储能科学与技术 ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (5): 1570-1588.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0093
屈康康( ), 刘亚华(
), 刘亚华( ), 洪叠, 沈兆曦, 韩效钊, 张旭
), 洪叠, 沈兆曦, 韩效钊, 张旭
收稿日期:2023-02-22
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-05-29
通讯作者:
刘亚华
E-mail:qukangkang1999@163.com;liuyahua@hfut.edu.cn
作者简介:屈康康(1999—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为液流电池,E-mail:qukangkang1999@163.com;
基金资助:
Kangkang QU( ), Yahua LIU(
), Yahua LIU( ), Die HONG, Zhaoxi SHEN, Xiaozhao HAN, Xu ZHANG
), Die HONG, Zhaoxi SHEN, Xiaozhao HAN, Xu ZHANG
Received:2023-02-22
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-05-29
Contact:
Yahua LIU
E-mail:qukangkang1999@163.com;liuyahua@hfut.edu.cn
摘要:
中性水系有机液流电池是一种采用在中性条件下水溶性的有机电活性材料作为电解质,通过其可逆氧化还原过程实现能量的存储和释放的电化学储能技术,具有成本低廉、性能易于调控、操作安全性高等优势,在可再生能源的规模化并网和智能化分配方面显示出巨大的应用潜力。本文结合中性水系液流电池的研究现状,对基于二茂铁衍生物与TEMPO衍生物的正极电解质的发展现状、面临的主要挑战和未来发展方向进行了详细的综述和讨论,全面总结并比较了二茂铁衍生物与TEMPO衍生物的改性策略以及作为水系有机液流电池正极电解质的发展前景。相比之下,TEMPO衍生物在电极电势、溶解度、电池容量等方面都有着显著优势,被认为更具发展前景,但其长期循环稳定性略显不足。在已提出的诸多改性措施中,增大空间位阻与静电排斥是两大典型的策略。本文通过对TEMPO衍生物降解机理的分析总结,发现其降解主要是氮氧基键受到质子攻击断裂导致,笔者认为在TEMPO环上引入保护基团有望成为进一步提高其结构稳定性的新策略。
中图分类号:
屈康康, 刘亚华, 洪叠, 沈兆曦, 韩效钊, 张旭. 中性水系有机液流电池正极电解质的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1570-1588.
Kangkang QU, Yahua LIU, Die HONG, Zhaoxi SHEN, Xiaozhao HAN, Xu ZHANG. Research progress on positive electrolytes for neutral aqueous organic redox flow battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1570-1588.
表1
基于二茂铁的正极电解质的分子结构、溶解度、电势、理论电容量、扩散系数( D )、反应速率常数( k0 )以及文献出处"
| 名称 | 分子结构 | 溶解度/(mol/L) | 电势E1/2 /V | 理论比容量/(Ah/L) | D/(cm2/s) | k0/(cm/s) | 能量效率 EE | 电压效率 VE | 文献出处 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FcNCl | 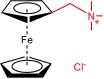 | 4 | 0.61 (vs NHE) | 107.2 | 3.74×10-6 | 3.66×10-5 | 72% (40 mA/cm2) | 72% (40 mA/cm2) | [ |
| FcN2Br2 |  | 3.1 | 0.61 (vs NHE) | 83.1 | 3.64×10-6 | 4.60×10-6 | 70% (40 mA/cm2) | 70% (40 mA/cm2) | [ |
| FC1N112-Br |  | 2.9 | 0.418—0.467 (vs Ag/AgCl) | 77.7 | / | / | / | / | [ |
| BTMAP-Fc | 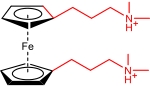 | 1.9 | 0.39(vs SHE) | 50.9 | 6.2×10-10 | 1.40×10-2 | / | / | [ |
| 1,1’FcDS | 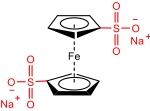 | 0.3 (1 NaNO3, 0.5 EG) | 0.651 (vs Ag/AgCl) | 16.1 | 1.29×10-6 | / | 60% (25 mA/cm2) | / | [ |
| Fc-SO3NH4 |  | 0.22 (1 NaCl) | 0.38 (vs Ag/AgCl) | 5.9 | 3.79×10-8 | / | 63.75% (20 mA/cm2) | 66.99% (20 mA/cm2) | [ |
| HMFc⊂HP-β-CD | 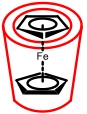 | 0.28 | 0.52 (vs NHE) | 4.23 | 2.22×10-6 | 3.70×10-2 | / | / | [ |
表3
基于TEMPO的正极电解质的分子结构、溶解度、电势、理论电容量、扩散系数( D )、反应速率常数( k0 )以及文献出处"
| 名称 | 分子结构 | 溶解度/(mol/L) | 电势E1/2/V | 理论电容量/(Ah/L) | D/(cm2/s) | k0/(cm/s) | 能量效率EE | 电压效率VE | 文献出处 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-OH-TEMPO | 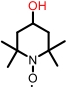 | 2.1 | 0.60 V (vs Ag/AgCl) | 56.3 | 2.95×10-5 | 2.6×10-4 | 62.5% (40 mA/cm2) | 62.1% (40 mA/cm2) | [ |
| 4-SO3K-TEMPO | 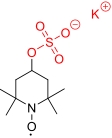 | >1 (2 ZnCl2,1 NH4Cl) | 0.61 V (vs Ag/AgCl) | >26.7 | 2.98×10-6 | 1.91×10-3 | — | 52% (80 mA/cm2) | [ |
| 4-COONa-TEMPO | 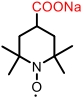 | 2.5 | 0.60 V (vs Ag/AgCl) | 67 | 5.45×10-6 | 2.1×10-2 | 64% (40 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| TEMPTMA | 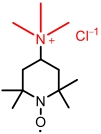 | 3.2 | 0.79 (vs Ag/AgCl) | 85.8 | 4.8×10-6 | 4.2×10-2 | 50% (70 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| TMAP-TEMPO | 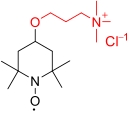 | 4.62 | 0.81 V (vs SHE) | 123.8 | 3.48×10-6 | 1.02×10-2 | 93.41% (10 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| N2-TEMPO |  | 3.0 | >0.80 V (vs SHE) | 80.4 | 5.15×10-6 | — | 70.3% (40 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| Ploy(TEMPO) |  | — | 0.70 V (vs Ag/AgCl) | — | 7.0×10-8 | 4.1×10-4 | 75% (40 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| 1-methyl-imidazolium functio-nalized TEMPO |  | — | 0.71 V (vs Ag/AgCl) | — | — | — | 93.7% (1.25 mA/cm2) | 97.7% (1.25 mA/cm2) | [ |
| (TPABPy)Cl3 |  | >1.5 | 0.967 V (vs SHE) | >37.6 | 2.97×10-6 | 7.50×10-2 | 70.6% (60 mA/cm2) | 71.1% (60 mA/cm2) | [ |
| Pyr-TEMPO | 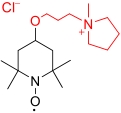 | >3.35 | 0.81 V (vs SHE) | >89.8 | 4.07×10-6 | 1.42×10-2 | 84% (40 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| PSS-TEMPO | 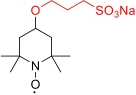 | >2.0 | 0.805 V (vs SHE) | >53.6 | 3.36×10-6 | 5.29×10-3 | 80% (40 mA/cm2) | — | [ |
| 1 | JIN S, SHAO Y Q, GAO X S, et al. Designing interphases for practical aqueous zinc flow batteries with high power density and high areal capacity[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(39): doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq4456. |
| 2 | 2021年全国电力工业统计数据发布[N]. 国家电网报, 2022-01-27(1). |
| 3 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. |
| 4 | SERVICE R F. Advances in flow batteries promise cheap backup power[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6414): 508-509. |
| 5 | LIN K X, CHEN Q, GERHARDT M R, et al. Alkaline quinone flow battery[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6255): 1529-1532. |
| 6 | SINGH V, KIM S, KANG J, et al. Aqueous organic redox flow batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2019, 12(9): 1988-2001. |
| 7 | ZHAO E W, LIU T, JÓNSSON E, et al. In situ NMR metrology reveals reaction mechanisms in redox flow batteries[J]. Nature, 2020, 579(7798): 224-228. |
| 8 | PERRY M L. BATTERIES. Expanding the chemical space for redox flow batteries[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6255): 1452. |
| 9 | 夏力行, 刘昊, 刘琳, 等. 有机氧化还原液流电池的研究进展[J]. 电化学, 2018, 24(5): 466-487. |
| XIA L (H /X), LIU H, LIU L, et al. Recent progresses in organic redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2018, 24(5): 466-487. | |
| 10 | 杨霖霖, 王少鹏, 倪蕾蕾, 等. 新型液流电池研究进展[J]. 上海电气技术, 2015, 8(1): 46-49. |
| YANG L L, WANG S P, NI L L, et al. The progression on the development of new redox flow batteries[J]. Journal, 2015, 8(1): 46-49. | |
| 11 | SÁNCHEZ-DÍEZ E, VENTOSA E, GUARNIERI M, et al. Redox flow batteries: Status and perspective towards sustainable stationary energy storage[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 481: doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228804. |
| 12 | ARCHANA K S, SURESH S, RAGUPATHY P, et al. Investigations on new Fe-Mn redox couple based aqueous redox flow battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 345: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020. 136245. |
| 13 | JEENA C B, ELSA P, MOLY P P, et al. A dendrite free Zn‐Fe hybrid redox flow battery for renewable energy storage[J]. Energy Storage, 2021, 4: doi: 10.1002/est2.275. |
| 14 | SHIN M, NOH C, KWON Y. Stability enhancement for all‐iron aqueous redox flow battery using iron-3-[bis(2‐hydroxyethyl) amino]-2-hydroxy propane sulfonic acid complex and ferrocyanide as redox couple[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 46: 6866-6875. |
| 15 | SHOU-GUANG Y, SUN X F, XIAO M, et al. Optimization analysis of the internal structure of flow-assisted zinc-nickel battery driven by a propeller[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 11(2): 1-8. |
| 16 | ZHEN Y H, ZHANG C J, YUAN J S, et al. A high-performance all-iron non-aqueous redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 445: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227331. |
| 17 | HU J, YUE M, ZHANG H M, et al. A boron nitride nanosheets composite membrane for a long-life zinc-based flow battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(17): 6715-6719. |
| 18 | XU Z Y,WU M C. Toward dendrite-free deposition in zinc-based flow batteries: status and prospects[J]. Batteries, 2022, 8: doi: 10.3390/batteries8090117. |
| 19 | KHOR A, LEUNG P, MOHAMED M R, et al. Review of zinc-based hybrid flow batteries: From fundamentals to applications[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2018, 8: 80-108. |
| 20 | MUNDARAY E, SÁEZ A, SOLLA-GULLÓN J, et al. New insights into the performance of an acid-base electrochemical flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 506: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2021.230233. |
| 21 | ANDREWS J, SEIF MOHAMMADI S. Towards a 'proton flow battery': Investigation of a reversible PEM fuel cell with integrated metal-hydride hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(4): 1740-1751. |
| 22 | LIANG Q, CHEN F M, WANG S F, et al. An organic flow desalination battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 20: 203-207. |
| 23 | LIU Y, CHEN Q, SUN P, et al. Organic electrolytes for aqueous organic flow batteries[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2021, 20: doi: 10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100634. |
| 24 | ZHANG C K, LI X F. Perspective on organic flow batteries for large-scale energy storage[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 30: doi:10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100836. |
| 25 | DUAN W, LI B, LU D, et al. Towards an all-vanadium redox flow battery with higher theoretical volumetric capacities by utilizing the VO2+/V3+ couple[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2018, 27: 1381-1385. |
| 26 | HSIEH W Y, LEU C H, WU C H, et al. Measurement of local current density of all-vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 271: 245-251. |
| 27 | CHEN H, ZHANG X Y, ZHANG S R, et al. A comparative study of iron-vanadium and all-vanadium flow battery for large scale energy storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132403. |
| 28 | WEI X, NIE Z, LUO Q, et al. Nanoporous polytetrafluoroethylene/silica composite separator as a high-performance all-vanadium redox flow battery membrane[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3: 1215-1220. |
| 29 | 张华民. 全钒液流电池的技术进展、不同储能时长系统的价格分析及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(9): 2772-2780. |
| ZHANG H M. Development, cost analysis considering various durations, and advancement of vanadium flow batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2772-2780. | |
| 30 | WILK A, SZYPULSKA-KOZIARSKA D, WISZNIEWSKA B. The toxicity of vanadium on gastrointestinal, urinary and reproductive system, and its influence on fertility and fetuses malformations[J]. Postepy Higieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej (Online), 2017, 71(0): 850-859. |
| 31 | 袁治章, 刘宗浩, 李先锋. 液流电池储能技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(9): 2944-2958. |
| YUAN Z Z, LIU Z H, LI X F. Research progress of flow battery technologies[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2944-2958. | |
| 32 | RAMAR A, WANG F M, FOENG R, et al. Organic redox flow battery: Are organic redox materials suited to aqueous solvents or organic solvents?[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 558: doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03399-1. |
| 33 | HUSKINSON B, MARSHAK M P, SUH C, et al. A metal-free organic-inorganic aqueous flow battery[J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7482): 195-198. |
| 34 | WEI X, PAN W, DUAN W, et al. Materials and systems for organic redox flow batteries: status and challenges[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2: 2187-2204. |
| 35 | TANG L, LEUNG P, MOHAMED M R, et al. Capital cost evaluation of conventional and emerging redox flow batteries for grid storage applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 437: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141460. |
| 36 | NGUYEN T P, EASLEY A D, KANG N R, et al. Polypeptide organic radical batteries[J]. Nature, 2021, 593(7857): 61-66. |
| 37 | BEH EUGENE S, DIANA D P, GRACIA REBECCA L, et al. A neutral pH aqueous organic-organometallic redox flow battery with extremely high capacity retention[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(3): 639-644. |
| 38 | JIN M, FELL E M, VINA-LOPEZ L, et al. Near neutral pH redox flow battery with low permeability and long-lifetime phosphonated viologen active species[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10: doi: 10.1002/aenm.202000100. |
| 39 | 陈倩如. 水系有机液流电池正极电解质的制备及性能研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, . |
| CHEN Q R. Preparation and properties of cathode electrolyte for water-based organic flow battery[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, . | |
| 40 | COSIMBESCU L, WEI X L, VIJAYAKUMAR M, et al. Anion-tunable properties and electrochemical performance of functionalized ferrocene compounds[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 1-9. |
| 41 | GOODWIN C A P, GIANSIRACUSA M J, GREER S M, et al. Isolation and electronic structures of derivatized manganocene, ferrocene and cobaltocene anions[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2021, 13(3): 243-248. |
| 42 | MALISCHEWSKI M, ADELHARDT M, SUTTER J, et al. Isolation and structural and electronic characterization of salts of the decamethylferrocene dication[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6300): 678-682. |
| 43 | YAN Q H, ZHI N, YANG L, et al. A highly sensitive uric acid electrochemical biosensor based on a nano-cube cuprous oxide/ferrocene/uricase modified glassy carbon electrode[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1-10. |
| 44 | HU B, DEBRULER C, RHODES Z, et al. Long-cycling aqueous organic redox flow battery (AORFB) toward sustainable and safe energy storage[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(3): 1207-1214. |
| 45 | KIM S, KIM D, HWANG G, et al. A bromide-ligand ferrocene derivative redox species with high reversibility and electrochemical stability for aqueous redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 869: doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem. 2020.114131. |
| 46 | ZHAO Z L, ZHANG B S, SCHRAGE B, et al. Investigations into aqueous redox flow batteries based on ferrocene bisulfonate[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3: 10270-10277. |
| 47 | YAO Y W, XU H, TIAN Z Z, et al. Simple-synthesized sulfonated ferrocene ammonium for aqueous redox flow batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4: 8052-8058. |
| 48 | LI Y Y, XU Z A, LIU Y H, et al. Functioning water-insoluble ferrocenes for aqueous organic flow battery via host-guest inclusion[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(2): 745-752. |
| 49 | CHEN Q R, LI Y Y, LIU Y H, et al. Designer ferrocene catholyte for aqueous organic flow batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(5): 1295-1301. |
| 50 | WINSBERG J, HAGEMANN T, JANOSCHKA T, et al. Redox-flow batteries: from metals to organic redox-active materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56: 686-711. |
| 51 | 刘静嘉, 张宇婷, 蔡辉宇, 等. TEMPO及其衍生物在有机液流电池体系中的应用[J]. 大学化学, 2017, 32(11): 32-44. |
| LIU J J, ZHANG Y T, CAI H Y, et al. TEMPO and lts derivatives in organic redox-flow batteries[J]. University Chemistry, 2017, 32(11): 32-44. | |
| 52 | HU X Q, QI X T, CHEN J R, et al. Catalytic N-radical cascade reaction of hydrazones by oxidative deprotonation electron transfer and TEMPO mediation[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 1-12. |
| 53 | YOKOI T, OTANI T, ISHII K. In vivo fluorescence bioimaging of ascorbic acid in mice: Development of an efficient probe consisting of phthalocyanine, TEMPO, and albumin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-9. |
| 54 | JI L L, DAI Y Y, YAN S M, et al. A fast electrochromic polymer based on TEMPO substituted polytriphenylamine[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-9. |
| 55 | JIE X M, SHANG Y P, CHEN Z N, et al. Differentiation between enamines and tautomerizable imines in the oxidation reaction with TEMPO[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-10. |
| 56 | NUTTING J E, RAFIEE M, STAHL S S. Tetramethylpiperidine N-oxyl (TEMPO), phthalimide N-oxyl (PINO), and related N-oxyl species: Electrochemical properties and their use in electrocatalytic reactions[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(9): 4834-4885. |
| 57 | LIU T, WEI X L, NIE Z, et al. A total organic aqueous redox flow battery employing a low cost and sustainable methyl viologen anolyte and 4-HO-TEMPO catholyte[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6: doi: 10.1002/aenm.201501449. |
| 58 | JAN W, CHRISTIAN S, ALMUT S, et al. Aqueous 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl catholytes for a high-capacity and high current density oxygen-insensitive hybrid-flow battery[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(2): 411-416. |
| 59 | LIU B, TANG C W, JIANG H R, et al. Carboxyl-functionalized TEMPO catholyte enabling high-cycling-stability and high-energy-density aqueous organic redox flow batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9: 6258-6265. |
| 60 | JANOSCHKA T, MARTIN N, HAGER M D, et al. An aqueous redox-flow battery with high capacity and power: The TEMPTMA/MV system[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2016, 55(46): 14427-14430. |
| 61 | LIU Y H, GOULET M A, TONG L C, et al. A long-lifetime all-organic aqueous flow battery utilizing TMAP-TEMPO radical[J]. Chem, 2019, 5: 1861-1870. |
| 62 | HU B, HU M W, LUO J, et al. A stable, low permeable TEMPO catholyte for aqueous total organic redox flow batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 12: doi: 10.1002/aenm.202102577. |
| 63 | JANOSCHKA T, MARTIN N, MARTIN U, et al. An aqueous, polymer-based redox-flow battery using non-corrosive, safe, and low-cost materials[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7607): S9-S10. |
| 64 | CHANG Z J, HENKENSMEIER D, CHEN R Y. Shifting redox potential of nitroxyl radical by introducing an imidazolium substituent and its use in aqueous flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 418: 11-16. |
| 65 | HU S Z, WANG L W, YUAN X Z, et al. Viologen-decorated TEMPO for neutral aqueous organic redox flow batteries[J]. Energy Material Advances, 2021, 2021: 1-8. |
| 66 | PAN M G, GAO L Z, LIANG J C, et al. Reversible redox chemistry in pyrrolidinium‐based TEMPO radical and extended viologen for high-voltage and long-life aqueous redox flow batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12: doi: 10.1002/aenm.202103478. |
| 67 | GAO M Q, SALLA M, SONG Y X, et al. High-power near-neutral aqueous all organic redox flow battery enabled with a pair of anionic redox species[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2022, 61(41): doi: 10.1002/anie.202208223. |
| 68 | LUO J, HU B, HU M W, et al. Status and prospects of organic redox flow batteries toward sustainable energy storage[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(9): 2220-2240. |
| 69 | WINSBERG J, STOLZE C, MUENCH S, et al. TEMPO/phenazine combi-molecule: a redox-active material for symmetric aqueous redox-flow batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1: 976-980. |
| 70 | JANOSCHKA T, FRIEBE C, HAGER M D, et al. An approach toward replacing vanadium: A single organic molecule for the anode and cathode of an aqueous redox-flow battery[J]. ChemistryOpen, 2017, 6(2): 216-220. |
| 71 | ZHU Y Z, YANG F, NIU Z H, et al. Enhanced cyclability of organic redox flow batteries enabled by an artificial bipolar molecule in neutral aqueous electrolyte[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 417: 83-89. |
| 72 | HEILAND N, CIDARÉR C, ROHR C, et al. Design and evaluation of a boron dipyrrin electrophore for redox flow batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(21): 4215-4222. |
| 73 | HAGEMANN T, WINSBERG J, HÄUPLER B, et al. A bipolar nitronyl nitroxide small molecule for an all-organic symmetric redox-flow battery[J]. NPG Asia Materials, 2017, 9(1): e340. |
| 74 | TAYLOR P, MILLER J L, BUTLER P. Energy storage opportunities analysis phase ii final report a study for the doe energy storage systems program[N]. Sandia National Laboratories, 2002-05-01. |
| 75 | 朱兆武, 张旭堃, 苏慧, 等. 全钒液流电池提高电解液浓度的研究与应用现状[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(11): 3439-3446. |
| ZHU Z W, ZHANG X K, SU H, et al. Research and application of increasing electrolyte concentration in all vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 3439-3446. |
| [1] | 李林泽, 张向文. 基于组合频率阻抗特征的锂离子电池健康状态估算[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1705-1712. |
| [2] | 雷蕾, 高鹏, 冯娜娜, 蔡坤鹏, 张海, 张扬. 锆酸镧锂固态电解质合成过程多因素影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1625-1635. |
| [3] | 张吉栋, 杨展, 黄建国. 基于天然纤维素物质的C/TiO2/CuMoO4 微-纳结构复合纤维材料构筑及其电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1616-1624. |
| [4] | 时文超, 刘宇, 张博冕, 李琪, 韩春华, 麦立强. 电解液添加剂稳定水系电池锌负极界面的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603. |
| [5] | 李金涛, 牟粤, 王静, 邱景义, 明海. 高镍正极材料的稳定改性方法研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1636-1654. |
| [6] | 王津, 张少飞, 孙金峰, 李田田. 纳米多孔合金快速燃烧氧化及高效储能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1480-1489. |
| [7] | 易永利, 于冉, 李武, 金翼, 戴哲仁. Mo, Al掺杂的Li7La3Zr2O12 基复合固态电解质的制备及全固态电池性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1490-1499. |
| [8] | 周俊龙, 赵鲁康, 刘朝孟, 高宣雯, 骆文彬. 量子点及其复合材料作为碱金属离子电池负极的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1392-1408. |
| [9] | 王轩臣, 王达, 刘朝孟, 高宣雯, 骆文彬. 钾离子电池电解液的研究进展及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1409-1426. |
| [10] | 余永诗, 夏先明, 黄弘扬, 姚雨, 芮先宏, 钟国彬, 苏伟, 余彦. 钠金属负极人工界面保护层的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1380-1391. |
| [11] | 朱璟, 申晓宇, 岑官骏, 乔荣涵, 郝峻丰, 季洪祥, 田孟羽, 金周, 詹元杰, 武怿达, 闫勇, 贲留斌, 俞海龙, 刘燕燕, 黄学杰. 锂电池百篇论文点评(2023.2.1—2023.3.31)[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(5): 1553-1569. |
| [12] | 黄渭彬, 张彪, 范金成, 杨伟, 邹汉波, 陈胜洲. ZIF-8复合PEO基固态电解质的制备与改性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(4): 1083-1092. |
| [13] | 张顺, 曾芳磊, 李宁, 袁宁一. 高阻燃硫正极的制备及其性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(4): 1018-1024. |
| [14] | 杨基鹏, 叶强. 基于Bi3+ 过膜缓释策略的在线铋沉积对铁铬液流电池性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(4): 1075-1082. |
| [15] | 程志翔, 曹伟, 户波, 程云芳, 李鑫, 姜丽华, 金凯强, 王青松. 储能用大容量磷酸铁锂电池热失控行为及燃爆传播特性[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(3): 923-933. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
