Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2021, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (6): 1931-1942.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0148
• Special issue of hydrogen energy and fuel cell • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tingting HAN( ), Yuxi WU, Ziheng XIE, Xiuxia MENG, Jinjin ZHANG, Yujiao XIE, Fangyong YU(
), Yuxi WU, Ziheng XIE, Xiuxia MENG, Jinjin ZHANG, Yujiao XIE, Fangyong YU( ), Naitao YANG
), Naitao YANG
Received:2021-04-08
Revised:2021-05-08
Online:2021-11-05
Published:2021-11-03
CLC Number:
Tingting HAN, Yuxi WU, Ziheng XIE, Xiuxia MENG, Jinjin ZHANG, Yujiao XIE, Fangyong YU, Naitao YANG. Recent advances in carbon deposition mechanism and performance improvement of Ni-based anode for solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1931-1942.
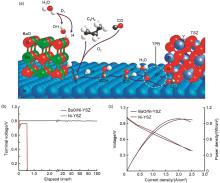
Fig. 3
(a) proposed mechanism for water-mediated carbon removal on the anode with BaO/Ni interfaces; (b) terminal voltages measured at 750 ℃ as a function of time for the different cells with 500 mA/cm2; (c) typical current-voltage characteristics and the corresponding power densities measured at 750 ℃ for cells with configurations of BaO/Ni-YSZ|YSZ|SDC/LSCF and Ni-YSZ|YSZ|SDC/LSCF[36]"
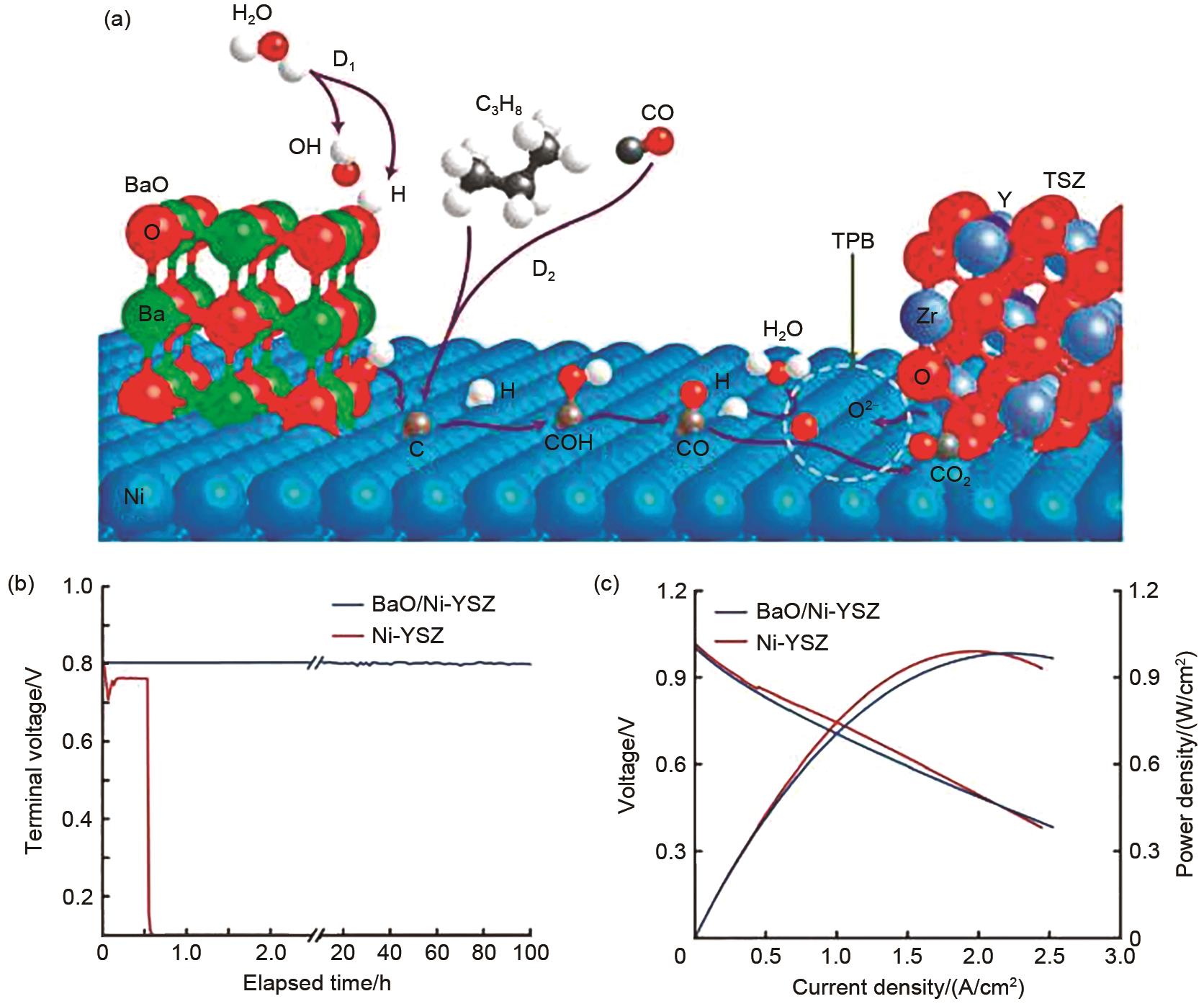
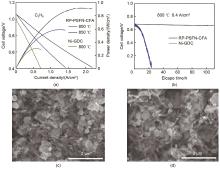
Fig. 4
(a) typical current-voltage characteristics and the corresponding power densities measured for different cells; (b) terminal voltages measured at 800 ℃ as a function of time for the different cells with 0.4 A/cm2 [45]; Typical SEM images of the PSCFN after exposed to CH4 at 850 ℃ for (c) 30 min and (d) 600 min[46]"

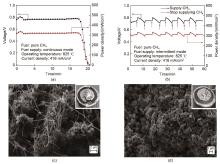
Fig. 5
Voltage and power density versus time for the cell operated under the (a) continuous and (b) intermittent fuel supply mode; SEM images of the anode and electronic photos of the cracked cell (the inset at bottom-left) after the (c) continuous and (d) intermittent fuel supply mode test [56]"
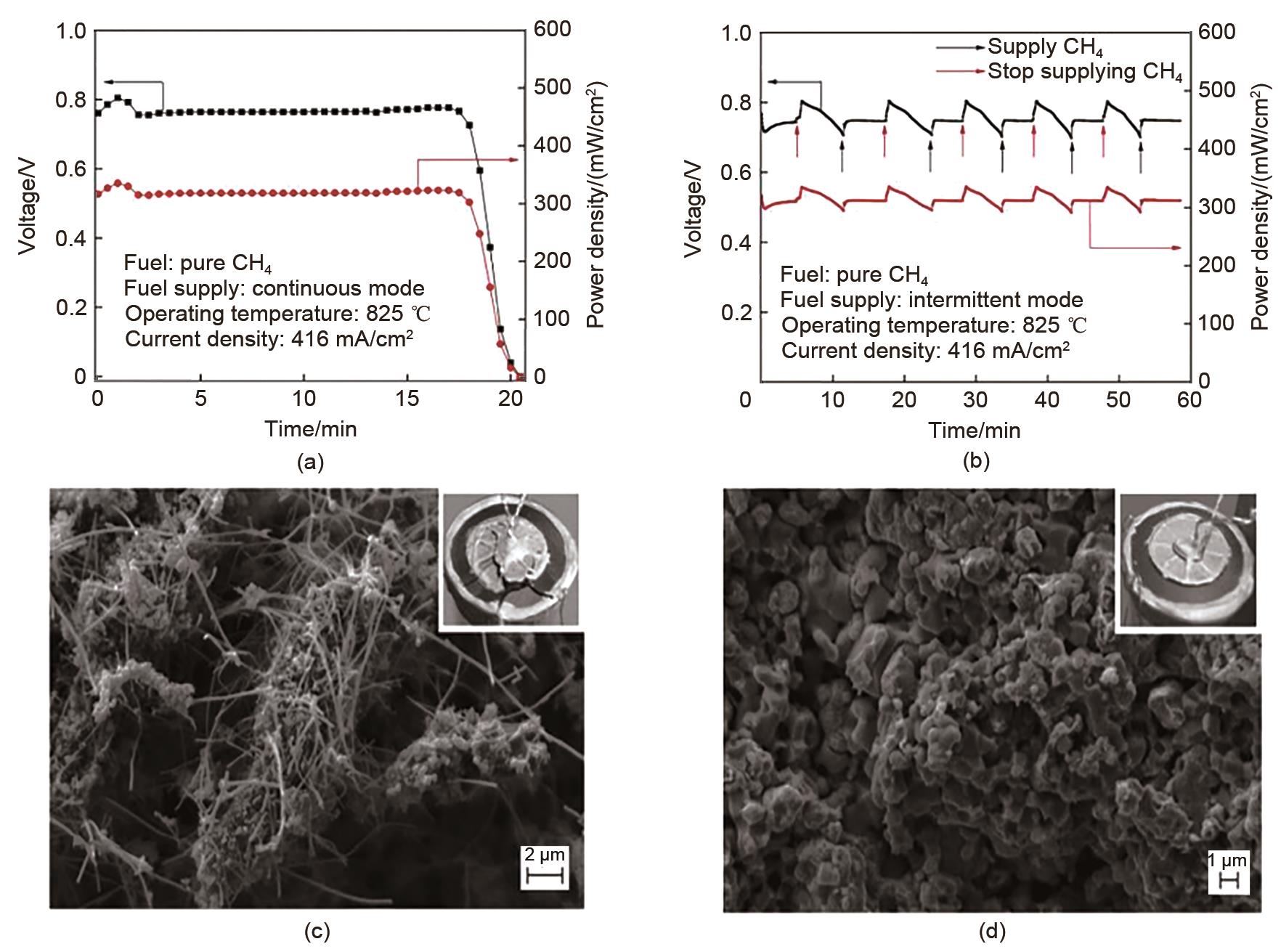
Table 1
Summary of electrochemical performance of SOFCs with different anode materials"
| 阳极 | 电解质/阴极 | 燃料 | 操作温度/℃ | 最大功率密度/(mW/cm2) | 稳定性 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-SDC/YSZ | YSZ/LSM-SDC | Methane | 700 | 400 | 0.5 V下超过80 h | [ |
| Ni-ScSZ/YSZ | YSZ/LSM | 3% H2O-CH4 | 1000 | 850 | 1 A/cm2, 1000 ℃下超过250 h | [ |
| Ni-Cu/YSZ | YSZ/LSM | Methane | 800 | 440 | 0.5 V下超过500 h | [ |
| Ni-Sn/YSZ | YSZ/LSM | Wet methane | 800 | 1010 | 0.3 A/cm2, 650 ℃下超过120 h | [ |
| 5%BaO-Ni/YSZ | YSZ/LSM | Dry methane | 800 | 22 | 20 A/cm2下超过8 h | [ |
| Au-Ni/GDC | YSZ/LSM-YSZ | CH4-rich Internal Steam | 850 | 410 | 0.81 V下超过200 h | [ |
| Au-Mo-Ni/GDC | YSZ/LSM | 22 vol% H2O-CH4 | 800 | — | 57 A/cm2下超过140 h | [ |
| Ni-GDC-NiMn2O4 | GDC/LSCF-GDC | CH4 | 700 | 1208 | 0.4 A/cm2, 650 ℃下超过100 h | [ |
| Ni0.9Fe0.1/GDC | GDC/LSCF | Dry methane | 650 | 350 | 0.2 A/cm2下超过50 h | [ |
| BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3-δ | — | 3% H2O-CH4 | 750 | — | 1.02 V下超过24 h | [ |
| La0.8Sr0.2Cr1-xRuxO3-δ-Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.9 | GDC/LSGM | H2 | 800 | 530 | 0.3 A/cm2下超过300 h | [ |
| Ba(Ce0.9Y0.1)0.8Ni0.2O3-δ/Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 | GDC/LSCF-GDC | CH4 | 750 | 211 | 0.2 A/cm2下超过100 h | [ |
| CeCoCu | YSZ-ScCeSc/LSM | Methane | 850 | 446.4 | — | [ |
| CeO2-Ni-YSZ | YSZ/LSM-YSZ | Ethanol | 750 | 220 | 0.55 V下超过7 h | [ |
| BaO-Ni-YSZ | YSZ/LSM-YSZ | Ethanol | 750 | 110 | 0.8 V下超过8 h | [ |
| 1 | CAO T, HUANG K, SHI Y X, et al. Recent advances in high-temperature carbon-air fuel cells[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(2): 460-490. |
| 2 | SHABRI H A, OTHMAN M H D, MOHAMED M A, et al. Recent progress in metal-ceramic anode of solid oxide fuel cell for direct hydrocarbon fuel utilization: A review[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 212: 106626. |
| 3 | LIU J, ZHOU M Y, ZHANG Y P, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of carbon at high temperature: Principles and applications[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(4): 4107-4117. |
| 4 | YU F Y, HAN T T, WANG Z G, et al. Recent progress in direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell: Advanced anode catalysts, diversified carbon fuels, and heat management[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(5): 4283-4300. |
| 5 | GÜR T M. Comprehensive review of methane conversion in solid oxide fuel cells: Prospects for efficient electricity generation from natural gas[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2016, 54: 1-64. |
| 6 | WANG W, SU C, WU Y, et al. Progress in solid oxide fuel cells with nickel-based anodes operating on methane and related fuels[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(10): 8104-8151. |
| 7 | LIN Y B, ZHAN Z L, LIU J, et al. Direct operation of solid oxide fuel cells with methane fuel[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2005, 176(23/24): 1827-1835. |
| 8 | BARTHOLOMEW C H. Mechanisms of catalyst deactivation[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2001, 212(1/2): 17-60. |
| 9 | LU H B, HUA D, IQABL T, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of the coke formation progress on the nickel-based anode of solid oxide fuel cells[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 91: 40-47. |
| 10 | LU H B, IQBAL T, ZHANG S Z, et al. Mechanical response of nickel-based anodes in solid oxide fuel cells during carbon deposition using reaction molecular dynamics[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 117: 104787. |
| 11 | LI C, SHI Y X, CAI N S. Performance improvement of direct carbon fuel cell by introducing catalytic gasification process[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(15): 4660-4666. |
| 12 | LI C, SHI Y X, CAI N S. Mechanism for carbon direct electrochemical reactions in a solid oxide electrolyte direct carbon fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(2): 754-763. |
| 13 | EIGENBRODT B C, POMFRET M B, STEINHURST D A, et al. Direct, in situ optical studies of Ni-YSZ anodes in solid oxide fuel cells operating with methanol and methane[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(6): 2895-2903. |
| 14 | KIM Y, KIM J H, BAE J, et al. In situ analyses of carbon dissolution into Ni-YSZ anode materials[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(24): 13281-13288. |
| 15 | PODYACHEVA O Y, ISMAGILOV Z R, SHALAGINA A E, et al. Structural changes in a nickel-copper catalyst during growth of nitrogen-containing carbon nanofibers by ethylene/ammonia decomposition[J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(10): 2792-2801. |
| 16 | SUN C W, SU R, CHEN J, et al. Carbon formation mechanism of C2H2 in Ni-based catalysts revealed by in situ electron microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(5): 8413-8420. |
| 17 | XIAO J, XIE Y M, LIU J, et al. Deactivation of nickel-based anode in solid oxide fuel cells operated on carbon-containing fuels[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 268: 508-516. |
| 18 | XIAO J, XIE Y, ZHANG L, et al. The effect of carbon fiber growth on the deactivation of nickel-based anode for solid oxide fuel cells operated on methane[J]. ECS Transactions, 2013, 57(1): 2969-2976. |
| 19 | YU F Y, XIAO J, ZHANG Y P, et al. New insights into carbon deposition mechanism of nickel/yttrium-stabilized zirconia cermet from methane by in situ investigation[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 256: 113910. |
| 20 | PARK S, VOHS J M, GORTE R J. Direct oxidation of hydrocarbons in a solid-oxide fuel cell[J]. Nature, 2000, 404(6775): 265-267. |
| 21 | ALVARADO FLORES J J, ÁVALOS RODRÍGUEZ M L, ANDRADE ESPINOSA G, et al. Advances in the development of titanates for anodes in SOFC[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(24): 12529-12542. |
| 22 | MURRAY E P, TSAI T, BARNETT S A. A direct-methane fuel cell with a ceria-based anode[J]. Nature, 1999, 400(6745): 649-651. |
| 23 | MATSUI T, EGUCHI K, SHIRAI K, et al. Redox-induced self-modification of cermet anodes of Ni-CeO2-based oxide for solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(13): F1368-F1374. |
| 24 | ZHANG L S, GAO J F, TIAN R F, et al. Samaria-doped ceria modified Ni/YSZ anode for direct methane fuel in tubular solid oxide fuel cells by impregnation method[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2009, 22(4): 429-434. |
| 25 | KIM H, LU C, WORRELL W L, et al. Cu-Ni cermet anodes for direct oxidation of methane in solid-oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149(3): A247. |
| 26 | MIZUTANI Y, TAMURA M, KAWAI M, et al. Development of high-performance electrolyte in SOFC[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1994, 72: 271-275. |
| 27 | NOMURA K, MIZUTANI Y, KAWAI M, et al. Aging and Raman scattering study of scandia and yttria doped zirconia[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2000, 132(3/4): 235-239. |
| 28 | SUMI H, PUENGJINDA P, MUROYAMA H, et al. Effects of crystal Structure of yttria- and scandia-stabilized zirconia in nickel-based SOFC anodes on carbon deposition and oxidation behavior[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(15): 6048-6054. |
| 29 | SUMI H, UKAI K, MIZUTANI Y, et al. Performance of nickel-scandia-stabilized zirconia cermet anodes for SOFCs in 3% H2O-CH4[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2004, 174(1/2/3/4): 151-156. |
| 30 | LIN Y C, WEI W C J. Porous Cu-Ni-YSZ cermets using CH4 fuel for SOFC[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(46): 24253-24262. |
| 31 | KAN H, LEE H. Sn-doped Ni/YSZ anode catalysts with enhanced carbon deposition resistance for an intermediate temperature SOFC[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010, 97(1/2): 108-114. |
| 32 | FARRELL B, LINIC S. Direct electrochemical oxidation of ethanol on SOFCs: Improved carbon tolerance of Ni anode by alloying[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 183: 386-393. |
| 33 | HELVEG S, LÓPEZ-CARTES C, SEHESTED J, et al. Atomic-scale imaging of carbon nanofibre growth[J]. Nature, 2004, 427(6973): 426-429. |
| 34 | NIKOLLA E, HOLEWINSKI A, SCHWANK J, et al. Controlling carbon surface chemistry by alloying: Carbon tolerant reforming catalyst[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(35): 11354-11355. |
| 35 | NIKOLLA E, SCHWANK J, LINIC S. Comparative study of the kinetics of methane steam reforming on supported Ni and Sn/Ni alloy catalysts: The impact of the formation of Ni alloy on chemistry[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2009, 263(2): 220-227. |
| 36 | YANG L, CHOI Y, QIN W, et al. Promotion of water-mediated carbon removal by nanostructured Barium oxide/nickel interfaces in solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2: 357. |
| 37 | ISLAM S, HILL J M. Barium oxide promoted Ni/YSZ solid-oxide fuel cells for direct utilization of methane[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(6): 1922-1929. |
| 38 | NIAKOLAS D K, OUWELTJES J P, RIETVELD G, et al. Au-doped Ni/GDC as a new anode for SOFCs operating under rich CH4 internal steam reforming[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(15): 7898-7904. |
| 39 | NEOFYTIDIS C, DRACOPOULOS V, NEOPHYTIDES S G, et al. Electrocatalytic performance and carbon tolerance of ternary Au-Mo-Ni/GDC SOFC anodes under CH4-rich Internal Steam Reforming conditions[J]. Catalysis Today, 2018, 310: 157-165. |
| 40 | LI Q, WANG X, JIA L, et al. High performance and carbon-deposition resistance metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell with a nickel-manganese spinel modified anode[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2020, 17: 100473. |
| 41 | KAN H, LEE H. Enhanced stability of Ni-Fe/GDC solid oxide fuel cell anodes for dry methane fuel[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2010, 12(1): 36-39. |
| 42 | WANG J B, JANG J C, HUANG T J. Study of Ni-Samaria-doped ceria anode for direct oxidation of methane in solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 122(2): 122-131. |
| 43 | LI M, HUA B, JIANG S P, et al. BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3-δ as highly active and carbon tolerant anode for direct hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(28): 15975-15981. |
| 44 | TAO S W, IRVINE J T S. A redox-stable efficient anode for solid-oxide fuel cells[J]. Nature Materials, 2003, 2(5): 320-323. |
| 45 | YANG C H, LI J, LIN Y, et al. In situ fabrication of CoFe alloy nanoparticles structured (Pr0.4Sr0.6)3(Fe0.85Nb0.15)2O7 ceramic anode for direct hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 11: 704-710. |
| 46 | ZHANG P, GUAN G Q, KHAERUDINI D S, et al. Mechanisms of methane decomposition and carbon species oxidation on the Pr0.42Sr0.6Co0.2Fe0.7Nb0.1O3–σ electrode with high catalytic activity[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(45): 22816-22823. |
| 47 | LIU Y Y, JIA L C, LI J, et al. High-performance Ni in situ exsolved Ba(Ce0.9Y0.1)0.8Ni0.2O3–δ/Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 composite anode for SOFC with long-term stability in methane fuel[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 193: 108033. |
| 48 | LIU J, BARNETT S A. Operation of anode-supported solid oxide fuel cells on methane and natural gas[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2003, 158(1/2): 11-16. |
| 49 | ALZATE-RESTREPO V, HILL J M. Effect of anodic polarization on carbon deposition on Ni/YSZ anodes exposed to methane[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2008, 342(1/2): 49-55. |
| 50 | KOH J H, YOO Y S, PARK J W, et al. Carbon deposition and cell performance of Ni-YSZ anode support SOFC with methane fuel[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 149(3/4): 157-166. |
| 51 | HORITA T, YAMAJI K, KATO T, et al. Imaging of CH4 decomposition around the Ni/YSZ interfaces under anodic polarization[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 145(2): 133-138. |
| 52 | VAYENAS C G, BEBELIS S, NEOPHYTIDES S, et al. Non-faradaic electrochemical modification of catalytic activity in solid electrolyte cells[J]. Applied Physics A, 1989, 49(1): 95-103. |
| 53 | MCINTOSH S, GORTE R J. Direct hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4845-4866. |
| 54 | 张雨舒. SOFC系统甲烷水蒸汽重整Ni基催化剂性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. |
| ZHANG Y S. The Ni-based catalyst performance study for methane steam reforming in solid oxide fuel cell system[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. | |
| 55 | HAN Z Y, YANG Z B, HAN M F. Cell-protecting regeneration from anode carbon deposition using in situ produced oxygen and steam: A combined experimental and theoretical study[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34(12): 2375-2383. |
| 56 | JIAO Y, ZHANG L Q, AN W T, et al. Controlled deposition and utilization of carbon on Ni-YSZ anodes of SOFCs operating on dry methane[J]. Energy, 2016, 113: 432-443. |
| 57 | TRIMM D L. Catalysts for the control of coking during steam reforming[J]. Catalysis Today, 1999, 49(1/2/3): 3-10. |
| 58 | ARENA F, FRUSTERI F, PARMALIANA A. Alkali promotion of Ni/MgO catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 1999, 187(1): 127-140. |
| 59 | FRUSTERI F, ARENA F, CALOGERO G, et al. Potassium-enhanced stability of Ni/MgO catalysts in the dry-reforming of methane[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2001, 2(2): 49-56. |
| 60 | WANG Y H, LIU H M, XU B Q. Durable Ni/MgO catalysts for CO2 reforming of methane: Activity and metal-support interaction[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2009, 299(1/2): 44-52. |
| 61 | LAY E, METCALFE C, KESLER O. The influence of incorporating MgO into Ni-based cermets by plasma spraying on anode microstructural and chemical stability in dry methane[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 218: 237-243. |
| 62 | HUA B, LI M, CHI B, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance and carbon deposition resistance of Ni-YSZ anode of solid oxide fuel cells by in situ formed Ni-MnO layer for CH4 on-cell reforming[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(4): 1150-1158. |
| 63 | LI M, HUA B, PU J, et al. Electrochemical performance and carbon deposition resistance of M-BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3–δ (M = Pd, Cu, Ni or NiCu) anodes for solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 7667. |
| 64 | HUA B, LI M, LUO J L, et al. Carbon-resistant Ni-Zr0.92Y0.08O2–δ supported solid oxide fuel cells using Ni-Cu-Fe alloy cermet as on-cell reforming catalyst and mixed methane-steam as fuel[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 303: 340-346. |
| 65 | BABAEI A, ZHANG L, LIU E J, et al. Performance and carbon deposition over Pd nanoparticle catalyst promoted Ni/GDC anode of SOFCs in methane, methanol and ethanol fuels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(20): 15301-15310. |
| 66 | WANG W, ZHU H Y, YANG G M, et al. A NiFeCu alloy anode catalyst for direct-methane solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 258: 134-141. |
| 67 | LI Z W, JIANG B, WANG Z G, et al. High carbon resistant Ni@Ni phyllosilicate@SiO2 core shell hollow sphere catalysts for low temperature CH4 dry reforming[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2018, 27: 238-246. |
| 68 | SARRUF B J M, HONG J E, STEINBERGER-WILCKENS R, et al. Ceria-Co-Cu-based SOFC anode for direct utilisation of methane or ethanol as fuels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(8): 5297-5308. |
| 69 | 程亮, 罗凌虹, 林囿辰, 等. Ni/YSZ阳极浸渍CeO2及BaO对SOFC电池抗积碳的影响[J]. 陶瓷学报, 2017, 38(5): 746-751. |
| CHENG L, LUO L H, LIN Y C, et al. Effect of Ni/YSZ anode impregnation on CeO2 and BaO on anti carbon deposition of SOFC[J]. Journal of Ceramics, 2017, 38(5): 746-751. |
| [1] | Changyang LIU, Liuzhen BIAN, Jianquan GAO, Jihua PENG, Jun PENG, Shengli AN. Electrochemical performance of La0.7Sr0.3Fe0.9Ni0.1O3-δ symmetric electrode for solid oxide fuel cell with CO as fuel [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2059-2065. |
| [2] | Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Apr. 1, 2022 to May 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2007-2022. |
| [3] | Ronghan QIAO, Guanjun CEN, Xiaoyu SHEN, Mengyu TIAN, Hongxiang JI, Feng TIAN, Wenbin QI, Zhou JIN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2022 to Mar. 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1289-1304. |
| [4] | Lei LI, Zhao LI, Dan JI, Huichang NIU. Overcharge induced thermal runaway behaviors of pouch-type lithium-ion batteries with LFP and NCM cathodes: the differences and reasons [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1419-1427. |
| [5] | Hui TIAN, Dong HUA, Maoli MAN, Chunzhe LIU, Guojun LI, Xiongwen ZHANG. Experimental study on carbon deposition characteristics of planar solid oxide fuel cell [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1314-1321. |
| [6] | Honghui WANG, Zeqin WU, Deren CHU. Thermal behavior of lithium titanate based Li ion batteries under slight over-discharging condition [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1305-1313. |
| [7] | Qiannan LIU, Weiping HU, Zhe HU. Research progress of phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1201-1210. |
| [8] | Guanjun CEN, Jing ZHU, Ronghan QIAO, Xiaoyu SHEN, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Feng TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Dec. 1, 2021 to Jan. 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 1077-1092. |
| [9] | Hui TIAN, Dong HUA, Maoli MAN, Chunzhe LIU, Guojun LI, Xiongwen ZHANG. Numerical study on carbon deposition characteristics of planar solid oxide fuel cell [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 291-296. |
| [10] | Mengyu TIAN, Jing ZHU, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xiaoyu SHEN, Hongxiang JI, Feng TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries(Oct. 1, 2021 to Nov. 30, 2021) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 297-312. |
| [11] | Penghui LI, Caiwen WU, Jianpeng REN, Wenjuan WU. Research progress of lignin as electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 66-77. |
| [12] | Zhihui GUO, Xiaodan CUI, Linshuang ZHAO, Jiawei CHEN. Fire and gas explosion hazards of high-nickel lithium-ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 193-200. |
| [13] | Wenchao LIAN, Libin LEI, Bo LIANG, Chao WANG, Lei WEI, Zhipeng TIAN, Jianping LIU, Huazheng YANG, Jiajian LIANG, Tao SHI. Utilization and synthesis of ammonia in proton-conducting solid oxide electrochemical devices [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1998-2007. |
| [14] | Yuxi WU, Tingting HAN, Ziheng XIE, Lin LI, Yanwen SONG, Jiacang LIANG, Jinjin ZHANG, Fangyong YU, Naitao YANG. Recent progress in direct carbon solid oxide fuel cells: Carbon fuels and reverse Boudouard reaction catalysts [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1977-1986. |
| [15] | Lina ZHENG, Wenzhong WANG, Kaijie JIA, Shaofeng QIU, Haoyuan ZHU, Fangyong YU, Xiuxia MENG, Jinjin ZHANG, Naitao YANG. Three-dimensional printing technologies in the field of solid oxide fuel cells [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 1952-1962. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
