Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (6): 1807-1823.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0033
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cong SUO( ), Yangfeng WANG, Zichen ZHU, Yan YANG(
), Yangfeng WANG, Zichen ZHU, Yan YANG( )
)
Received:2024-01-10
Revised:2024-02-02
Online:2024-06-28
Published:2024-06-26
Contact:
Yan YANG
E-mail:suocong.fshy@sinopec.com;yangyan.fshy@sinopec.com
CLC Number:
Cong SUO, Yangfeng WANG, Zichen ZHU, Yan YANG. Research progress of soft carbon as negative electrodes in sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1807-1823.
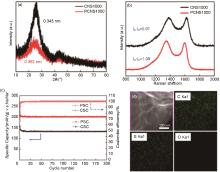
Fig. 8
(a) XRD patterns of CNS1000 and PCNS1000[50]; (b) Measurement of long-term cyclic stability of PCNS1000[50]; (c) Cyclic properties of CSC and PSC materials at 100 mA/g[52]; (d) Element mapping of STEM images and corresponding C-K, S-K, and O-K distributions for SG selected regions[53]"
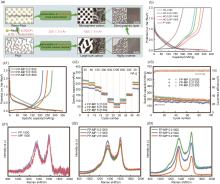
Fig. 10
(a) Schematic diagram of asphalt and resin co-carbonization[62]; (b) The second cycle charge-discharge curve of carbon material[62]; (c1) Initial constant discharge/charge curve of hard-soft carbon composite at 30 mA/g; (c2) Rate properties of hard-soft carbon composites at 30-1200 mA/g; (c3) Cyclic properties of hard-soft carbon composites at 150 mA/g[63]; (d) Raman spectra of FP-1000 and MP-1000 (d1); FP-MP-1000 samples in different proportions (d2); Sample FP-MP 5:2 at the different carbonization temperature (d3) [63]"
Table 1
Electrochemical properties of negative electrodes of soft carbon materials under different strategies"
| 调控策略 | 材料名称 | 可逆容量 | ICE/% | 倍率性能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多孔结构 | ZAD-3-800 | 293 mAh/g at 0.05 A/g | 60 | 53 mAh/g at 5A/g | [ |
| 多孔结构 | MPC | 331 mAh/g at 0.03 A/g | 45 | 103 mAh/g at 0.5A/g | [ |
| 多孔结构 | 3DHSC | 215 mAh/g at 0.05 A/g | 60 | 121 mAh/g at 1A/g | [ |
| 杂原子引入 | PCNS1000 | 302 mAh/g at 0.1 A/g | 67 | 175 mAh/g at 0.5A/g | [ |
| 杂原子引入 | NC-1200 | 201 mAh/g at 0.02 A/g | 49.5 | 85 mAh/g at 0.5A/g | [ |
| 杂原子引入 | PSC | 275 mAh/g at 0.01 A/g | 66 | 180 mAh/g at 1A/g | [ |
| 杂原子引入 | SC-600 | 500 mAh/g at 0.02 A/g | 30 | 300 mAh/g at 1A/g | [ |
| 杂原子引入 | NPSC4-700 | 500 mAh/g at 0.1 A/g | 81 | 162 mAh/g at 1A/g | [ |
| 软硬碳复合 | HC-0.2P-1000 | 349.9 mAh/g at 0.01 A/g | 60.9 | 294.3 mAh/g at 1A/g | [ |
| 软硬碳复合 | HC-SC | 306.8 mAh/g at 0.5 A/g | 55 | 144.9 mAh/g at 10A/g | [ |
| 软硬碳复合 | NFC | 345 mAh/g at 0.1 A/g | 53.4 | 217 mAh/g at 2A/g | [ |
| 交联结构构建 | HCPOP-ox12 | 312 mAh/g at C/20 | 90 | — | [ |
| 交联结构构建 | AC | 268.3 mAh/g at 0.03 A/g | 82 | 200 mAh/g at 1C | [ |
| 交联结构构建 | MCF750 | 272 mAh/g at 0.1 A/g | 90 | 121 mAh/g at 10 A/g | [ |
| 交联结构构建 | Fe0.25H | 306 mAh/g at 0.025 A/g | 60 | 150 mAh/g at 2 A/g | [ |
| 1 | LI J B, YAN D, ZHANG X J, et al. ZnS nanoparticles decorated on nitrogen-doped porous carbon polyhedra: A promising anode material for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(38): 20428-20438. |
| 2 | 陈珂君, 范利君. 钴掺杂FeS2的可控制备及储钠特性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(10): 3056-3063. |
| CHEN K J, FAN L J. Controllable synthesis of Co2+-doped FeS2 and their sodium storage performances[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(10): 3056-3063. | |
| 3 | 陈娜, 李安琪, 郭子祥, 等. 钠离子电池普鲁士蓝材料结构构建及优化的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(11): 3340-3351. |
| CHEN N, LI A Q, GUO Z X, et al. Research progress on the construction and optimization of Prussian blue material structure for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(11): 3340-3351. | |
| 4 | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: Present and future[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529-3614. |
| 5 | KULOVA T L, SKUNDIN A M. From lithium-ion to sodium-ion battery[J]. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 2017, 66(8): 1329-1335. |
| 6 | ROJO T, HU Y S, FORSYTH M, et al. Sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(17): 1800880. |
| 7 | ONG S P, CHEVRIER V L, HAUTIER G, et al. Voltage, stability and diffusion barrier differences between sodium-ion and lithium-ion intercalation materials[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(9): 3680-3688. |
| 8 | LI L, ZHENG Y, ZHANG S L, et al. Recent progress on sodium ion batteries: Potential high-performance anodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(9): 2310-2340. |
| 9 | GEBERT F, KNOTT J, GORKIN R III, et al. Polymer electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 36: 10-30. |
| 10 | ZHAO Y, KANG Y Q, WOZNY J, et al. Recycling of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2023, 8(9): 623-634. |
| 11 | SARKAR S, ROY S, HOU Y L, et al. Recent progress in amorphous carbon-based materials for anodes of sodium-ion batteries: Synthesis strategies, mechanisms, and performance[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(18): 3693-3723. |
| 12 | MA C Y, XU T T, WANG Y. Advanced carbon nanostructures for future high performance sodium metal anodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 25: 811-826. |
| 13 | LU Y X, ZHAO C L, QI X G, et al. Pre-oxidation-tuned microstructures of carbon anodes derived from pitch for enhancing Na storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(27): 1800108. |
| 14 | WANG P Z, ZHU X S, WANG Q Q, et al. Kelp-derived hard carbons as advanced anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(12): 5761-5769. |
| 15 | DU W S, SUN C, SUN Q. The recent progress of pitch nanoengineering to obtain the carbon anode for high-performance sodium ion batteries[J]. Materials, 2023, 16(13): 4871. |
| 16 | SIDDIQUI W G M K, NAEEM M, REHMAN N A. Topological characterization of carbon graphite and crystal cubic carbon structures[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(9): 1496. |
| 17 | KIPLING J J, SHERWOOD J N, SHOOTER P V, et al. Factors influencing the graphitization of polymer carbons[J]. Carbon, 1964, 1(3): 315, IN19, 319-318, IN20, 320. |
| 18 | AHMAD S, COPIC D, GEORGE C, et al. Hierarchical assemblies of carbon nanotubes for ultraflexible Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(31): 6705-6710. |
| 19 | OKAMOTO Y. Density functional theory calculations of alkali metal (Li, Na, and K) graphite intercalation compounds[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(1): 16-19. |
| 20 | DOEFF M M, MA Y P, VISCO S J, et al. Electrochemical insertion of sodium into carbon[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1993, 140(12): 169-170. |
| 21 | 张鼎, 叶子贤, 刘镇铭, 等. 钠离子电池黑磷基负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(8): 2482-2490. |
| ZHANG D, YE Z X, LIU Z M, et al. Research progress of black phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2482-2490. | |
| 22 | IGARASHI D, TATARA R, FUJIMOTO R, et al. Electrochemical intercalation of rubidium into graphite, hard carbon, and soft carbon[J]. Chemical Science, 2023, 14(40): 11056-11066. |
| 23 | JIANG M C, SUN N, ALI SOOMRO R, et al. The recent progress of pitch-based carbon anodes in sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 55: 34-47. |
| 24 | DOU X W, HASA I, SAUREL D, et al. Hard carbons for sodium-ion batteries: Structure, analysis, sustainability, and electrochemistry[J]. Materials Today, 2019, 23: 87-104. |
| 25 | SAUREL D, SEGALINI J, JAUREGUI M, et al. A SAXS outlook on disordered carbonaceous materials for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 21: 162-173. |
| 26 | QIAO S Y, ZHOU Q W, MA M, et al. Advanced anode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(12): 11220-11252. |
| 27 | GUAN T T, ZHANG G L, ZHAO J H, et al. Insight into the oxidative reactivity of pitch fractions for predicting and optimizing the oxidation stabilization of pitch[J]. Fuel, 2019, 242: 184-194. |
| 28 | YU M F, LOURIE O, DYER M J, et al. Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load[J]. Science, 2000, 287(5453): 637-640. |
| 29 | YUAN X M, ZHU B, FENG J K, et al. Biomass bone-derived, N/P-doped hierarchical hard carbon for high-energy potassium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2021, 139: 111282. |
| 30 | ZHANG F, YAO Y G, WAN J Y, et al. High temperature carbonized grass as a high performance sodium ion battery anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(1): 391-397. |
| 31 | CONG L, TIAN G R, LUO D X, et al. Hydrothermally assisted transformation of corn stalk wastes into high-performance hard carbon anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 871: 114249. |
| 32 | SUN N, QIU J S, XU B. Understanding of sodium storage mechanism in hard carbons: Ongoing development under debate[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(27): 2200715. |
| 33 | KIM J H, JUNG M J, KIM M J, et al. Electrochemical performances of lithium and sodium ion batteries based on carbon materials[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 61: 368-380. |
| 34 | ZHANG L P, WANG W, LU S F, et al. Carbon anode materials: A detailed comparison between Na-ion and K-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(11): 2003640. |
| 35 | STEVENS D A, DAHN J R. The mechanisms of lithium and sodium insertion in carbon materials[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(8): A803. |
| 36 | JIAN Z L, BOMMIER C, LUO L L, et al. Insights on the mechanism of Na-ion storage in soft carbon anode[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(5): 2314-2320. |
| 37 | CHENG D J, ZHOU X Q, HU H Y, et al. Electrochemical storage mechanism of sodium in carbon materials: A study from soft carbon to hard carbon[J]. Carbon, 2021, 182: 758-769. |
| 38 | ANJI REDDY M, HELEN M, GROß A, et al. Insight into sodium insertion and the storage mechanism in hard carbon[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(12): 2851-2857. |
| 39 | LIU H, JIA M Q, YUE S F, et al. Creative utilization of natural nanocomposites: Nitrogen-rich mesoporous carbon for a high-performance sodium ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(20): 9572-9579. |
| 40 | LIU H, JIA M Q, SUN N, et al. Nitrogen-rich mesoporous carbon as anode material for high-performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(49): 27124-27130. |
| 41 | LIAO Y L, HU J H, ZHOU X M. Porous hard carbon microtubes from renewable cotton as high-performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32(2): 1631-1640. |
| 42 | HE X J, LI X J, MA H, et al. ZnO template strategy for the synthesis of 3D interconnected graphene nanocapsules from coal tar pitch as supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 340: 183-191. |
| 43 | HE X J, ZHANG H B, ZHANG H, et al. Direct synthesis of 3D hollow porous graphene balls from coal tar pitch for high performance supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(46): 19633-19640. |
| 44 | WENZEL S, HARA T, JANEK J, et al. Room-temperature sodium-ion batteries: Improving the rate capability of carbon anode materials by templating strategies[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(9): 3342-3345. |
| 45 | LI X S, ZHAO H H, ZHANG C, et al. One-pot fabrication of pitch-derived soft carbon with hierarchical porous structure and rich sp2 carbon for sodium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32(17): 21944-21956. |
| 46 | CAO B, LIU H, XU B, et al. Mesoporous soft carbon as an anode material for sodium ion batteries with superior rate and cycling performance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(17): 6472-6478. |
| 47 | QIU D, CAO T F, ZHANG J, et al. Precise carbon structure control by salt template for high performance sodium-ion storage[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019, 31: 101-106. |
| 48 | DAMODAR D, GHOSH S, USHA RANI M, et al. Hard carbon derived from sepals of Palmyra palm fruit calyx as an anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 438: 227008. |
| 49 | ZHU Y Y, WANG Y H, WANG Y T, et al. Research progress on carbon materials as negative electrodes in sodium-and potassium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon Energy, 2022, 4(6): 1182-1213. |
| 50 | HAO M Y, XIAO N, WANG Y W, et al. Pitch-derived N-doped porous carbon nanosheets with expanded interlayer distance as high-performance sodium-ion battery anodes[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 177: 328-335. |
| 51 | MISHRA R, PANIGRAHY S, BARMAN S. Single-source-derived nitrogen-doped soft carbons for application as anode for sodium-ion storage[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.2c00564. |
| 52 | MIAO Y L, ZONG J, LIU X J. Phosphorus-doped pitch-derived soft carbon as an anode material for sodium ion batteries[J]. Materials Letters, 2017, 188: 355-358. |
| 53 | WANG X L, LI G, HASSAN F M, et al. Sulfur covalently bonded graphene with large capacity and high rate for high-performance sodium-ion batteries anodes[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 15: 746-754. |
| 54 | MISHRA R, PANDA P, BARMAN S. Synthesis of sulfur-doped porous carbon for supercapacitor and gas adsorption applications[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(3): 2585-2600. |
| 55 | LI Z, CAO Y J, LI G Y, et al. High rate capability of S-doped ordered mesoporous carbon materials with directional arrangement of carbon layers and large d-spacing for sodium-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 366: 137466. |
| 56 | HE L, SUN Y R, WANG C L, et al. High performance sulphur-doped pitch-based carbon materials as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2020, 35(4): 420-427. |
| 57 | 肖雪, 李佳纯, 孟祥桐, 等. 硫掺杂针状焦基多孔碳的制备及其储钠性能[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2023, 29(9): 162-170. |
| XIAO Xue, LI Jianchun, MENG Xiangtong, et al. Preparation of sulfur-doped needle coke-based porous carbon for robust sodium-ion storage[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2023, 29(9): 162-170. | |
| 58 | SUN L, SONG X Y, LIU Y X, et al. Spongy-like N, S-codoped ultrathin layered carbon assembly for realizing high performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. FlatChem, 2021, 28: 100258. |
| 59 | QI Y H, FAN W Y, NAN G Z. Free-standing, binder-free polyacrylonitrile/asphalt derived porous carbon fiber-A high capacity anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Letters, 2017, 189: 206-209. |
| 60 | ZHAO P Y, ZHANG J, LI Q, et al. Electrochemical performance of fulvic acid-based electrospun hard carbon nanofibers as promising anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 334: 170-178. |
| 61 | LI Y M, MU L Q, HU Y S, et al. Pitch-derived amorphous carbon as high performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 2: 139-145. |
| 62 | YIN X P, ZHAO Y F, WANG X, et al. Modulating the graphitic domains of hard carbons derived from mixed pitch and resin to achieve high rate and stable sodium storage[J]. Small, 2022, 18(5): e2105568. |
| 63 | XIE F, XU Z, JENSEN A C S, et al. Hard–soft carbon composite anodes with synergistic sodium storage performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(24): 1901072. |
| 64 | XUE Y C, GAO M Y, WU M R, et al. A promising hard carbon-soft carbon composite anode with boosting sodium storage performance[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(19): 4010-4015. |
| 65 | WANG Y W, XIAO N, WANG Z Y, et al. Ultrastable and high-capacity carbon nanofiber anodes derived from pitch/polyacrylonitrile for flexible sodium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2018, 135: 187-194. |
| 66 | LU Y X, ZHAO C L, QI X G, et al. Pre-oxidation-tuned microstructures of carbon anodes derived from pitch for enhancing Na storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(27): 1800108. |
| 67 | DAHER N, HUO D, DAVOISNE C, et al. Impact of preoxidation treatments on performances of pitch-based hard carbons for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(7): 6501-6510. |
| 68 | SUN Y, LU P, LIANG X, et al. High-yield microstructure-controlled amorphous carbon anode materials through a pre-oxidation strategy for sodium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 786: 468-474. |
| 69 | WANG Y W, XIAO N, WANG Z Y, et al. Rational design of high-performance sodium-ion battery anode by molecular engineering of coal tar pitch[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.098. |
| 70 | LIU X, ZHU Y Y, LIU N, et al. Catalytic synthesis of hard/soft carbon hybrids with heteroatom doping for enhanced sodium storage[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2019, 4(12): 3551-3558. |
| [1] | Yu LI, Dandan LI, Fei XIE, bin TANG, Xiaohui RONG, Qinqin LIANG, Yongsheng HU. Recent progress of cathode presodiation strategies in sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1748-1757. |
| [2] | Yangfeng WANG, Jiaao HOU, Zichen ZHU, Cong SUO, Shuandi HOU. Research progress on hard-carbon closed-pore structure of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 555-569. |
| [3] | Yonggang CHANG, Jinhao ZHANG, Wei XIE, Xiuchun LI, Yilin WANG, Chengmeng CHEN. Capacity enhancement strategy of hard carbon anode for sodium-ion battery: A review [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 544-554. |
| [4] | Lishuai ZHANG, Yifei ZHANG, Yiyang MA, Sibo ZHAO, Hongquan LIU, Shengting SHI, Yanjun ZHONG. Research progress on sodium-ion battery cathode materials based on iron-based prussian blue analogues [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 525-543. |
| [5] | Yijie YAO, Junwei ZHANG, Yanjun ZHAO, Hongcheng LIANG, Dongni ZHAO. Effect of interfacial dynamics on low temperature performance of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 30-41. |
| [6] | Yuman ZHANG, Lingling FAN, Chongyang YANG. Effects of different anode materials on the cyclic performance of high-power LiFePO4 energy storage devices [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3245-3253. |
| [7] | Dingbang HAO, Yongli LI. Na0.85Ni0.3Fe0.2Mn0.5O1.95F0.05@CuO cathode materials for high-rate and long cycling stability sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2489-2498. |
| [8] | Yuan YAO, Ruoqi ZONG, Jianli GAI. Research progress of antimony- and bismuth-based metallic anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2649-2664. |
| [9] | Lijun FAN, Baozhou WU, Kejun CHEN. Controllable synthesis of FeS2 with different morphologies and their sodium storage performances [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2541-2549. |
| [10] | Haotian WANG, Yonggang WANG, Xiaoli DONG. Advances in low-temperature organic batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2259-2269. |
| [11] | Renchao FENG, Yu DONG, Xinyu ZHU, Cai LIU, Sheng CHEN, Da LI, Ruoyu GUO, Bin WANG, Jionghui WANG, Ning LI, Yuefeng SU, Feng WU. Research progress on graphite oxide-based anodes for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1835-1848. |
| [12] | Qingyi LIU. Energy storage mechanism and performance enhancement strategies of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1871-1873. |
| [13] | Ruirui ZHAO, Yanqiu PENG, Xuejun LAI, Zhilong WU, Jie GAO, Wencheng XU, Lina WANG, Qin DING, Yongjin FANG, Yuliang CAO. Capacity fading mechanism of Na4Fe3(PO4)2P2O7 based sodium-ion battery during calendar aging [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(11): 4124-4132. |
| [14] | Haoran CAI, Lijue YAN, Xu YANG, Huilin PAN. Structural evolution and sodium-storage performance of O3/P2-Na x Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 multiphasic cathode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2707-2714. |
| [15] | Shiying ZHAN, Huanhuan LI, Fang HU. The research process of cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ioncapacitors [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2799-2810. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
