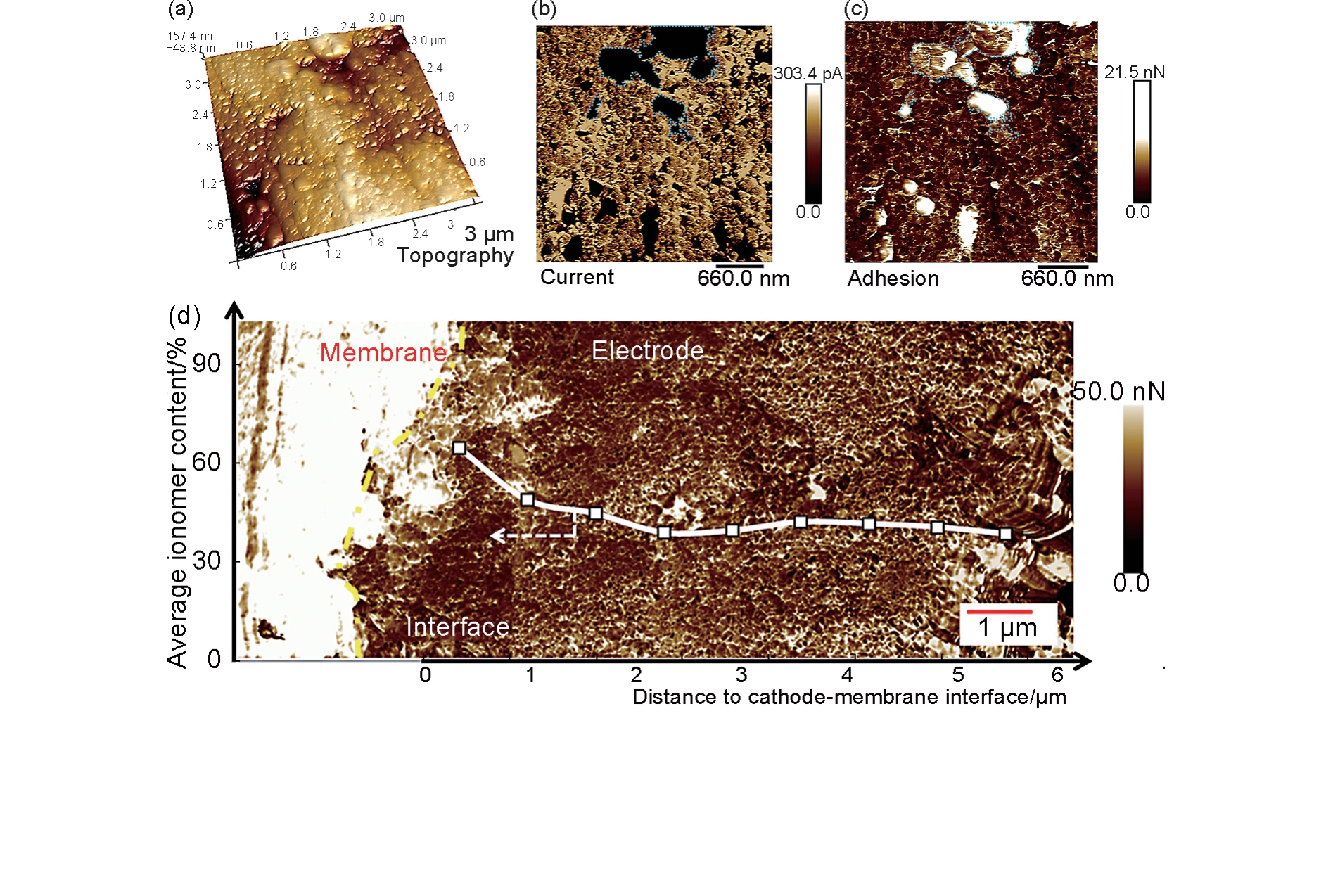
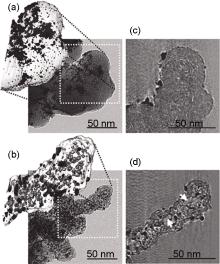
Fig. 10
3D reconstructed images and 2D TEM projections of the two kinds of Pt/Cs, (a) TEC10V50E and (b) TEC10E50E. The gray and black particles in 3D images of part (b) correspond to Pt particles inside and at the surface of carbon substrate. Parts (c) and (d) are the digitally sliced images of TEC10V50E and TEC10E50E. The small pores can be visible inside the carbon as indicated by white arrows in part (d)[37]"

Fig. 11
Representative IL-SEM images of the cathodic catalytic layer highlighting different types of catalyst changes from BOL (fresh) to after each AST session until EOL (14,000 cycles overall). The red circles mark general growth of particles, the yellow dashed square shows particles that migrate and coalesce, and the blue dashed circle represents particles that first grow and then shrink. The markers are not comprehensive and only illustrate the main degradation effects during the AST cycling procedure. Scale bar = 50 nm[40]"
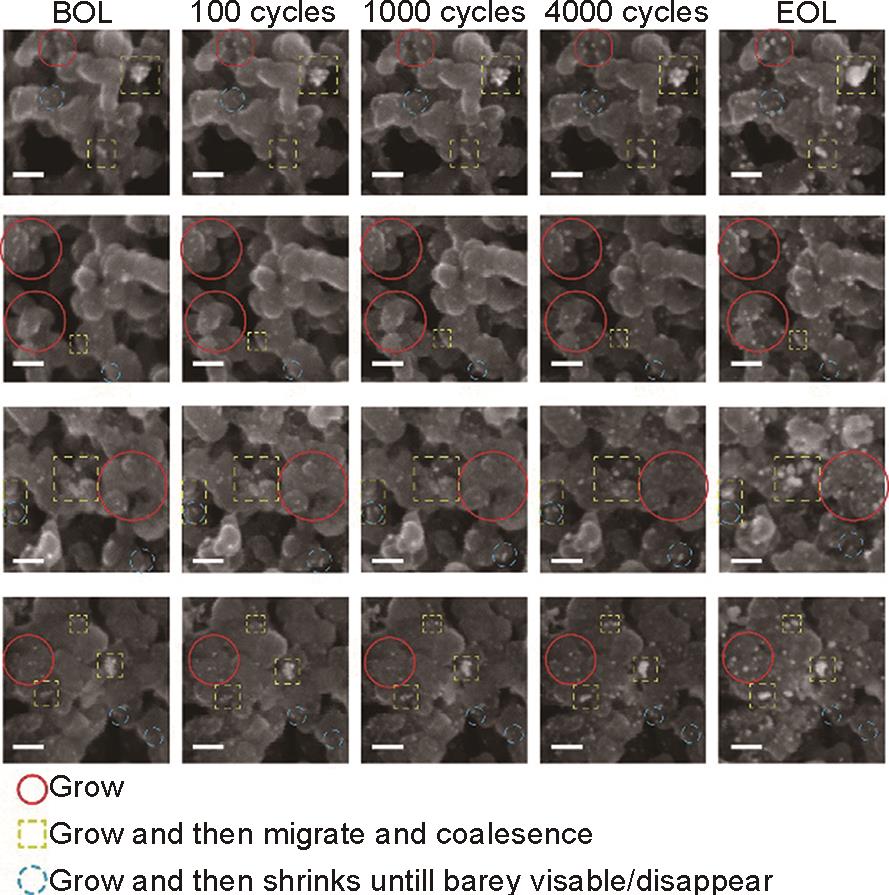
Fig. 12
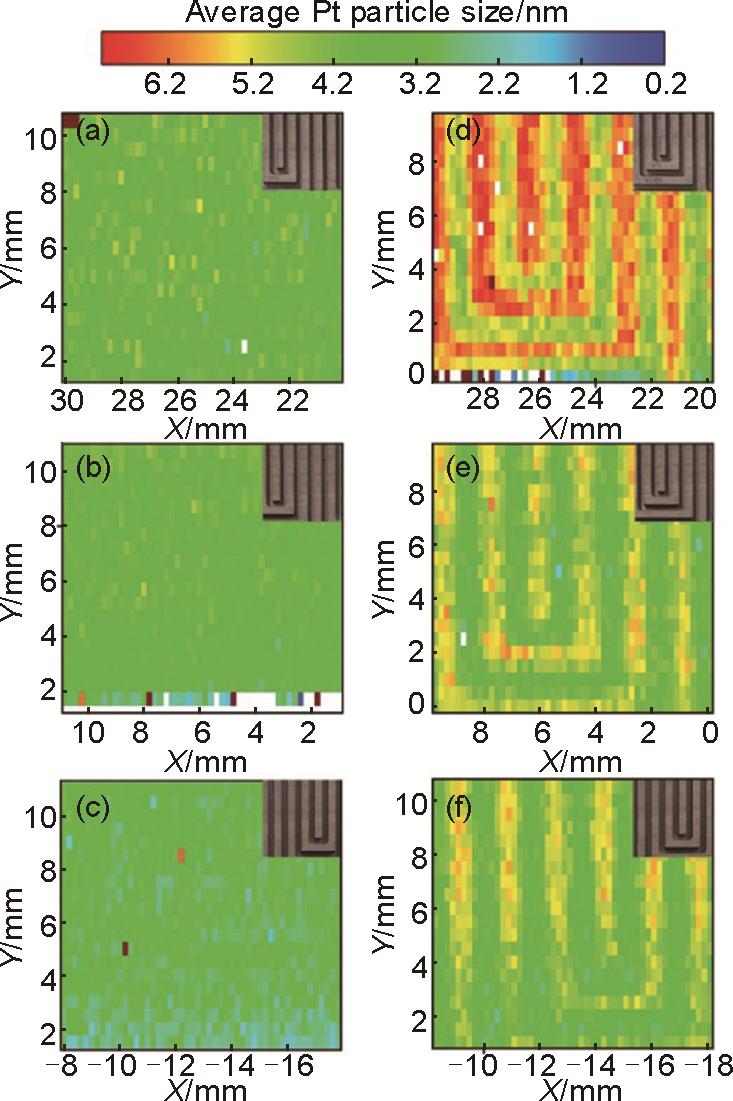
Pt catalyst nanoparticle size mapping of 1 cm × 1 cm area (a) near air outlet of the non-aged MEA (b) in the middle of the flow field of the non-aged MEA, (c) near air inlet of the non-aged MEA, (d) near gas outlet of the post-AST MEA, (e) in the middle of the flow field of the post-AST MEA, and (f) near gas inlet of the post-AST MEA. Insets show the corresponding flow field geometry for each measured 1 cm × 1 cm location[41]"
| 1 | WANG Y, CHEN K S, MISHLER J, et al. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research[J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(4): 981-1007. DOI:10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.09.030. |
| 2 | 吴小员, 卢新宝, 董嘉璇, 等. 燃料电池汽车地方政策研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(6): 1987-1997. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0455. |
| WU X Y, LU X B, DONG J X, et al. Local policy for fuel cell vehicles[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1987-1997. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0455. | |
| 3 | OHMA A, MASHIO T, SATO K, et al. Analysis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell catalyst layers for reduction of platinum loading at Nissan[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(28): 10832-10841. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.04.058. |
| 4 | XIE B, ZHANG G B, XUAN J, et al. Three-dimensional multi-phase model of PEM fuel cell coupled with improved agglomerate sub-model of catalyst layer[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 199: 112051. DOI:10.1016/j.enconman. 2019.112051. |
| 5 | FAN J T, CHEN M, ZHAO Z L, et al. Bridging the gap between highly active oxygen reduction reaction catalysts and effective catalyst layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6: 475-486. DOI:10.1038/s41560-021-00824-7. |
| 6 | LI X Y, WANG X J, HE J, et al. Construction of homogeneous catalyst layers at proton exchange membrane fuel cell cathodes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2023, 170(4): 044511. DOI:10.1149/1945-7111/accb0e. |
| 7 | KARAN K. PEFC catalyst layer: Recent advances in materials, microstructural characterization, and modeling[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 5(1): 27-35. DOI:10.1016/j.coelec.2017.08.018. |
| 8 | GWAK G, LEE J, GHASEMI M, et al. Analyzing oxygen transport resistance and Pt particle growth effect in the cathode catalyst layer of polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(24): 13414-13427. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.080. |
| 9 | SHIN S J, LEE J K, HA H Y, et al. Effect of the catalytic ink preparation method on the performance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 106(1/2): 146-152. DOI:10.1016/S0378-7753(01)01045-X. |
| 10 | SUZUKI T, TSUSHIMA S, HIRAI S. Characterization of the PEMFC catalyst layer by cross-sectional visualization and performance evaluation[J]. ECS Transactions, 2010, 33(1): 1465-1470. DOI:10.1149/1.3484639. |
| 11 | DURST J, LAMIBRAC A, CHARLOT F, et al. Degradation heterogeneities induced by repetitive start/stop events in proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Inlet vs. outlet and channel vs. land[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 138: 416-426. DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.03.021. |
| 12 | THIELE S, VIERRATH S, KLINGELE M, et al. Tomographic analysis of polymer electrolyte fuel cell catalyst layers: Methods, validity and challenges[J]. ECS Transactions, 2015, 69(17): 409-418. DOI:10.1149/06917.0409ecst. |
| 13 | BLOM D A, DUNLAP J R. Preparation of cross-sectional samples of proton exchange membrane fuel cells for TEM characterization[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2003, 9(S02): 802-809. DOI:10.1017/s1431927603444012. |
| 14 | DE A MELO L G, HITCHCOCK A P, BEREJNOV V, et al. Evaluating focused ion beam and ultramicrotome sample preparation for analytical microscopies of the cathode layer of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 312: 23-35. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.02.019. |
| 15 | MORENO-ATANASIO R, WILLIAMS R A, JIA X D. Combining X-ray microtomography with computer simulation for analysis of granular and porous materials[J]. Particuology, 2010, 8(2): 81-99. DOI:10.1016/j.partic.2010.01.001. |
| 16 | EPTING W K, GELB J, LITSTER S. Resolving the three-dimensional microstructure of polymer electrolyte fuel cell electrodes using nanometer-scale X-ray computed tomography[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(3): 555-560. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201101525. |
| 17 | POKHREL A, EL HANNACH M, ORFINO F P, et al. Failure analysis of fuel cell electrodes using three-dimensional multi-length scale X-ray computed tomography[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 329: 330-338. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016. 08.092. |
| 18 | LITSTER S, EPTING W K, WARGO E A, et al. Morphological analyses of polymer electrolyte fuel cell electrodes with nano-scale computed tomography imaging[J]. Fuel Cells, 2013, 13(5): 935-945. DOI:10.1002/fuce.201300008. |
| 19 | SINGH R, AKHGAR A R, SUI P C, et al. Dual-beam FIB/SEM characterization, statistical reconstruction, and pore scale modeling of a PEMFC catalyst layer[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(4): F415-F424. DOI:10.1149/2.036404jes. |
| 20 | NAN N, WANG J X. FIB-SEM three-dimensional tomography for characterization of carbon-based materials[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 2019: 8680715. DOI:10.1155/2019/8680715. |
| 21 | ZIEGLER C, THIELE S, ZENGERLE R. Direct three-dimensional reconstruction of a nanoporous catalyst layer for a polymer electrolyte fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(4): 2094-2097. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.09.044. |
| 22 | SCHULENBURG H, SCHWANITZ B, LINSE N, et al. 3D imaging of catalyst support corrosion in polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(29): 14236-14243. DOI:10.1021/jp203016u. |
| 23 | OKUMURA M, NODA Z, MATSUDA J, et al. Correlating cathode microstructure with PEFC performance using FIB-SEM and TEM[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(9): F928-F934. DOI:10.1149/2.0581709jes. |
| 24 | KURODA C S, YAMAZAKI Y. Novel technique of MEA sample preparation using a focused ion beam for scanning electron microscope investigation[J]. ECS Transactions, 2007, 11(1): 509-516. DOI:10.1149/1.2780964. |
| 25 | KATAYANAGI Y, SHIMIZU T, HASHIMASA Y, et al. Cross-sectional observation of nanostructured catalyst layer of polymer electrolyte fuel cell using FIB/SEM[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 280: 210-216. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.085. |
| 26 | MONTEIRO S N, PACIORNIK S. From historical backgrounds to recent advances in 3D characterization of materials: An overview[J]. JOM, 2017, 69(1): 84-92. DOI:10.1007/s11837-016-2203-8. |
| 27 | LI J, MALIS T, DIONNE S. Recent advances in FIB–TEM specimen preparation techniques[J]. Materials Characterization, 2006, 57(1): 64-70. DOI:10.1016/j.matchar.2005.12.007. |
| 28 | HUANG J, LI Z, ZHANG J B. Review of characterization and modeling of polymer electrolyte fuel cell catalyst layer: The blessing and curse of ionomer[J]. Frontiers in Energy, 2017, 11(3): 334-364. DOI:10.1007/s11708-017-0490-6. |
| 29 | MORE K, BORUP R, REEVES K. Identifying contributing degradation phenomena in PEM fuel cell membrane electride assemblies via electron microscopy[J]. ECS Transactions, 2006, 3(1): 717. DOI:10.1149/1.2356192. |
| 30 | LOPEZ-HARO M, GUÉTAZ L, PRINTEMPS T, et al. Three-dimensional analysis of Nafion layers in fuel cell electrodes[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5229. DOI:10.1038/ncomms 6229. |
| 31 | HIESGEN R, MORAWIETZ T, HANDL M, et al. Atomic force microscopy on cross sections of fuel cell membranes, electrodes, and membrane electrode assemblies[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 162: 86-99. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.122. |
| 32 | KOMINI BABU S, CHUNG H T, ZELENAY P, et al. Resolving electrode morphology's impact on platinum group metal-free cathode performance using nano-CT of 3D hierarchical pore and ionomer distribution[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(48): 32764-32777. DOI:10.1021/acsami.6b08844. |
| 33 | NORMILE S J, ZENYUK I V. Imaging ionomer in fuel cell catalyst layers with synchrotron nano transmission X-ray microscopy[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2019, 335: 38-46. DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2019. 02.017. |
| 34 | PARK Y C, TOKIWA H, KAKINUMA K, et al. Effects of carbon supports on Pt distribution, ionomer coverage and cathode performance for polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 315: 179-191. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2016.02.091. |
| 35 | MIDGLEY P A, WEYLAND M. 3D electron microscopy in the physical sciences: The development of Z-contrast and EFTEM tomography[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2003, 96(3/4): 413-431. DOI:10.1016/S0304-3991(03)00105-0. |
| 36 | NISHIOKA H, NIIHARA K I, KANEKO T, et al. Three-dimensional structure of a polymer/clay nanocomposite characterized by transmission electron microtomography[J]. Composite Interfaces, 2006, 13(7): 589-603. DOI:10.1163/156855406778440695. |
| 37 | ITO T, MATSUWAKI U, OTSUKA Y, et al. Three-dimensional spatial distributions of Pt catalyst nanoparticles on carbon substrates in polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Electrochemistry, 2011, 79(5): 374-376. DOI:10.5796/electrochemistry.79.374. |
| 38 | HUNGRÍA A B, CALVINO J J, HERNÁNDEZ-GARRIDO J C. HAADF-STEM electron tomography in catalysis research[J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2019, 62(12): 808-821. DOI:10.1007/s11244-019-01200-2. |
| 39 | SNEED B T, CULLEN D A, REEVES K S, et al. 3D analysis of fuel cell electrocatalyst degradation on alternate carbon supports[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(35): 29839-29848. DOI:10.1021/acsami.7b09716. |
| 40 | SHOKHEN V, STRANDBERG L, SKOGLUNDH M, et al. Impact of accelerated stress tests on the cathodic catalytic layer in a proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell studied by identical location scanning electron microscopy[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(9): 11200-11212. DOI:10.1021/acsaem.2c01790. |
| 41 | CHENG L, KHEDEKAR K, REZAEI TALARPOSHTI M, et al. Mapping of heterogeneous catalyst degradation in polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(28): 2000623. DOI:10.1002/aenm.202000623. |
| [1] | Jianru ZHANG, Qiyu WANG, Qinghao LI, Xianying ZHANG, Bitong WANG, Xiqian YU, Hong LI. Physical characterization techniques and applications in lithium battery failure analysis [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 286-309. |
| [2] | Qiquan ZENG, Maji LUO, Yinlong YANG, Qingze HUANG. Life prediction of fuel cells based on the LSTM-UPF hybrid method [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 963-970. |
| [3] | Jing BAI, Huifang FAN, Siqi CUI, Chuang XU, Yi ZHANG, Size GUAN, Hanfei YANG, Yifei JIA, Shuwei GENG, Huifan ZHENG. Experimental study on heat dissipation performance of automotive fuel cells [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 390-395. |
| [4] | Chao YU, Gechuanqi PAN. Molecular dynamics study on structure and thermal properties of high-performance chloride molten salt [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(12): 4368-4380. |
| [5] | Chengbin JIN, Yiyu HUANG, Xinyong TAO, Ouwei SHENG. Formation mechanism of dead lithium in lithium metal batteries and its solutions [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 24-35. |
| [6] | Yonghui ZHANG, Jie FU, Xianfeng LI, Changkun ZHANG. Research progress on in-situ characterization techniques for aqueous organic flow batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2971-2984. |
| [7] | Yongshuai YU, Yongfeng LIU, Pucheng PEI, Lu ZHANG, Shengzhuo YAO. Effect of cathode relative humidity on membrane water content and performance of PEMFC [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(6): 1755-1764. |
| [8] | Heqing TIAN, Zhaoyang KOU, Junjie ZHOU, Yinsheng YU. Molecular dynamics simulation of structure and thermal properties of LiCl-KCl molten salt nanofluids [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 654-660. |
| [9] | Xing WANG, Jun SUN, Ningfang CHEN, Li YAN. Modeling of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell cooling system based on the Simscape temperature control strategy [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 857-869. |
| [10] | Keke LIU, Yongfeng LIU, Pucheng PEI, Shengzhuo YAO, Lu ZHANG. Design of a novel flow channel structure of PEMFC based on Koch snowflake [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(11): 3361-3368. |
| [11] | Yezhou HU, Shuang WANG, Tao SHEN, Ye ZHU, Deli WANG. Recent progress in confined noble-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1264-1277. |
| [12] | Siqi LYU, Na LI, Haosen CHEN, Shuqiang JIAO, Weili SONG. Progresses in visualization and quantitative analysis of the electrode process in rechargeable batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 795-817. |
| [13] | Zhenyi WANG, Sai ZHANG, Shiwang HU. Fractal modeling and thermal chemical coupling of electrode microstructure of lithium battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 3574-3582. |
| [14] | Jiahao YANG, Zhaoping SHI, Yibo WANG, Junjie GE, Changpeng LIU, Wei XING. In-situ/operando characterization techniques for oxygen evolution in acidic media [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1877-1890. |
| [15] | Zhihao LI, Hao PENG, Yaqin CHEN. Neural network prediction model for temperature distribution of proton exchange membrane fuel cell membrane electrode assembly [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2053-2059. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
