储能科学与技术 ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (5): 1589-1603.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0089
时文超1( ), 刘宇1, 张博冕1, 李琪2(
), 刘宇1, 张博冕1, 李琪2( ), 韩春华1, 麦立强1(
), 韩春华1, 麦立强1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-22
修回日期:2023-03-25
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-05-29
通讯作者:
李琪,麦立强
E-mail:swcshawn@163.com;liqi1@xhlab.cn;mlq518@whut.edu.cn
作者简介:时文超(1996—),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为水系锌离子电池体系的界面工程,E-mail:swcshawn@163.com;
基金资助:
Wenchao SHI1( ), Yu LIU1, Bomian ZHANG1, Qi LI2(
), Yu LIU1, Bomian ZHANG1, Qi LI2( ), Chunhua HAN1, Liqiang MAI1(
), Chunhua HAN1, Liqiang MAI1( )
)
Received:2023-02-22
Revised:2023-03-25
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-05-29
Contact:
Qi LI, Liqiang MAI
E-mail:swcshawn@163.com;liqi1@xhlab.cn;mlq518@whut.edu.cn
摘要:
水系锌金属电池(AZMBs)由于价格低廉、安全性高,在大规模储能领域极具潜力。然而,锌金属在常规水系电解液中并不稳定,界面处容易产生锌枝晶、析氢和腐蚀等副反应,导致AZMBs循环寿命较短。其中,电解液添加剂可以有效调控锌负极界面的化学特性和反应过程,显著提升其界面稳定性,大幅延长AZMBs的循环寿命。因此,对电解液添加剂稳定锌负极的相关研究进行总结,并对目前存在的关键问题提出新的解决思路非常必要。本文通过对近期相关文献进行探讨,简要介绍了锌负极目前面临的主要挑战及其相关机理,重点阐述了电解液添加剂对锌负极界面的主要调控机制,包括设计静电屏蔽层、贫水双电层(EDL)、原位固体电解质界面(SEI)层以及调控锌离子溶剂化鞘层。此外,还对不同添加剂类型进行了分类讨论,包括阳离子型、阴离子型、有机小分子型、有机聚合物型和其他类型,并分析了其各自的调控机理和对电化学性能的影响。最后,本文还对电解液添加剂策略稳定锌负极的未来发展方向提出了展望。
中图分类号:
时文超, 刘宇, 张博冕, 李琪, 韩春华, 麦立强. 电解液添加剂稳定水系电池锌负极界面的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603.
Wenchao SHI, Yu LIU, Bomian ZHANG, Qi LI, Chunhua HAN, Liqiang MAI. Research progress and prospect on electrolyte additives for stabilizing the zinc anode interface in aqueous batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603.
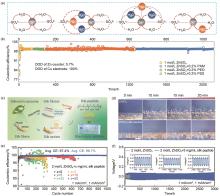
图6
(a) 加入和不加入聚合物添加剂的不同水电解质中的键合网络示意图[87];(b) 在不同聚合物添加剂的1 mol/L ZnSO4 水溶液中,在1 mA/cm2 、1 mAh/cm2 的测试条件下,Zn-Cu电池的库仑效率和循环性能[87];(c) 丝胶蛋白、丝素蛋白和具有不同构象和极性基团的肽分子之间的关系示意图,以及它们在AZMBs中作为电解液添加剂的应用[89];(d) 在电流密度为10 mA/cm2 时,含/不含丝肽的ZnSO4 电解质中Zn沉积形貌的原位光学观察[89];(e) 在含不同浓度的丝肽添加剂的ZnSO4 电解液中Zn-Cu电池的库仑效率[89];(f) 在含/不含丝肽的ZnSO4 电解液中Zn-Zn对称电池的循环性能[89]"


图7
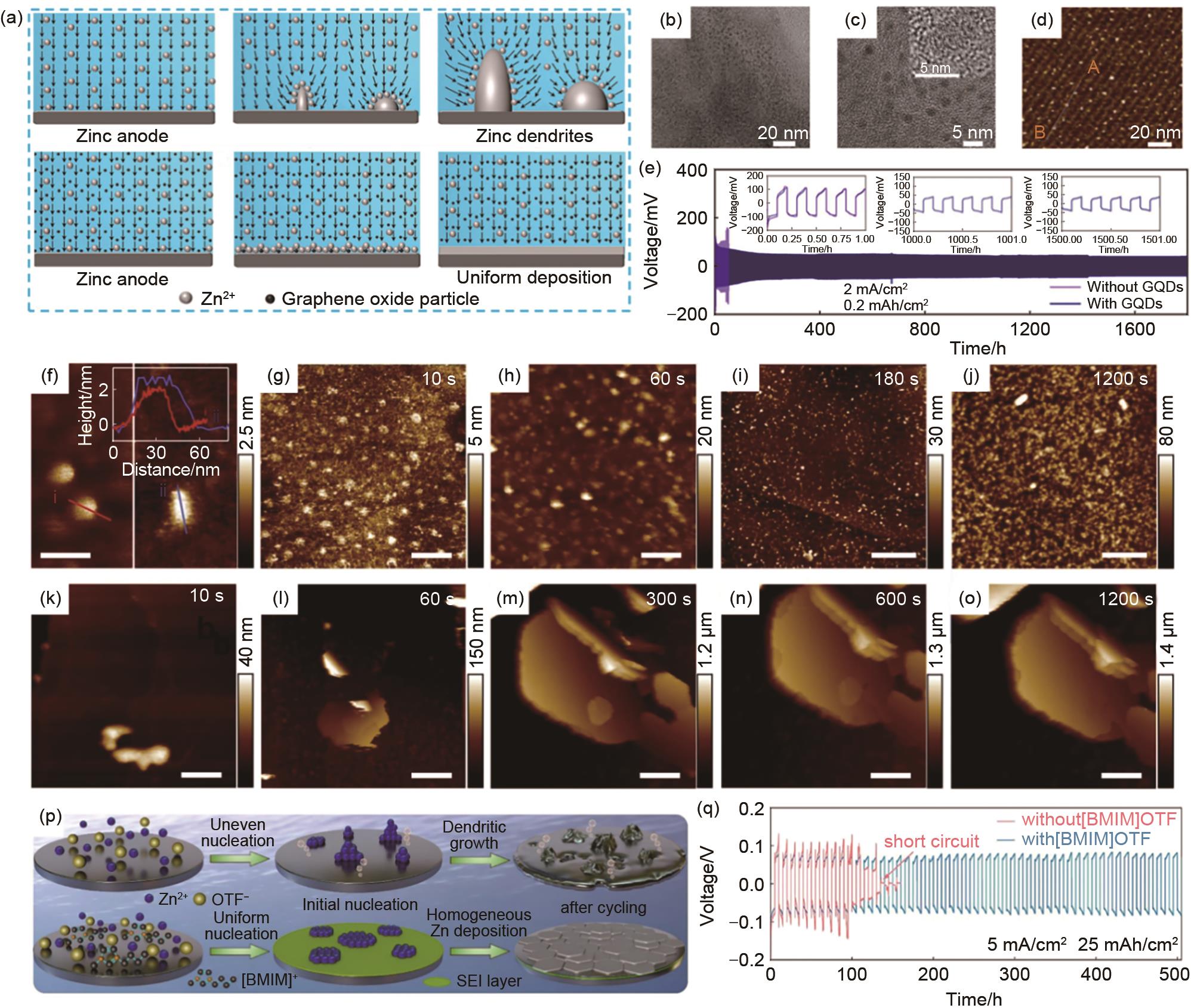
(a) 添加和不添加GO添加剂时锌负极表面电场分布,矢量场描述了电场的方向[91];(b)~(c) 制备的石墨烯量子点TEM图和HRTEM(c中的插图)[92];(d) 云母衬底上GQDs的AFM图和初始线A-B对应的高度剖面[92];(e) 在2 mA/cm2 下,添加和不添加GQDs的Zn||Zn对称电池的长循环曲线和相应的电压曲线[92];(f) 在云母上的纯C3N4QDs(左)和在高定向热解石墨上ZnSO4 水系电解液中的C3N4QDs(右),插图为对应线条的高度轮廓[93];(g)~(o) 在100 μA/cm2 的电流密度下,含C3N4QDs (g)~(j) 和不含C3N4QDs(k)~(o) 的HOPG上Zn沉积的原位AFM图[93];(p) 使用[BMIM]OTF添加剂稳定锌沉积过程的原理图[95];(q) 在5 mA/cm2 和25 mAh/cm2 下的循环性能[95]"
| 1 | CHU S, MAJUMDAR A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7411): 294-303. |
| 2 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7(1): 19-29. |
| 3 | BLANC L E, KUNDU D P, NAZAR L F. Scientific challenges for the implementation of Zn-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(4): 771-799. |
| 4 | OBAMA B. The irreversible momentum of clean energy[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6321): 126-129. |
| 5 | CAO J, ZHANG D D, ZHANG X Y, et al. A universal and facile approach to suppress dendrite formation for a Zn and Li metal anode[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(18): 9331-9344. |
| 6 | CAO L S, LI D, POLLARD T, et al. Fluorinated interphase enables reversible aqueous zinc battery chemistries[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(8): 902-910. |
| 7 | CHOI J W, AURBACH D. Promise and reality of post-lithium-ion batteries with high energy densities[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1(4): 1-16. |
| 8 | LI M, LU J, CHEN Z W, et al. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2018, 30(33): doi:10.1002/adma.201800561. |
| 9 | SONG M, TAN H, CHAO D L, et al. Recent advances in Zn-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(41): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201802564. |
| 10 | FANG G Z, ZHOU J, PAN A Q, et al. Recent advances in aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(10): 2480-2501. |
| 11 | ZENG X H, HAO J N, WANG Z J, et al. Recent progress and perspectives on aqueous Zn-based rechargeable batteries with mild aqueous electrolytes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 20: 410-437. |
| 12 | GUO X, ZHOU J, BAI C L, et al. Zn/MnO2 battery chemistry with dissolution-deposition mechanism[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2020, 16: doi: 10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100396. |
| 13 | CHAO D L, ZHU C R, SONG M, et al. A high-rate and stable quasi-solid-state zinc-ion battery with novel 2D layered zinc orthovanadate array[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2018, 30(32): doi: 10.1002/adma.201803181. |
| 14 | JIA X X, LIU C F, NEALE Z G, et al. Active materials for aqueous zinc ion batteries: Synthesis, crystal structure, morphology, and electrochemistry[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(15): 7795-7866. |
| 15 | KUNDU D P, ADAMS B D, DUFFORT V, et al. A high-capacity and long-life aqueous rechargeable zinc battery using a metal oxide intercalation cathode[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(10): 1-8. |
| 16 | KONAROV A, VORONINA N, JO J H, et al. Present and future perspective on electrode materials for rechargeable zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(10): 2620-2640. |
| 17 | CHEN L N, AN Q Y, MAI L Q. Recent advances and prospects of cathode materials for rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2019, 6(17): doi: 10.1002/admi.201900387. |
| 18 | MA L, SCHROEDER M A, BORODIN O, et al. Realizing high zinc reversibility in rechargeable batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2020, 5(10): 743-749. |
| 19 | DAI Y H, LIAO X B, YU R H, et al. Quicker and more Zn2+ storage predominantly from the interface[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2021, 33(26): doi: 10.1002/adma.202100359. |
| 20 | LI M, ZHANG Y X, HU J S, et al. Universal multifunctional hydrogen bond network construction strategy for enhanced aqueous Zn2+/proton hybrid batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 100: doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107539. |
| 21 | WU B K, LUO W, LI M, et al. Achieving better aqueous rechargeable zinc ion batteries with heterostructure electrodes[J]. Nano Research, 2021, 14(9): 3174-3187. |
| 22 | MA L T, ZHI C Y. Zn electrode/electrolyte interfaces of Zn batteries: A mini review[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2021, 122: doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2020.106898. |
| 23 | JIA H, WANG Z Q, TAWIAH B, et al. Recent advances in zinc anodes for high-performance aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 70: doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104523. |
| 24 | HUANG J H, GUO Z W, MA Y Y, et al. Recent progress of rechargeable batteries using mild aqueous electrolytes[J]. Small Methods, 2019, 3(1): doi: 10.1002/smtd.201800272. |
| 25 | LI Y B, FU J, ZHONG C, et al. Recent advances in flexible zinc-based rechargeable batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(1): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201802605. |
| 26 | LI Y G, DAI H J. Recent advances in zinc-air batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(15): 5257-5275. |
| 27 | ZHENG J X, ZHAO Q, TANG T, et al. Reversible epitaxial electrodeposition of metals in battery anodes[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6465): 645-648. |
| 28 | WANG Z, HUANG J H, GUO Z W, et al. A metal-organic framework host for highly reversible dendrite-free zinc metal anodes[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(5): 1289-1300. |
| 29 | XIE X S, LIANG S Q, GAO J W, et al. Manipulating the ion-transfer kinetics and interface stability for high-performance zinc metal anodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(2): 503-510. |
| 30 | WANG W X, HUANG G, WANG Y Z, et al. Organic acid etching strategy for dendrite suppression in aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(6): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202102797. |
| 31 | ZHANG Q, DAI Y H, ZHAO K N, et al. Dynamic reconstruction of Ni-Zn alloy solid-electrolyte interface for highly stable Zn anode[J]. Nano Research, 2022: 1-8. |
| 32 | HAO J N, LI B, LI X L, et al. An In-depth study of Zn metal surface chemistry for advanced aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2020, 32(34): doi: 10.1002/adma.202003021. |
| 33 | HAO J N, LI X L, ZHANG S L, et al. Designing dendrite-free zinc anodes for advanced aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(30): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202001263. |
| 34 | PARK S H, BYEON S Y, PARK J H, et al. Insight into the critical role of surface hydrophilicity for dendrite-free zinc metal anodes[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(9): 3078-3085. |
| 35 | DENG C B, XIE X S, HAN J W, et al. Stabilization of Zn metal anode through surface reconstruction of a cerium-based conversion film[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(51): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202103227. |
| 36 | KANG L T, CUI M W, JIANG F Y, et al. Nanoporous CaCO3 coatings enabled uniform Zn stripping/plating for long-life zinc rechargeable aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(25): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201801090. |
| 37 | YANG H J, CHANG Z, QIAO Y, et al. Constructing a super-saturated electrolyte front surface for stable rechargeable aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(24): 9377-9381. |
| 38 | ZHOU X, CHEN R P, CUI E H, et al. A novel hydrophobic-zincophilic bifunctional layer for stable Zn metal anodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 55: 538-545. |
| 39 | LIU Y, GUO T, LIU Q, et al. Ultrathin ZrO2 coating layer regulates Zn deposition and raises long-life performance of aqueous Zn batteries[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2022, 28: doi: 10.1016/j.mtener.2022.101056. |
| 40 | WANG Z Q, DONG L B, HUANG W Y, et al. Simultaneously regulating uniform Zn2+ flux and electron conduction by MOF/rGO interlayers for high-performance Zn anodes[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13(1): doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00594-7. |
| 41 | LI C, SUN Z T, YANG T, et al. Directly grown vertical graphene carpets as Janus separators toward stabilized Zn metal anodes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(33): doi: 10.1002/adma.202003425. |
| 42 | QIN Y, LIU P, ZHANG Q, et al. Advanced filter membrane separator for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2020, 16(39): doi: 10.1002/smll.202003106. |
| 43 | WANG F, BORODIN O, GAO T, et al. Highly reversible zinc metal anode for aqueous batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2018, 17(6): 543-549. |
| 44 | MA L T, CHEN S M, LI X L, et al. Liquid-free all-solid-state zinc batteries and encapsulation-free flexible batteries enabled by in situ constructed polymer electrolyte[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2020, 59(52): 23836-23844. |
| 45 | ZHAO J W, ZHANG J, YANG W H, et al. "Water-in-deep eutectic solvent" electrolytes enable zinc metal anodes for rechargeable aqueous batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 57: 625-634. |
| 46 | WAN F, ZHANG L L, DAI X, et al. Aqueous rechargeable zinc/sodium vanadate batteries with enhanced performance from simultaneous insertion of dual carriers[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-11. |
| 47 | GENG L S, MENG J S, WANG X P, et al. Eutectic electrolyte with unique solvation structure for high-performance zinc-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2022, 61(31): doi: 10.1002/anie.202206717. |
| 48 | GENG L S, WANG X P, HAN K, et al. Eutectic electrolytes in advanced metal-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(1): 247-260. |
| 49 | LI M, WANG X P, HU J S, et al. Comprehensive H2O molecules regulation via deep eutectic solvents for ultra-stable zinc metal anode[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(8): doi: 10.1002/anie.202215552. |
| 50 | LIU Y, AN Y K, WU L, et al. Interfacial chemistry modulation via amphoteric glycine for a highly reversible zinc anode[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(1): 552-560. |
| 51 | LIU Q, CHEN R P, XU L, et al. Steric molecular combing effect enables ultrafast self-healing electrolyte in quasi-solid-state zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(8): 2825-2832. |
| 52 | XING Z H, HUANG C D, HU Z L. Advances and strategies in electrolyte regulation for aqueous zinc-based batteries[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2022, 452: doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214299. |
| 53 | YAN H H, ZHANG X K, YANG Z W, et al. Insight into the electrolyte strategies for aqueous zinc ion batteries[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2022, 452: doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214297. |
| 54 | LIU C X, XIE X S, LU B G, et al. Electrolyte strategies toward better zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(3): 1015-1033. |
| 55 | DU Y X, LI Y, XU B B, et al. Electrolyte salts and additives regulation enables high performance aqueous zinc ion batteries: A mini review[J]. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2022, 18(43): doi: 10.1002/smll.202104640. |
| 56 | GUO S, QIN L P, ZHANG T S, et al. Fundamentals and perspectives of electrolyte additives for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 34: 545-562. |
| 57 | GAO P, RU Q, YAN H L, et al. A durable Na0.56V2O5 nanobelt cathode material assisted by hybrid cationic electrolyte for high-performance aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(1): 283-288. |
| 58 | LI W, WANG K L, CHENG S J, et al. A long-life aqueous Zn-ion battery based on Na3V2(PO4)2F3 cathode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 15: 14-21. |
| 59 | LASKA C A, AUINGER M, BIEDERMANN P U, et al. Effect of hydrogen carbonate and chloride on zinc corrosion investigated by a scanning flow cell system[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 159: 198-209. |
| 60 | TANG B Y, SHAN L T, LIANG S Q, et al. Issues and opportunities facing aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(11): 3288-3304. |
| 61 | LU W J, XIE C X, ZHANG H M, et al. Inhibition of zinc dendrite growth in zinc-based batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(23): 3996-4006. |
| 62 | YUAN L B, HAO J N, KAO C C, et al. Regulation methods for the Zn/electrolyte interphase and the effectiveness evaluation in aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(11): 5669-5689. |
| 63 | XU W W, WANG Y. Recent progress on zinc-ion rechargeable batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2019, 11(1): doi: 10.1007/s40820-019-0322-9. |
| 64 | WANG F, HU E Y, SUN W, et al. A rechargeable aqueous Zn2+-battery with high power density and a long cycle-life[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(11): 3168-3175. |
| 65 | DING F, XU W, GRAFF G L, et al. Dendrite-free lithium deposition via self-healing electrostatic shield mechanism[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(11): 4450-4456. |
| 66 | WANG P J, XIE X S, XING Z Y, et al. Mechanistic insights of Mg2+-electrolyte additive for high-energy and long-life zinc-ion hybrid capacitors[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(30): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202101158. |
| 67 | QIU Q L, CHI X W, HUANG J Q, et al. Highly stable plating/stripping behavior of zinc metal anodes in aqueous zinc batteries regulated by quaternary ammonium cationic salts[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2021, 8(5): 858-865. |
| 68 | XU W N, ZHAO K N, HUO W C, et al. Diethyl ether as self-healing electrolyte additive enabled long-life rechargeable aqueous zinc ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 62: 275-281. |
| 69 | HUANG C, ZHAO X, LIU S, et al. Stabilizing zinc anodes by regulating the electrical double layer with saccharin anions[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(38): doi: 10.1002/adma.202100445. |
| 70 | ZHAO Z M, ZHAO J W, HU Z L, et al. Long-life and deeply rechargeable aqueous Zn anodes enabled by a multifunctional brightener-inspired interphase[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(6): 1938-1949. |
| 71 | ZENG X H, MAO J F, HAO J N, et al. Electrolyte design for in situ construction of highly Zn2+-conductive solid electrolyte interphase to enable high-performance aqueous Zn-ion batteries under practical conditions[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla), 2021, 33(11): doi: 10.1002/adma.202007416. |
| 72 | HAO J N, YUAN L B, YE C, et al. Boosting zinc electrode reversibility in aqueous electrolytes by using low-cost antisolvents[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2021, 60(13): 7366-7375. |
| 73 | CHANG Z, YANG H, QIAO Y, et al. Tailoring the solvation sheath of cations by constructing electrode front‐faces for rechargeable batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022: doi: 10.1002/adma.202201339. |
| 74 | BAYAGUUD A, LUO X, FU Y P, et al. Cationic surfactant-type electrolyte additive enables three-dimensional dendrite-free zinc anode for stable zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(9): 3012-3020. |
| 75 | GUAN K L, TAO L, YANG R, et al. Anti-corrosion for reversible zinc anode via a hydrophobic interface in aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(9): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202103557. |
| 76 | LI Y H, WU P F, ZHONG W, et al. A progressive nucleation mechanism enables stable zinc stripping-plating behavior[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(10): 5563-5571. |
| 77 | ZHAO R R, WANG H F, DU H R, et al. Lanthanum nitrate as aqueous electrolyte additive for favourable zinc metal electrodeposition[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1-9. |
| 78 | ZHONG Y, CHENG Z X, ZHANG H W, et al. Monosodium glutamate, an effective electrolyte additive to enhance cycling performance of Zn anode in aqueous battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 98: doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107220. |
| 79 | HAN D L, WANG Z X, LU H T, et al. A self-regulated interface toward highly reversible aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(9): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202102982. |
| 80 | ZHANG W, DAI Y H, CHEN R W, et al. Highly reversible zinc metal anode in a dilute aqueous electrolyte enabled by a pH buffer additive[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2023, 62(5): doi: 10.1002/anie.202212695. |
| 81 | QIU M J, SUN P, QIN A M, et al. Metal-coordination chemistry guiding preferred crystallographic orientation for reversible zinc anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 49: 463-470. |
| 82 | WU Z Z, LI M, TIAN Y H, et al. Cyclohexanedodecol-assisted interfacial engineering for robust and high-performance zinc metal anode[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00846-0. |
| 83 | ZENG X M, MENG X J, JIANG W, et al. In-situ constructing polyacrylamide interphase enables dendrite-free zinc anode in aqueous batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 378: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138106. |
| 84 | ZHANG D H, WARREN A J, LI G J, et al. Electrodeposition of zinc in aqueous electrolytes containing high molecular weight polymers[J]. Macromolecules, 2020, 53(7): 2694-2701. |
| 85 | YAN M D, XU C L, SUN Y, et al. Manipulating Zn anode reactions through salt anion involving hydrogen bonding network in aqueous electrolytes with PEO additive[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 82: doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105739. |
| 86 | JIN Y, HAN K S, SHAO Y Y, et al. Stabilizing zinc anode reactions by polyethylene oxide polymer in mild aqueous electrolytes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(43): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202003932. |
| 87 | YAN M D, DONG N L, ZHAO X S, et al. Tailoring the stability and kinetics of Zn anodes through trace organic polymer additives in dilute aqueous electrolyte[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(9): 3236-3243. |
| 88 | GUO G L, TAN X P, WANG K D, et al. High-efficiency and stable Zn-Na3V2(PO4)3 aqueous battery enabled by electrolyte-induced interphasial engineering[J]. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(11): doi: 10.1002/cssc.202200313. |
| 89 | WANG B J, ZHENG R, YANG W, et al. Synergistic solvation and interface regulations of eco-friendly silk peptide additive enabling stable aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(23): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202112693. |
| 90 | SUN C, WU C P, GU X X, et al. Interface engineering via Ti3C2Tx MXene electrolyte additive toward dendrite-free zinc deposition[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13(1): doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00612-8. |
| 91 | ABDULLA J, CAO J, ZHANG D D, et al. Elimination of zinc dendrites by graphene oxide electrolyte additive for zinc-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(5): 4602-4609. |
| 92 | ZHANG H, GUO R T, LI S, et al. Graphene quantum dots enable dendrite-free zinc ion battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 92: doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106752. |
| 93 | ZHANG W Y, DONG M Y, JIANG K R, et al. Self-repairing interphase reconstructed in each cycle for highly reversible aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1-12. |
| 94 | PERIYAPPERUMA K, POZO-GONZALO C, MACFARLANE D R, et al. High Zn concentration pyrrolidinium-dicyanamide-based ionic liquid electrolytes for Zn2+/Zn0 electrochemistry in a flow environment[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(9): 4580-4590. |
| 95 | CHEN J Z, ZHOU W J, QUAN Y H, et al. Ionic liquid additive enabling anti-freezing aqueous electrolyte and dendrite-free Zn metal electrode with organic/inorganic hybrid solid electrolyte interphase layer[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 53: 629-637. |
| [1] | 余永诗, 夏先明, 黄弘扬, 姚雨, 芮先宏, 钟国彬, 苏伟, 余彦. 钠金属负极人工界面保护层的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1380-1391. |
| [2] | 张慧敏, 王京, 王一博, 郑家新, 邱景义, 曹高萍, 张浩. 锂离子电池SEI多尺度建模研究展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(2): 366-382. |
| [3] | 翟朋博, 常冬梅, 毕志杰, 赵宁, 郭向欣. 锂镧锆氧(LLZO)基固态锂电池界面关键问题研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(9): 2847-2865. |
| [4] | 翁素婷, 刘泽鹏, 杨高靖, 张思蒙, 张啸, 方遒, 李叶晶, 王兆翔, 王雪锋, 陈立泉. 冷冻电镜表征锂电池中的辐照敏感材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(3): 760-780. |
| [5] | 林乙龙, 肖敏, 韩东梅, 王拴紧, 孟跃中. 锂离子电池化成技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(1): 50-58. |
| [6] | 吴洁, 江小标, 杨旸, 吴勇民, 朱蕾, 汤卫平. NASICON结构Li1+xAlxTi2-x(PO4)3(0≤x≤0.5)固体电解质研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(5): 1472-1488. |
| [7] | 黄晓, 吴林斌, 黄祯, 林久, 许晓雄. 锂离子固体电解质研究中的电化学测试方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 479-500. |
| [8] | 高翔, 朱紫瑞. 原子力显微镜在锂离子电池研究中的应用[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(1): 75-82. |
| [9] | 张 涛,张晓平,温兆银. 固态锂空气电池研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5(5): 702-712. |
| [10] | 李放放,陈仕谋. 高压锂离子电池电解液添加剂研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5(4): 436-442. |
| [11] | 许晓雄, 邱志军, 官亦标, 黄祯, 金翼. 全固态锂电池技术的研究现状与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2013, 2(4): 331-341. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
