Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (1): 212-230.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0848
Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-11-24
Revised:2023-12-23
Online:2024-01-05
Published:2024-01-22
Contact:
Xin GUO
E-mail:zhou_li@hust.edu.cn;xguo@hust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Zhuo LI, Xin GUO. Solidification of polymer-based electrolytes for energy-density solid-state batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 212-230.
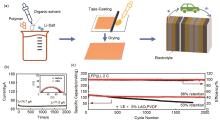
Fig. 2
(a) Preparation of polymer-based electrolytes and solid-state batteries via the casting method; (b) Li-ion transference number of PVDF-LiAlO2 composite polymer-based electrolyte,and (c) electrochemical performances of LiFePO4||Li solid-state batteries with PVDF-LiAlO2 composite polymer-based electrolytes[43]"


Fig. 3
(a) Illustration of the solidification process of the PAN-PEO/LiTFSI polymer-based electrolyte via electrospinning; (b) image of PAN-PEO/LiTFSI polymer-based electrolyte; (c) electrochemical performances of Li||LiFePO4 solid-state batteries with the PAN-PEO/LiTFSI polymer-based electrolyte[45]"
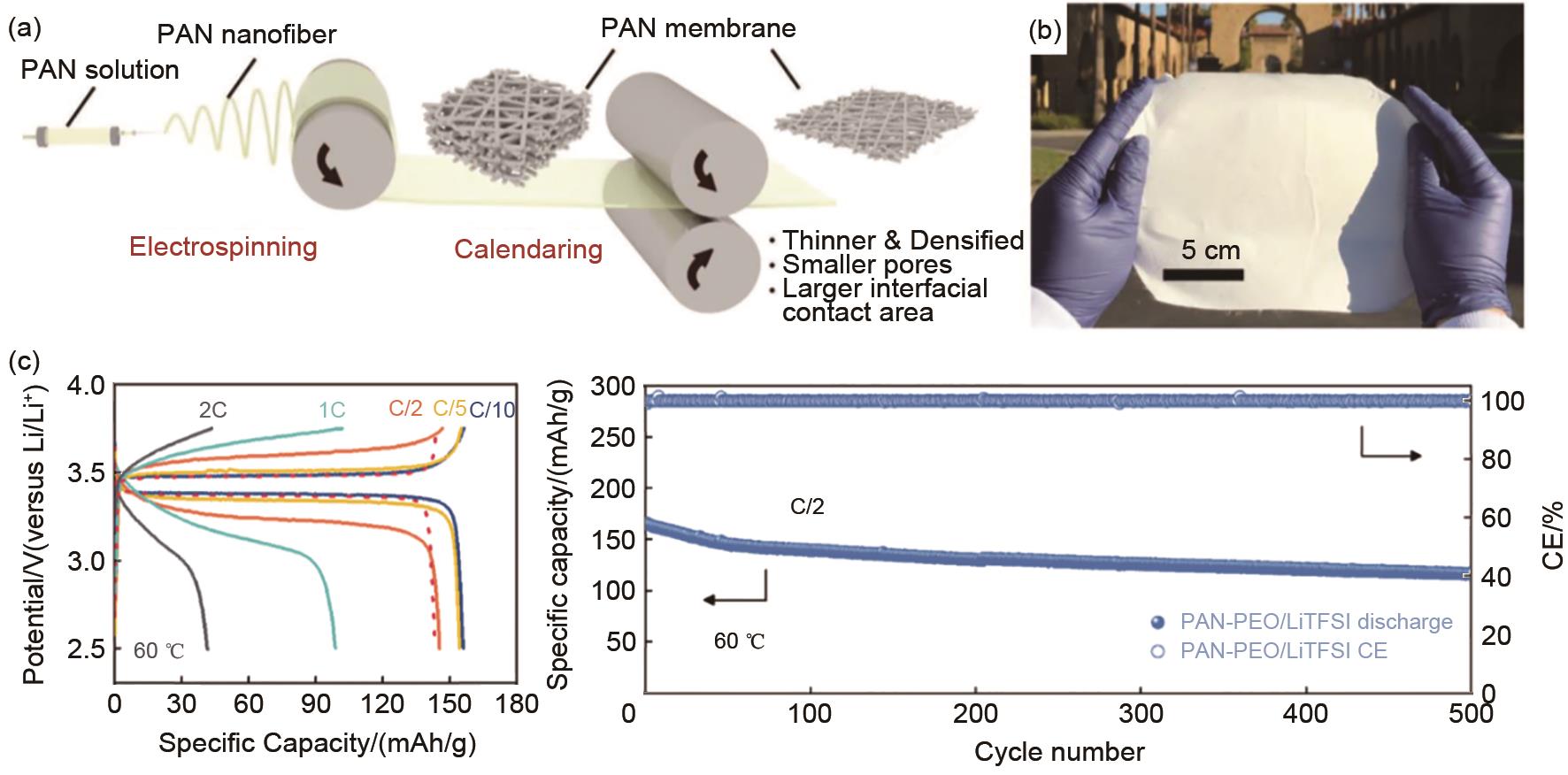
Fig. 4
(a) Involved chemical process for the solidification of ETPTA-based polymer-based electrolyte; (b) images of ETPTA based polymer-based electrolyte; (c) ionic conductivities of ETPTA based polymer-based electrolyte[52]; (d) Illustrating polymer-based electrolytes via ring-opening polymerization of diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-A, poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidylether and diamino-poly(propylene oxide)[53]"
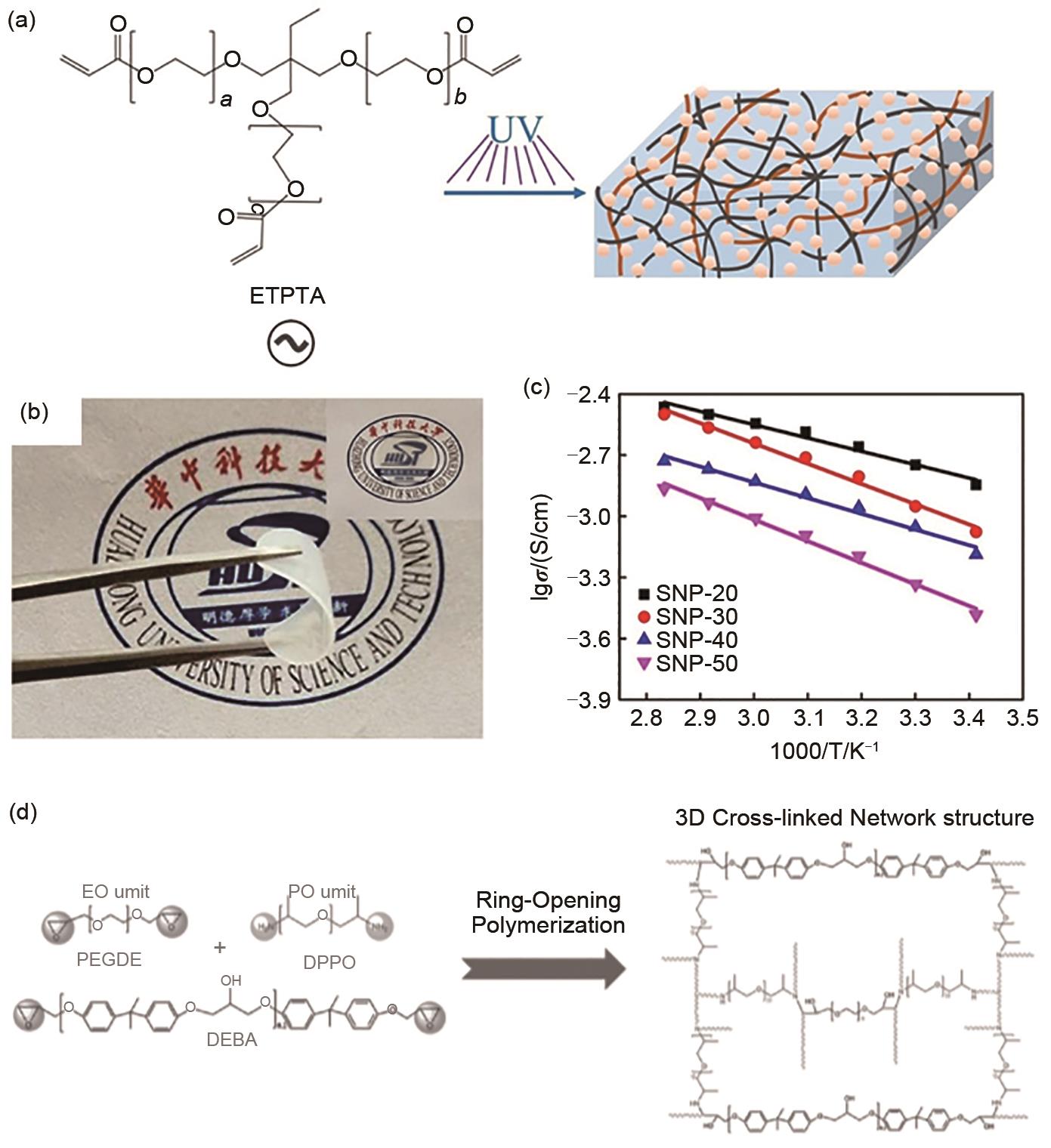
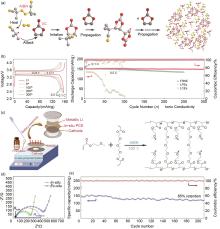
Fig. 6
(a) Illustration of polymerization process of the VC monomer; (b) electrochemical performances of LiFePO4||Li solid-state batteries with PVC electrolyte[67]; (c) Illustration of preparation of PEGMEA/TEGDA cross-linked polymer-based electrolyte; (d) electrochemical impedance spectra of LiFePO4||Li solid-state batteries prepared by in-situ and ex-situ polymerization; (e) Cycle performances of LiFePO4||Li solid-state batteries prepared by in-situ polymerization[68]"

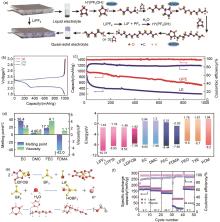
Fig. 9
(a) Involved chemical processes in the polymerization of DOL induced by LiPF6; Electrochemical performance of Li||S cells based on the PDOL-based electrolyte (b) charge-discharge curves, (c) cycle performances[82]; (d) Key materials screening for polymer-based electrolytes; (e) Chemical processes involved in the polymerization of TXE to POM; (f) Electrochemical performances of the Li||NCM811 battery with POM polymer-based electrolyte at different temperatures[84]"
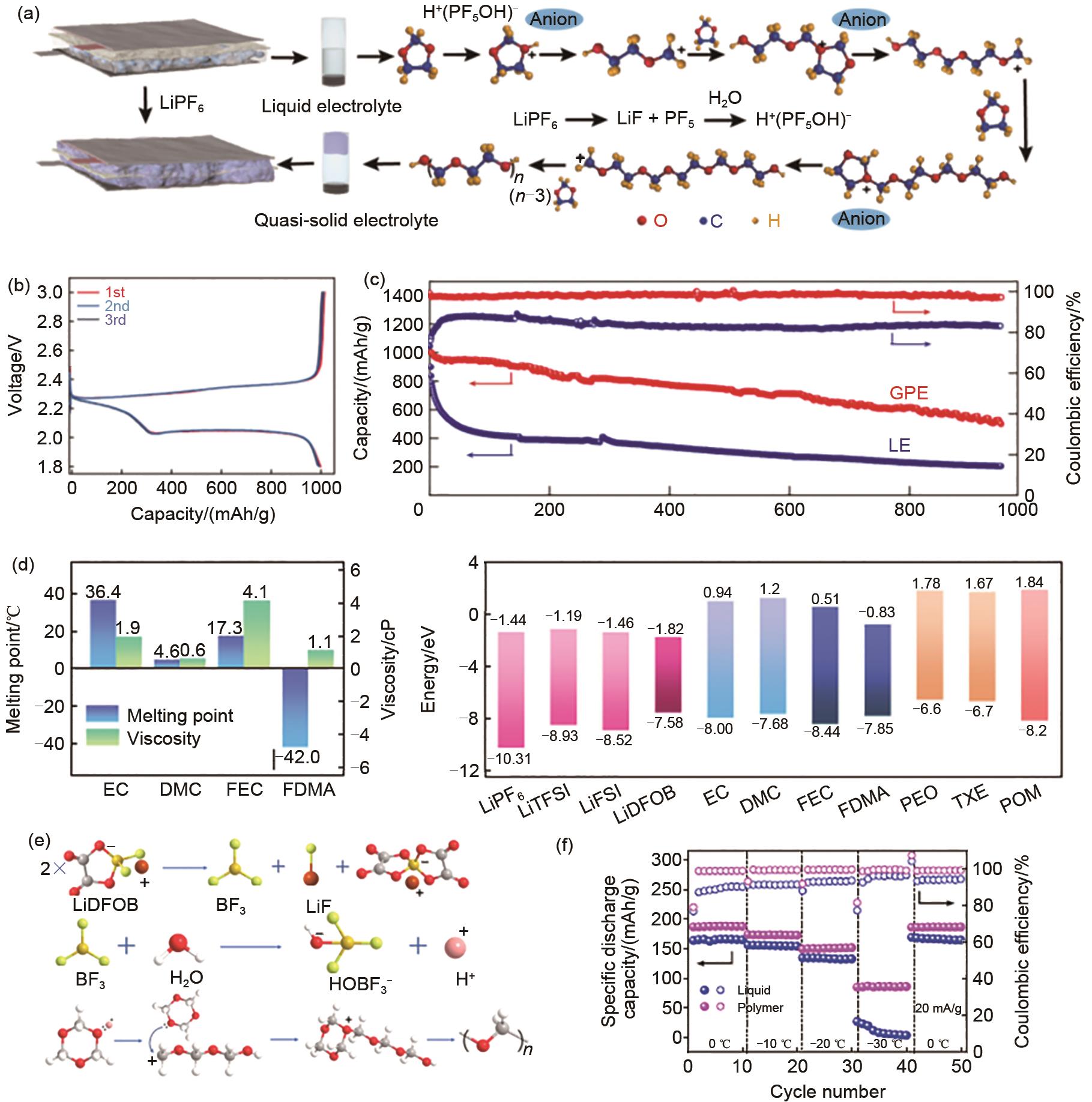
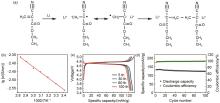
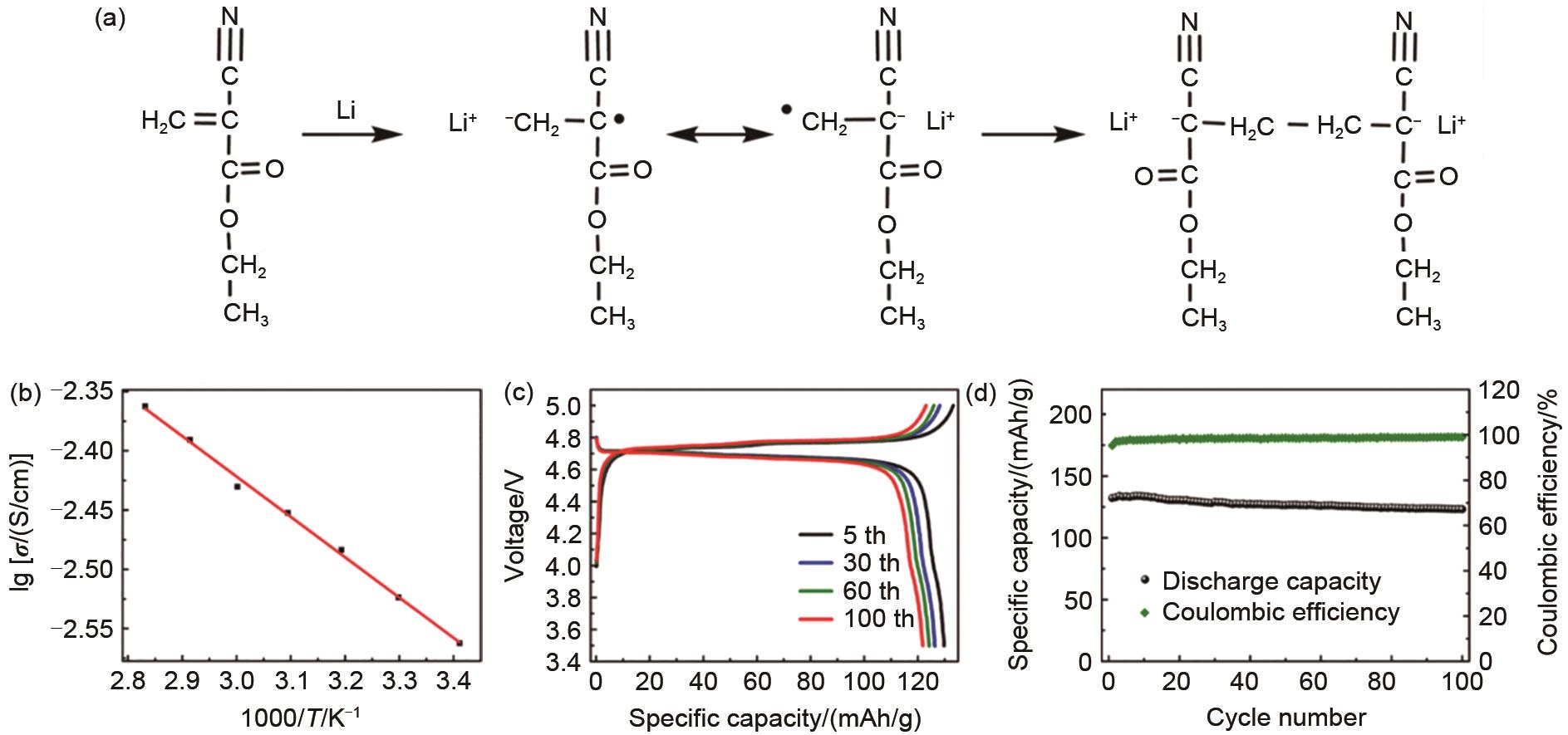
Fig. 11
(a) Anionic polymer reaction mechanism of cyanoacrylate initiated by Li metal; (b) Ionic conductivities of the poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate)-based electrolyte; Electrochemical performances of poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate)-based electrolyte in the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4||Li battery (c) charge-discharge curves, (d) cycle performance[91]"
| 1 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 2 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. |
| 3 | MOTAVALLI J. Technology: A solid future[J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7575): S96-S97. |
| 4 | 李杨, 丁飞, 桑林, 等. 全固态锂离子电池关键材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5(5): 615-626. |
| LI Y, DING F, SANG L, et al. A review of key materials for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2016, 5(5): 615-626. | |
| 5 | JANEK J, ZEIER W G. A solid future for battery development[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16141. |
| 6 | HU Y S. Batteries: Getting solid[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16042. |
| 7 | TIAN Y S, ZENG G B, RUTT A, et al. Promises and challenges of next-generation "beyond Li-ion" batteries for electric vehicles and grid decarbonization[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(3): 1623-1669. |
| 8 | 李泓. 全固态锂电池: 梦想照进现实[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2018, 7(2): 188-193. |
| LI H. All-solid lithium battery: Dreams may come[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(2): 188-193. | |
| 9 | BANERJEE A, WANG X F, FANG C C, et al. Interfaces and interphases in all-solid-state batteries with inorganic solid electrolytes[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(14): 6878-6933. |
| 10 | ZOU Z Y, LI Y J, LU Z H, et al. Mobile ions in composite solids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(9): 4169-4221. |
| 11 | MANTHIRAM A, YU X W, WANG S F. Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2: 16103. |
| 12 | ZHAO Q, STALIN S, ZHAO C Z, et al. Designing solid-state electrolytes for safe, energy-dense batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2020, 5(3): 229-252. |
| 13 | ZHOU D, SHANMUKARAJ D, TKACHEVA A, et al. Polymer electrolytes for lithium-based batteries: Advances and prospects[J]. Chem, 2019, 5(9): 2326-2352. |
| 14 | LOPEZ J, MACKANIC D G, CUI Y, et al. Designing polymers for advanced battery chemistries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2019, 4(5): 312-330. |
| 15 | LU X A, WANG Y M, XU X Y, et al. Polymer-based solid-state electrolytes for high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries-review[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(38): 2301746. |
| 16 | CHEN R S, LI Q H, YU X Q, et al. Approaching practically accessible solid-state batteries: Stability issues related to solid electrolytes and interfaces[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(14): 6820-6877. |
| 17 | 张建军, 杨金凤, 吴瀚, 等. 二次电池用原位生成聚合物电解质的研究进展[J]. 高分子学报, 2019, 50(9): 890-914. |
| ZHANG J J, YANG J F, WU H, et al. Research progress of in situ generated polymer electrolyte for rechargeable batteries[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2019, 50(9): 890-914. | |
| 18 | LI Q A, YANG Y, YU X Q, et al. A 700 W⋅h⋅kg-1 rechargeable pouch type lithium battery[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2023, 40(4): 048201. |
| 19 | WANG Z Y, SHEN L, DENG S G, et al. 10 μm-thick high-strength solid polymer electrolytes with excellent interface compatibility for flexible all-solid-state lithium-metal batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(25): e2100353. |
| 20 | FAN L Z, HE H C, NAN C W. Tailoring inorganic-polymer composites for the mass production of solid-state batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6(11): 1003-1019. |
| 21 | BI Z J, GUO X X. Solidification for solid-state lithium batteries with high energy density and long cycle life[J]. Energy Materials, 2022, 2(2): 200011. |
| 22 | CHO Y G, HWANG C, CHEONG D S, et al. Gel polymer electrolytes: Gel/solid polymer electrolytes characterized by in situ gelation or polymerization for electrochemical energy systems (adv. mater. 20/2019)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(20): e1804909. |
| 23 | ZHAO Q, LIU X, STALIN S, et al. Solid-state polymer electrolytes with in-built fast interfacial transport for secondary lithium batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(5): 365-373. |
| 24 | XIANG J W, ZHANG Y, ZHANG B, et al. A flame-retardant polymer electrolyte for high performance lithium metal batteries with an expanded operation temperature[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(6): 3510-3521. |
| 25 | ZHAO C Z, ZHAO Q, LIU X, et al. Rechargeable lithium metal batteries with an In-built solid-state polymer electrolyte and a high voltage/loading Ni-rich layered cathode[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(12): e1905629. |
| 26 | ZHANG S H, SUN F, DU X F, et al. In-situ polymerized lithium salt as polymer electrolyte enabling high safety lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(6): 2591-2602. |
| 27 | LIU Q, WANG L, HE X M. Toward practical solid-state polymer lithium batteries by in situ polymerization process: A review[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(30): 2300798. |
| 28 | XIAO G Y, XU H, BAI C, et al. Progress and perspectives of in situ polymerization method for lithium-based batteries[J]. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2023, 2(4): 609-634. |
| 29 | LI Z, FU J L, GUO X. How to commercialize solid-state batteries: A perspective from solid electrolytes[J]. National Science Open, 2023, 2(1): 20220036. |
| 30 | CHEN L, LI Y T, LI S P, et al. PEO/garnet composite electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: From "ceramic-in-polymer" to "polymer-in-ceramic"[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 46: 176-184. |
| 31 | LI D, CHEN L, WANG T S, et al. 3D fiber-network-reinforced bicontinuous composite solid electrolyte for dendrite-free lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(8): 7069-7078. |
| 32 | XUE Z G, HE D, XIE X L. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(38): 19218-19253. |
| 33 | LI Z, FU J L, ZHOU X Y, et al. Ionic conduction in polymer-based solid electrolytes[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(10): 2201718. |
| 34 | ZHANG X E, LIU T, ZHANG S F, et al. Synergistic coupling between Li6.75La3Zr1.75Ta0.25O12 and poly(vinylidene fluoride) induces high ionic conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal stability of solid composite electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(39): 13779-13785. |
| 35 | YAO P C, ZHU B, ZHAI H W, et al. PVDF/palygorskite nanowire composite electrolyte for 4 V rechargeable lithium batteries with high energy density[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(10): 6113-6120. |
| 36 | LIU J F, WU Z Y, STADLER F J, et al. High dielectric poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based polymer enables uniform lithium-ion transport in solid-state ionogel electrolytes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(26): e202300243. |
| 37 | XIAO W, WANG Z Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Enhanced performance of P(VDF-HFP)-based composite polymer electrolytes doped with organic-inorganic hybrid particles PMMA-ZrO2 for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 382: 128-134. |
| 38 | LIU W, LIU N A, SUN J E, et al. Ionic conductivity enhancement of polymer electrolytes with ceramic nanowire fillers[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(4): 2740-2745. |
| 39 | LIN Z Y, GUO X W, WANG Z C, et al. A wide-temperature superior ionic conductive polymer electrolyte for lithium metal battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 73: 104786. |
| 40 | LI Z, HUANG H M, ZHU J K, et al. Ionic conduction in composite polymer electrolytes: Case of PEO: Ga-LLZO composites[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(1): 784-791. |
| 41 | LI Z, GUO X. Integrated interface between composite electrolyte and cathode with low resistance enables ultra-long cycle-lifetime in solid-state lithium-metal batteries[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2021, 64(4): 673-680. |
| 42 | LI Z, SHA W X, GUO X. Three-dimensional garnet framework-reinforced solid composite electrolytes with high lithium-ion conductivity and excellent stability[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(30): 26920-26927. |
| 43 | ZHOU X Y, LI X G, LI Z, et al. Hybrid electrolytes with an ultrahigh Li-ion transference number for lithium-metal batteries with fast and stable charge/discharge capability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(34): 18239-18246. |
| 44 | WU J F, YU Z Y, WANG Q, et al. High performance all-solid-state sodium batteries actualized by polyethylene oxide/Na2Zn2TeO6 composite solid electrolytes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 24: 467-471. |
| 45 | MA Y X, WAN J Y, YANG Y F, et al. Scalable, ultrathin, and high-temperature-resistant solid polymer electrolytes for energy-dense lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(15): doi:10.1002/aenm.202103720. |
| 46 | ZENG X X, YIN Y X, LI N W, et al. Reshaping lithium plating/stripping behavior via bifunctional polymer electrolyte for room-temperature solid Li metal batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(49): 15825-15828. |
| 47 | ZENG X X, YIN Y X, SHI Y, et al. Lithiation-derived repellent toward lithium anode safeguard in quasi-solid batteries[J]. Chem, 2018, 4(2): 298-307. |
| 48 | ZHANG Y, YU L, ZHANG X D, et al. A smart risk-responding polymer membrane for safer batteries[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(5): eade5802. |
| 49 | WEI Z Y, ZHANG Z H, CHEN S J, et al. UV-cured polymer electrolyte for LiNi0.85Co0.05Al0.1O2// Li solid state battery working at ambient temperature[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 22: 337-345. |
| 50 | HA H J, KIL E H, KWON Y H, et al. UV-curable semi-interpenetrating polymer network-integrated, highly bendable plastic crystal composite electrolytes for shape-conformable all-solid-state lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(4): 6491-6499. |
| 51 | DUAN H, YIN Y X, ZENG X X, et al. In-situ plasticized polymer electrolyte with double-network for flexible solid-state lithium-metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 10: 85-91. |
| 52 | XIE H X, FU Q G, LI Z, et al. Ultraviolet-cured semi-interpenetrating network polymer electrolytes for high-performance quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Chemistry, 2021, 27(28): 7773-7780. |
| 53 | LI Z, WENG S T, FU J L, et al. Nonflammable quasi-solid electrolyte for energy-dense and long-cycling lithium metal batteries with high-voltage Ni-rich layered cathodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 47: 542-550. |
| 54 | LU Q W, HE Y B, YU Q P, et al. Dendrite-free, high-rate, long-life lithium metal batteries with a 3D cross-linked network polymer electrolyte[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(13): 1604460. |
| 55 | WANG W P, ZHANG J A, CHOU J A, et al. Solidifying cathode-electrolyte interface for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(2): 2000791. |
| 56 | WU H, TANG B, DU X F, et al. LiDFOB initiated in situ polymerization of novel eutectic solution enables room-temperature solid lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(23): 2003370. |
| 57 | YUAN Z X, ZHANG H, HU S J, et al. Research progress of ion-initiated in situ generated solid polymer electrolytes for high-safety lithium batteries[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 1064. |
| 58 | 李文涛, 钟海, 麦耀华. 锂二次电池中的原位聚合电解质[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(6): 988-997. |
| LI W T, ZHONG H, MAI Y H. In-situ polymerization electrolytes for lithium rechargeable batteries[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(6): 988-997. | |
| 59 | CHAI J C, LIU Z H, MA J, et al. In situ generation of poly (vinylene carbonate) based solid electrolyte with interfacial stability for LiCoO2 lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2017, 4(2): 1600377. |
| 60 | LV Z L, ZHOU Q, ZHANG S, et al. Cyano-reinforced in situ polymer electrolyte enabling long-life cycling for high-voltage lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 37: 215-223. |
| 61 | CHEN M, ZHONG M J, JOHNSON J A. Light-controlled radical polymerization: Mechanisms, methods, and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(17): 10167-10211. |
| 62 | BONARDI A H, BONARDI F, NOIRBENT G, et al. Free-radical polymerization upon near-infrared light irradiation, merging photochemical and photothermal initiating methods[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2020, 58(2): 300-308. |
| 63 | VIJAYAKUMAR V, ANOTHUMAKKOOL B, KURUNGOT S, et al. in situ polymerization process: An essential design tool for lithium polymer batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(5): 2708-2788. |
| 64 | JU J W, WANG Y T, CHEN B B, et al. Integrated interface strategy toward room temperature solid-state lithium batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(16): 13588-13597. |
| 65 | WANG A X, GENG S X, ZHAO Z F, et al. In situ cross-linked plastic crystal electrolytes for wide-temperature and high-energy-density lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(17): 2201861. |
| 66 | KITZ P G, LACEY M J, NOVÁK P, et al. Operando investigation of the solid electrolyte interphase mechanical and transport properties formed from vinylene carbonate and fluoroethylene carbonate[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 477: 228567. |
| 67 | TAN S J, YUE J P, TIAN Y F, et al. In-situ encapsulating flame-retardant phosphate into robust polymer matrix for safe and stable quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 39: 186-193. |
| 68 | LI Z, XIE H X, ZHANG X Y, et al. in situ thermally polymerized solid composite electrolytes with a broad electrochemical window for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(7): 3892-3900. |
| 69 | LI Z, ZHOU X Y, GUO X. High-performance lithium metal batteries with ultraconformal interfacial contacts of quasi-solid electrolyte to electrodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 29: 149-155. |
| 70 | ZHOU D, LIU R L, ZHANG J, et al. In situ synthesis of hierarchical poly(ionic liquid)-based solid electrolytes for high-safety lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 33: 45-54. |
| 71 | ZHU J, ZHANG J P, ZHAO R Q, et al. in situ 3D crosslinked gel polymer electrolyte for ultra-long cycling, high-voltage, and high-safety lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 57: 92-101. |
| 72 | SCHAPPACHER M, DEFFIEUX A. Nature of active species in the living cationic polymerization of vinyl ethers initiated by hydrogen halide/zinc halide systems[J]. Macromolecules, 1991, 24(14): 4221-4223. |
| 73 | AOSHIMA S, KANAOKA S. A renaissance in living cationic polymerization[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2009, 109(11): 5245-5287. |
| 74 | HWANG S S, CHO C G, KIM H. Room temperature cross-linkable gel polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries by in situ cationic polymerization of divinyl ether[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12(7): 916-919. |
| 75 | ZHANG J J, WEN H J, YUE L P, et al. In situ formation of polysulfonamide supported poly(ethylene glycol) divinyl ether based polymer electrolyte toward monolithic sodium ion batteries[J]. Small, 2017, 13(2): 10.1002/smll.201601530. |
| 76 | NUYKEN O, PASK S. Ring-opening polymerization—An introductory review[J]. Polymers, 2013, 5(2): 361-403. |
| 77 | ZHOU D, HE Y B, CAI Q, et al. Investigation of cyano resin-based gel polymer electrolyte: in situ gelation mechanism and electrode-electrolyte interfacial fabrication in lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(47): 20059-20066. |
| 78 | ZHANG J N, WU H, DU X F, et al. Smart deep eutectic electrolyte enabling thermally induced shutdown toward high-safety lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(3): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202202529. |
| 79 | PENCZEK St, DUDA Andrzej, KUBISA Przemyslaw, SLOMKOWSKI Stanislaw. Ionic and Coordination Ring‐Opening Polymerization. In Macromolecular Engineering, 2007,doi: 10.1002/9783527815562. mme0026. |
| 80 | KUBISA P, PENCZEK S. Cationic activated monomer polymerization of heterocyclic monomers[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 1999, 24(10): 1409-1437. |
| 81 | PENCZEK S, PRETULA J, SLOMKOWSKI S. Ring-opening polymerization[J]. Chemistry Teacher International, 2021, 3(2): 33-57. |
| 82 | LIU F Q, WANG W P, YIN Y X, et al. Upgrading traditional liquid electrolyte via in situ gelation for future lithium metal batteries[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(10): eaat5383. |
| 83 | MA Q A, YUE J P, FAN M, et al. Formulating the electrolyte towards high-energy and safe rechargeable lithium-metal batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(30): 16554-16560. |
| 84 | LI Z, YU R, WENG S T, et al. Tailoring polymer electrolyte ionic conductivity for production of low-temperature operating quasi-all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 482. |
| 85 | HIRAO A, GOSEKI R, ISHIZONE T. Advances in living anionic polymerization: From functional monomers, polymerization systems, to macromolecular architectures[J]. Macromolecules, 2014, 47(6): 1883-1905. |
| 86 | ISHIZONE T, GOSEKI R. Anionic addition polymerization (fundamental)[M]// Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 1-11. |
| 87 | KITAURA T, KITAYAMA T. Anionic polymerization of methyl methacrylate by difunctional lithium amide initiators with trialkylsilyl protection[J]. Polymer Journal, 2013, 45(10): 1013-1018. |
| 88 | PARK J, KIM A, KIM B S. Anionic ring-opening polymerization of functional epoxide monomers in the solid state[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 5855. |
| 89 | BROCAS A L, MANTZARIDIS C, TUNC D, et al. Polyether synthesis: From activated or metal-free anionic ring-opening polymerization of epoxides to functionalization[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2013, 38(6): 845-873. |
| 90 | HONG K L, UHRIG D, MAYS J W. Living anionic polymerization[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 1999, 4(6): 531-538. |
| 91 | CUI Y Y, CHAI J C, DU H P, et al. Facile and reliable in situ polymerization of poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate)-based polymer electrolytes toward flexible lithium batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(10): 8737-8741. |
| 92 | LEI X F, LIU X Z, MA W Q, et al. Flexible lithium–air battery in ambient air with an In Situ formed gel electrolyte[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(49): 16131-16135. |
| 93 | ITO S, UNEMOTO A, OGAWA H, et al. Application of quasi-solid-state silica nanoparticles-ionic liquid composite electrolytes to all-solid-state lithium secondary battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 208: 271-275. |
| 94 | YI Q A, ZHANG W Q, LI S Q, et al. Durable sodium battery with a flexible Na3Zr2Si2PO12-PVDF-HFP composite electrolyte and sodium/carbon cloth anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(41): 35039-35046. |
| 95 | KIM J K, SCHEERS J, PARK T J, et al. Superior ion-conducting hybrid solid electrolyte for all-solid-state batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(4): 636-641. |
| 96 | XU D, SU J M, JIN J, et al. In situ generated fireproof gel polymer electrolyte with Li6.4Ga0.2La3Zr2O12 As initiator and ion-conductive filler[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(25): 1900611. |
| [1] | Feng LI, Xiaobin CHENG, Jinda LUO, Hongbin YAO. Metal chloride solid-state electrolytes and all-solid-state batteries: State-of-the-art developments and perspectives [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 193-211. |
| [2] | LI Yitao, SHEN Kaier, PANG Quanquan. Advance in organics enhanced sulfide-based solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1902-1918. |
| [3] | Wenlin YAN, Fan WU, Hong LI, Liquan CHEN. Application of Si-based anodes in sulfide solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 821-835. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

