Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (2): 601-612.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0674
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuelin LI1( ), Zhiyu LIU2, Sen GUO1, Xiaojun LIU1, Pengliang ZHANG1, Chengcheng WANG1, Yuan LIANG1, Rui WANG2(
), Zhiyu LIU2, Sen GUO1, Xiaojun LIU1, Pengliang ZHANG1, Chengcheng WANG1, Yuan LIANG1, Rui WANG2( )
)
Received:2024-07-22
Revised:2024-08-22
Online:2025-02-28
Published:2025-03-18
Contact:
Rui WANG
E-mail:17006586@ceic.com;rui.wang.ej@chnenergy.com.cn
CLC Number:
Yuelin LI, Zhiyu LIU, Sen GUO, Xiaojun LIU, Pengliang ZHANG, Chengcheng WANG, Yuan LIANG, Rui WANG. Research progress on electrode structure design of vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 601-612.
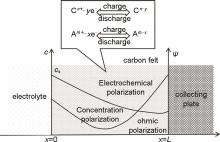
Fig. 1
Polarization diagram of a flow battery,where L represents the thickness of carbon felt, c represents the electrolyte concentration, cs represents the electrolyte concentration on the carbon felt end face, ψl represents the liquid phase potential, and ψs represents the solid phase potential"
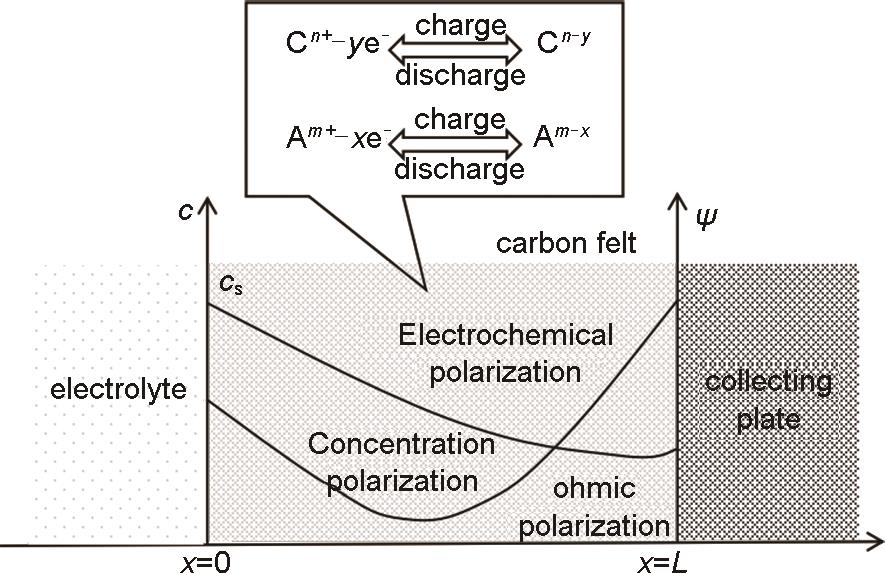
Fig. 5
(a) Multilayer electrode structure compression before and after comparison[43]; (b) Schematic diagram of gradient electrode design for VRFB[35]; (c) Cell structures with different electrode layer porosity[44]; (d) Schematic diagram of liquid flow pool with double electrode structure[45]"
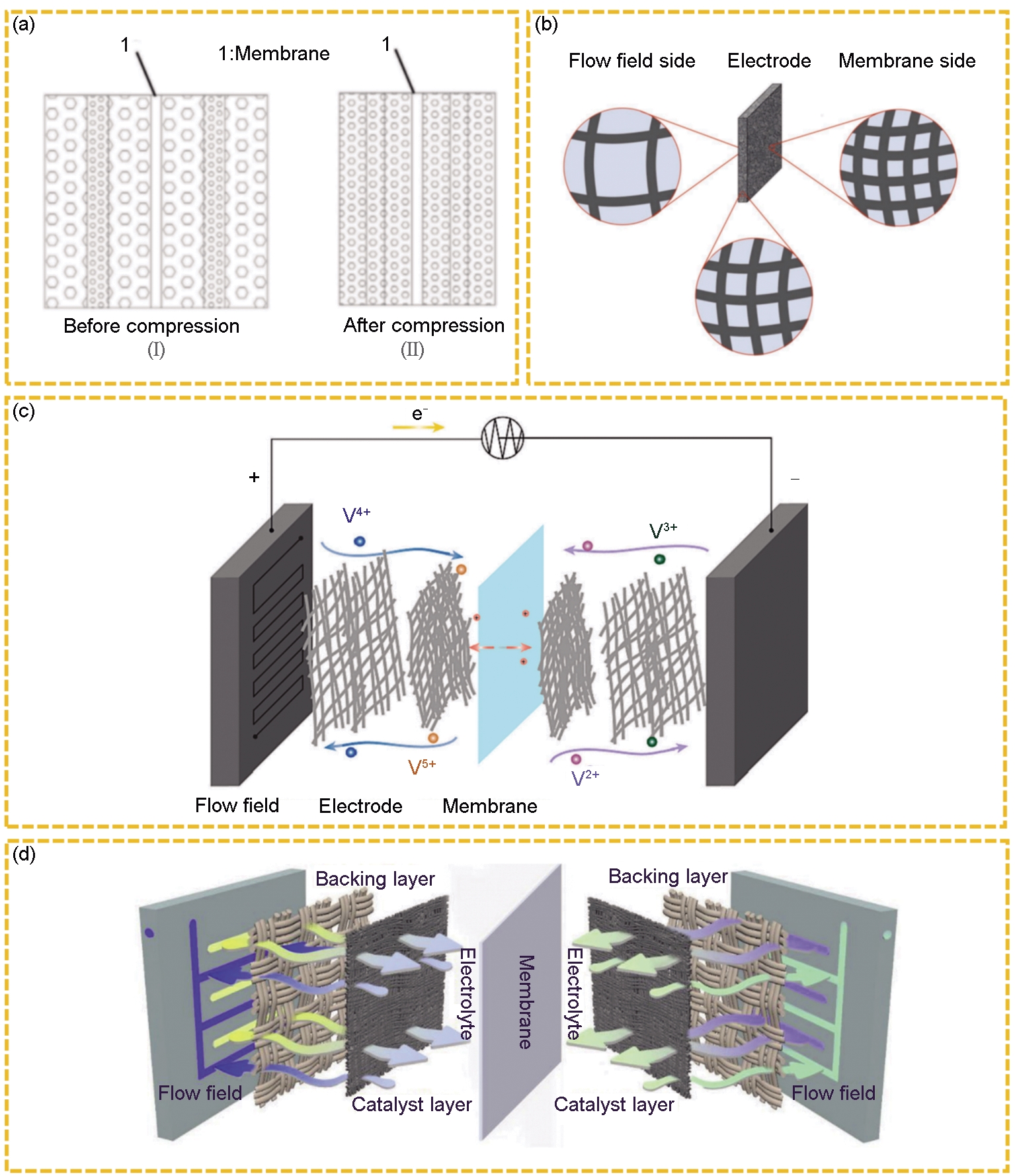
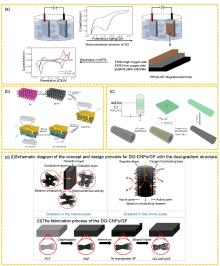
Fig. 6
(a) Preparation diagram and cyclic voltammetry diagram of novel composite electrode (ERGO-GP)[47]; (b) Manufacturing process of dual-functional gradient GO-rGO/GF electrode material[48]; (c) Schematic diagram of the synthesis process of CNF-AECF electrodes[49]; (d) DG-CNFs/GF electrode and synthesis process diagram[3]"

| 1 | LU M Y, YANG W W, BAI X S, et al. Performance improvement of a vanadium redox flow battery with asymmetric electrode designs[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 319: 210-226. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.06.158. |
| 2 | WANG Z Y, REN J Y, SUN J, et al. Characterizations and selections of electrodes with optimal performance for large-scale vanadium redox flow batteries through lab-scale experiments[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 549: 232094. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232094. |
| 3 | XU Z Y, JING M H, LIU J G, et al. Advanced dual-gradient carbon nanofibers/graphite felt composite electrode for the next-generation vanadium flow battery[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 136: 32-42. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2022. 06.051. |
| 4 | GAO J Y, YANG Y J, REN Y J, et al. A novel hafnium boride catalyst for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Ionics, 2022, 28(9): 4273-4282. DOI: 10.1007/s11581-022-04656-7. |
| 5 | SUN B, SKYLLAS-KAZACOS M. Modification of graphite electrode materials for vanadium redox flow battery application-I. Thermal treatment[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1992, 37(7): 1253-1260. DOI: 10.1016/0013-4686(92)85064-r. |
| 6 | LIU T, LI X F, XU C, et al. Activated carbon fiber paper based electrodes with high electrocatalytic activity for vanadium flow batteries with improved power density[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(5): 4626-4633. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b14478. |
| 7 | YUE L, LI W S, SUN F Q, et al. Highly hydroxylated carbon fibres as electrode materials of all-vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(11): 3079-3090. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon. 2010.04.044. |
| 8 | ZHANG W G, XI J Y, LI Z H, et al. Electrochemical activation of graphite felt electrode for VO2+/VO2 + redox couple application[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 89: 429-435. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.11.072. |
| 9 | ZHANG Z Y, XI J Y, ZHOU H P, et al. KOH etched graphite felt with improved wettability and activity for vanadium flow batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 218: 15-23. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.09.099. |
| 10 | BUSACCA C, DI BLASI O, GIACOPPO G, et al. High performance electrospun nickel manganite on carbon nanofibers electrode for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 355: 136755. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136755. |
| 11 | JING M H, ZHANG X S, FAN X Z, et al. CeO2 embedded electrospun carbon nanofibers as the advanced electrode with high effective surface area for vanadium flow battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 215: 57-65. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.08.095. |
| 12 | 孙洁. 基于流道结构设计的液流电池多孔电极中离子传质改进研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021. DOI: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx. 2021.002951. |
| SUN J. Study on improvement of ion mass transfer in porous electrode of flow battery based on flow channel structure design[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021. DOI: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2021.002951. | |
| 13 | AARON D, TANG Z J, PAPANDREW A B, et al. Polarization curve analysis of all-vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2011, 41(10): 1175-1182. DOI: 10.1007/s10800-011-0335-7. |
| 14 | XU Q, ZHAO T S. Determination of the mass-transport properties of vanadium ions through the porous electrodes of vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(26): 10841-10848. DOI: 10. 1039/C3CP51944A. |
| 15 | 赵天寿, 蒋浩然, 李文甲. 流体电池的化学工程科学问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(2): 170-177. DOI: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2023.02.003. |
| ZHAO T S, JIANG H R, LI W J. Chemical engineering scientific issue in flow cells[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2023, 37(2): 170-177. DOI: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2023.02.003. | |
| 16 | WANG Q, QU Z G, JIANG Z Y, et al. The numerical study of vanadium redox flow battery performance with different electrode morphologies and electrolyte inflow patterns[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 33: 101941. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101941. |
| 17 | EMMETT R K, ROBERTS M E. Recent developments in alternative aqueous redox flow batteries for grid-scale energy storage[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 506: 230087. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230087. |
| 18 | IYER V A, SCHUH J K, MONTOTO E C, et al. Assessing the impact of electrolyte conductivity and viscosity on the reactor cost and pressure drop of redox-active polymer flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 361: 334-344. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.06.052. |
| 19 | PARK S K, SHIM J, YANG J H, et al. The influence of compressed carbon felt electrodes on the performance of a vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 116: 447-452. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.073. |
| 20 | GUNDLAPALLI R, JAYANTI S. Effect of electrode compression and operating parameters on the performance of large vanadium redox flow battery cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 427: 231-242. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.04.059. |
| 21 | ZHANG K Y, YAN C W, TANG A. Unveiling electrode compression impact on vanadium flow battery from polarization perspective via a symmetric cell configuration[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 479: 228816. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2020.228816. |
| 22 | OH K, WON S, JU H. Numerical study of the effects of carbon felt electrode compression in all-vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 181: 13-23. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta. 2015.02.212. |
| 23 | BECKER M, BREDEMEYER N, TENHUMBERG N, et al. Polarization curve measurements combined with potential probe sensing for determining current density distribution in vanadium redox-flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 307: 826-833. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.01.011. |
| 24 | AARON D S, LIU Q, TANG Z, et al. Dramatic performance gains in vanadium redox flow batteries through modified cell architecture[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 206: 450-453. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.12.026. |
| 25 | HOUSER J, PEZESHKI A, CLEMENT J T, et al. Architecture for improved mass transport and system performance in redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 351: 96-105. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.083. |
| 26 | BHATTARAI A, WAI N, SCHWEISS R, et al. Advanced porous electrodes with flow channels for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 341: 83-90. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.11.113. |
| 27 | BHATTARAI A, WAI N, SCHWEISS R, et al. Vanadium redox flow battery with slotted porous electrodes and automatic rebalancing demonstrated on a 1 kW system level[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 236: 437-443. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.001. |
| 28 | LYU W R, LUO Y S, XU Y H, et al. Laser perforated porous electrodes in conjunction with interdigitated flow field for mass transfer enhancement in redox flow battery[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 224: 125313. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2024.125313. |
| 29 | ZHENG Q, XING F, LI X F, et al. Dramatic performance gains of a novel circular vanadium flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 277: 104-109. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2014.11.142. |
| 30 | YUE M, ZHENG Q, XING F, et al. Flow field design and optimization of high power density vanadium flow batteries: A novel trapezoid flow battery[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(2): 782-795. DOI: 10.1002/aic.15959. |
| 31 | GURIEFF N, CHEUNG C Y, TIMCHENKO V, et al. Performance enhancing stack geometry concepts for redox flow battery systems with flow through electrodes[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2019, 22: 219-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2019.02.014. |
| 32 | ZHENG Q, XING F, LI X F, et al. Flow field design and optimization based on the mass transport polarization regulation in a flow-through type vanadium flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 324: 402-411. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2016.05.110. |
| 33 | KIM J, PARK H. Recent advances in porous electrodes for vanadium redox flow batteries in grid-scale energy storage systems: A mass transfer perspective[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 545: 231904. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2022.231904. |
| 34 | LAN J J, LI K, YANG L, et al. Hierarchical nano-electrocatalytic reactor for high performance polysulfides redox flow batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(20): 20492-20501. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano. 3c07085. |
| 35 | JIANG H R, ZHANG B W, SUN J, et al. A gradient porous electrode with balanced transport properties and active surface areas for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 440: 227159. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2019.227159. |
| 36 | MAYRHUBER I, DENNISON C R, KALRA V, et al. Laser-perforated carbon paper electrodes for improved mass-transport in high power density vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 260: 251-258. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2014.03.007. |
| 37 | LEE K M, PAHLEVANINEZHAD M, SMITH V, et al. Improvement of vanadium redox flow battery performance obtained by compression and laser perforation of electrospun electrodes[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2023, 35: 101333. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtener.2023.101333. |
| 38 | ZHOU X L, ZENG Y K, ZHU X B, et al. A high-performance dual-scale porous electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 325: 329-336. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.06.048. |
| 39 | KOK M D R, KHALIFA A, GOSTICK J T. Multiphysics simulation of the flow battery cathode: Cell architecture and electrode optimization[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(7): A1408-A1419. DOI: 10.1149/2.1281607jes. |
| 40 | KABTAMU D M, CHEN J Y, CHANG Y C, et al. Water-activated graphite felt as a high-performance electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 341: 270-279. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.12.004. |
| 41 | WANG R, LI Y S, HE Y L. Achieving gradient-pore-oriented graphite felt for vanadium redox flow batteries: Meeting improved electrochemical activity and enhanced mass transport from nano- to micro-scale[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(18): 10962-10970. DOI: 10.1039/C9TA00807A. |
| 42 | JIANG H R, SHYY W, WU M C, et al. A bi-porous graphite felt electrode with enhanced surface area and catalytic activity for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 233: 105-113. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.033. |
| 43 | 刘盛林, 张华民, 马相坤, 等. 液流电池电极结构及液流电池电堆: CN 106549161A[P]. 2017-03-29. |
| LIU S L, ZHANG H M, MA X K, et al. Electrode structure of flow battery and flow battery stack: CN 106549161A[P]. 2017-03-29. | |
| 44 | ZHANG Z H, ZHANG B W, WEI L, et al. A composite electrode with gradient pores for high-performance aqueous redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 61: 106755. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2023.106755. |
| 45 | WU Q X, LYU Y H, LIN L Y, et al. An improved thin-film electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries enabled by a dual layered structure[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 410: 152-161. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.11.020. |
| 46 | CHEN W, KANG J L, SHU Q, et al. Analysis of storage capacity and energy conversion on the performance of gradient and double-layered porous electrode in all-vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Energy, 2019, 180: 341-355. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.05.037. |
| 47 | JING M H, ZHANG C L, QI X C, et al. Gradient-microstructural porous graphene gelatum/flexible graphite plate integrated electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(1): 916-923. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.10.123. |
| 48 | HU G J, JING M H, WANG D W, et al. A gradient bi-functional graphene-based modified electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 13: 66-71. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2017.12.026. |
| 49 | SUN J, JIANG H R, WU M C, et al. Aligned hierarchical electrodes for high-performance aqueous redox flow battery[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 271: 115235. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy. 2020.115235. |
| [1] | Haotian WANG, Yonggang WANG, Xiaoli DONG. Advances in low-temperature organic batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2259-2269. |
| [2] | Ran XU, Baodong WANG, Shaoliang WANG, Qi ZHANG, Lei ZHANG, Ziyang FENG. Research progress on heteroatom-doped electrodes used in all vanadium redox flow batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1849-1860. |
| [3] | Cong SUO, Yangfeng WANG, Zichen ZHU, Yan YANG. Research progress of soft carbon as negative electrodes in sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1807-1823. |
| [4] | Yu ZHANG, Yao YAO, Rui LIU, Lei JIN, Fei XUE, Peng ZHOU, Binyu XIONG. A joint estimation method for SOC/SOP of all vanadium redox batteries based on online parameter identification and ensemble Kalman filtering [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(11): 4089-4101. |
| [5] | Yanqi LIU, Zhaohai SONG, Tian HE, Zuoqiang DAI, Zongmin ZHENG. Research progress on integrated air electrodes for rechargeable Zn-air batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 383-397. |
| [6] | Meng LI, Yue WANG, Jingyi QIU, Yuehua WEN, Zhenwei ZHU, Wenjie MENG. Study on impedance of lithium-ion batteries with lithium iron phosphate and graphite system under low temperature [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(11): 3538-3544. |
| [7] | Xuan WANG, Qiang YE. The aggravation of side reactions caused by insufficient localized liquid supply in an all-vanadium redox flow battery stack [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1455-1467. |
| [8] | Jian YAO, Zhaoyang LIU, Hai WANG, Jiadong WANG, Xuanwen GAO, Jianzhong LI, Zhaomeng LIU, Yuchun ZHAI, Wenbin LUO. Exploration of mixed positive and negative electrodes of spent lithium iron phosphate batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(12): 3759-3767. |
| [9] | Zhaowu ZHU, Xukun ZHANG, Hui SU, Jian ZHANG, Lina WANG. Research and application of increasing electrolyte concentration in all vanadium redox flow battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 3439-3446. |
| [10] | Mingchang HU, Xueqing ZHOU, Xueyan HUANG, Jianjun XUE. Solvent-free fabrication of zinc-air electrodes and their battery performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2090-2096. |
| [11] | Kehuan XIE, Chuanchang LI, Jian CHEN, Longhai YU, zhun TAN, Weihai QIN. Simulation model advances in vanadium redox flow battery energy storage and monitoring method for state of charge [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2363-2372. |
| [12] | Dechao GUO, Yimin GUO, Qiwen ZHANG, Xiangyun CI, Fengrong HE. Preparation and characterization of solvent-free dry electrodes for lithium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(4): 1311-1316. |
| [13] | Yanming CUI, Zhihua ZHANG, Yuanqiao HUANG, Jiu LIN, Xiayin YAO, Xiaoxiong XU. Prototype all-solid-state battery electrodes preparation and assembly technology [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 836-847. |
| [14] | Chunyan YANG, Yunlong MA, Xiaoqiong FENG, Shiying ZHANG, Changsheng AN, Jingfeng LI. Research progress of carbon-based materials in aluminum-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 432-439. |
| [15] | Jian SHEN, Bixiong HUANG, Zhaokang XIE, Jiayin LI, Ningning LIU, Zhiqiang JIA. Internal structure layout and optimization design of FSEC racing power battery box [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(S1): 31-38. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
