Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (9): 2825-2833.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0374
• Special Issue for the 10th Anniversary • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jun ZHANG1,2,3( ), Qi LI2,3, Ying TAO2,3, Quanhong YANG1,2,3(
), Qi LI2,3, Ying TAO2,3, Quanhong YANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2022-07-02
Revised:2022-07-25
Online:2022-09-05
Published:2022-08-30
Contact:
Quanhong YANG
E-mail:zhjun20@tju.edu.cn;qhyangcn@tju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Jun ZHANG, Qi LI, Ying TAO, Quanhong YANG. Sieving carbons for sodium-ion batteries: Origin and progress[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2825-2833.
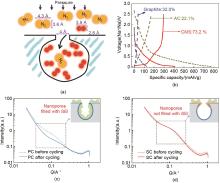
Fig. 3
(a) Schematic of carbon molecular sieve for N2/O2 separation; (b) Charge-discharge curves at first cycle of graphite, activated carbon and carbon molecular sieve; (c) SAXS patterns of porous carbon (PC) and (d) sieving carbon (SC) anodes before and after (dashed line) five full cycles at a current density of 50 mA/g. Inset: the relative location of the SEI to the nanopores. The SEI is a green irregular shape with yellow solid circles (sodium ions) inside[26]"
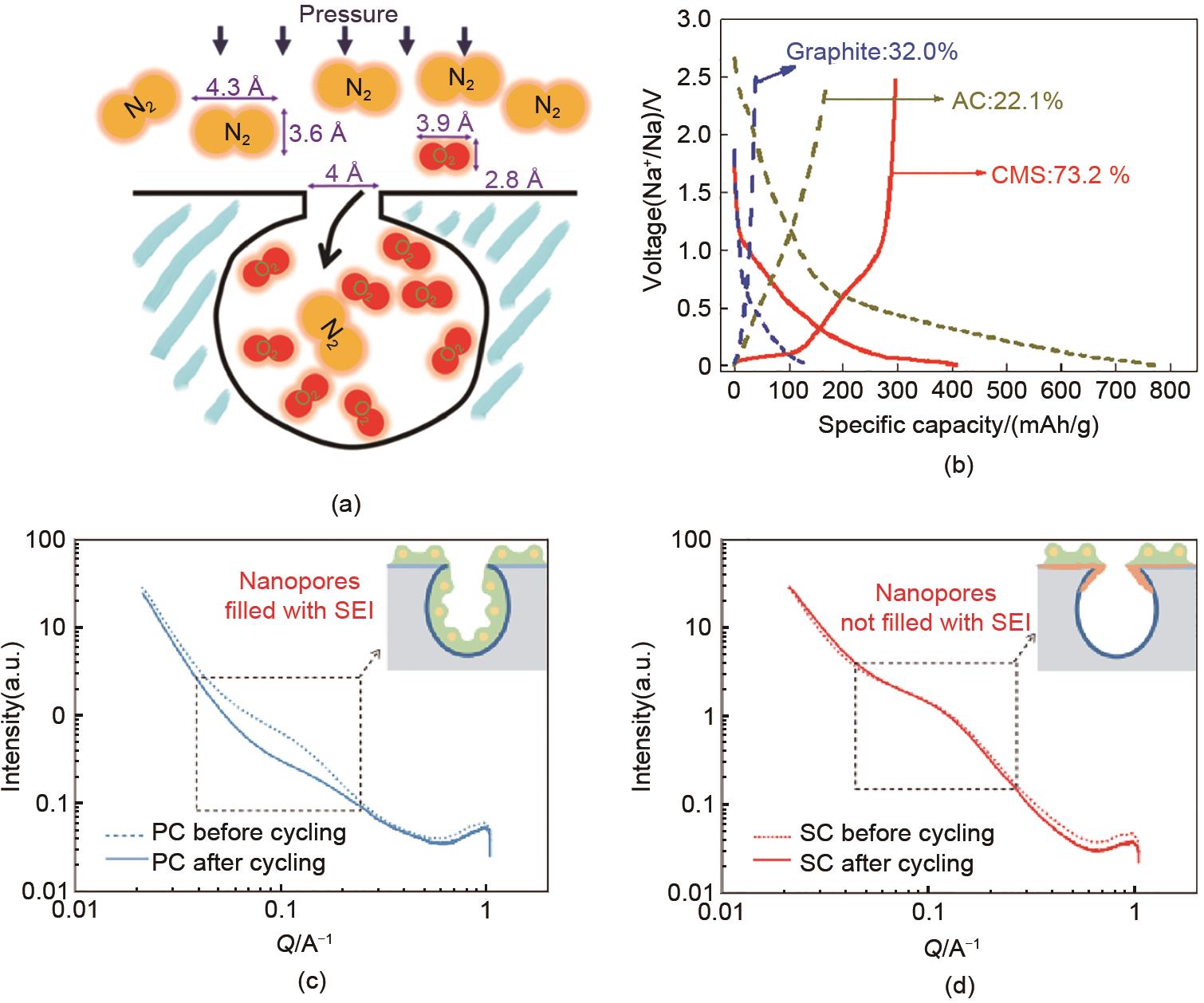
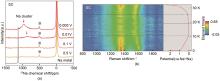
Fig. 4
Characterizing the sodium storage mechanism of SC (a) 23Na MAS ssNMR spectra of SC anodes at various states of charge in the first cycle. The spinning sideband is labeled with an asterisk (?); (b) Operando Raman spectra of SC anodes during the first charge/discharge at a current density of 50 mA/g[26]"

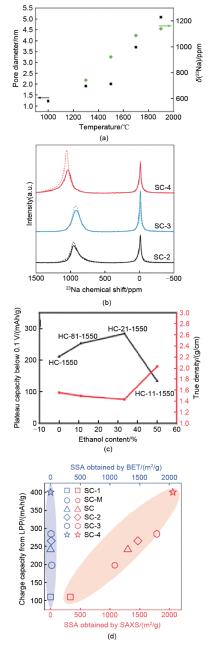
Fig. 6
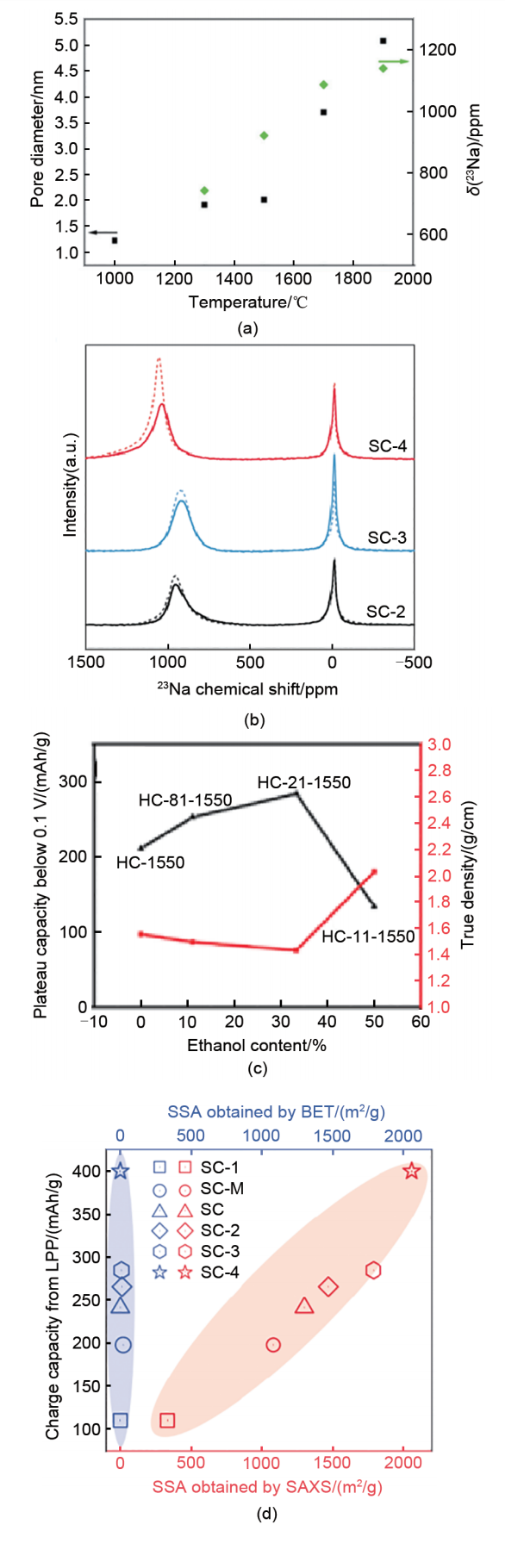
Rational design principles for sieving carbon anodes. (a) Relationship between the pore diameter, quasi-metallic Na peak shift and sample pyrolysis temperature[27]; (b) Ex-situ23Na 55 kHz ssNMR spectra of SCs at 0.005 V for the 10th discharge at 50 mA/g (solid curves). The dashed curves are the corresponding ssNMR spectra of SCs at 0.005 V for the first discharge[26]; (c) Relationship among the plateau capacity (0.1-0 V), true density, and EtOH content; (d) Charge capacity from the low-potential plateau versus SSA obtained by SAXS and N2 adsorption for the SC anodes[26]"
| 1 | HUANG X J, MENG Q B, CHEN H, et al. Renewable energy conversion, storage, and efficient utilization[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6389): 47-51. |
| 2 | DRESSELHAUS M S, THOMAS I L. Alternative energy technologies[J]. Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 332-337. |
| 3 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7(1): 19-29. |
| 4 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 5 | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: Present and future[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529-3614. |
| 6 | VAALMA C, BUCHHOLZ D, WEIL M, et al. A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3(4): 1-11. |
| 7 | 陆雅翔, 赵成龙, 容晓晖, 等. 室温钠离子电池材料及器件研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(12): doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180847. |
| LU Y X, ZHAO C L, RONG X H, et al. Research progress of materials and devices for room-temperature Na-ion batteries[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(12): doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180847. | |
| 8 | PAN H L, HU Y S, CHEN L Q. Room-temperature stationary sodium-ion batteries for large-scale electric energy storage[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(8): doi: 10.1039/c3ee40847g. |
| 9 | 容晓晖, 陆雅翔, 戚兴国, 等. 钠离子电池:从基础研究到工程化探索[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(2): 515-522. |
| RONG X H, LU Y X, QI X G, et al. Na-ion batteries: From fundamental research to engineering exploration[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 515-522. | |
| 10 | JACHE B, ADELHELM P. Use of graphite as a highly reversible electrode with superior cycle life for sodium-ion batteries by making use of co-intercalation phenomena[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(38): 10169-10173. |
| 11 | LIU Y Y, MERINOV B V, GODDARD W A. Origin of low sodium capacity in graphite and generally weak substrate binding of Na and Mg among alkali and alkaline earth metals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(14): 3735-3739. |
| 12 | SAUREL D, ORAYECH B, XIAO B W, et al. From charge storage mechanism to performance: A roadmap toward high specific energy sodium-ion batteries through carbon anode optimization[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(17): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201703268. |
| 13 | JIAN Z L, BOMMIER C, LUO L L, et al. Insights on the mechanism of Na-ion storage in soft carbon anode[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(5): 2314-2320. |
| 14 | LI Y M, HU Y S, QI X G, et al. Advanced sodium-ion batteries using superior low cost pyrolyzed anthracite anode: Towards practical applications[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 5: 191-197. |
| 15 | STEVENS D A, DAHN J R. High capacity anode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(4): doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2004.05.016. |
| 16 | YAMAMOTO H, MURATSUBAKI S, KUBOTA K, et al. Synthesizing higher-capacity hard-carbons from cellulose for Na- and K-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(35): 16844-16848. |
| 17 | LUO W, BOMMIER C, JIAN Z L, et al. Low-surface-area hard carbon anode for na-ion batteries via graphene oxide as a dehydration agent[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(4): 2626-2631. |
| 18 | LU Y X, ZHAO C L, QI X G, et al. Pre-oxidation-tuned microstructures of carbon anodes derived from pitch for enhancing Na storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(27): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201800108. |
| 19 | ZHANG S W, LV W, LUO C, et al. Commercial carbon molecular sieves as a high performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 3: 18-23. |
| 20 | STEVENS D A, DAHN J R. The mechanisms of lithium and sodium insertion in carbon materials[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(8): doi: 10.1149/1.1379565. |
| 21 | QIU S, XIAO L F, SUSHKO M L, et al. Manipulating adsorption-insertion mechanisms in nanostructured carbon materials for high-efficiency sodium ion storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(17): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201700403. |
| 22 | BOMMIER C, SURTA T W, DOLGOS M, et al. New mechanistic insights on Na-ion storage in nongraphitizable carbon[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(9): 5888-5892. |
| 23 | STRATFORD J M, ALLAN P K, PECHER O, et al. Mechanistic insights into sodium storage in hard carbon anodes using local structure probes[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2016, 52(84): 12430-12433. |
| 24 | MORIKAWA Y, NISHIMURA S I, HASHIMOTO R I, et al. Mechanism of sodium storage in hard carbon: An X-ray scattering analysis[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(3): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201903176. |
| 25 | WINTER M, BARNETT B, XU K. Before Li ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(23): 11433-11456. |
| 26 | LI Q, LIU X S, TAO Y, et al. Sieving carbons promise practical anodes with extensible low-potential plateaus for sodium batteries[J]. National Science Review, 2022, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwac084. |
| 27 | AU H, ALPTEKIN H, JENSEN A C S, et al. A revised mechanistic model for sodium insertion in hard carbons[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(10): 3469-3479. |
| 28 | ZHANG B, GHIMBEU C M, LABERTY C, et al. Correlation between microstructure and Na storage behavior in hard carbon[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(1): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201501588. |
| 29 | ZHENG Y H, LU Y X, QI X G, et al. Superior electrochemical performance of sodium-ion full-cell using poplar wood derived hard carbon anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 18: 269-279. |
| 30 | LI Y M, MU L Q, HU Y S, et al. Pitch-derived amorphous carbon as high performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 2: 139-145. |
| 31 | WANG Z H, FENG X, BAI Y, et al. Probing the energy storage mechanism of quasi-metallic Na in hard carbon for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(11): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202003854. |
| 32 | MENG Q S, LU Y X, DING F X, et al. Tuning the closed pore structure of hard carbons with the highest Na storage capacity[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(11): 2608-2612. |
| [1] | Kaiqiang GUO, Haiying CHE, Haoran ZHANG, Jianping LIAO, Huang ZHOU, Yunlong ZHANG, Hangda CHEN, Zhan SHEN, Haimei LIU, Zifeng MA. Preparation and characterization of B2O3-coated NaNi1/3Fe1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2980-2988. |
| [2] | Xin SHEN, Rui ZHANG, Chenzi ZHAO, Peng WU, Yutong ZHANG, Jundong ZHANG, Lizhen FAN, Quanbing LIU, Aibing CHEN, Qiang ZHANG. Recent advances in mechano-electrochemistry in lithium metal batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2781-2797. |
| [3] | Chang SUN, Zerong DENG, Ningbo JIANG, Lulu ZHANG, Hui FANG, Xuelin YANG. Recent research progress of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate as cathode material for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1184-1200. |
| [4] | Qiannan LIU, Weiping HU, Zhe HU. Research progress of phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1201-1210. |
| [5] | Suting WENG, Zepeng LIU, Gaojing YANG, Simeng ZHANG, Xiao ZHANG, Qiu FANG, Yejing LI, Zhaoxiang WANG, Xuefeng WANG, Liquan CHEN. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) characterizing beam-sensitive materials in lithium metal batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 760-780. |
| [6] | Chenlu YU, Xiaohua TIAN, Zhejuan ZHANG, Zhuo SUN. Research progress of specific capacity improvements of silicon-based anodes in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(6): 1614-1628. |
| [7] | Hongming YI, Zhiqiang LYU, Huamin ZHANG, Mingming SONG, Qiong ZHENG, Xianfeng LI. Recent progress and application challenges in V-based polyanionic compounds for cathodes of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1350-1369. |
| [8] | Wei ZHENG, Qiong LIU, Zhouguang LU. Modulating anionic redox reaction in layered transition metal oxides for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1416-1427. |
| [9] | Yongsheng GAO, Guanghai CHEN, Xinran WANG, Ying BAI, Chuan WU. Safety of electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries: Strategies and progress [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1309-1317. |
| [10] | Xingguo QI, Weigang WANG, Yongsheng HU, Qiang ZHANG. Surface modification research of layered oxide materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1396-1401. |
| [11] | Xiaohui ZHU, Yuhang ZHUANG, Yang ZHAO, Mingzhu NI, Jing XU, Hui XIA. Development of layered cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1340-1349. |
| [12] | BIAN Jingjing, CHU Shiyong, XI Kaiying, GUO Shaohua, ZHOU Haoshen. Role of Sn doping in layered chromium-based cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 385-391. |
| [13] | LIANG Jumei, GUO Yumeng, WANG Mingxuan, XILI Dege, ZHANG Lijuan. Recent research progress of tin oxide as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(5): 813-820. |
| [14] | LIU Mengyun, GU Tiantian, ZHOU Min, WANG Kangli, CHENG Shijie, JIANG Kai. Conjugated carbonyl compounds as electrode materials for sodium-ion/potassium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(6): 1171-1181. |
| [15] | ZHOU Anxing, JIANG Liwei, YUE Jinming, SUO Liumin, HU Yongsheng, LI Hong, HUANG Xuejie, CHEN Liquan. Research progress on lithium based Water-in-salt electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(6): 972-986. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
