Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (8): 2482-2490.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0178
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ding ZHANG1( ), Zixian YE1, Zhenming LIU1, Qun YI1, Lijuan SHI1, Huijuan GUO1, Yi HUANG1, Li WANG2(
), Zixian YE1, Zhenming LIU1, Qun YI1, Lijuan SHI1, Huijuan GUO1, Yi HUANG1, Li WANG2( ), Xiangming HE2
), Xiangming HE2
Received:2023-03-25
Revised:2023-04-07
Online:2023-08-05
Published:2023-08-23
Contact:
Li WANG
E-mail:zhangding@wit.edu.cn;wang-l@tsinghua.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Ding ZHANG, Zixian YE, Zhenming LIU, Qun YI, Lijuan SHI, Huijuan GUO, Yi HUANG, Li WANG, Xiangming HE. Research progress of black phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2482-2490.

Fig. 2
(a) Specific capability and coulombic efficiency of the 4-RBP anode at current density of 1 A/g[25];(b) The specific capacity of 4-RBP at different current density[25]; (c) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of the NTO/C-BP hybrids[26];(d) Electrochemical measurements of NTO/C and NTO/C-BP: Cycling performance at 200 mA/g[26]; (e) Performance of 100 cycles at current densities of 100 mA/g, 200 mA/g, and 500 mA/g[29]"


Fig. 4
(a) Cyclic performance of E-BP/PEDOT and E-BP electrodes at different current densities[32]; (b) Schematic diagram of the sodiation of BP-G and BP-G/PANI electrodes[33]; (c) Rct of BP, BP-G, and BP-G/PANI[33]; (d) SEM images of cross section of BP-G/PANI and BP-G electrodes before and after cycling[33]; (e) Cyclic performance of BP-G/PANI at different current densities[33]"

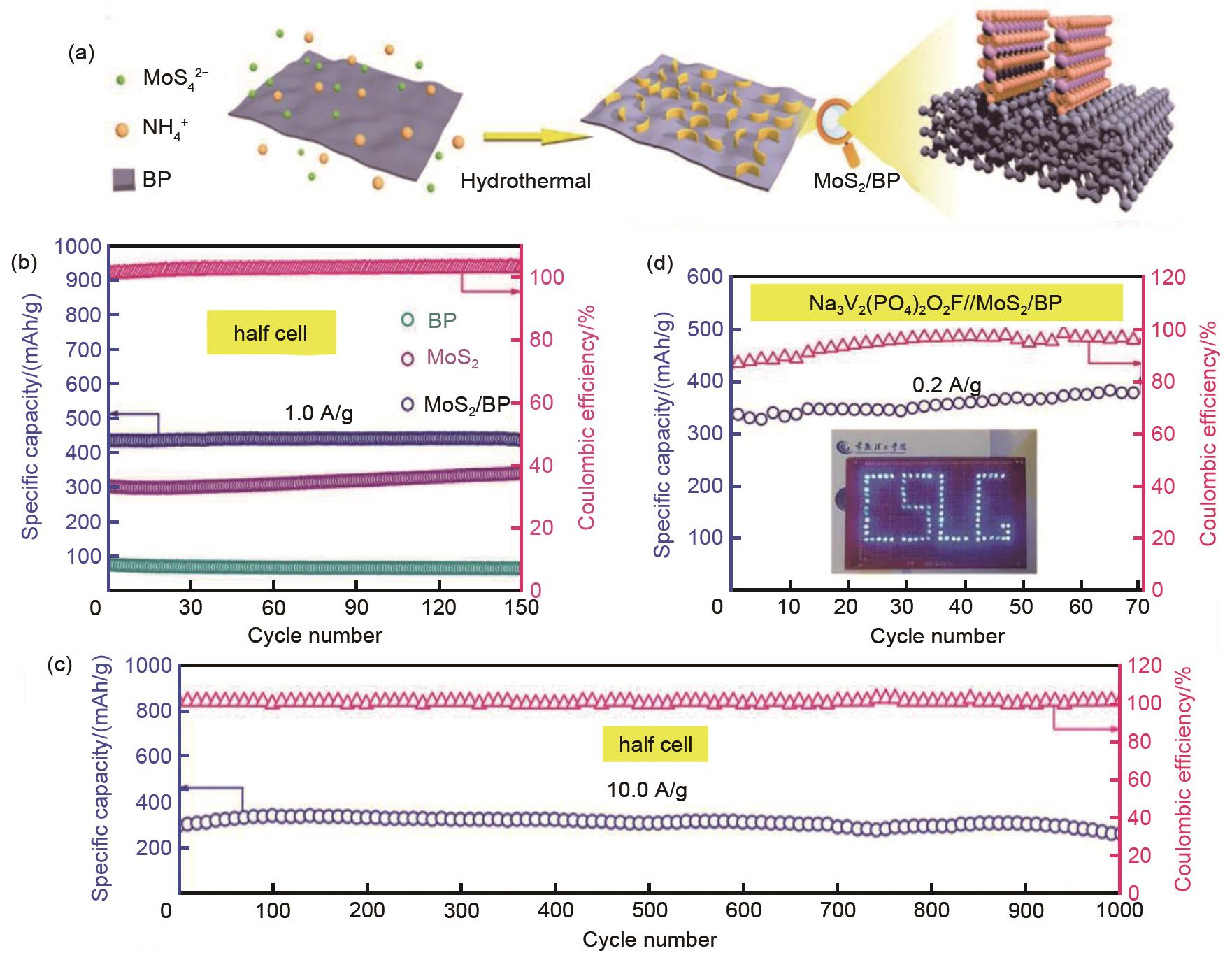
Fig. 5
(a) Schematic explanation for the MoS2 nanosheets on a BP nanosheets support in the MoS2/BP composite; (b) Cycling stability of MoS2/BP at 1 A/g in comparison with MoS2 and BP electrodes; (c) Long-term cycling stability of the MoS2/BP composite at 10 A/g; (d) Anti-static charge-discharge performance of full battery at 0.2 A/g [37]"
| 1 | KIM H, HONG J, PARK Y U, et al. Sodium storage behavior in natural graphite using ether-based electrolyte systems[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(4): 534-541. |
| 2 | XU Y L, SWAANS E, BASAK S, et al. Reversible Na-ion uptake in Si nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(2): 1501436. |
| 3 | ZHANG Y F, LI M, HUANG F B, et al. 3D porous Sb-Co nanocomposites as advanced anodes for sodium-ion batteries and potassium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 499: 143907. |
| 4 | YU Z X, LI X F, YAN B, et al. Rational design of flower-like tin sulfide @ reduced graphene oxide for high performance sodium ion batteries[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2017, 96: 516-523. |
| 5 | PARK Y, SHIN D S, WOO S H, et al. Sodium terephthalate as an organic anode material for sodium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(26): 3562-3567. |
| 6 | KANG H Y, LIU Y C, CAO K Z, et al. Update on anode materials for Na-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(35): 17899-17913. |
| 7 | SANTHOSHKUMAR P, SHAJI N, NANTHAGOPAL M, et al. Multichannel red phosphorus with a nanoporous architecture: A novel anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 470: 228459. |
| 8 | QIAN J F, WU X Y, CAO Y L, et al. High capacity and rate capability of amorphous phosphorus for sodium ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(17): 4633-4636. |
| 9 | ZHOU J B, LIU X Y, CAI W L, et al. Wet-chemical synthesis of hollow red-phosphorus nanospheres with porous shells as anodes for high-performance lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(29): 1700214. |
| 10 | FU Y Q, WEI Q L, ZHANG G X, et al. Batteries: Advanced phosphorus-based materials for lithium/sodium-ion batteries: Recent developments and future perspectives (adv. energy mater. 13/2018)[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(13): 1870057. |
| 11 | KIM Y, PARK Y, CHOI A, et al. An amorphous red phosphorus/carbon composite as a promising anode material for sodium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(22): 3045-3049. |
| 12 | LI W J, CHOU S L, WANG J Z, et al. Simply mixed commercial red phosphorus and carbon nanotube composite with exceptionally reversible sodium-ion storage[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13(11): 5480-5484. |
| 13 | SONG J X, YU Z X, GORDIN M L, et al. Chemically bonded phosphorus/graphene hybrid as a high performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(11): 6329-6335. |
| 14 | SUN J, LEE H W, PASTA M, et al. Carbothermic reduction synthesis of red phosphorus-filled 3D carbon material as a high-capacity anode for sodium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 4: 130-136. |
| 15 | BRIDGMAN P W. Two new modifications of phosphorus[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1914, 36(7): 1344-1363. |
| 16 | AKAHAMA Y, KOBAYASHI M, KAWAMURA H. Raman study of black phosphorus up to 13 GPa[J]. Solid State Communications, 1997, 104(6): 311-315. |
| 17 | LI Y Y, HU Z X, LIN S H, et al. Giant anisotropic Raman response of encapsulated ultrathin black phosphorus by uniaxial strain[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(19): 1600986. |
| 18 | LI L K, YU Y J, YE G J, et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(5): 372-377. |
| 19 | CHURCHILL H O H, JARILLO-HERRERO P. Phosphorus joins the family[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014, 9(5): 330-331. |
| 20 | YUAN J T, NAJMAEI S, ZHANG Z H, et al. Photoluminescence quenching and charge transfer in artificial heterostacks of monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides and few-layer black phosphorus[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(1): 555-563. |
| 21 | XIA F N, WANG H, JIA Y C. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4458. |
| 22 | TIOUITCHI G, ALI M A, BENYOUSSEF A, et al. An easy route to synthesize high-quality black phosphorus from amorphous red phosphorus[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 236: 56-59. |
| 23 | HEMBRAM K P S S, JUNG H, YEO B C, et al. Unraveling the atomistic sodiation mechanism of black phosphorus for sodium ion batteries by first-principles calculations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(27): 15041-15046. |
| 24 | XU G L, CHEN Z H, ZHONG G M, et al. Nanostructured black phosphorus/ketjenblack-multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite as high performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(6): 3955-3965. |
| 25 | LIU H W, TAO L, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Bridging covalently functionalized black phosphorus on graphene for high-performance sodium-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(42): 36849-36856. |
| 26 | SONG T B, CHEN H, XU Q J, et al. Black phosphorus stabilizing Na2Ti3O7/C each other with an improved electrochemical property for sodium-ion storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(43): 37163-37171. |
| 27 | XU Y L, PENG B, MULDER F M. A high-rate and ultrastable sodium ion anode based on a novel Sn4P3-P@Graphene nanocomposite[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(3): 1701847. |
| 28 | HAGHIGHAT-SHISHAVAN S, NAZARIAN-SAMANI M, NAZARIAN-SAMANI M, et al. Strong, persistent superficial oxidation-assisted chemical bonding of black phosphorus with multiwall carbon nanotubes for high-capacity ultradurable storage of lithium and sodium[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(21): 10121-10134. |
| 29 | LI M Y, MURALIDHARAN N, MOYER K, et al. Solvent mediated hybrid 2D materials: Black phosphorus-graphene heterostructured building blocks assembled for sodium ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(22): 10443-10449. |
| 30 | RAMIREDDY T, XING T, RAHMAN M M, et al. Phosphorus-carbon nanocomposite anodes for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(10): 5572-5584. |
| 31 | LIU Y H, LIU Q Z, ZHANG A Y, et al. Room-temperature pressure synthesis of layered black phosphorus-graphene composite for sodium-ion battery anodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(8): 8323-8329. |
| 32 | ZHANG Y, SUN W P, LUO Z Z, et al. Functionalized few-layer black phosphorus with super-wettability towards enhanced reaction kinetics for rechargeable batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 40: 576-586. |
| 33 | JIN H C, ZHANG T M, CHUANG C H, et al. Synergy of black phosphorus-graphite-polyaniline-based ternary composites for stable high reversible capacity Na-ion battery anodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(18): 16656-16661. |
| 34 | CALLEGARI D, COLOMBI S, NITTI A, et al. Autonomous self-healing strategy for stable sodium-ion battery: A case study of black phosphorus anodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(11): 13170-13182. |
| 35 | GUO X, ZHANG W X, ZHANG J Q, et al. Boosting sodium storage in two-dimensional phosphorene/Ti3C2Tx MXene nanoarchitectures with stable fluorinated interphase[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(3): 3651-3659. |
| 36 | SU J C, XIAO B, JIA Z H. A first principle study of black phosphorene/N-doped graphene heterostructure: Electronic, mechanical and interface properties[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 528: 146962. |
| 37 | ZHANG C R, LIANG T T, DONG H L, et al. Interfacial electron modulation of MoS2/black phosphorus heterostructure toward high-rate and high-energy density half/full sodium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 5(17): 6639-6647. |
| 38 | WANG Y W, TIAN W, ZHANG H J, et al. Black phosphorene/NP heterostructure as a novel anode material for Li/Na-ion batteries[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2022, 24(33): 19697-19704. |
| [1] | Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Junfeng HAO, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yida WU, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Apr. 1, 2023 to May 31, 2023) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2333-2348. |
| [2] | Yuwen ZHAO, Huan YANG, Junpeng GUO, Yi ZHANG, Qi SUN, Zhijia ZHANG. Application of magnetic metal elements in sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1332-1347. |
| [3] | Junpeng GUO, Qi SUN, Yuefang CHEN, Yuwen ZHAO, Huan YANG, Zhijia ZHANG. Preparation of three-dimensional multistage iron oxide/carbon nanofiber integrated electrode and sodium storage performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1469-1479. |
| [4] | Jing ZHU, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Junfeng HAO, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yida WU, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2023 to Mar. 31, 2023) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1553-1569. |
| [5] | Jingjing RUAN, Fuyuan LIU, Shenshen LI, Guihong GAO, Yanxia LIU. Preparation of rod-like silicon-based material by carbon reduction and its application in lithium slurry batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1051-1058. |
| [6] | Xueli CHENG, Weifu ZHANG, Chengcheng LUO, Xiaoya YUAN. Preparation of three-dimensional graphene/Fe3O4 composites by one-step hydrothermal method and their lithium storage performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1066-1074. |
| [7] | Xiaoyu SHEN, Jing ZHU, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Junfeg HAO, Mengyu TIAN, Hongxiang JI, Zhou JIN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Dec. 1, 2022 to Jan. 31, 2023) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 639-653. |
| [8] | Xue YUAN, Hongji LI, Wenhui BAI, Zhengxi LI, Libin YANG, Kai WANG, Zhe CHEN. Application of biomass-derived carbon-based anode materials in sodium ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 721-742. |
| [9] | Shugang LIU, Bo MENG, Zhenglong LI, Yaxiong YANG, Jian CHEN. Electrochemical performance of chemical prelithiated Li x (Mg, Ni, Zn, Cu, Co) 1-x O high-entropy oxide as anode material for lithium ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 743-753. |
| [10] | Mengyu TIAN, Yida WU, Junfeng HAO, Jing ZHU, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xiaoyu SHEN, Hongxiang JI, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Oct. 1, 2022 to Nov. 30, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 1-15. |
| [11] | Wenshu ZHANG, Fangyuan HU, Hao HUANG, Xudong WANG, Man YAO. Sodium storage anode based on titanium-based MXene and its performance regulation mechanism [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 35-41. |
| [12] | Shuya GONG, Yue WANG, Meng LI, Jingyi QIU, Hong WANG, Yuehua WEN, Bin XU. Research progress on TiNb2O7 anodes for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2921-2932. |
| [13] | Jing ZHU, Yida WU, Junfeng HAO, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xiaoyu SHEN, Mengyu TIAN, Hongxiang JI, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Jun. 1, 2022 to Jul. 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 3035-3050. |
| [14] | Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Apr. 1, 2022 to May 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2007-2022. |
| [15] | Xiongwen XU, Yang NIE, Jian TU, Zheng XU, Jian XIE, Xinbing ZHAO. Abuse performance of pouch-type Na-ion batteries based on Prussian blue cathode [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2030-2039. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
