• XXXX •
王世宁1,2( ), 方遒1, 李叶晶4(
), 方遒1, 李叶晶4( ), 王雪锋1,2,3(
), 王雪锋1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-16
修回日期:2025-08-14
通讯作者:
李叶晶,王雪锋
E-mail:1778556446@qq.com;liyejing@ustb.edu.cn;wxf@iphy.ac.cn
作者简介:王世宁(2001—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为基于冷冻电镜电池材料的结构表征和机理探索,E-mail:1778556446@qq.com;
基金资助:
Shining WANG1,2( ), Qiu FANG1, Yejing LI4(
), Qiu FANG1, Yejing LI4( ), Xuefeng WANG1,2,3(
), Xuefeng WANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-07-16
Revised:2025-08-14
Contact:
Yejing LI, Xuefeng WANG
E-mail:1778556446@qq.com;liyejing@ustb.edu.cn;wxf@iphy.ac.cn
摘要:
硅-石墨(Si-Gr)复合负极结合硅的高比容量与石墨的结构稳定性,被视为下一代高能量密度锂离子电池的关键负极材料。然而,硅在嵌/脱锂过程中的严重体积效应,其与石墨在物理化学性质和嵌锂机制上的显著差异,导致了复杂的内部相互作用。这些作用引发了如颗粒破碎、不稳定的固体电解质界面膜持续重构、以及离子传输动力学恶化等多尺度结构失效问题,严重制约了复合负极的商业化进程。本文从多物理场视角出发,系统性地梳理了现有硅-石墨复合负极内部的相互作用机制的研究进展,指出锂化不均匀性和机械应力的累积是限制电极性能的核心因素,为理解复合电极的失效机制提供了深刻见解,并提出未来研究应从被动地适应体积变化,转向主动地调控电极内部的应力-电化学环境,实现长寿命、高能量密度硅基负极材料。
中图分类号:
王世宁, 方遒, 李叶晶, 王雪锋. 硅-石墨复合负极在多物理场视角下的相互作用机制[J]. 储能科学与技术, doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0648.
Shining WANG, Qiu FANG, Yejing LI, Xuefeng WANG. Interaction Mechanisms in Silicon-Graphite Composite Anodes from a Multi-physics Perspective[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0648.
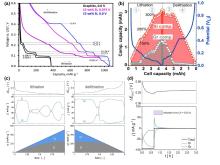
图3
(a)石墨电极在C/120电流密度,硅-石墨复合电极在C/140电流密度下充放电的电压-容量曲线[20];(b)硅-石墨复合电极嵌锂和脱锂过程中石墨和硅各自的容量贡献,显示的百分比是硅颗粒膨胀的估计值[36];(c)质量比为1:13的硅-石墨复合负极在嵌锂与脱锂过程中电势的分布(上)、比电流分布(中)及比容量贡献(下);(d)锂化和随后松弛期间的电极电压以及石墨和硅各自的比电流[37]注:公式(1)x¯=∑jIjhklmjhklFjhkl2∑jIjhklmjhklxjFjhkl2在该公式中,xj、Ijhkl、mjhkl和Fjhkl分别是j相的相对嵌锂量(以LiC6为基准)、j相布拉格峰的相对积分强度、j相衍射的多重度以及相应的散射因子。"
| [1] | YU H, J DUAN, W DU, et al. China's energy storage industry: Develop status, existing problems and countermeasures [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 71: 767-84. |
| [2] | 廖雅贇, 周峰, 张颖曦, 等. 锂离子电池快充石墨负极材料研究进展[J] 储能科学与技术,2024,13(1):130-42 |
| LIAO Y Y, ZHOU F, ZHANG Y X, et al. Research progress on graphite anode materials for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries[J] Energy Storage Science and Technology,2024,13(1):130-42 | |
| [3] | SOLANGI K H, M R ISLAM, R SAIDUR, et al. A review on global solar energy policy [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15(4): 2149-63. |
| [4] | SCROSATI B, J HASSOUN, Y-K SUN. Lithium-ion batteries. A look into the future [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(9): 3287-95. |
| [5] | NITTA N, G YUSHIN. High-capacity anode materials for lithium-ion batteries: choice of elements and structures for active particles [J]. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2014, 31(3): 317-36. |
| [6] | SHU Z X, R S MCMILLAN, J J MURRAY. Electrochemical intercalation of lithium into graphite [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1993, 140(4): 922-7. |
| [7] | TARASCON J-M, M ARMAND. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 359-67. |
| [8] | CHAN C K, H PENG, G LIU, et al. High-performance lithium battery anodes using silicon nanowires [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(1): 31-5. |
| [9] | WANG J, W HUANG, Y S KIM, et al. Scalable synthesis of nanoporous silicon microparticles for highly cyclable lithium-ion batteries [J]. Nano Research, 2020, 13(6): 1558-63. |
| [10] | OBROVAC M N, L CHRISTENSEN. Structural changes in silicon anodes during lithium insertion/extraction [J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2004, 7(5): A93-A6. |
| [11] | WU H, G CHAN, J W CHOI, et al. Stable cycling of double-walled silicon nanotube battery anodes through solid–electrolyte interphase control [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(5): 310-5. |
| [12] | CHRISTENSEN J, J NEWMAN. Stress generation and fracture in lithium insertion materials [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2006, 10(5): 293-319. |
| [13] | POVIA M, J SOTTMANN, G PORTALE, et al. Operando SAXS/WAXS on the a-P/C as the anode for Na-ion batteries [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(11): 5917-23. |
| [14] | KASAVAJJULA U, C WANG, A J APPLEBY. Nano- and bulk-silicon-based insertion anodes for lithium-ion secondary cells [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 163(2): 1003-39. |
| [15] | KO M, S CHAE, J CHO. Challenges in accommodating volume change of si anodes for li‐ion batteries [J]. ChemElectroChem, 2015, 2(11): 1645-51. |
| [16] | LI Z, Y ZHANG, T LIU, et al. Silicon anode with high initial coulombic efficiency by modulated trifunctional binder for high-areal-capacity lithium-ion batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(20): 1903110. |
| [17] | YANG G, S FRISCO, R TAO, et al. Robust solid/electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation on si anodes using glyme-based electrolytes [J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(5): 1684-93. |
| [18] | CAO Z, X ZHENG, Q QU, et al. Electrolyte design enabling a high-safety and high-performance si anode with a tailored electrode–electrolyte interphase [J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(38): 2103178. |
| [19] | BAI S, W BAO, K QIAN, et al. Elucidating the role of prelithiation in si‐based anodes for interface stabilization [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(28). |
| [20] | KLETT M, J A GILBERT, K Z PUPEK, et al. Layered oxide, graphite and silicon-graphite electrodes for lithium-ion cells: effect of electrolyte composition and cycling windows [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(1): A6095-A102. |
| [21] | 周军华, 罗飞, 褚赓, 等. 锂离子电池纳米硅碳负极材料研究进展[J] 储能科学与技术,2020,9(2):569-82 |
| ZHOU J H, LUO F, CHU G, et al. Research progress on nano silicon-carbon anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J] Energy Storage Science and Technology,2020,9(2):569-82 | |
| [22] | ZHANG H, Y YANG, D REN, et al. Graphite as anode materials: fundamental mechanism, recent progress and advances [J]. ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS, 2021, 36: 147-70. |
| [23] | MANDELTORT L, J T YATES. Rapid atomic li surface diffusion and intercalation on graphite: a surface science study [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(47): 24962-7. |
| [24] | HARRIS S J, E K RAHANI, V B SHENOY. Direct in situ observation and numerical simulations of non-shrinking-core behavior in an MCMB graphite composite electrode [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(9): A1501-A7. |
| [25] | AGRAWAL S, P BAI. Operando electrochemical kinetics in particulate porous electrodes by quantifying the mesoscale spatiotemporal heterogeneities [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(12): 2003344. |
| [26] | LIU X H, J W WANG, S HUANG, et al. In situ atomic-scale imaging of electrochemical lithiation in silicon [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(11): 749-56. |
| [27] | ZHANG Q, W ZHANG, W WAN, et al. Lithium insertion in silicon nanowires: an ab initio study [J]. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(9): 3243-9. |
| [28] | DIDIER C, W K PANG, Z GUO, et al. Phase evolution and intermittent disorder in electrochemically lithiated graphite determined using in operando neutron diffraction [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(6): 2518-31. |
| [29] | AURBACH D, B MARKOVSKY, I WEISSMAN, et al. On the correlation between surface chemistry and performance of graphite negative electrodes for Li ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45(1): 67-86. |
| [30] | HOFMANN U, W RüDORFF. The formation of salts from graphite by strong acids [J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1938, 34(0): 1017-21. |
| [31] | WENG S, S WU, Z LIU, et al. Localized‐domains staging structure and evolution in lithiated graphite [J]. Carbon Energy, 2023, 5(1): c224. |
| [32] | WEN C J, R A HUGGINS. Chemical diffusion in intermediate phases in the lithium-silicon system [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1981, 37(3): 271-8. |
| [33] | NGUYEN H T, F YAO, M R ZAMFIR, et al. Highly interconnected si nanowires for improved stability li‐ion battery anodes [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2011, 1(6): 1154-61. |
| [34] | LI J, J R DAHN. An In situ X-ray diffraction study of the reaction of Li with crystalline Si [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2007, 154(3): A156. |
| [35] | KEY B, M MORCRETTE, J-M TARASCON, et al. Pair distribution function analysis and solid state NMR studies of silicon electrodes for lithium ion batteries: understanding the (de)lithiation mechanisms [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(3): 503-12. |
| [36] | YAO K P C, J S OKASINSKI, K KALAGA, et al. Operando quantification of (de)lithiation behavior of silicon–graphite blended electrodes for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(8): 1803380. |
| [37] | HEUBNER C, T LIEBMANN, O LOHRBERG, et al. Understanding component‐specific contributions and internal dynamics in silicon/graphite blended electrodes for high-energy lithium-ion batteries [J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2022, 5(1): e202100182. |
| [38] | LIU X H, L Q ZHANG, L ZHONG, et al. Ultrafast electrochemical lithiation of individual si nanowire anodes [J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(6): 2251-8. |
| [39] | LEE S W, M T MCDOWELL, J W CHOI, et al. Anomalous shape changes of silicon nanopillars by electrochemical lithiation [J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(7): 3034-9. |
| [40] | YANG H, S HUANG, X HUANG, et al. Orientation-dependent interfacial mobility governs the anisotropic swelling in lithiated silicon nanowires [J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(4): 1953-8. |
| [41] | PIETSCH P, D WESTHOFF, J FEINAUER, et al. Quantifying microstructural dynamics and electrochemical activity of graphite and silicon-graphite lithium ion battery anodes [J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 12909. |
| [42] | MCDOWELL M T, I RYU, S W LEE, et al. Studying the kinetics of crystalline silicon nanoparticle lithiation with in situ transmission electron microscopy [J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(45): 6034-41. |
| [43] | ZHAO K, M PHARR, Q WAN, et al. Concurrent reaction and plasticity during initial lithiation of crystalline silicon in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(3): A238-A43. |
| [44] | HöLDERLE T, D PETZ, V KOCHETOV, et al. Structural response of silicon-containing graphite anodes on lithium intercalation [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2025, 75: 104042. |
| [45] | MOON J, H C LEE, H JUNG, et al. Interplay between electrochemical reactions and mechanical responses in silicon–graphite anodes and its impact on degradation [J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 2714. |
| [46] | BERHAUT C L, M MIROLO, D Z DOMINGUEZ, et al. Charge dynamics induced by lithiation heterogeneity in silicon‐graphite composite anodes [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(44): 2301874. |
| [47] | KIM J, M-H KIM, Y KIM, et al. Unveiling the role of electrode-level heterogeneity alleviated in a silicon-graphite electrode under operando microscopy [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 57: 269-76. |
| [48] | LI X, Y CHEN, Y LU, et al. Spatial‐dependent coupling of electrochemistry, mass transport, and stress in silicon‐graphite composite electrodes for lithium‐ion batteries [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(3): 2413560. |
| [49] | JURNG S, Z L BROWN, J KIM, et al. Effect of electrolyte on the nanostructure of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and performance of lithium metal anodes [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(9): 2600-8. |
| [50] | VEITH G M, M DOUCET, J K BALDWIN, et al. Direct determination of solid-electrolyte interphase thickness and composition as a function of state of charge on a silicon anode [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(35): 20339-49. |
| [51] | YANG G, S ZHANG, S WENG, et al. Anionic effect on enhancing the stability of a solid electrolyte interphase film for lithium deposition on graphite [J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(12): 5316-23. |
| [52] | HE Y, L JIANG, T CHEN, et al. Progressive growth of the solid–electrolyte interphase towards the Si anode interior causes capacity fading [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(10): 1113-20. |
| [53] | QIAN G, Y LI, H CHEN, et al. Revealing the aging process of solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx anode [J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1-9. |
| [54] | 于春辉, 何姿颖, 张晨曦, 等. 硅基负极与电解液化学反应的分析与抑制策略[J] 储能科学与技术,2022,11(6):1749-59 |
| YU C H, HE Z Y, ZHANG C X, et al. Analysis and suppression strategies of chemical reactions between silicon-based anodes and electrolytes[J] Energy Storage Science and Technology,2022,11(6):1749-59 | |
| [55] | TAN D H S, Y-T CHEN, H YANG, et al. Carbon-free high-loading silicon anodes enabled by sulfide solid electrolytes [J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1494-9. |
| [56] | FANG Q, S XU, X SHA, et al. Interfacial degradation of silicon anodes in pouch cells [J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(17): 6368-76. |
| [57] | SHIN H, J PARK, S HAN, et al. Component-/structure-dependent elasticity of solid electrolyte interphase layer in Li-ion batteries: Experimental and computational studies [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 277: 169-79. |
| [1] | 胡力月, 黄威, 周云, 周英强, 邵常政, 王柯. 基于模糊推理的储能系统锂离子电池模组热扩散概率评估方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(7): 2662-2674. |
| [2] | 王薇, 梁惠施, 李棉刚, 周奎, 王薇, 王姿尧, 史梓男. 基于迁移学习的锂电池不可逆析锂监测方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(7): 2698-2706. |
| [3] | 熊峰, 孔得朋, 平平, 张越, 任宪通, 吕耀. 电热耦合诱导三元锂离子电池热失控特性[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(7): 2752-2760. |
| [4] | 翁雯媛, 沈斌, 朱建功, 汪洋, 路华鹏, 何乌利雅苏, 刘浩男, 戴海峰, 魏学哲. 锂离子电池阳极危害性析锂原位检测综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(7): 2575-2589. |
| [5] | 张子敬, 原蓓蓓, 李红, 高颖. 锂离子电池热失控气体检测分析及预警[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(7): 2820-2832. |
| [6] | 刘佳辉, 卞伟翔, 李大伟. 锂电池石墨复合电极力-电耦合性能原位测量分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2240-2247. |
| [7] | 陈峥, 多功东, 申江卫, 沈世全, 刘昱, 魏福星. 基于容量增量分析与VMD-GWO-KELM的锂电池健康状态估计[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2476-2487. |
| [8] | 阮晶晶, 巫湘坤, 李勇慧, 赵冲冲, 李珅珅, 王童飞, 梁圣杰, 高桂红. 低成本干法石墨厚电极的制备与性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2248-2255. |
| [9] | 韩丹丹, 张武卫, 张亮, 王宗江. 核壳结构LiMn1-y Fe y PO4/C正极材料设计与电化学性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2215-2222. |
| [10] | 王功瑞, 张安萍, 任萱萱, 杨铭哲, 韩宇宁, 吴忠帅. 高电压钴酸锂正极:关键挑战、改性策略与未来展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2278-2319. |
| [11] | 周海洋, 张振东, 盛雷, 朱泽华, 张晓军, 张春风. 储能用锂电池浸没式热性能调控仿真及热安全实验研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1866-1874. |
| [12] | 宋海飞, 王乐红, 原义栋, 赵天挺, 陈捷. 基于改进卡尔曼算法的电池采样电压滤波估计[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 2106-2113. |
| [13] | 曾州岚, 尚雷, 胡志金, 王宗凡, 辛小超, 刘瑛. 高容量锂离子电池正极补锂材料Li5FeO4@C的性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1875-1883. |
| [14] | 莫子鸣, 饶宗昕, 杨建飞, 杨孟昊, 蔡黎明. 锂离子电池过充热失控气热模型构建及关键参数影响分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1784-1796. |
| [15] | 彭磊, 倪照鹏, 于越, 孙福鹏, 夏修龙, 张鹏, 孙思博. 过充导致三元锂电池电动汽车火灾的试验研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1484-1495. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
