Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (5): 1748-1757.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.1085
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yu LI1( ), Dandan LI2, Fei XIE1(
), Dandan LI2, Fei XIE1( ), bin TANG2, Xiaohui RONG1, Qinqin LIANG2, Yongsheng HU1(
), bin TANG2, Xiaohui RONG1, Qinqin LIANG2, Yongsheng HU1( )
)
Received:2024-11-19
Revised:2024-11-25
Online:2025-05-28
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
Fei XIE, Yongsheng HU
E-mail:3510709270@qq.com;fxie@iphy.ac.cn;yshu@iphy.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Yu LI, Dandan LI, Fei XIE, bin TANG, Xiaohui RONG, Qinqin LIANG, Yongsheng HU. Recent progress of cathode presodiation strategies in sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1748-1757.
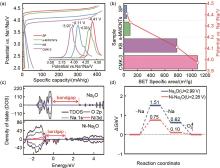
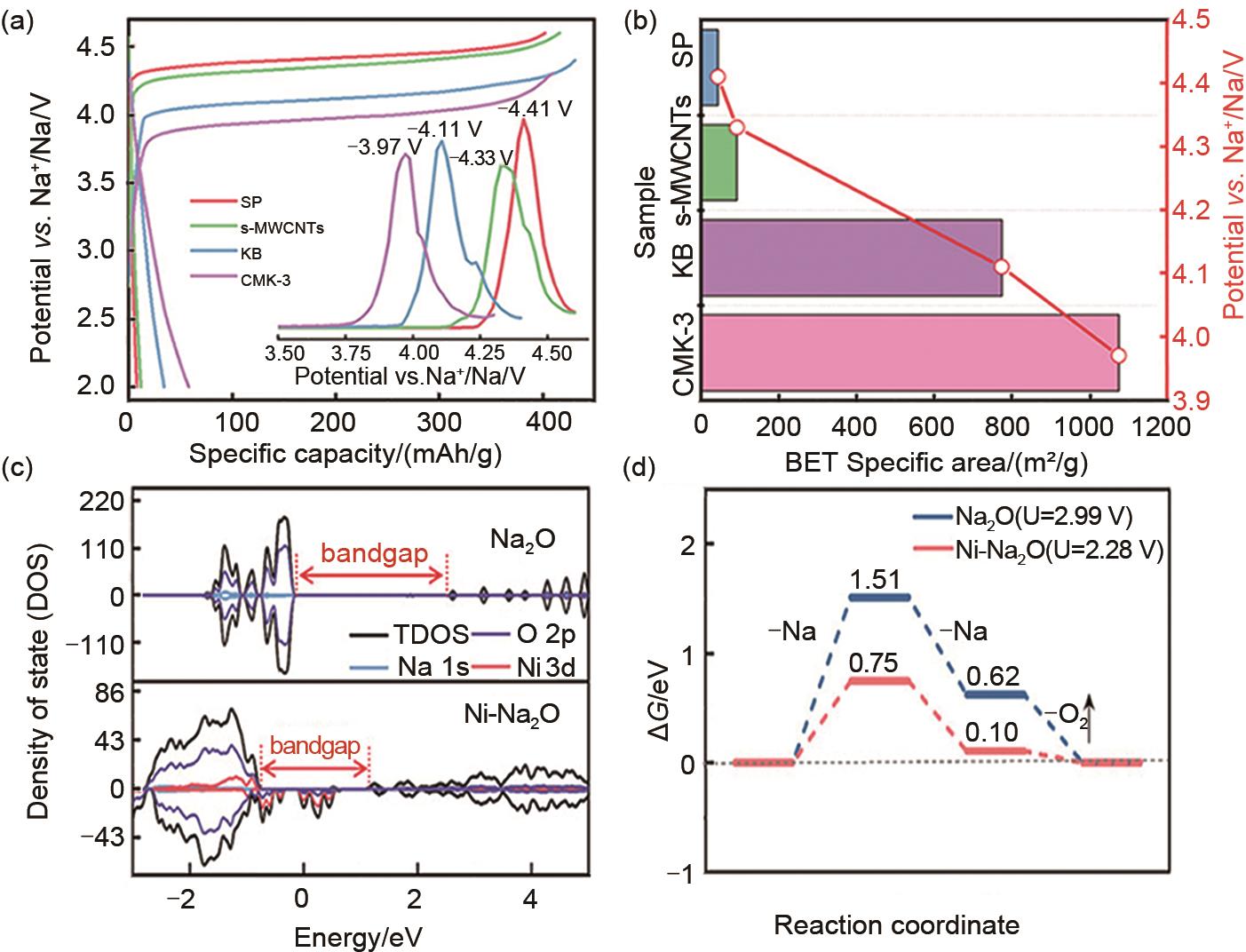
Fig. 3
(a) Effect of different conductive additives on electrochemical oxidation potential of Na2C2O4; (b) Relationship between oxidation potential and specific surface area of conductive additives[21]; (c) Voltage -specific capacity profile for (Na2O + NiO) composite cathode and the pure Na2O cathode; (d) The density of states (DOS) of Na2O (top) and NiO-Na2O (bottom)[35]"
| 1 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. DOI: 10.1126/science.1212741. |
| 2 | YANG Z G, ZHANG J L, KINTNER-MEYER M C W, et al. Electrochemical energy storage for green grid[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2011, 111(5): 3577-3613. DOI: 10.1021/cr100290v. |
| 3 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. DOI: 10.1038/451652a. |
| 4 | GOODENOUGH J B, PARK K S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(4): 1167-1176. DOI: 10.1021/ja3091438. |
| 5 | WHITTINGHAM M S. Lithium batteries and cathode materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4271-4302. DOI: 10.1021/cr 020731c. |
| 6 | HU Y S, LI Y Q. Unlocking sustainable Na-ion batteries into industry[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(11): 4115-4117. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.1c02292. |
| 7 | XIE F, LU Y X, CHEN L Q, et al. Recent progress in presodiation technique for high-performance Na-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2021, 38(11): 118401. DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/38/11/118401. |
| 8 | LIU X X, TAN Y C, LIU T C, et al. A simple electrode-level chemical presodiation route by solution spraying to improve the energy density of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(50): 1903795. DOI: 10.1002/adfm. 2019 03795. |
| 9 | LIU M C, ZHANG J Y, GUO S H, et al. Chemically presodiated hard carbon anodes with enhanced initial coulombic efficiencies for high-energy sodium ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(15): 17620-17627. DOI: 10.1021/acsami. 0c02230. |
| 10 | WANG H B, XIAO Y Z, SUN C, et al. A type of sodium-ion full-cell with a layered NaNi0.5Ti0.5O2 cathode and a pre-sodiated hard carbon anode[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(129): 106519-106522. DOI: 10.1039/C5RA21235A. |
| 11 | PI Y Q, GAN Z W, YAN M Y, et al. Insight into pre-sodiation in Na3V2(PO4)2F3/C @ hard carbon full cells for promoting the development of sodium-ion battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 413: 127565. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127565. |
| 12 | MOEEZ I, JUNG H G, LIM H D, et al. Presodiation strategies and their effect on electrode-electrolyte interphases for high-performance electrodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(44): 41394-41401. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b14381. |
| 13 | ZHANG B, DUGAS R, ROUSSE G, et al. Insertion compounds and composites made by ball milling for advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10308. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10308. |
| 14 | MARTINEZ DE ILARDUYA J, OTAEGUI L, LÓPEZ DEL AMO J M, et al. NaN3 addition, a strategy to overcome the problem of sodium deficiency in P2-Na0.67 [Fe0.5Mn0.5] O2 cathode for sodium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 337: 197-203. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.10.084. |
| 15 | ZHANG Q, GAO X W, SHI Y, et al. Electrocatalytic-driven compensation for sodium ion pouch cell with high energy density and long lifespan[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 39: 54-59. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.04.011. |
| 16 | SATHIYA M, THOMAS J, BATUK D, et al. Dual stabilization and sacrificial effect of Na2CO3 for increasing capacities of Na-ion cells based on P2-NaxMO2 electrodes[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(14): 5948-5956. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b01542. |
| 17 | SHEN B L, ZHAN R M, DAI C L, et al. Manipulating irreversible phase transition of NaCrO2 towards an effective sodium compensation additive for superior sodium-ion full cells[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 553: 524-529. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.06.056. |
| 18 | PARK K, YU B C, GOODENOUGH J B. Electrochemical and chemical properties of Na2NiO2 as a cathode additive for a rechargeable sodium battery[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(19): 6682-6688. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b02684. |
| 19 | SHANMUKARAJ D, KRETSCHMER K, SAHU T, et al. Highly efficient, cost effective, and safe sodiation agent for high-performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(18): 3286-3291. DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201801099. |
| 20 | PAN X X, CHOJNACKA A, BÉGUIN F. Advantageous carbon deposition during the irreversible electrochemical oxidation of Na2C4O4 used as a presodiation source for the anode of sodium-ion systems[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 40: 22-30. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.04.048. |
| 21 | NIU Y B, GUO Y J, YIN Y X, et al. High-efficiency cathode sodium compensation for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(33): 2001419. DOI: 10.1002/adma. 202001419. |
| 22 | YANG Y, WANG Z F, DU C C, et al. Decoupling the air sensitivity of Na-layered oxides[J]. Science, 2024, 385(6710): 744-752. DOI: 10.1126/science.adm9223. |
| 23 | 聂阳. 一种负极补钠添加剂、负极材料及钠离子电池: CN110707308B[P]. 2022.09.16. |
| 24 | 徐凯琪, 门双, 钟国彬, 等. 一种钠离子电池负极补钠添加剂、钠离子电池负极极片和钠离子电池: CN110690437B[P]. 2021-04-23. |
| XU K Q, MEN S, ZHONG G B, et al. Sodium-ion battery anode sodium supplement additive, sodium-ion battery anode pole piece and sodium-ion battery: CN110690437B[P]. 2021-04-23. | |
| 25 | 乔齐齐, 王鹏飞, 施泽涛, 等. 一种补锂或补钠的添加剂及其制备方法和应用: CN116454281A[P]. 2023-07-18. |
| QIAO Q Q, WANG P F, SHI Z T, et al. Additive for supplementing lithium or sodium as well as preparation method and application of additive: CN116454281A[P]. 2023-07-18. | |
| 26 | 张帅帅, 谢芳, 王卫江, 等. 一种补锂或补钠材料的制备方法及其所得产品和应用: CN116344819A[P]. 2023-06-27. |
| ZHANG S S, XIE F, WANG W J, et al. Preparation method of lithium or sodium supplementing material, product obtained by preparation method and application of product: CN116344819A[P]. 2023-06-27. | |
| 27 | 杨雪, 谢芳, 张帅帅. 正极补钠添加剂及其制备方法和应用: CN116111072A[P]. 2023-05-12. |
| YANG X, XIE F, ZHANG S S. Positive electrode sodium supplement additive and preparation method and application thereof: CN116111072A[P]. 2023-05-12. | |
| 28 | 李魁, 曾伟雄, 李尚. 一种纳米草酸钠复合的正极活性材料及其应用: CN115954445B [P/OL]. |
| LI K, ZENG W X, LI S. A nano-sodium oxalate-composited positive electrode active material and its application: CN115954445B [P/OL]. | |
| 29 | ZHANG T, KONG J, SHEN C, et al. Converting residual alkali into sodium compensation additive for high-energy Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(11): 4753-4761. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c02075. |
| 30 | 王海燕, 张睿, 唐有根, 等. 一种钠离子电池正极补钠添加剂、补钠方法、正极、柔性电极: CN114566650A[P]. 2022-05-31. |
| WANG H Y, ZHANG R, TANG Y G, et al. Sodium ion battery positive electrode sodium supplementing additive, sodium supplementing method, positive electrode and flexible electrode: CN114566650A[P]. 2022-05-31. | |
| 31 | 董少海, 肖厚文, 米源, 等. 一种提升钠离子电池首次库伦效率和能量密度的方法、正极浆料、正极片和钠离子电池: CN116646460A[P]. 2023-08-25. |
| DONG S H, XIAO H W, MI Y, et al. Method for improving first coulombic efficiency and energy density of sodium ion battery, positive electrode slurry, positive electrode plate and sodium ion battery: CN116646460A[P]. 2023-08-25. | |
| 32 | 周勇, 尚佩, 吴志荣, 等. 一种钠离子电池正极片及其制备方法及钠离子电池: CN116190570A[P]. 2023-05-30. |
| ZHOU Y, SHANG P, WU Z R, et al. Sodium-ion battery positive plate, preparation method thereof and sodium-ion battery: CN116190570A[P]. 2023-05-30. | |
| 33 | 刘静, 等. 一种钠离子电池正极浆料、正极极片、电池、制备方法: CN115663179A[P]. 2023-01-31. |
| LIU J, et al. Sodium-ion battery positive electrode slurry, positive electrode plate, battery and preparation method: CN115663179A[P]. 2023-01-31. | |
| 34 | 张国栋, 王巍, 文佳琪. 复合补钠材料及制备方法、正极极片、钠电池、用电设备: CN116826060B [P/OL]. |
| ZHANG G D, WANG W, WEN J Q. Composite sodium-supplementing materials and their preparation method, positive electrode plates, sodium batteries and electrical equipment: CN116826060B [P/OL]. | |
| 35 | CHEN Y L, ZHU Y L, SUN Z F, et al. Achieving high-capacity cathode presodiation agent via triggering anionic oxidation activity in sodium oxide[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(36): 2407720. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202407720. |
| 36 | 杨行, 张庆, 戚兴国, 等. 一种预钠化正极极片及其应用以及一种钠离子电池及其制备方法: CN114649504A[P]. 2022-06-21. |
| YANG X, ZHANG Q, QI X G, et al. Pre-sodium-modified positive pole piece, application of pre-sodium-modified positive pole piece, sodium-ion battery and preparation method of sodium-ion battery: CN114649504A[P]. 2022-06-21. | |
| 37 | 李静如, 王世冠, 赵子萌, 等. 补钠材料及其制备方法、正极极片、电极组件、电池和用电装置: CN116632220A[P]. 2023-08-22. |
| LI J R, WANG S G, ZHAO Z M, et al. Sodium supplementing material and preparation method thereof, positive pole piece, electrode assembly, battery and electric device: CN116632220A[P]. 2023-08-22. | |
| 38 | 文佳琪, 黄汉川, 王巍. 补钠组合物、正极极片及其制备方法、钠离子电池: CN116706075A[P]. 2023-09-05. |
| WEN J Q, HUANG H C, WANG W. Sodium supplementing composition, positive pole piece, preparation method of positive pole piece and sodium ion battery: CN116706075A[P]. 2023-09-05. | |
| 39 | CAO M Y, XU L, GUO Y J, et al. Air-stable Na3.5C6O6 as a sodium compensation additive in cathode of Na-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(42): 2400498. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202400498. |
| 40 | LIU X X, TAN Y C, WANG W Y, et al. Ultrafine sodium sulfide clusters confined in carbon nano-polyhedrons as high-efficiency presodiation reagents for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(23): 27057-27065. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c05144. |
| 41 | GUO Y J, NIU Y B, WEI Z, et al. Insights on electrochemical behaviors of sodium peroxide as a sacrificial cathode additive for boosting energy density of Na-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(2): 2772-2778. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c20870. |
| 42 | 聂阳, 孔权, 徐雄文. 一种补钠组合物及钠离子电池: CN115117558A[P]. 2022-09-27. |
| NIE Y, KONG Q, XU X W. Sodium supplementing composition and sodium ion battery: CN115117558A[P]. 2022-09-27. | |
| 43 | ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG C H, GUO Y J, et al. Refined electrolyte and interfacial chemistry toward realization of high-energy anode-free rechargeable sodium batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(47): 25643-25652. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c07804. |
| 44 | 江卫军, 周世波, 郝雷明, 等. 一种钠离子电池及其制备方法: CN114583174B [P/OL]. |
| JIANG W J, ZHOU S B, HAO L M, et al. A sodium-ion battery and its preparation method: CN114583174B [P/OL]. |
| [1] | Yangfeng WANG, Jiaao HOU, Zichen ZHU, Cong SUO, Shuandi HOU. Research progress on hard-carbon closed-pore structure of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 555-569. |
| [2] | Yonggang CHANG, Jinhao ZHANG, Wei XIE, Xiuchun LI, Yilin WANG, Chengmeng CHEN. Capacity enhancement strategy of hard carbon anode for sodium-ion battery: A review [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 544-554. |
| [3] | Lishuai ZHANG, Yifei ZHANG, Yiyang MA, Sibo ZHAO, Hongquan LIU, Shengting SHI, Yanjun ZHONG. Research progress on sodium-ion battery cathode materials based on iron-based prussian blue analogues [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 525-543. |
| [4] | Yijie YAO, Junwei ZHANG, Yanjun ZHAO, Hongcheng LIANG, Dongni ZHAO. Effect of interfacial dynamics on low temperature performance of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 30-41. |
| [5] | Dingbang HAO, Yongli LI. Na0.85Ni0.3Fe0.2Mn0.5O1.95F0.05@CuO cathode materials for high-rate and long cycling stability sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2489-2498. |
| [6] | Yuan YAO, Ruoqi ZONG, Jianli GAI. Research progress of antimony- and bismuth-based metallic anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2649-2664. |
| [7] | Hong ZHOU, Zhulin XIN, Hao FU, Qiang ZHANG, Feng WEI. Analysis of the key materials employed in solid-state lithium batteries based on patent data mining [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2386-2398. |
| [8] | Renchao FENG, Yu DONG, Xinyu ZHU, Cai LIU, Sheng CHEN, Da LI, Ruoyu GUO, Bin WANG, Jionghui WANG, Ning LI, Yuefeng SU, Feng WU. Research progress on graphite oxide-based anodes for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1835-1848. |
| [9] | Cong SUO, Yangfeng WANG, Zichen ZHU, Yan YANG. Research progress of soft carbon as negative electrodes in sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1807-1823. |
| [10] | Ruirui ZHAO, Yanqiu PENG, Xuejun LAI, Zhilong WU, Jie GAO, Wencheng XU, Lina WANG, Qin DING, Yongjin FANG, Yuliang CAO. Capacity fading mechanism of Na4Fe3(PO4)2P2O7 based sodium-ion battery during calendar aging [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(11): 4124-4132. |
| [11] | Haoran CAI, Lijue YAN, Xu YANG, Huilin PAN. Structural evolution and sodium-storage performance of O3/P2-Na x Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 multiphasic cathode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2707-2714. |
| [12] | Yuwen ZHAO, Huan YANG, Junpeng GUO, Yi ZHANG, Qi SUN, Zhijia ZHANG. Application of magnetic metal elements in sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1332-1347. |
| [13] | Kejun CHEN, Lijun FAN. Controllable synthesis of Co2+-doped FeS2 and their sodium storage performances [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(10): 3056-3063. |
| [14] | Kaiqiang GUO, Haiying CHE, Haoran ZHANG, Jianping LIAO, Huang ZHOU, Yunlong ZHANG, Hangda CHEN, Zhan SHEN, Haimei LIU, Zifeng MA. Preparation and characterization of B2O3-coated NaNi1/3Fe1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2980-2988. |
| [15] | Jun ZHANG, Qi LI, Ying TAO, Quanhong YANG. Sieving carbons for sodium-ion batteries: Origin and progress [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2825-2833. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
