Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (4): 1225-1238.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0075
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoping ZHANG( ), Yuanjia RONG, Qianyan WANG, Menglin GAO, Yaling LIAO, Minsheng WU, Xinxin ZHUANG, Zhongyu HUANG, Meijun WAN, Weirong CHEN(
), Yuanjia RONG, Qianyan WANG, Menglin GAO, Yaling LIAO, Minsheng WU, Xinxin ZHUANG, Zhongyu HUANG, Meijun WAN, Weirong CHEN( )
)
Received:2024-01-25
Revised:2024-02-10
Online:2024-04-26
Published:2024-04-22
Contact:
Xiaoping ZHANG, Weirong CHEN
E-mail:zxp@swjtu.edu.cn;wrchen@swjtu.cn
CLC Number:
Xiaoping ZHANG, Yuanjia RONG, Qianyan WANG, Menglin GAO, Yaling LIAO, Minsheng WU, Xinxin ZHUANG, Zhongyu HUANG, Meijun WAN, Weirong CHEN. Advancements in insitu characterization techniques for lithium-oxygen batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1225-1238.

Fig. 1
(a) A schematic view of micro-scale all-solid-state Li-O2 battery assembled in the ESEM chamber[14]; (b) Product morphology observed during the discharge process[14]; (c) Growth process of a spherical particle during the discharge process. Yellow arrows indicate that the spherical particle grew up at TPI[14];(d) Decomposition process of the spherical particle during the charge process. Red arrows indicate the position where the particle decomposed[14]"

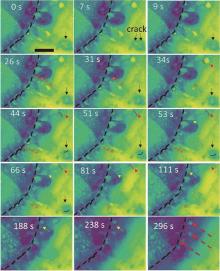
Fig. 2
Time-sequential STEM images showing the full charge process at the glassy carbon electrode. The dashed black lines indicate the surface of carbon electrode. The solid and dashed arrows with different colors indicate the decomposition kinetics of specific Li2O2 particles. The dashed red arrows at 296 s indicate the deactivated Li2O2 particles[20]"
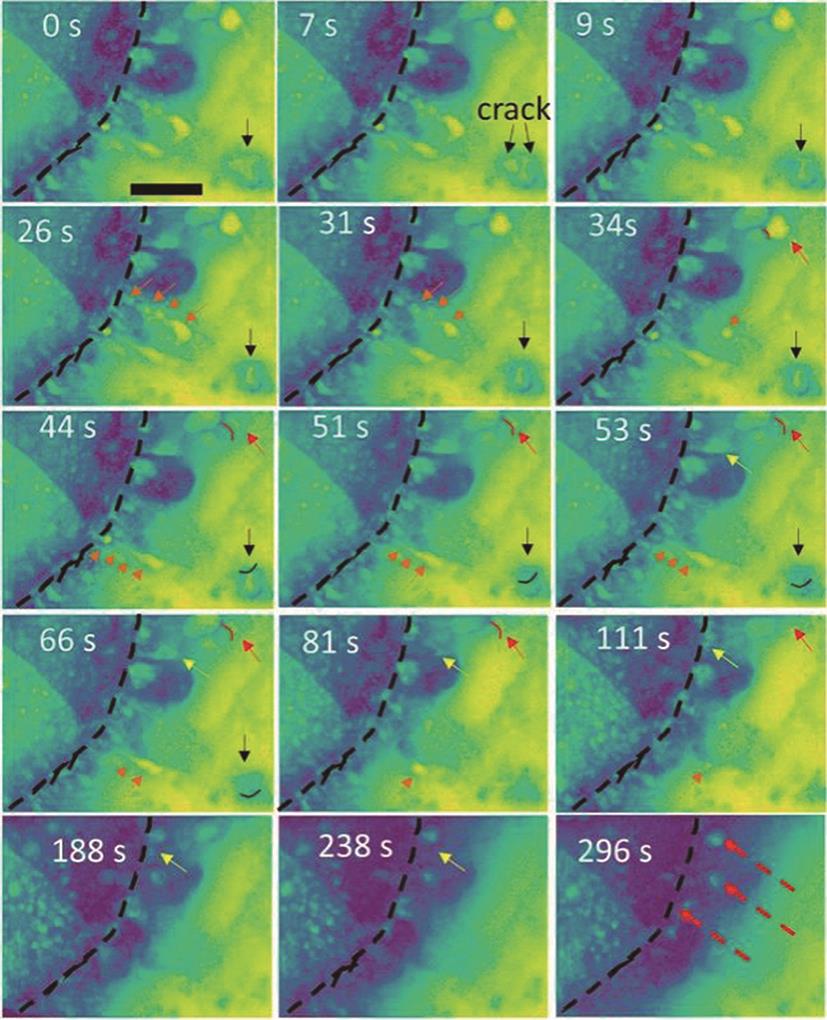

Fig. 6
(a) Insitu XRD patterns of Li2O2 during charge. The left image is the charging curve. The two images on the right are the enlarged XRD patterns[35]; (b) Insitu XRD patterns of Li2O during charge. The left image is the charging curve. The two images on the right are the enlarged XRD patterns[35]; (c) Left: the residual Li2O2 ratios for the electrodes with the same amount of different electrocatalysts (MNT, 0.5% Ru/MNT, 2% Ru/MNT and home-made Ru nano particles) after charging for 15 h at a constant current density; right: the operando SR-PXD patterns of an electrode with 2% Ru/MNT collected every 30 min during charging for 15 h at a constant current density[35]"

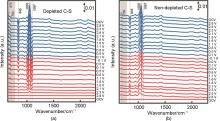
Fig. 7
In-situ FTIR spectra with external reflection configuration obtained on Cu electrode in (a) deoxygenated and (b) oxygenated 0.1 mol/L LiClO4-DMSO electrolytes, respectively[39]. The dashed lines represent the appearance/change of FT-IR peaks at various potentials. The “◇” represents peaks of DMSO solvent"

Fig. 10
Design of a lithium-oxygen cell for in-situ NMR experiment[42]: (a) Schematic drawing and model of the double-compartment cylindrical cell and (b) Photograph and model of the cell mounted on the NMR probehead; (c) NMR line-fitting of the operando spectra at t = 2 h (beginning of discharge), 18 h (end of the first discharge) and 40 h (end of first charge) reveals the spectral evolution at the different cycling periods[42]"
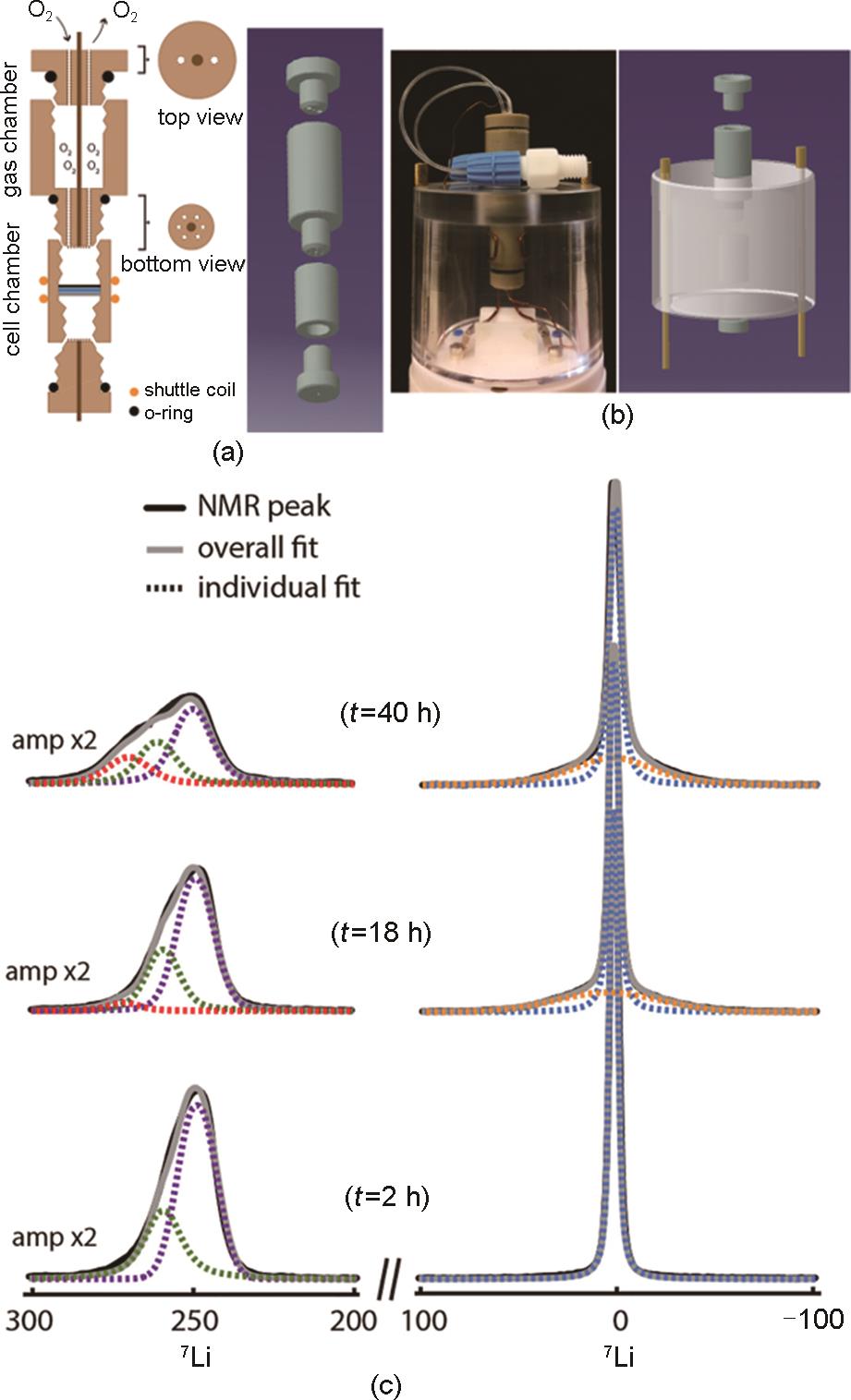
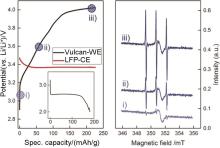
Fig. 11
Charging curve of Li2O2 in an in-situ EPR cell with 0.5 mol/L LiTFSI in diglyme containing 0.1 mol/L 4-oxo-TEMP as a spin trap under an argon atmosphere; inset: previous discharge in a standard cell under an oxygen atmosphere (left) and in-situ EPR spectra, recorded at the different charging potentials(right)[43]"
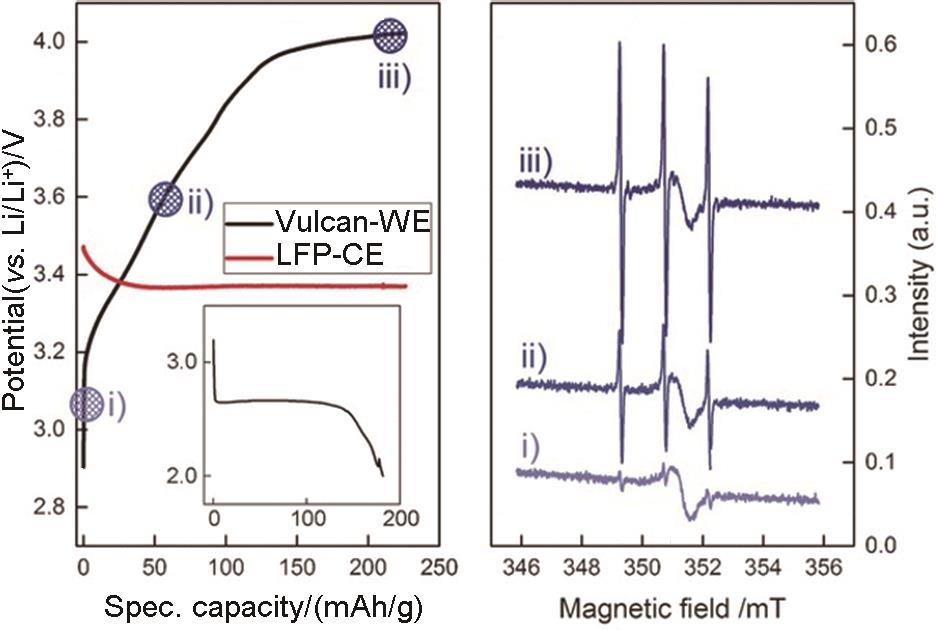
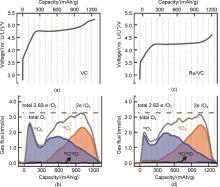
Fig. 14
(a)The charging profiles of Li-O2 cells with the VC electrode[49]; (b)?OEMS O2 evolution analysis of Li-O2 cells with the VC electrode[49]; (c)?The charging profiles of Li-O2 cells with the Ru/VC electrode[49]; (d)?OEMS O2 evolution analysis of Li-O2 cells with the Ru/VC electrode[49]"

| 1 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451: 652-657. |
| 2 | BRUCE P G, SCROSATI B, TARASCON J M. Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(16): 2930-2946. |
| 3 | TARASCON J M, ARMAND M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Nature, 2001, 414: 359-367. |
| 4 | ZHANG W J. A review of the electrochemical performance of alloy anodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(1): 13-24. |
| 5 | LIN D C, LIU Y Y, CUI Y. Reviving the lithium metal anode for high-energy batteries[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12: 194-206. |
| 6 | LU Y C, GALLANT B M, KWABI D G, et al. Lithium-oxygen batteries: Bridging mechanistic understanding and battery performance[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(3): 750-768. |
| 7 | WHITTINGHAM M S. Lithium batteries and cathode materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4271-4301. |
| 8 | BRANDT K. Historical development of secondary lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1994, 69(3/4): 173-183. |
| 9 | SADD M, XIONG S Z, BOWEN J R, et al. Investigating microstructure evolution of lithium metal during plating and stripping via operando X-ray tomographic microscopy[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 854. |
| 10 | LI X, ZHENG J M, REN X D, et al. Dendrite-free and performance-enhanced lithium metal batteries through optimizing solvent compositions and adding combinational additives[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(15): 1703022. |
| 11 | KANG J H, LEE J, JUNG J W, et al. Lithium-air batteries: Air-breathing challenges and perspective[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11): 14549-14578. |
| 12 | KANG S, MO Y F, ONG S P, et al. A facile mechanism for recharging Li2O2 in Li-O2 batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(16): 3328-3336. |
| 13 | LI H Y, GUO S H, ZHOU H S. In-situ/operando characterization techniques in lithium-ion batteries and beyond[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 59: 191-211. |
| 14 | ZHENG H, XIAO D D, LI X, et al. New insight in understanding oxygen reduction and evolution in solid-state lithium-oxygen batteries using an in situ environmental scanning electron microscope[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(8): 4245-4249. |
| 15 | ZHOU S Y, LIU K G, YING Y F, et al. Perspective of operando/in situ scanning electron microscope in rechargeable batteries[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2023, 41: 101374. |
| 16 | MÉTOIS J J, NITSCHE S, HEYRAUD J C. An ultra-high-vacuum transmission and scanning electron microscope for crystal growth experiments[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1989, 27(4): 349-357. |
| 17 | 陆敬予, 柯承志, 龚正良, 等. 原位表征技术在全固态锂电池中的应用[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(19): 236-262. |
| LU J Y, KE C Z, GONG Z L, et al. Application of in situ characterization techniques in all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(19): 236-262. | |
| 18 | SU Q M, XIE J, Du G H, et al. In situ transmission electron microscopy observation of electrochemical behavior of CoS2 in lithium-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(4): 3016-3022. |
| 19 | KUSHIMA A, KOIDO T, FUJIWARA Y, et al. Charging/discharging nanomorphology asymmetry and rate-dependent capacity degradation in Li-oxygen battery[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(12): 8260-8265. |
| 20 | HE K, BI X, YUAN Y, et al. Operando liquid cell electron microscopy of discharge and charge kinetics in lithium-oxygen batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 49: 338-345. |
| 21 | AHN S, ZOR C, YANG S X, et al. Why charging Li-air batteries with current low-voltage mediators is slow and singlet oxygen does not explain degradation[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2023, 15: 1022-1029. |
| 22 | YANG C C, HAN J H, LIU P, et al. Direct observations of the formation and redox-mediator-assisted decomposition of Li2O2 in a liquid-cell Li-O2 microbattery by scanning transmission electron microscopy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(41): 1702752. |
| 23 | HOU C, HAN J H, LIU P, et al. Synergetic effect of liquid and solid catalysts on the energy efficiency of Li-O2 batteries: Cell performances and operando STEM observations[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(3): 2183-2190. |
| 24 | SHIM J H, KANG H, LEE S H, et al. Utilization of electron-beam irradiation under atomic-scale chemical mapping for evaluating the cycling performance of lithium transition metal oxide cathodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(4): 2429-2437. |
| 25 | WANG X F, LI Y J, MENG Y S. Cryogenic electron microscopy for characterizing and diagnosing batteries[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(11): 2225-2234. |
| 26 | LI Y Z, LI Y B, PEI A, et al. Atomic structure of sensitive battery materials and interfaces revealed by cryo-electron microscopy[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6362): 506-510. |
| 27 | LLEWELLYN A V, MATRUGLIO A, BRETT D J L, et al. Using in-situ laboratory and synchrotron-based X-ray diffraction for lithium-ion batteries characterization: A review on recent developments[J]. Condensed Matter, 2020, 5(4): 75. |
| 28 | XU C, MÄRKER K, LEE J H, et al. Bulk fatigue induced by surface reconstruction in layered Ni-rich cathodes for Li-ion batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2021, 20: 84-92. |
| 29 | WEN Y X, DING S J, MA C C, et al. In situ TEM visualization of Ag catalysis in Li-O2 nanobatteries[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(5): 6833-6839. |
| 30 | WANG M M, SONG Z B, BI J X, et al. Probing interfacial electrochemistry by in situ atomic force microscope for battery characterization[J]. Battery Energy, 2023, 2(6): 20230006. |
| 31 | SHEN Z Z, LANG S Y, ZHOU C, et al. In situ realization of water-mediated interfacial processes at nanoscale in aprotic Li-O2 batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(46): 2002339. |
| 32 | WEN R, BYON H R. In situ monitoring of the Li-O2 electrochemical reaction on nanoporous gold using electrochemical AFM[J]. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(20): 2628-2631. |
| 33 | CORTÉS H A, CORTI H R. In-situ characterization of discharge products of lithium-oxygen battery using flow electrochemical atomic force microscopy[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2021, 230: 113369. |
| 34 | YAO K P C, KWABI D G, QUINLAN R A, et al. Thermal stability of Li2O2 and Li2O for Li-air batteries: In situ XRD and XPS studies[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(6): A824-A831. |
| 35 | ZHANG T, AMINE R, BI X X, et al. Exploring the charge reactions in a Li-O2 system with lithium oxide cathodes and nonaqueous electrolytes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(26): 15615-15620. |
| 36 | GAO R, ZHOU D, NING D, et al. Probing the self-boosting catalysis of LiCoO2 in Li-O2 battery with multiple in situ/operando techniques[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(28): 2002223. |
| 37 | LUO X Y, PIERNAVIEJA-HERMIDA M, LU J, et al. Pd nanoparticles on ZnO-passivated porous carbon by atomic layer deposition: An effective electrochemical catalyst for Li-O2 battery[J]. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(16): 164003. |
| 38 | MA L, WANG L G, LIU T C, et al. Probing distinctive redox mechanism in Ni-rich cathode via real-time quick X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(1): e2201173. |
| 39 | ZHAO Z W, PANG L, WU Y Y, et al. In situ spectroscopic probing of oxygen crossover effects on solid electrolyte interphase in aprotic lithium-oxygen batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(29): 2301127. |
| 40 | JOSEPETTI D M, SOUSA B P, RODRIGUES S A J, et al. The initial stages of Li2O2 formation during oxygen reduction reaction in Li-O2 batteries: The significance of Li2O2 in charge-transfer reactions within devices[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 88: 223-231. |
| 41 | GE A M, NAGAI R, NEMOTO K, et al. Unraveling the solvent stability on the cathode surface of Li-O2 batteries by using in situ vibrational spectroscopies[J]. Faraday Discussions, 2024, 248: 119-133. |
| 42 | GAUTHIER M, NGUYEN M H, BLONDEAU L, et al. Operando NMR characterization of a metal-air battery using a double-compartment cell design[J]. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 113: 101731. |
| 43 | WANDT J, JAKES P, GRANWEHR J, et al. Singlet oxygen formation during the charging process of an aprotic lithium-oxygen battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(24): 6892-6895. |
| 44 | 杨家豪, 施兆平, 王意波, 等. 用于酸性析氧反应研究的原位表征技术[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(6): 1877-1890. |
| YANG J H, SHI Z P, WANG Y B, et al. In-situ/operando characterization techniques for oxygen evolution in acidic media[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1877-1890. | |
| 45 | 徐伦. 高性能锂/氧气电池制备及其基础性能研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2014. |
| XU L. Design and investigation of lithium/oxygen batteries with advanced performances[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2014. | |
| 46 | TSIOUVARAS N, MEINI S, BUCHBERGER I, et al. A novel on-line mass spectrometer design for the study of multiple charging cycles of a Li-O2 battery[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(3): A471-A477. |
| 47 | LIANG Z J, ZOU Q L, XIE J, et al. Suppressing singlet oxygen generation in lithium-oxygen batteries with redox mediators[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(9): 2870-2877. |
| 48 | LIANG Z J, ZOU Q L, WANG Y, et al. Recent progress in applying in situ/operando characterization techniques to probe the solid/liquid/gas interfaces of Li-O2 batteries[J]. Small Methods, 2017, 1(7): 1700150. |
| 49 | WANG Y, LU Y C. Isotopic labeling reveals active reaction interfaces for electrochemical oxidation of lithium peroxide[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(21): 6962-6966. |
| 50 | LAI N C, CONG G T, LIANG Z J, et al. A highly active oxygen evolution catalyst for lithium-oxygen batteries enabled by high-surface-energy facets[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(8): 1511-1521. |
| 51 | LIANG Z, WANG W, LU Y C. The path toward practical Li-air batteries[J]. Joule, 2022, 6(11): 2458-2473. |
| 52 | GÖLDNER V, ULKE J, KIRCHNER B, et al. Electrochemistry-mass spectrometry bridging the gap between suspect and target screening of valsartan transformation products in wastewater treatment plant effluent[J]. Water Research, 2023, 244: 120525. |
| 53 | KIM S, KIM H S, KIM B, et al. In situ gas analysis by differential electrochemical mass spectrometry for advanced rechargeable batteries: A review[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(39): 2301983. |
| 54 | SIM R, LANGDON J, MANTHIRAM A. Design of an online electrochemical mass spectrometry system to study gas evolution from cells with lean and volatile electrolytes[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(6): 2201438. |
| [1] | Xupeng XU, Xuming XU, Hongyan CHEN, LIANGYaru, Weixin LEI, Zengsheng MA, Guoxin CHEN, Peiling KE. Applications of in situ characterization techniques in the study of lithium-sulfur battery mechanisms [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1239-1252. |
| [2] | Su YAN, Fangfang ZHONG, Junwei LIU, Mei DING, Chuankun JIA. Key materials and advanced characterization of high-energy-density flow battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 143-156. |
| [3] | Cai TANG, Jiangmin JIANG, Xinfeng WANG, Guangfa LIU, Yanhua CUI, Quanchao ZHUANG. Research progress of Li/CF x primary batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1093-1109. |
| [4] | Kejun CHEN, Lijun FAN. Controllable synthesis of Co2+-doped FeS2 and their sodium storage performances [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(10): 3056-3063. |
| [5] | Siqi LYU, Na LI, Haosen CHEN, Shuqiang JIAO, Weili SONG. Progresses in visualization and quantitative analysis of the electrode process in rechargeable batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 795-817. |
| [6] | Zhiwei ZHAO, Zhi YANG, Zhangquan PENG. Application of time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry in lithium-based rechargeable batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 781-794. |
| [7] | Yuexia LI, Quanbing LIU. Application of MXene-based nanomaterials in electrocatalysis for oxygen reduction reaction [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1918-1930. |
| [8] | ZHANG Sanpei,WEN Zhaoyin. Review on sodium-air batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2016, 5(3): 249-257. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
