Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (6): 2320-2335.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.1223
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhaoting YIN( ), Wei GUO(
), Wei GUO( ), Jinxin WANG, Yang MENG
), Jinxin WANG, Yang MENG
Received:2024-12-24
Revised:2025-01-05
Online:2025-06-28
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Wei GUO
E-mail:qujiang000@126.com;weiguo-nwpu@nwpu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Zhaoting YIN, Wei GUO, Jinxin WANG, Yang MENG. Modification strategies and development prospects for positive electrodes for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2320-2335.
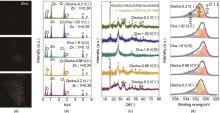
Fig. 7
The Zn2+and H+ co-embedding energy storage mechanism in Zn-VO x batteries[32] (a) Changes in Zn2+ energy spectrum during discharge process; Changes in the (b) Zn/V content ratio in the cathode material during the charging and discharging process; (c) Non in situ XRD pattern; (d) XPS spectra of O1s[13]"
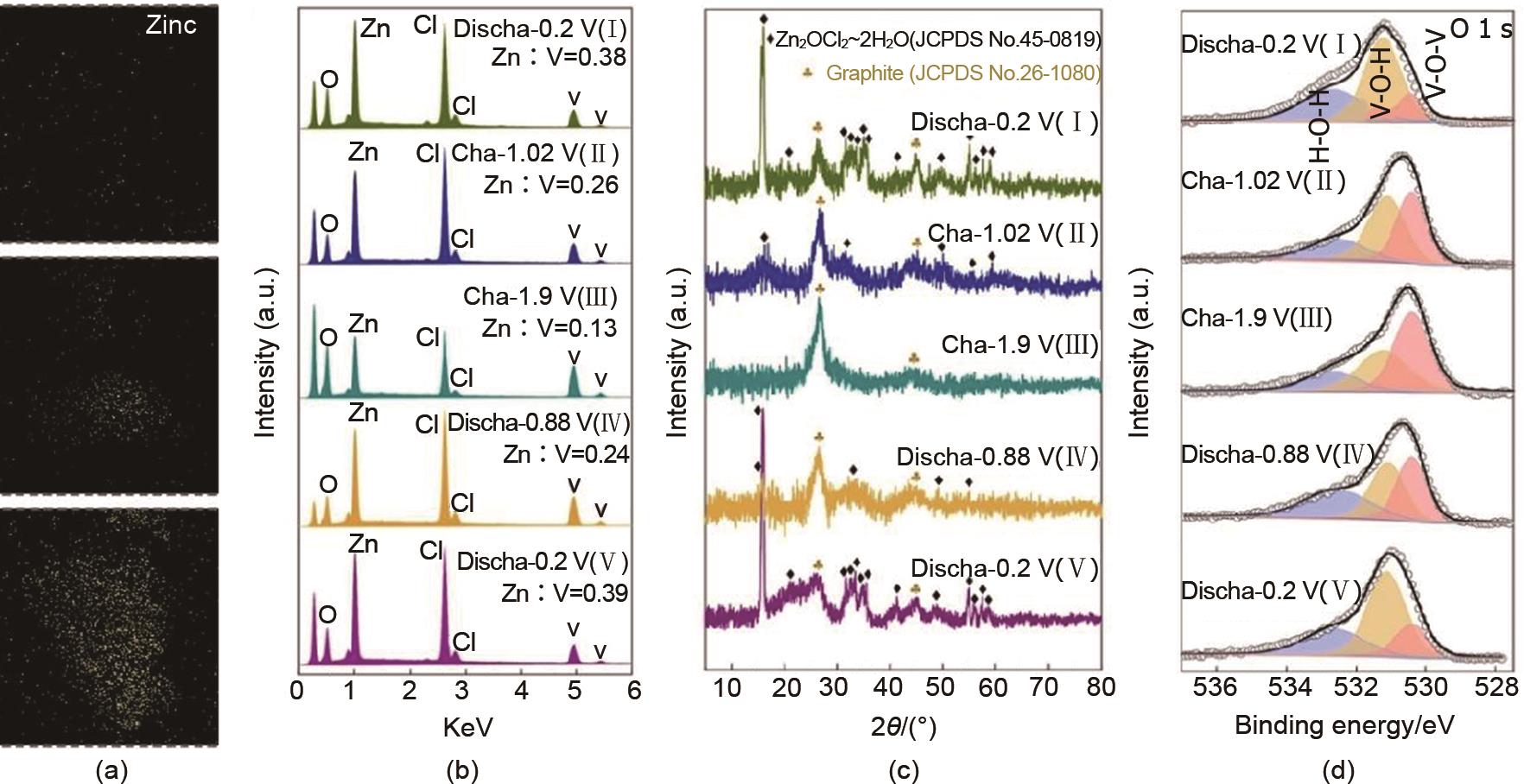
Fig. 13
(a) preparation process, (b) EPR spectrum, O 1s spectrum, and (d) variation of oxygen vacancy to lattice oxygen ratio of reversible manganese based cathode material rich in oxygen vacancies[58]; (e) Preparation process of NiCo2O4 cathode material rich in oxygen vacancies (Od-NiCo2O4), (f) oxygen vacancy content and (g) Co2+/Co3+ ratio at different electrochemical activation times, (h) effect of different oxygen vacancy contents on the average adsorption energy of OH-, (i) Logan curve, and (j) capacity retention rate of the entire battery after 8000 cycles[60]"
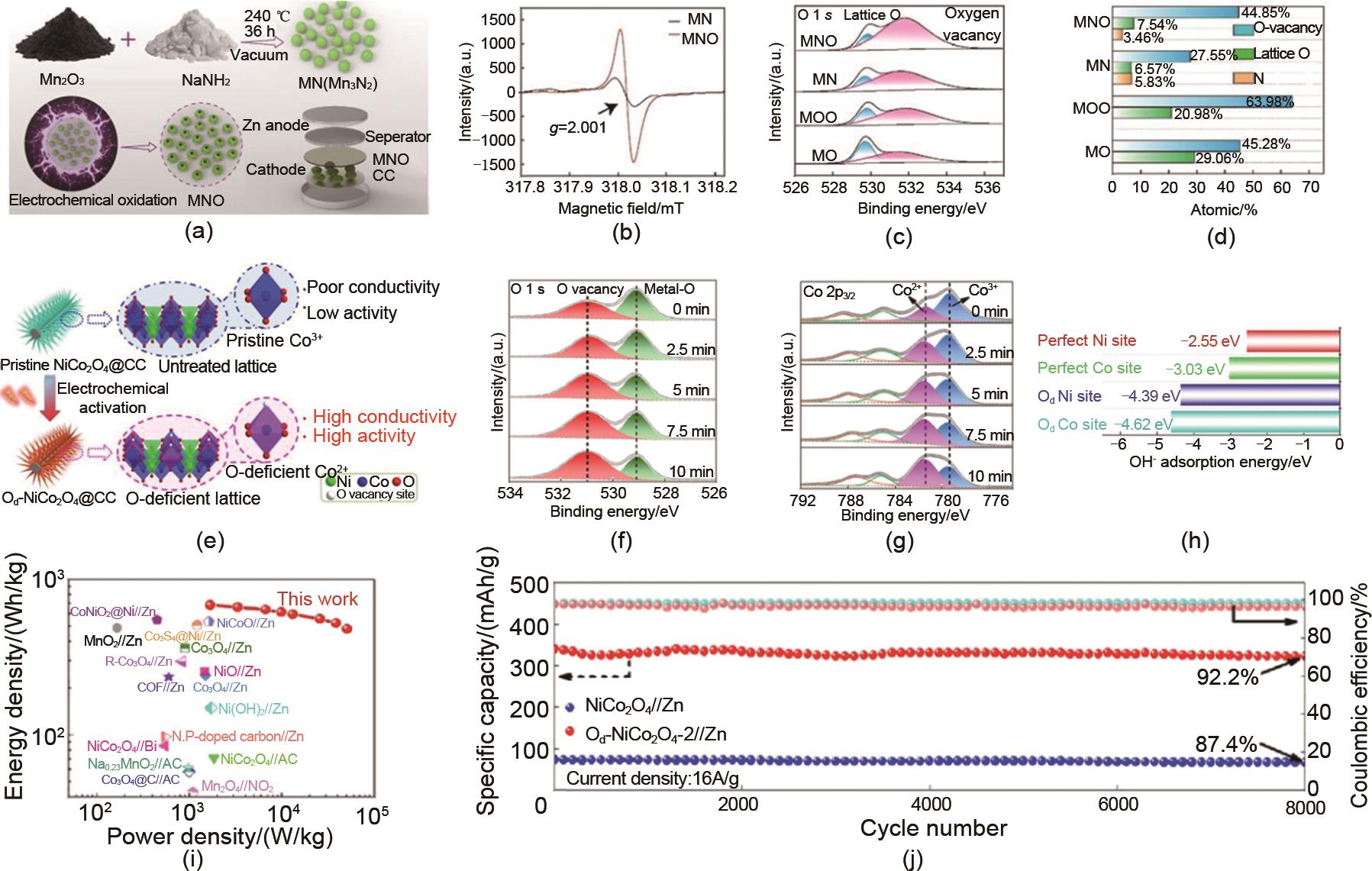
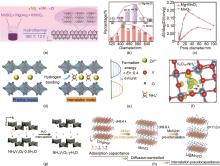
Fig. 14
(a) Preparation process, (b) Particle size, and (c) Average pore size of magnesium doped layered MnO2 cathode[51]; (d) preparation process, (e) formation energy and (f) hydrogen bonding interaction model between NH4+ and VO of V6O13 (VO-NH) cathode with ammonium intercalation[62]; (g) preparation of water molecule intercalated NH4V3O8 nano cathode[64]; (h) Double ion sequential intercalation for Li@MnVO cathode[70]"
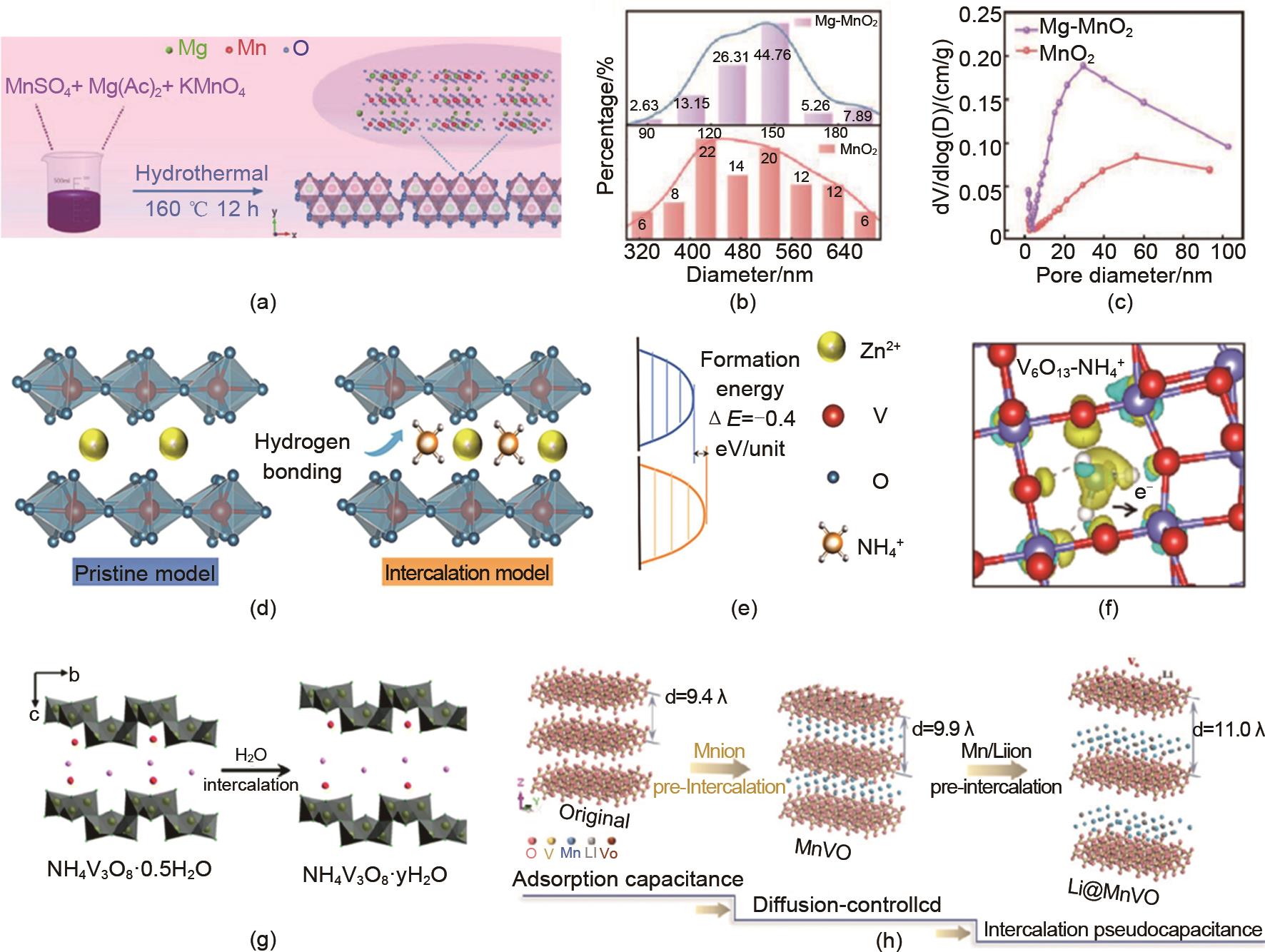
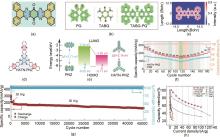
Fig. 15
(a) Molecular structure, (b) π electron localization (ELF-π) and (c) π electron localization orbital locator (LOL-π) of TABQ-PQ molecules[52]; (d) Molecular structure, (e) LUMO/LUMO energy levels, (f) Rate performance, (g) Cycling performance and (h) Power density and energy density comparison of HATN-PNZ[30]"
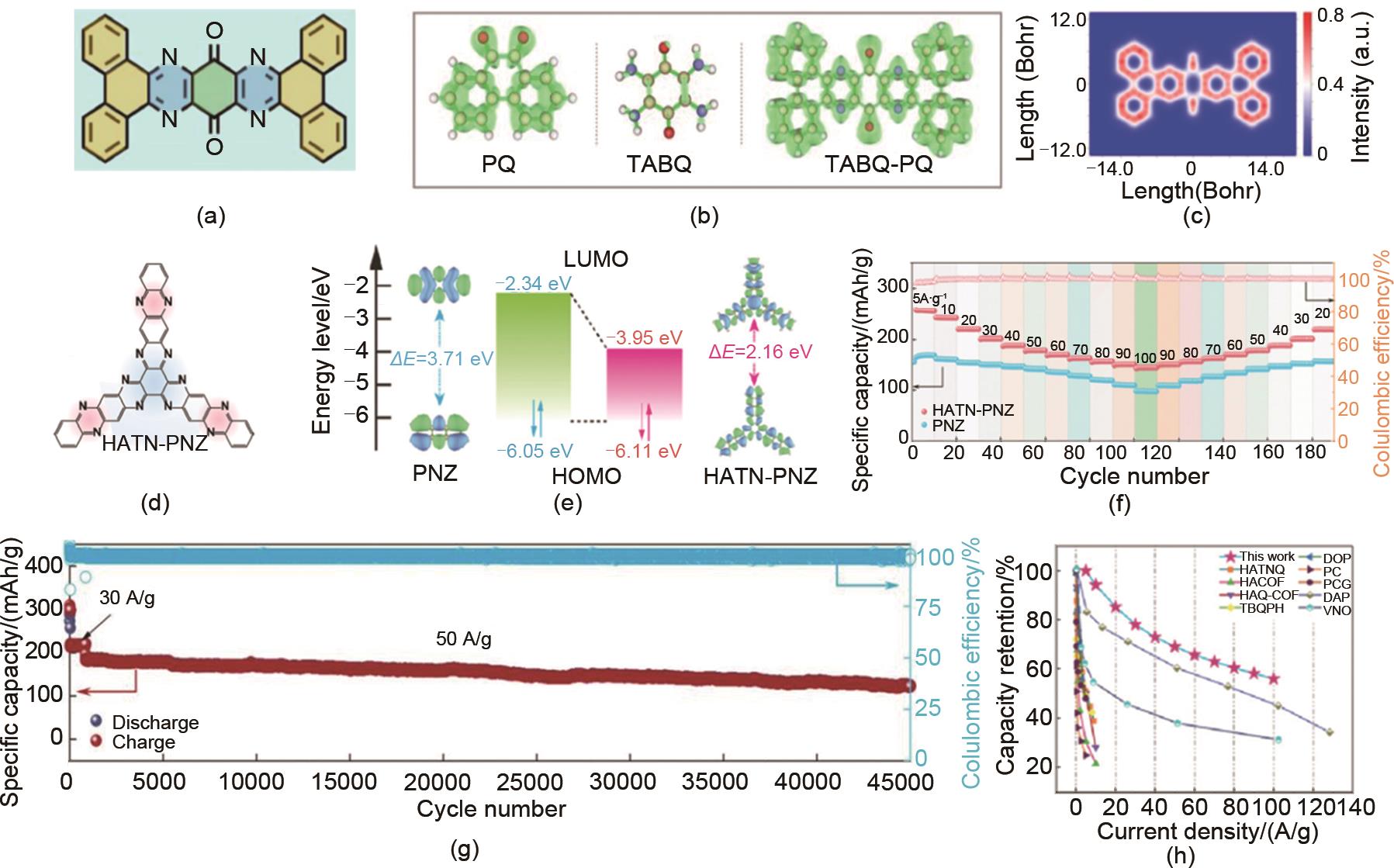
Table 1
Summary of different cathode materials and performance improvement strategies for aqueous zinc ion batteries"
| 正极材料 | 性能提升策略 | 工作电压/V | 放电容量(mAh/g)/ 电流密度(A/g) | 循环性能(%)(电流密度(A/g), 次数) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MnCO3@Mn3O4 | 构建异质结构 | 0.4~1.9 | 174 (0.1) | 77.32(1.0,1000) | [ |
| VO-E | 构建异质结构 | 0.3~1.9 | 516 (0.5) | 85.5(20,5000) | [ |
| MNO | 制造氧空位 | 0.4~1.9 | 283(0.3) | 92.5(3,1000) | [ |
| δ-MnO2-2.0 | 调控氧空位 | 0.9~1.9 | 551.8(0.5) | 83(3,1500) | [ |
| Od-NiCo2O4 | 制造氧空位 | 0~0.57 | 418.9(1.0) | 99.8(16,10000) | [ |
| Mg-MnO2 | 阳离子掺杂 | 1.0~1.8 | 370 (0.6) | 87.07(0.6,300) | [ |
| Cu-Bi2-xSe3 | 阳离子掺杂 | 0.2~1.6 | 288.5(0.2) | 46.6(10,4000) | [ |
| VO-NH | 阳离子掺杂 | 0.2~1.6 | 396.1(0.5) | 80.2(10,10000) | [ |
| NH4V3O8·0.5H2O | 水分子插层 | 0.4~1.3 | 399(0.2) | 82.7(0.2,120) | [ |
| HATN-PNZ | 大π共轭平面增加疏水性 | 0.05~1.65 | 257(5.0) | 99.8(50,45000) | [ |
| TABQ-PQ | 大π共轭平面增加疏水性 | 0.2~1.2 | 200(0.1) | 90.8(5.0,30000) | [ |
| MnOF0.04 | 引入阴离子配位 | 0.9~1.8 | 241.9(0.2) | 76.2(5,3500) | [ |
| MnO2@CeO2 | 材料复合 | 0.8~1.8 | 355(1.0) | 89.68(3,1000) | [ |
| MnO@PC | 增强自发溶解活性 | 0.8~1.9 | 223(0.2) | 89(2.0,2000) | [ |
| MNVO | 氧离子掺杂 | 0.3~1.6 | 368(0.5) | 90.2(10,5000) | [ |
| PANI-M | 质子自掺杂 | 0.6~1.6 | 270(0.5) | 87(15,4000) | [ |
| Cu2O-CDs | 构建异质结构 | 0.2~1.2 | 339(0.2) | 63(0.1,100) | [ |
| ZnTe@C NWs | 构建异质结构 | 0.2~1.6 | 309(1.0) | 74(1,400) | [ |
| AlMO | 阳离子掺杂 | 0.8~1.8 | 268.2(0.5) | 100(4,15000) | [ |
| PVP-MnO2 | 有机分子插层 | 0.8~1.8 | 309(0.25) | 100(10,20000) | [ |
| V6O13-x /rGO | 构建异质结构 | 0.2~1.6 | 376.8(0.5) | 92(5,3000) | [ |
| NSVOHI | 水分子插层 | 0.4~1.6 | 426(0.5) | 91(1.3,200) | [ |
| PEDOT-MnO2 | 有机分子插层 | 0.8~1.8 | 300(0.2) | 100(0.2,100) | [ |
| PEDOT-MoO3 | 有机分子插层 | 0.2~1.4 | 270.5(5.0) | 77.6(30,500) | [ |
| LPVO | 有机分子插层 | 0.2~1.4 | 303(0.5) | 94(5,800) | [ |
| V-EG | 有机分子插层 | 0.2~1.8 | 516(0.5) | 81.1(20,10000) | [ |
| EDA-VO | 有机分子插层 | 0.4~1.4 | 382.6(0.5) | 99.95(5,10000) | [ |
| NMOH | 双分子共嵌入 | 0.8~1.9 | 389.8(0.2) | 100(0.5,400) | [ |
| Li@MnVO | 双离子顺序插层 | 0.2~1.6 | 232(4.0) | 99(10,5000) | [ |
| 1 | 国家发展改革委 国家能源局关于加快推动新型储能发展的指导意见[EB/OL]. [2021-7-15]. https://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/2021-07/15/c_1310079331.htm. |
| 2 | XU Z M, ZHANG W Y, WANG X Z, et al. High-rate and long-life flexible aqueous rechargeable zinc-ion battery enabled by hierarchical core-shell heterostructures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(4): 2172-2183. DOI: 10.1039/D3TA06183C. |
| 3 | WU X Y, JI X L. Aqueous batteries get energetic[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2019, 11(8): 680-681. DOI: 10.1038/s41557-019-030 0-3. |
| 4 | CHAO D L, ZHOU W H, XIE F X, et al. Roadmap for advanced aqueous batteries: From design of materials to applications[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(21): eaba4098. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba4098. |
| 5 | DING L Y, WANG L, GAO J C, et al. Facile Zn2+ desolvation enabled by local coordination engineering for long-cycling aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(32): 2301648. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202301648. |
| 6 | SHEN S C, MA D T, OUYANG K F, et al. An in situ electrochemical amorphization electrode enables high-power high-cryogenic capacity aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(38): 2304255. DOI: 10.1002/adfm. 202304255. |
| 7 | TANG B Y, SHAN L T, LIANG S Q, et al. Issues and opportunities facing aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(11): 3288-3304. DOI: 10.1039/C9EE02526J. |
| 8 | HU L F, WU Z Y, LU C J, et al. Principles of interlayer-spacing regulation of layered vanadium phosphates for superior zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(7): 4095-4106. DOI: 10.1039/D1EE01158H. |
| 9 | LI C W, LIU C, WANG Y, et al. Drastically-enlarged interlayer-spacing MoS2 nanocages by inserted carbon motifs as high performance cathodes for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 49: 144-152. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.202 2.03.048. |
| 10 | LI S W, LIU Y C, ZHAO X D, et al. Sandwich-like heterostructures of MoS2/graphene with enlarged interlayer spacing and enhanced hydrophilicity as high-performance cathodes for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(12): 2007480. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202007480. |
| 11 | SUN R, DONG S Y, GUO X C, et al. Construction of 2D sandwich-like Na2V6O16·3H2O@MXene heterostructure for advanced aqueous zinc ion batteries[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 655: 226-233. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.20 23.11.020. |
| 12 | PU X M, SONG T B, TANG L B, et al. Rose-like vanadium disulfide coated by hydrophilic hydroxyvanadium oxide with improved electrochemical performance as cathode material for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 437: 226917. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226917. |
| 13 | ZHANG Q, ZHANG Y, FU L J, et al. A novel and improved hydrophilic vanadium oxide-based cathode for aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 354: 136721. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136721. |
| 14 | ZHANG C, WU Z H, YANG C Q, et al. Rational regulation of optimal oxygen vacancy concentrations on VO2 for superior aqueous zinc-ion battery cathodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(31): 40903-40913. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c 05618. |
| 15 | ZHOU Y, WANG C, CHEN F R, et al. Scalable fabrication of NiCoMnO4 yolk-shell microspheres with gradient oxygen vacancies for high-performance aqueous zinc ion batteries[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 626: 314-323. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.06.152. |
| 16 | XU C J, LI B H, DU H D, et al. Energetic zinc ion chemistry: The rechargeable zinc ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(4): 933-935. DOI: 10.1002/anie.2 0106307. |
| 17 | KUNDU D, ADAMS B D, DUFFORT V, et al. A high-capacity and long-life aqueous rechargeable zinc battery using a metal oxide intercalation cathode[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16119. DOI: 10.1038/nenergy.2016.119. |
| 18 | ZHAO Q, HUANG W W, LUO Z Q, et al. High-capacity aqueous zinc batteries using sustainable quinone electrodes[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(3): eaao1761. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aao1761. |
| 19 | ZHONG C, LIU B, DING J, et al. Decoupling electrolytes towards stable and high-energy rechargeable aqueous zinc-manganese dioxide batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2020, 5(6): 440-449. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-020-0584-y. |
| 20 | YUAN Y F, SHARPE R, HE K, et al. Understanding intercalation chemistry for sustainable aqueous zinc-manganese dioxide batteries[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2022, 5(10): 890-898. DOI: 10. 1038/s41893-022-00919-3. |
| 21 | LI Y Q, ZHENG X L, CARLSON E Z, et al. In situ formation of liquid crystal interphase in electrolytes with soft templating effects for aqueous dual-electrode-free batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2024, 9(11): 1350-1359. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-024-01638-z. |
| 22 | DAI Y H, LU R H, ZHANG C Y, et al. Zn2+-mediated catalysis for fast-charging aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2024, 7(7): 776-784. DOI: 10.1038/s41929-024-01169-6. |
| 23 | YANG W B, XIE X K, WU R, et al. Research status and prospects of cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the China Coal Society, 2022, 47(9): 3351-3364. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.NE22.0411. |
| 24 | CHEN D, LU M J, CAI D, et al. Recent advances in energy storage mechanism of aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 54: 712-726. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.20 20.06.016. |
| 25 | SUN W, WANG F, HOU S, et al. Zn/MnO2 battery chemistry with H+ and Zn2+ coinsertion[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(29): 9775-9778. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b04471. |
| 26 | CHAO D L, ZHOU W H, YE C, et al. An electrolytic Zn-MnO2 battery for high-voltage and scalable energy storage[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(23): 7823-7828. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201904174. |
| 27 | LI Y D, LI Y H, LIU Q S, et al. Revealing the dominance of the dissolution-deposition mechanism in aqueous Zn-MnO2 batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(6): e202318444. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202318444. |
| 28 | YUAN C L, ZHANG Y, PAN Y, et al. Investigation of the intercalation of polyvalent cations (Mg2+, Zn2+) into λ-MnO2 for rechargeable aqueous battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 116: 404-412. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.090. |
| 29 | ZHANG N, CHENG F Y, LIU J X, et al. Rechargeable aqueous zinc-manganese dioxide batteries with high energy and power densities[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 405. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00467-x. |
| 30 | LI S L, SHANG J, LI M L, et al. Design and synthesis of a π-conjugated N-heteroaromatic material for aqueous zinc-organic batteries with ultrahigh rate and extremely long life[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(50): 2207115. DOI: 10.1002/adma.2022 07115. |
| 31 | XIE M, WANG R, WANG N N, et al. MnO2@CeO2 composite cathode for aqueous zinc-ion batteries: Enhanced electrical conductivity and stability through Mn-O-Ce bonds[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(40): 21927-21936. DOI: 10.1039/D3TA04837C. |
| 32 | WANG Z H, SONG Y, WANG J, et al. Vanadium oxides with amorphous-crystalline heterointerface network for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(13): e202216290. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202216290. |
| 33 | FANG G Z, LIANG S Q, CHEN Z X, et al. Simultaneous cationic and anionic redox reactions mechanism enabling high-rate long-life aqueous zinc-ion battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(44): 1905267. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201905267. |
| 34 | WAN F, ZHANG Y, ZHANG L L, et al. Reversible oxygen redox chemistry in aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(21): 7062-7067. DOI: 10.1002/an ie.201902679. |
| 35 | LV H, WANG J L, GAO X Y, et al. Electrochemical performance and mechanism of bimetallic organic framework for advanced aqueous Zn ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(40): 47094-47102. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c10552. |
| 36 | JIA D D, SHEN Z L, LV Y H, et al. In situ electrochemical tuning of MIL-88B(V)@rGO into amorphous V2O5@rGO as cathode for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(2): 2308319. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.2 02308319. |
| 37 | LIU Y H, MA Y D, YANG W T, et al. Spontaneously dissolved MnO: A better cathode material for rechargeable aqueous zinc-manganese batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 473: 145490. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145490. |
| 38 | WANG X R, WANG Y L, NAVEED A, et al. Magnesium ion doping and micro-structural engineering assist NH4V4O10 as a high-performance aqueous zinc ion battery cathode[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(48): 2306205. DOI: 10.1002/adfm. 202306205. |
| 39 | GUO J B, HE B, GONG W B, et al. Emerging amorphous to crystalline conversion chemistry in Ca-doped VO2 cathodes for high-capacity and long-term wearable aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(11): 2303906. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202303906. |
| 40 | YIN C J, PAN C L, PAN Y S, et al. Proton self-doped polyaniline with high electrochemical activity for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(11): 2300574. DOI: 10.1002/smtd. 202300574. |
| 41 | ZHANG Q, LIU P G, WANG T, et al. Core-shell structures of Cu2O constructed by carbon quantum dots as high-performance zinc-ion battery cathodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(45): 24823-24835. DOI: 10.1039/D3TA05705D. |
| 42 | LI J W, ZHANG L, XIN W L, et al. Rationally designed ZnTe@C nanowires with superior zinc storage performance for aqueous Zn batteries[J]. Small, 2023, 19(52): 2304916. DOI: 10.1002/smll. 202304916. |
| 43 | YAN Z C, LI J W, LIU H G, et al. A reversible six-electron transfer cathode for advanced aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(47): e202312000. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202312000. |
| 44 | HUANG Q F, SHAO L Y, SHI X Y, et al. Na3V2O2(PO4)2F nanoparticles@reduced graphene oxide: A high-voltage polyanionic cathode with enhanced reaction kinetics for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 468: 143738. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.143738. |
| 45 | WANG K N, WANG J W, CHEN P M, et al. Structural transformation by crystal engineering endows aqueous zinc-ion batteries with ultra-long cyclability[J]. Small, 2023, 19(29): 23005 85. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202300585. |
| 46 | LIU Z X, QIN L P, CAO X X, et al. Ion migration and defect effect of electrode materials in multivalent-ion batteries[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 125: 100911. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmatsci. 2021.100911. |
| 47 | ZHANG A Q, ZHAO R, WANG Y H, et al. Hybrid superlattice-triggered selective proton grotthuss intercalation in δ-MnO2 for high-performance zinc-ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2023, 135(51): e202313163. DOI: 10.1002/ange.202313163. |
| 48 | LI C, YUN X R, CHEN Y F, et al. Unravelling the proton hysteresis mechanism in vacancy modified vanadium oxides for High-Performance aqueous zinc ion battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 477: 146901. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.20 23.146901. |
| 49 | GUO C C, ZHOU R Y, LIU X R, et al. Activating the MnS0.5Se0.5 microspheres as high-performance cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries: Insight into in situ electrooxidation behavior and energy storage mechanisms[J]. Small, 2024, 20(15): 2306237. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202306237. |
| 50 | GOU L, LI J R, LIANG K, et al. Bi-MOF modulating MnO2 deposition enables ultra-stable cathode-free aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2023, 19(17): 2208233. DOI: 10.1002/smll.20 2208233. |
| 51 | XIA J J, ZHOU Y R, ZHANG J, et al. Triggering high capacity and superior reversibility of manganese oxides cathode via magnesium modulation for Zn// MnO2 batteries[J]. Small, 2023, 19(37): 2301906. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202301906. |
| 52 | SUN T J, ZHANG W J, ZHA Z T, et al. Designing a solubility-limited small organic molecule for aqueous zinc-organic batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 59: 102778. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2023.102778. |
| 53 | SUN Q Q, SUN T, DU J Y, et al. A sulfur heterocyclic quinone cathode towards high-rate and long-cycle aqueous Zn-organic batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(22): 2301088. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202301088. |
| 54 | ZHENG C, HUANG Z H, SUN F F, et al. Oxygen-vacancy-reinforced vanadium oxide/graphene heterojunction for accelerated zinc storage with long life span[J]. Small, 2024, 20(6): 2306275. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202306275. |
| 55 | LI T, TONG J J, LIU S Y, et al. Butterfly-Tie like MnCO3@Mn3O4 heterostructure enhanced the electrochemical performances of aqueous zinc ion batteries[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 656: 504-512. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.11.129. |
| 56 | LI Y, LI X, DUAN H, et al. Aerogel-structured MnO2 cathode assembled by defect-rich ultrathin nanosheets for zinc-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 441: 136008. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136008. |
| 57 | LI Y, YANG W, YANG W, et al. High-performance zinc-ion batteries enabled by electrochemically induced transformation of vanadium oxide cathodes[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 60: 233-240. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.01.025. |
| 58 | LIU Y, GUO S L, LING W, et al. In-situ oriented oxygen-defect-rich MnNO via nitridation and electrochemical oxidation based on industrial-scale Mn2O3 to achieve high-performance aqueous zinc ion battery[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 76: 11-18. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.08.038. |
| 59 | WANG Y W, ZHANG Y X, GAO G, et al. Effectively modulating oxygen vacancies in flower-like δ-MnO2 nanostructures for large capacity and high-rate zinc-ion storage[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 219. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-023-01194-3. |
| 60 | ZHANG Y, SUN D, WANG Y X, et al. Facile electrochemically induced vacancy modulation of NiCo2O4 cathode toward high-performance aqueous Zn-based battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 453: 139736. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.139736. |
| 61 | ZONG Y, CHEN H C, WANG J S, et al. Cation defect-engineered boost fast kinetics of two-dimensional topological Bi2Se3 cathode for high-performance aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(51): 2306269. DOI: 10.1002/adma.20230 6269. |
| 62 | WU Z A, YAO J, CHEN C, et al. Ammonium intercalation engineering regulated structural stability of V6O13 cathodes for durable zinc ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 479: 147889. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.147889. |
| 63 | YOO G, KOO B R, AN G. Nano-sized split V2O5 with H2O-intercalated interfaces as a stable cathode for zinc ion batteries without an aging process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 434: 134738. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134738. |
| 64 | JIANG H M, ZHANG Y F, PAN Z H, et al. NH4V3O8·0.5H2O nanobelts with intercalated water molecules as a high performance zinc ion battery cathode[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2020, 4(5): 1434-1443. DOI: 10.1039/D0QM00051E. |
| 65 | CHENG X J, XIANG Z P, YANG C, et al. Polar organic molecules inserted in vanadium oxide with enhanced reaction kinetics for promoting aqueous zinc-ion storage[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(9): 2311412. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202311412. |
| 66 | MA X M, CAO X X, YAO M L, et al. Organic-inorganic hybrid cathode with dual energy-storage mechanism for ultrahigh-rate and ultralong-life aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(6): 2105452. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202105452. |
| 67 | CHEN H, MA W B, GUO J D, et al. PEDOT-intercalated MnO2 layers as a high-performance cathode material for aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 932: 167688. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167688. |
| 68 | FANG Z T, LIU C, LI X G, et al. Systematic modification of MoO3-based cathode by the intercalation engineering for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(7): 2210010. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202210010. |
| 69 | HE W, FAN Z X, HUANG Z Q, et al. A Li+ and PANI co-intercalation strategy for hydrated V2O5 to enhance zinc ion storage performance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(36): 18962-18971. DOI: 10.1039/D2TA03145K. |
| 70 | JIANG H M, ZHANG Y F, WAQAR M, et al. Anomalous Zn2+ storage behavior in dual-ion-In-sequence reconstructed vanadium oxides[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(7): 2213127. DOI: 10.1 002/adfm.202213127. |
| 71 | ZHAI X Z, QU J, HAO S M, et al. Layered birnessite cathode with a displacement/intercalation mechanism for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2020, 12(1): 56. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-020-0397-3. |
| [1] | Jiahui LIU, Weixiang BIAN, Dawei LI. In situ measurement and analysis of the electromechanical coupling performance of composite graphite electrodes in lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2240-2247. |
| [2] | Huimin FAN, Haohong PENG, Hui MENG, Menghong TANG, Haohao YI, Jing DING, Jincheng LIU, Chengshan XU, Xuning FENG. Research and simulation analysis of swelling force characteristics in energy storage battery modules [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2488-2497. |
| [3] | Wenjie ZHANG, Dongsheng REN, Yu WU, Xinyu RUI, Xiang LIU, Xuning FENG, Languang LU. Thermal stability of key materials in Li10GeP12S2-based all-solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2193-2199. |
| [4] | Yonglong DUAN, Xia HUA, Zijiao HAN, Bing XIE, Shubo HU, Aikui LI. Research progress on capacity decay and inhibition technology of all-vanadium flow batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2540-2554. |
| [5] | Zhangjie XU, Zhengyue SUN, Xinyan ZHANG, Jiliang ZHANG, Yingchao YU, Chuang DONG. FeOOH coating on FeS as high-performance anode materials for Li-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2232-2239. |
| [6] | Zhenxin SUN, Zhiming ZHANG, Yi ZHANG, Haizhao LI, Haiyan LIAO, Liangjie WEI. Research on the energy storage configuration method based on entropy theory [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2431-2438. |
| [7] | Dandan HAN, Wuwei ZHANG, Liang ZHANG, Zongjiang WANG. Design and electrochemical performance of LiMn1-y Fe y PO4/C cathode materials with a core-shell structure [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2215-2222. |
| [8] | Jinzhen PING, Qinrun WEN. Surface defect detection of lithium battery based on electronic image processing technology [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2512-2514. |
| [9] | Zhen YAN, Qiang LIU, Huibin LI, Jun ZHANG, Yahui JIANG. Power optimization management method for photovoltaic microgrids based on the state of charge of hybrid energy storage systems [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 2067-2077. |
| [10] | Ping DING, Taotao LI, Linfeng ZHENG, Weixiong WU. SOH estimation of real-world power batteries based on Soft-DTW algorithm and multisource reature fusion [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 2081-2097. |
| [11] | Shunxin LIU, Haoyang LI, Jianxing ZHANG, Guang ZENG, Lingping XU. A study on the synergistic optimization of flow channel structures and guide plates in a 280 Ah air-cooled battery pack for energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1806-1817. |
| [12] | Xiaoru XU, Jianzhen OU, Jiawei LIU, Zhicong CHEN, Hao YE, Yinglong LIU, Yingli LIU, Zeyu LIN, Jingjing LIU, Junhui JIAN, Xu LUO, Jingmin FAN, Chao WANG, Libin LEI, Bo LIANG. Direct ammonia tubular fuel cell with an embedded microchannel ceramic cracking reactor [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1818-1828. |
| [13] | Congqing TANG, Jingsheng CAI. Recent advances in presodiation strategies for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1884-1899. |
| [14] | Zhiqiang LI, Yichun BA, Guangqiang SUN. Research on heat dissipation of cold plates with honeycomb and fork channels of lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1776-1783. |
| [15] | Zhoulan ZENG, Lei SHANG, Zhijin HU, Zongfan WANG, Xiaochao XIN, Ying LIU. Li5FeO4@C high capacity prelithium cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1875-1883. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
