储能科学与技术 ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (7): 2327-2347.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0323
收稿日期:2024-04-11
修回日期:2024-05-02
出版日期:2024-07-28
发布日期:2024-07-23
通讯作者:
刘德重,陈大鹏
E-mail:742010446@qq.com;ldzone@outlook.com;dpchenhust@gmail.com
作者简介:李想(1996—),女,博士,工程师,研究方向为化学电源,E-mail:742010446@qq.com;
Xiang LI( ), Dezhong LIU(
), Dezhong LIU( ), Kai YUAN, Dapeng CHEN(
), Kai YUAN, Dapeng CHEN( )
)
Received:2024-04-11
Revised:2024-05-02
Online:2024-07-28
Published:2024-07-23
Contact:
Dezhong LIU, Dapeng CHEN
E-mail:742010446@qq.com;ldzone@outlook.com;dpchenhust@gmail.com
摘要:
固态锂金属电池因其理论上的高能量密度和安全性成为下一代锂二次电池的重要发展方向。然而,由于低温下(≤0 ℃)固态电解质离子电导率下降、电解质/电极界面处阻抗增加,固态锂金属电池在低温下的电化学性能快速劣化,为推进固态锂金属电池的实用化进程,亟须提升固态电解质在低温下的性能。本文围绕固态电解质的先进新兴技术,从材料层面切入,对近年来受到广泛关注的固态锂金属电池在低温领域的进展进行了梳理。首先介绍了固态锂金属电池的低温化学特性和失效机制,从本体离子传输、界面电荷转移、电极表面结构、锂金属稳定性等方面进行了归纳和分析。其次根据不同类型的固体电解质,对低温运行的先进金属锂电池的设计技术进行了总结,详细介绍了无机、聚合物及复合固态电解质的设计原理、化学组成-性能关系及界面优化策略等。最后从新材料、新表征、新机理及新标准四个维度对低温固态锂金属电池的未来实用化研究方向进行了展望,为低温固态锂金属电池的合理设计提供参考。
中图分类号:
李想, 刘德重, 袁开, 陈大鹏. 用于低温锂金属电池的固态电解质技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2327-2347.
Xiang LI, Dezhong LIU, Kai YUAN, Dapeng CHEN. Solid-state electrolyte for low-temperature lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2327-2347.
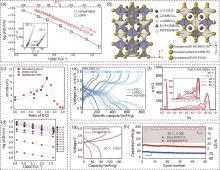
图3
(a) 用Arrhenius图计算Li9.54[Si0.6Ge0.4]1.74P1.44S11.1Br0.3O0.6 和LGPS的体电导率;(b) 通过精修分析确定的LSiPSBrO晶体结构示意图[34];(c) 简单固相反应制备的富氯硫银锗矿电解质的室温离子电导率与S/Cl比值的关系;(d) Li7-x PS6-x Cl x (x=1.0~2.0)相应的Arrhenius图[35];(e) 不同温度下FeS2|SE|Li全固态电池第2次循环的充放电曲线;(f) 根据基于LASI-80Si硫化物固态电解质的FeS2|SE|Li-In全固态电池的EIS测量结果计算的DRT光谱[40];NCM712/Li5.5PS4.5Cl1.5/In-Li和LNO@NCM712/Li5.5PS4.5Cl1.5/In-Li固态电池在2.4~3.7 V电压范围内在-20 ℃、0.05C条件下的 (g) 充放电曲线以及 (h) 循环性能[44]"

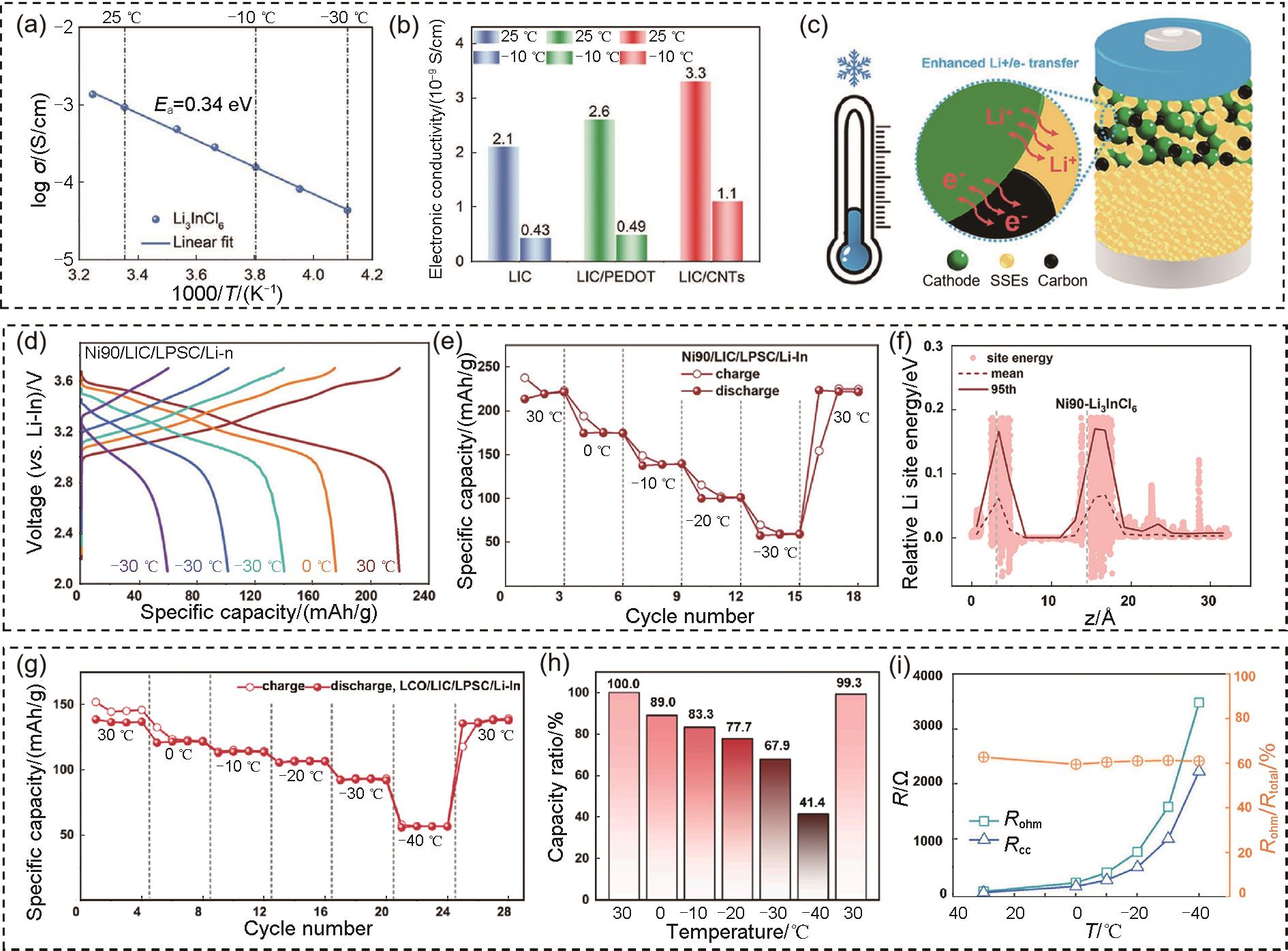
图 4
(a) 根据-30~35 ℃范围内的EIS测量得出的LIC SSEs的Arrhenius图;(b) 25 ℃和-10 ℃下LIC、LIC/PEDOT复合材料和LIC/CNTs复合材料的电子电导率;(c) 低温复合正极中Li+ 和电子转移示意图[47];在-30~30 ℃温度范围内,Ni90/LIC/LPSC/Li ASSBs的 (d) 第2次循环充放电曲线和 (e) 比容量的演变;(f) Ni90-Li3InCl6 界面沿 z 轴方向的Li位点能分布[49];(g) LCO/LIC/LPSC/Li ASSBs的比容量在30~-40 ℃范围内的变化;(h) 在每个温度下与30 ℃时的容量比;(i) 通过等效电路拟合得到的LCO/LIC/LPSC/Li-In ASSBs的 R-T 关系[50]"
| 1 | WANG Z X, SUN Z H, LI J, et al. Insights into the deposition chemistry of Li ions in nonaqueous electrolyte for stable Li anodes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(5): 3178-3210. |
| 2 | LIU B, ZHANG J G, XU W. Advancing lithium metal batteries[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(5): 833-845. |
| 3 | XIANG J W, YANG L Y, YUAN L X, et al. Alkali-metal anodes: From lab to market[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(10): 2334-2363. |
| 4 | 许卓, 郑莉莉, 陈兵, 等. 固态电池复合电解质研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(6): 2117-2126. |
| XU Z, ZHENG L L, CHEN B, et al. Overview of research on composite electrolytes for solid-state batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2117-2126. | |
| 5 | XIA S X, WU X S, ZHANG Z C, et al. Practical challenges and future perspectives of all-solid-state lithium-metal batteries[J]. Chem, 2019, 5 (4): 753-785. |
| 6 | SHEN Y B, ZHANG Y T, HAN S J, et al. Unlocking the energy capabilities of lithium metal electrode with solid-state electrolytes[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(9): 1674-1689. |
| 7 | CHEN S Q, WEI X Z, ZHANG G X, et al. All-temperature area battery application mechanism, performance, and strategies[J]. Innovation (Cambridge (Mass)), 2023, 4(4): 100465. |
| 8 | LI Z H, YAO Y X, SUN S, et al. 40 years of low-temperature electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2023, 62(37): e202303888. |
| 9 | WANG C Y, ZHANG G S, GE S H, et al. Lithium-ion battery structure that self-heats at low temperatures[J]. Nature, 2016, 529: 515-518. |
| 10 | ZHANG G S, GE S H, XU T, et al. Rapid self-heating and internal temperature sensing of lithium-ion batteries at low temperatures[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 218: 149-155. |
| 11 | LI S, KIRKALDY N, ZHANG C, et al. Optimal cell tab design and cooling strategy for cylindrical lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 492: 229594. |
| 12 | LIN J Y, LIU X H, LI S, et al. A review on recent progress, challenges and perspective of battery thermal management system[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 167: 120834. |
| 13 | XIA H R, ZHANG W, CAO S K, et al. A figure of merit for fast-charging Li-ion battery materials[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(6): 8525-8530. |
| 14 | ZHANG D M, MENG X L, HOU W Y, et al. Solid polymer electrolytes: Ion conduction mechanisms and enhancement strategies[J]. Nano Research Energy, 2023, 2: e9120050. |
| 15 | YANG T Q, WANG C, ZHANG W K, et al. A critical review on composite solid electrolytes for lithium batteries: Design strategies and interface engineering[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 84: 189-209. |
| 16 | KOBAYASHI T, OHNISHI T, OSAWA T, et al. In-operando lithium-ion transport tracking in an all-solid-state battery[J]. Small, 2022, 18(46): 2204455. |
| 17 | LU P S, ZHOU Z M, XIAO Z X, et al. Materials and chemistry design for low-temperature all-solid-state batteries[J]. Joule, 2024, 8(3): 635-657. |
| 18 | CHAE O B, LUCHT B L. Interfacial issues and modification of solid electrolyte interphase for Li metal anode in liquid and solid electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(14): 2203791. |
| 19 | LIU J, YUAN H, LIU H, et al. Unlocking the failure mechanism of solid state lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(4): 2100748. |
| 20 | FAMPRIKIS T, CANEPA P, DAWSON J A, et al. Fundamentals of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18: 1278-1291. |
| 21 | CAO D X, ZHANG K N, LI W, et al. Nondestructively visualizing and understanding the mechano-electro-chemical origins of "soft short" and "creeping" in all-solid-state batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(52): 2307998. |
| 22 | SUN H M, LIU Q N, CHEN J Z, et al. In situ visualization of lithium penetration through solid electrolyte and dead lithium dynamics in solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(12): 19070-19079. |
| 23 | 赵永智, 陈晨阳, 刘文燚, 等. 固态锂电池界面优化策略的研究进展[J]. 物理化学学报, 2023, 39(8): 45-61. |
| ZHAO Y Z, CHEN C Y, LIU W Y, et al. Research progress of interface optimization strategies for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2023, 39(8): 45-61. | |
| 24 | JIAO Y, WANG F, MA Y H, et al. Challenges and advances on low-temperature rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(6): 8082-8096. |
| 25 | WU D X, CHEN L Q, LI H, et al. Solid-state lithium batteries-from fundamental research to industrial progress[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 139: 101182. |
| 26 | KRAUSKOPF T, RICHTER F H, ZEIER W G, et al. Physicochemical concepts of the lithium metal anode in solid-state batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(15): 7745-7794. |
| 27 | YU G X, WANG Y P, LI K, et al. Plasma optimized Li7La3Zr2O12 with vertically aligned ion diffusion pathways in composite polymer electrolyte for stable solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 132874. |
| 28 | FENG W L, ZHAO Y F, XIA Y Y. Solid interfaces for the garnet electrolytes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(15): e2306111. |
| 29 | SONG H C, WANG S, SONG X Y, et al. Solar-driven all-solid-state lithium-air batteries operating at extreme low temperatures[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(4): 1205-1211. |
| 30 | WANG S, SONG H C, SONG X Y, et al. An extra-wide temperature all-solid-state lithium-metal battery operating from -73 ℃ to 120 ℃[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 39: 139-145. |
| 31 | SONG X Y, WANG M, WANG S, et al. A wide temperature solid-state Li-S battery enabled by a plasmon-enhanced copper–silicon nanowire photothermal current collector[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(42): 22584-22591. |
| 32 | ZHANG Q, CAO D X, MA Y, et al. Sulfide-based solid-state electrolytes: Synthesis, stability, and potential for all-solid-state batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(44): 1901131. |
| 33 | KAMAYA N, HOMMA K, YAMAKAWA Y, et al. A lithium superionic conductor[J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10: 682-686. |
| 34 | LI Y X, SONG S B, KIM H, et al. A lithium superionic conductor for millimeter-thick battery electrode[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6653): 50-53. |
| 35 | PENG L F, YU C, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Chlorine-rich lithium argyrodite enabling solid-state batteries with capabilities of high voltage, high rate, low-temperature and ultralong cyclability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 132896. |
| 36 | PENG L F, YU C, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Tuning solid interfaces via varying electrolyte distributions enables high‐performance solid‐state batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2023, 6 (2): e12308. |
| 37 | LU P S, XIA Y, SUN G C, et al. Realizing long-cycling all-solid-state Li-In||TiS2 batteries using Li6+ xMxAs1- xS5I (M=Si, Sn) sulfide solid electrolytes[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 4077. |
| 38 | WANG R, WU Z K, YU C, et al. Low temperature ensures FeS2 cathode a superior cycling stability in Li7P3S11-based all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2023, 10: 1108789. |
| 39 | LU P S, GONG S, GUO F L, et al. Amorphous bimetallic polysulfide for all-solid-state batteries with superior capacity and low-temperature tolerance[J]. Nano Energy, 2023, 118: 109029. |
| 40 | LU P S, XIA Y, HUANG Y L, et al. Wide-temperature, long-cycling, and high-loading pyrite all-solid-state batteries enabled by argyrodite thioarsenate superionic conductor[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(8): 2211211. |
| 41 | WANG Y P, YUAN P C, XU Z Y, et al. Ti3C2T MXene in situ transformed Li2TiO3 interface layer enabling 4.5 V-LiCoO2/sulfide all-solid-state lithium batteries with superior rate capability and cyclability[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(6): 108776. |
| 42 | KATO Y, HORI S, SAITO T, et al. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(4): 16030. |
| 43 | MORINO Y. Impact of surface coating on the low temperature performance of a sulfide-based all-solid-state battery cathode[J]. Electrochemistry, 2022, 90(2): 027001. |
| 44 | PENG L F, REN H T, ZHANG J Z, et al. LiNbO3-coated LiNi0.7Co0.1Mn0.2O2 and chlorine-rich argyrodite enabling high-performance solid-state batteries under different temperatures[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 43: 53-61. |
| 45 | ZHU Y Z, HE X F, MO Y F. Origin of outstanding stability in the lithium solid electrolyte materials: Insights from thermodynamic analyses based on first-principles calculations[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(42): 23685-23693. |
| 46 | 李枫, 程晓斌, 罗锦达, 等. 金属氯化物固态电解质及其全固态电池研究现状与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 193-211. |
| LI F, CHENG X B, LUO J D, et al. Metal chloride solid-state electrolytes and all-solid-state batteries: State-of-the-art developments and perspectives[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 193-211. | |
| 47 | DENG S X, JIANG M, CHEN N, et al. Regulating electronic conductivity at cathode interface for low-temperature halide-based all-solid-state batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(45): 2205594. |
| 48 | ZHANG Z C, JIA W Q, FENG Y, et al. An ultraconformal chemo-mechanical stable cathode interface for high-performance all-solid-state batteries at wide temperatures[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(10): 4453-4463. |
| 49 | LU P S, GONG S, WANG C H, et al. Superior low-temperature all-solid-state battery enabled by high-ionic-conductivity and low-energy-barrier interface[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(10): 7334-7345. |
| 50 | LU P S, WU Y J, WU D X, et al. Rate-limiting mechanism of all-solid-state battery unravelled by low-temperature test-analysis flow[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 67: 103316. |
| 51 | WANG C H, LIANG J W, KIM J T, et al. Prospects of halide-based all-solid-state batteries: From material design to practical application[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(36): eadc9516. |
| 52 | SHEN M N, WANG Z Y, CHENG D M, et al. Molecular regulated polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium metal batteries: Mechanisms and future prospects[J]. eTransportation, 2023, 18: 100264. |
| 53 | PAN L, FENG S F, SUN H, et al. Ultrathin, mechanically durable, and scalable polymer-in-salt solid electrolyte for high-rate lithium metal batteries[J]. Small, 2024: e2400272. |
| 54 | DING P, LIN Z, GUO X, et al. Polymer electrolytes and interfaces in solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2021, 51: 449-474. |
| 55 | XU S J, SUN Z H, SUN C G, et al. Homogeneous and fast ion conduction of PEO-based solid-state electrolyte at low temperature[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(51): 2007172. |
| 56 | LIN Z H, LIU J. Low-temperature all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries based on a di-cross-linked starch solid electrolyte[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(59): 34601-34606. |
| 57 | MO S K, AN H W, LIU Q S, et al. Multistage bridge engineering for electrolyte and interface enables quasi-solid batteries to operate at -40℃[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 65: 103179. |
| 58 | LI Z, FU J L, ZHOU X Y, et al. Ionic conduction in polymer-based solid electrolytes[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(10): e2201718. |
| 59 | YU J, LIN X D, LIU J P, et al. In situ fabricated quasi-solid polymer electrolyte for high-energy-density lithium metal battery capable of subzero operation[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 12 (2): 2102932. |
| 60 | XIANG J W, ZHANG Y, ZHANG B, et al. A flame-retardant polymer electrolyte for high performance lithium metal batteries with an expanded operation temperature[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(6): 3510-3521. |
| 61 | HU A Y, LIAO Z, HUANG J, et al. In-situ construction of dual lithium-ion migration channels in polymer electrolytes for lithium metal batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 448: 137661. |
| 62 | REN W, ZHANG Y, LV R, et al. In-situ formation of quasi-solid polymer electrolyte for improved lithium metal battery performances at low temperatures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 542: 231773. |
| 63 | LI M J, YANG J X, SHI Y Q, et al. Soluble organic cathodes enable long cycle life, high rate, and wide-temperature lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(5): e2107226. |
| 64 | LIN Z Y, GUO X W, WANG Z C, et al. A wide-temperature superior ionic conductive polymer electrolyte for lithium metal battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 73: 104786. |
| 65 | WANG D Y, JIN B Y, REN Y Y, et al. Bifunctional solid-state copolymer electrolyte with stabilized interphase for high-performance lithium metal battery in a wide temperature range[J]. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(16): e202200993. |
| 66 | YU L, YU L, LIU Q, et al. Monolithic task-specific ionogel electrolyte membrane enables high-performance solid-state lithium-metal batteries in wide temperature range[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 32 (14): 2110653. |
| 67 | WANG A X, GENG S X, ZHAO Z, et al. In situ cross‐linked plastic crystal electrolytes for wide‐temperature and high‐energy‐density lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32 (28): 2201861. |
| 68 | LI Z, YU R, WENG S T, et al. Tailoring polymer electrolyte ionic conductivity for production of low-temperature operating quasi-all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 482. |
| 69 | ZHANG J, CHOU J, LUO X X, et al. A fully amorphous, dynamic cross-linked polymer electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries operating at subzero-temperatures[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2024, 63(5): e202316087. |
| 70 | LIANG H M, WANG L, WANG A P, et al. Tailoring practically accessible polymer/inorganic composite electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries: A review[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 42. |
| 71 | GAN H H, YUAN J L, ZHANG Y, et al. Electrospun composite gel polymer electrolytes with high thermal conductivity toward wide temperature lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4 (8): 8130-8141. |
| 72 | LV F, LIU K X, WANG Z Y, et al. Ultraviolet-cured polyethylene oxide-based composite electrolyte enabling stable cycling of lithium battery at low temperature[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 596: 257-266. |
| 73 | CHEN Z, KIM G T, KIM J K, et al. Highly stable quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries: Reinforced Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3/Li interface by a protection interlayer[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(30): 2101339. |
| 74 | YANG K, CHEN L K, MA J B, et al. Stable interface chemistry and multiple ion transport of composite electrolyte contribute to ultra-long cycling solid-state LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2/lithium metal batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(46): 24668-24675. |
| 75 | ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG S, GENG S X, et al. Agglomeration-free composite solid electrolyte and enhanced cathode-electrolyte interphase kinetics for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 51: 19-28. |
| 76 | WANG Y, CHEN Z, WU Y X, et al. PVDF-HFP/PAN/PDA@LLZTO composite solid electrolyte enabling reinforced safety and outstanding low-temperature performance for quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(17): 21526-21536. |
| 77 | ZHANG X Y, FU C K, CHENG S C, et al. Novel PEO-based composite electrolyte for low-temperature all-solid-state lithium metal batteries enabled by interfacial cation-assistance[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 56: 121-131. |
| 78 | DE KLERK N J J, WAGEMAKER M. Space-charge layers in all-solid-state batteries; important or negligible?[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(10): 5609-5618. |
| 79 | SHI P R, MA J B, LIU M, et al. A dielectric electrolyte composite with high lithium-ion conductivity for high-voltage solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2023, 18: 602-610. |
| 80 | CUAN J, ZHOU Y, ZHOU T F, et al. Borohydride-scaffolded Li/Na/Mg fast ionic conductors for promising solid-state electrolytes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(1): e1803533. |
| 81 | HU C J, SHEN Y B, SHEN M, et al. Superionic conductors via bulk interfacial conduction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(42): 18035-18041. |
| 82 | WEI Y Q, LI Z L, CHEN Z C, et al. A wide temperature 10 V solid-state electrolyte with a critical current density of over 20 mA·cm-2[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(10): 4679-4692. |
| 83 | LI J, ZHANG H T, CUI Y Y, et al. Constructing interfacial gradient layers and enhancing lithium salt dissolution kinetics for high-rate solid-state batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 102: 107716. |
| 84 | LI J, CAI Y J, CUI Y Y, et al. Fabrication of asymmetric bilayer solid-state electrolyte with boosted ion transport enabled by charge-rich space charge layer for -20~70 ℃ lithium metal battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 95: 107027. |
| 85 | HUANG X, HUANG S, WANG T, et al. Polyether-b-amide based solid electrolytes with well-adhered interface and fast kinetics for ultralow temperature solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33 (27): 2300683. |
| 86 | LI X Y, WANG Y, XI K, et al. Quasi-solid-state ion-conducting arrays composite electrolytes with fast ion transport vertical-aligned interfaces for all-weather practical lithium-metal batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 210. |
| 87 | ZHANG Y F, HUANG J J, LIU H, et al. Lamellar ionic liquid composite electrolyte for wide-temperature solid-state lithium-metal battery[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13 (23): 2300156. |
| 88 | WANG X, DU T, DONG X, et al. Application of advanced wide-temperature range and flame retardant "leaf-vein" structured functionality composite quasi-solid-state electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 68: 103355 |
| 89 | ZHENG Y, YAO Y Z, OU J H, et al. A review of composite solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: Fundamentals, key materials and advanced structures[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(23): 8790-8839. |
| 90 | ZHU F L, BAO H F, WU X S, et al. High-performance metal-organic framework-based single ion conducting solid-state electrolytes for low-temperature lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(46): 43206-43213. |
| 91 | LI D, WANG J, GUO S, et al. Molecular-scale interface engineering of metal-organic frameworks toward ion transport enables high-performance solid lithium metal battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30 (50): 2003945. |
| 92 | ZHANG Q, LI D X, WANG J, et al. Multiscale optimization of Li-ion diffusion in solid lithium metal batteries via ion conductive metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(13): 6976-6982. |
| 93 | LIU Y, WANG S, JIANG Z, et al. Multifunctional asymmetric electrolyte membrane encouraging durable lithium-metal batteries in wide temperature variations[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 677: 121636. |
| 94 | YAO M, YU T H, RUAN Q Q, et al. High-voltage and wide-temperature lithium metal batteries enabled by ultrathin MOF-derived solid polymer electrolytes with modulated ion transport[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(39): 47163-47173. |
| 95 | LI X, HOU Q, HUANG W, et al. Solution-processable covalent organic framework electrolytes for all-solid-state Li-organic batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5 (11): 3498-3506. |
| [1] | 周洪, 辛竹琳, 付豪, 张强, 魏凤. 基于专利数据挖掘的固态锂电池关键材料分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2386-2398. |
| [2] | 李昌豪, 汪书苹, 杨献坤, 曾子琪, 周昕玥, 谢佳. 低温型锂离子电池中的非水电解质研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2286-2299. |
| [3] | 姜森, 陈龙, 孙创超, 王金泽, 李如宏, 范修林. 低温锂电池电解液的发展及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2270-2285. |
| [4] | 陆洋, 闫帅帅, 马骁, 刘誌, 章伟立, 刘凯. 低温锂电池电解液的研究与应用[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2224-2242. |
| [5] | 廖世接, 魏颖, 黄云辉, 胡仁宗, 许恒辉. 间二氟苯稀释剂稳定电极界面助力低温锂金属电池[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2124-2130. |
| [6] | 王美龙, 薛煜瑞, 胡文茜, 杜可遇, 孙瑞涛, 张彬, 尤雅. 低温磷酸铁锂电池用全醚高熵电解液的设计研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2131-2140. |
| [7] | 王浩天, 王永刚, 董晓丽. 基于有机电极材料的低温电池研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2259-2269. |
| [8] | 黄嘉琦, 熊杰明, 谭恩忠, 孙心语, 程李巍, 王华. 重新审视低温钠金属半电池[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2151-2160. |
| [9] | 徐雄文, 莫英, 周望, 姚环东, 洪娟, 雷化, 涂健, 刘继磊. 硬碳动力学特性对钠离子电池低温性能的影响及机制[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2141-2150. |
| [10] | 马国政, 陈金伟, 熊兴宇, 杨振忠, 周钢, 胡仁宗. SnSb-Li4Ti5O12 复合负极材料低温高倍率储锂特性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2107-2115. |
| [11] | 王文涛, 魏一凡, 黄鲲, 吕国伟, 张思瑶, 唐昕雅, 陈泽彦, 林清源, 母志鹏, 王昆桦, 才华, 陈军. 低温锂离子电池测试标准及研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2300-2307. |
| [12] | 林炜琦, 卢巧瑜, 陈宇鸿, 邱麟媛, 季钰榕, 管联玉, 丁翔. 低温钠离子电池正极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2348-2360. |
| [13] | 李征, 杨振忠, 王琼, 胡仁宗. 基于专利情报分析的锂离子电池用低温电解液的发展现状和研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2317-2326. |
| [14] | 程广玉, 刘新伟, 刘硕, 顾海涛, 王可. 调控电解液溶剂组分实现LCO/C低温18650电池循环寿命显著提升[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2171-2180. |
| [15] | 赵飞, 陈英华, 马征, 李茜, 明军. 钾离子电池低温电解质的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2308-2316. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
