储能科学与技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (6): 2278-2319.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.1256
王功瑞( ), 张安萍, 任萱萱, 杨铭哲, 韩宇宁, 吴忠帅(
), 张安萍, 任萱萱, 杨铭哲, 韩宇宁, 吴忠帅( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-29
修回日期:2025-04-04
出版日期:2025-06-28
发布日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
吴忠帅
E-mail:wanggongrui@dicp.ac.cn;wuzs@dicp.ac.cn
作者简介:王功瑞(1992—),男,博士,研究方向为双高储能器件的关键材料设计与快充储能机制,E-mail:wanggongrui@dicp.ac.cn;
基金资助:
Gongrui WANG( ), Anping ZHANG, Xuanxuan REN, Mingzhe YANG, Yuning HAN, Zhongshuai WU(
), Anping ZHANG, Xuanxuan REN, Mingzhe YANG, Yuning HAN, Zhongshuai WU( )
)
Received:2024-12-29
Revised:2025-04-04
Online:2025-06-28
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Zhongshuai WU
E-mail:wanggongrui@dicp.ac.cn;wuzs@dicp.ac.cn
摘要:
为了推动高端便携电子产品的进一步发展,迫切需要发展具有高能量密度、长循环寿命、高功率密度、宽温域的锂离子电池。作为便携场景下首选的正极材料,钴酸锂仍面临工作电压和比容量低、快充和宽温域下性能不足的挑战,难以满足高端先进电子设备的使用需求。本文系统地总结和讨论了高电压钴酸锂正极的失效机制和关键挑战,深入归纳探讨了多种改性策略的最新研究进展,并对未来研究方向进行了详细的展望。首先全面概括了高电压钴酸锂关键挑战,包括晶体结构、体相结构失效(相转变、层间滑移、裂纹萌生与扩展)、界面失效、复杂工况下的失效机制(高电压快充、高电压高温)。随后,对已发展的改性策略和改性机制进行了归纳总结,包括通过体相元素掺杂提升锂离子扩散速率和体相结构稳定性,包括锂位点、钴位点、氧位点和多位点掺杂;通过表界面化学调控提升表界面结构稳定性和离子/电子导电性,包括表面包覆(离子导体、电子导体、离子/电子双绝缘体材料)、原位结构修饰、电解液调控,以及界面原位电化学转化;通过其他策略优化电极中离子和电子的传输过程,包括黏结剂、导电剂和电极结构。最后,本文对前瞻性的观点和具有前景的研究方向进行了深入阐述,为下一代锂离子电池用高电压钴酸锂正极的设计制备提供了全面细致的建议和理论指导。
中图分类号:
王功瑞, 张安萍, 任萱萱, 杨铭哲, 韩宇宁, 吴忠帅. 高电压钴酸锂正极:关键挑战、改性策略与未来展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2278-2319.
Gongrui WANG, Anping ZHANG, Xuanxuan REN, Mingzhe YANG, Yuning HAN, Zhongshuai WU. High-voltage lithium cobalt oxide cathode: Key challenges, modification strategies and future prospectives[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2278-2319.
图4
Li(1-x)CoO2 中CoO6 层的层间滑移:(a) O3-LiCoO2(蓝色)通过在 ab 平面中连续滑动转化为O1-Li(1-x)CoO2 (橙色) 并伴随着 c 轴方向间距增大[33];(b) δ1=9.847°的O3-LiCoO2[33];(c) 带电的Li0.5CoO2 和放电的Li0.65CoO2, δ 分别为7.426°和5.761°[33];(d) δ5=0°的O1-LiCoO2[33];(e) 高压LCO在4.6 V时的阶梯状表面劣化示意图[34];LCO的TEM图:(f) 首次充电4.65 V和 (g) 200次循环后[35];LCO在[210]方向的倒易晶格:(h) 首次充电至4.65 V,(i) 首次放电至3 V,(j) 200次循环后[35]"
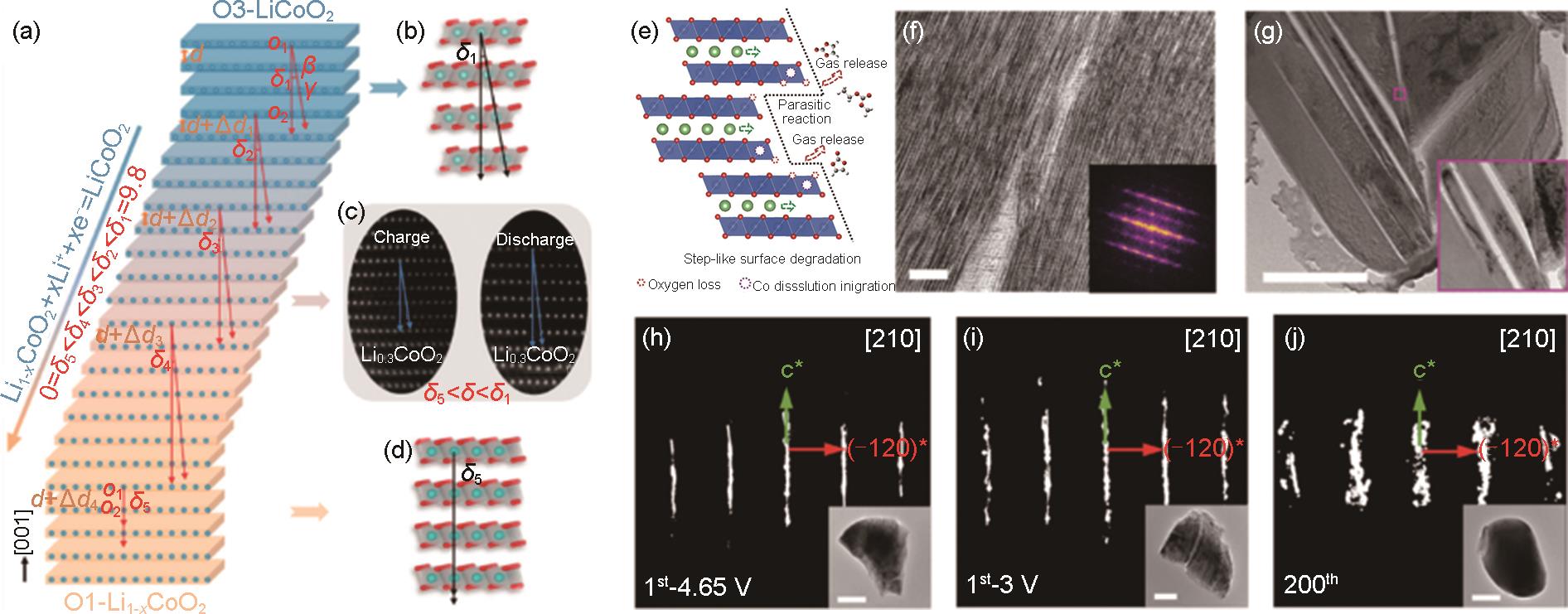
图6
高电压快充工况下的失效机制:(a)~(d) 首次循环充电状态下 (a),(b) rod-NMC和 (c),(d) gravel-NMC的 (a),(c) 颗粒和 (b),(d) 代表性纳米域的3D和2D Ni价态分布,比例尺为 (a),(c) 3 μm和 (b),(d) 1 μm[53];颗粒接触失效的可视化:(e) NCM颗粒中的选定区域,(f) 3D渲染图 (左),界面局域电阻分布计算图 (中),去除分离相的同一颗粒 (右),比例尺为 (e),(f) 10 μm[55];(g) NCM电极的显微断层扫描数据 (左) 和3D渲染的纳米断层扫描数据 (右);(h)~(j) 红色、绿色和蓝色渲染的三个代表性颗粒;(k) 上层和 (l) 底层的同层颗粒截面图[58];(m) 第二循环内不同SOC颗粒的锂离子含量分布[59]"
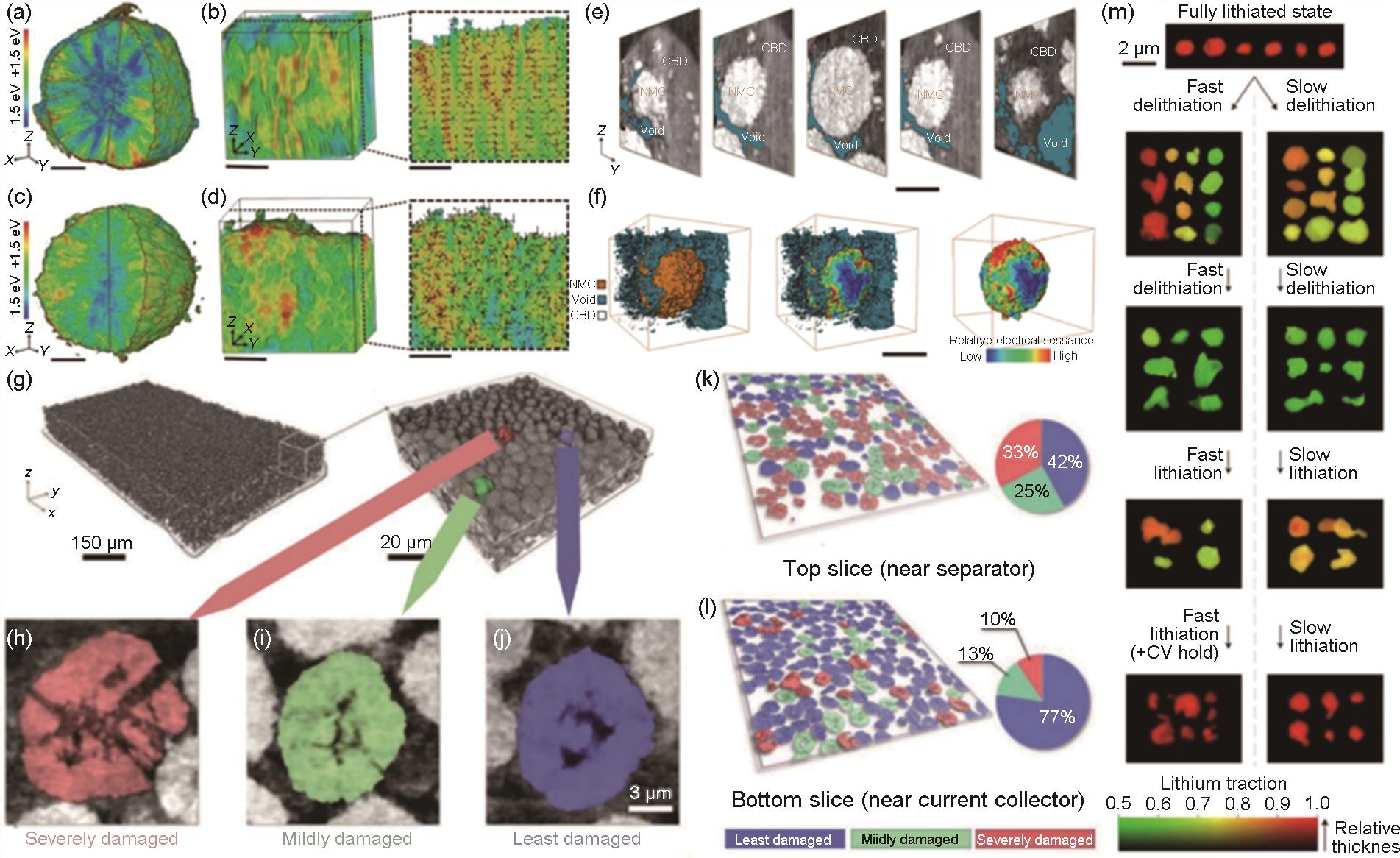
表1
各种掺杂剂改性的高压快充LCO性能对比(EC:碳酸乙烯酯,DEC:碳酸二乙酯,DMC:碳酸二甲酯,EMC:碳酸甲乙酯,FEC:氟碳酸乙烯酯,VC:碳酸亚乙烯酯)"
| Type | Dopants | Electrolyte | Mass loading /(mg/cm2) | Cutoff voltage (vs. Li+/Li)/V | Cyclability (capacity retention-ycles-rates) | Rate capability/(mAh/g-rates) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lithium ion site | Mg | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~3 | 4.6 | 84-100-1C | 138-4C | [ |
| Ni | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC | ~15.2 | 4.45 | 93%-100-1C | 150-5C | [ | |
| Cu | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | — | 4.4 | 89%-500-1C | 144-20C | [ | |
| W | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | — | 4.6 | 72%-100-0.1C | — | [ | |
| (SO4) n- | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC with 5% VC | ~2 | 4.6 | 88%-100-1C | 143-20C | [ | |
| cobalt ion site | Al | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC | ~3 | 4.6 | 94%-30-0.1C | — | [ |
| V | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | ~2 | 4.6 | 84%-100-1C93%-200-5C | 80-5C | [ | |
| Zr | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC | — | 4.5 | 75%-50-1C | 100-3C | [ | |
| oxygen io site | Se | 1.2 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~12 | 4.62 | 86%-120-0.25C | — | [ |
| multiple sites | Al, La | 1.2 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC | ~10 | 4.5 | 96%-50-0.1C | 165-2C | [ |
| Al, F | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | ~3 | 4.6 | 86%-200-1C | 108-10C | [ | |
| Mg, F | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | ~3 | 4.6 | 92%-100-1C84%-1000-5C | 140-5C | [ | |
| Mg, manganese (Mn) | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | — | 4.7 | 30%-50-0.2C | — | [ | |
| Ti, Mg, Ni | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC | ~1.8 | 4.5 | 90%-100-1C | 137-5C | [ | |
| Nb, W, Al | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC with 10% FEC | ~5 | 4.5 | 60%-1000-10C | 142-15C | [ | |
| Ti, Mg, Al | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC with 2% VC | ~4 | 4.5 | 97%-100-0.33C | 165-20C | [ | |
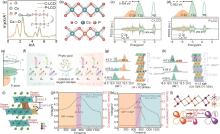
图8
(a) 傅里叶变换的Co k-edge XAFS;(b) C-LCO (上) 和P-LCO (下) 的CoO4 平面和Co—O键长;(c) C-LCO和 (d) P-LCO的PDOS和对应的Co 3d: t2g 和O 2p能隙图;(e) 电子轨道占位变化图;(f) C-LCO和P-LCO的Co自旋组态差图;(g) C-LCO和 (h) P-LCO在4.6 V附近各相含量的变化及O3相和H1-3相的结构示意图[81];(i) NH4VO3 处理的LCO (表示为NV-30LCO) 首次循环的精细晶体结构;(j) NV-30LCO和(k)空白LCO (表示为Bare-LCO) 的差分电化学质谱;(l) 计算出的CoO6/VO6 的Bader电荷和V掺杂的函数示意图[71]"
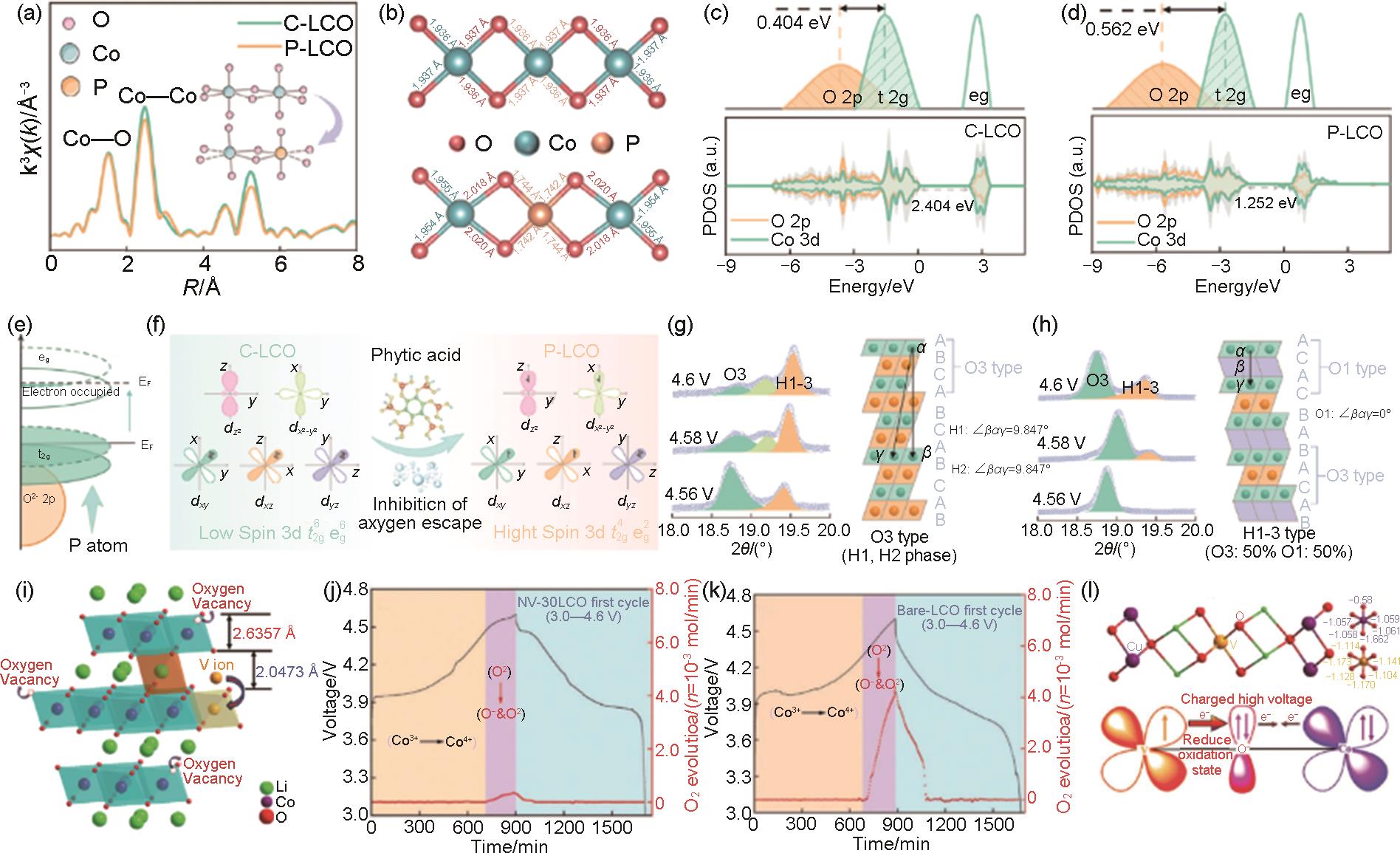
图11
(a) N@P和 (b) 原始 (Pri) 表面晶体结构示意图;(c) N@P (左) 和Pri (右) 的HAADF-STEM图;基于GITT的 (d) N@P和 (e) Pri电极的锂离子扩散系数;(f) 倍率性能;(g) 基于N@P软包电池在3.0~4.6 V下的循环性能[105];(h) 原始和磷酸化LCO的拉曼光谱;(i) 磷酸化LCO的O 1s XPS图;首圈循环 (j) 原始和 (k) 磷酸化LCO的F 1s XPS图[106];(l) 相干尖晶石Li x Co2O4 和Li2SO4 共包覆和高价态S梯度掺杂LCO的合成示意图;(m) EG-LCO-20+0.1S的原子分辨率HAADF-STEM图;(n) EG@-LCO-20, EG-LCO-20和EG-LCO-20+0.1S的倍率性能[104]"
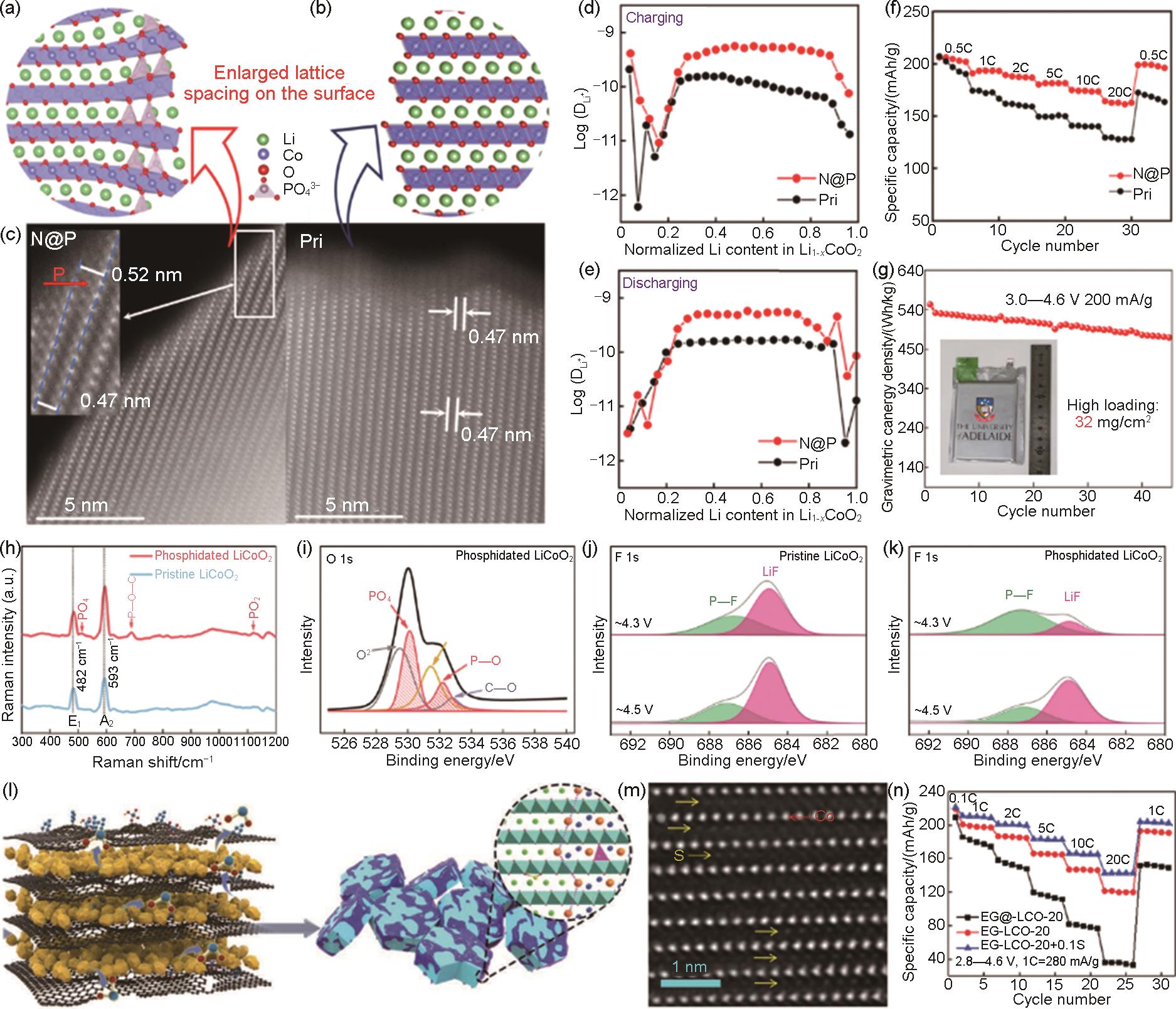
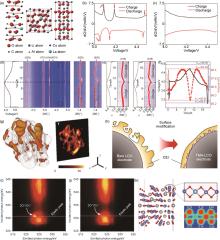
图12
(a) 掺杂CoCO3 、Co3O4 和D-LCO的结构示意图 (b) P-LCO和(c)D-LCO的dQ/dV 曲线(红色箭头表示各种相变);(d) D-LCO的XRD图谱演化对应的电压剖面图 (黑色虚线圆圈是指O3(I)-O3(II)跃迁),D-LCO和P-LCO的 (003) 峰演化;(e) D-LCO和P-LCO的 (015) 峰演变的等值线图;(f) D-LCO的电压曲线(黑色)和电池体积演变过程(红色)[74];(g) Ti的三维空间分布和元素分布;(h) 裸LCO和TMA-LCO之间CEI差异示意图;4.6 V充电状态下 (i) 裸露LCO和 (j) TMA-LCO的O K-edge RIXS图;(k) Ti掺杂板在Li0.29CoO2 中的优化原子结构[37]"
表2
不同包覆材料改性高压快充LCO性能比较"
| Type | Coating layer | Electrolyte | Mass loading/(mg/cm2) | Cutoff voltage (vs. Li/Li+)/V | Cyclability (capacity retention-cycles-rate) | Rate capbility/(mAh/g-rates) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dielectric materials | Al2O3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC | — | 4.5 | 71%-200-0.1C | — | [ |
| Al2O3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC | ~2 | 4.6 | 82.6%-500-1C | 100-10C | [ | |
| Al2O3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC | ~2 | 4.6 | 88%-200-0.5C | 165-3C | [ | |
| BaTiO3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | — | 4.2 | 90%-800-5C | 60-100C | [ | |
| Al-Zn-O | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | — | 4.6 | 65%-500-1C | 80-10C | [ | |
| MgO | 1 mol/L LiClO4 in PC | — | 4.4 | — | — | [ | |
| AlF | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | — | 4.6 | 80%-50-0.5C | — | [ | |
| ionic conductive materials | spinel LiCo x Mn2-x O4 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | — | 4.5 | 82%-300-0.2C | 143-10C | [ |
| spinel LiCo2O4 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC | ~2 | 4.6 | 97%-100-1C | 139-20C | [ | |
| spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 | 1.15 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC with 5% FEC, 3% 1,3-propane sultone and 2% adiponitrile | ~2.5 | 4.45 | 81%-400-0.5C | — | [ | |
| LiAlF | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~12.6 | 4.6 | 81%-200-0.1C | 100-3C | [ | |
| LiAlF | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | — | 4.6 | 78%-500-0.5C | 125-10C | [ | |
| LiAlO2 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~15 | 4.6 | 83%-50-0.25C | 100-0.5C | [ | |
| LiF | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC | — | 4.2 | 77%-100-1C | — | [ | |
| LiAlH4 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC/FEC | ~6 | 4.6 | 71%-1000-1C | 130-10C | [ | |
| LiCoPO4 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC with 5% FEC | ~3 | 4.6/4.7 | 87%-300-1C | 178-10C | [ | |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 | 1.2 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC | ~9 | 4.5 | 88%-400-0.3C | 163-6C | [ | |
| LiZr2(PO4)3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC | ~1.5 | 4.6 | 75%-100-0.5C | 75-5C | [ | |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | ~3 | 4.6 | 88%-100-0.5C | 100-5C | [ | |
| electronic conductive materials | graphene | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | — | 4.2 | 85%-200-1C | 100-5C | [ |
| multiple materials | AlPO4, Li3PO4 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~3 | 4.6 | 88%-200-0.5C | 149-5C | [ |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5P3O12, Al-doped ZnO | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DMC | ~2 | 4.6 | 77%-350-1C | 139-10C | [ | |
| LiF and Li2Co Ti3O8 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~8 | 4.6 | 81%-200-0.1C | 130-3C | [ | |
| Li2SrSiO4 and Al2O3 | 1 mol/L LiPF6 in EC/DEC | ~3 | 4.5 | 64%-500-10C | 80-10C | [ | |
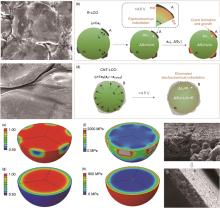
图14
(a) R-LCO中LCO颗粒和炭黑的SEM图;(b) 对R-LCO进行高压充电时LCO晶体的电化学压痕和裂纹形成示意图;(c) CNT包覆的LCO颗粒的SEM图;(d) CNT-LCO在高压下充电时防止LCO晶体产生电化学压痕和裂纹的方案。R-LCO和CNT-LCO电化学压痕的有限元模拟;(e) R-LCO中LCO颗粒中的Li浓度;(f) R-LCO中LCO的von Mises应力场;(g) CNT-LCO中LCO颗粒中的Li浓度;(h) CNT-LCO中LCO的von Mises应力场;(i) 独立的CNT-LCO电极在压制前的图,附图显示了CNT-LCO中的LCO颗粒;(j) 独立CNT-LCO电极滚压至高密度后的图[153]"
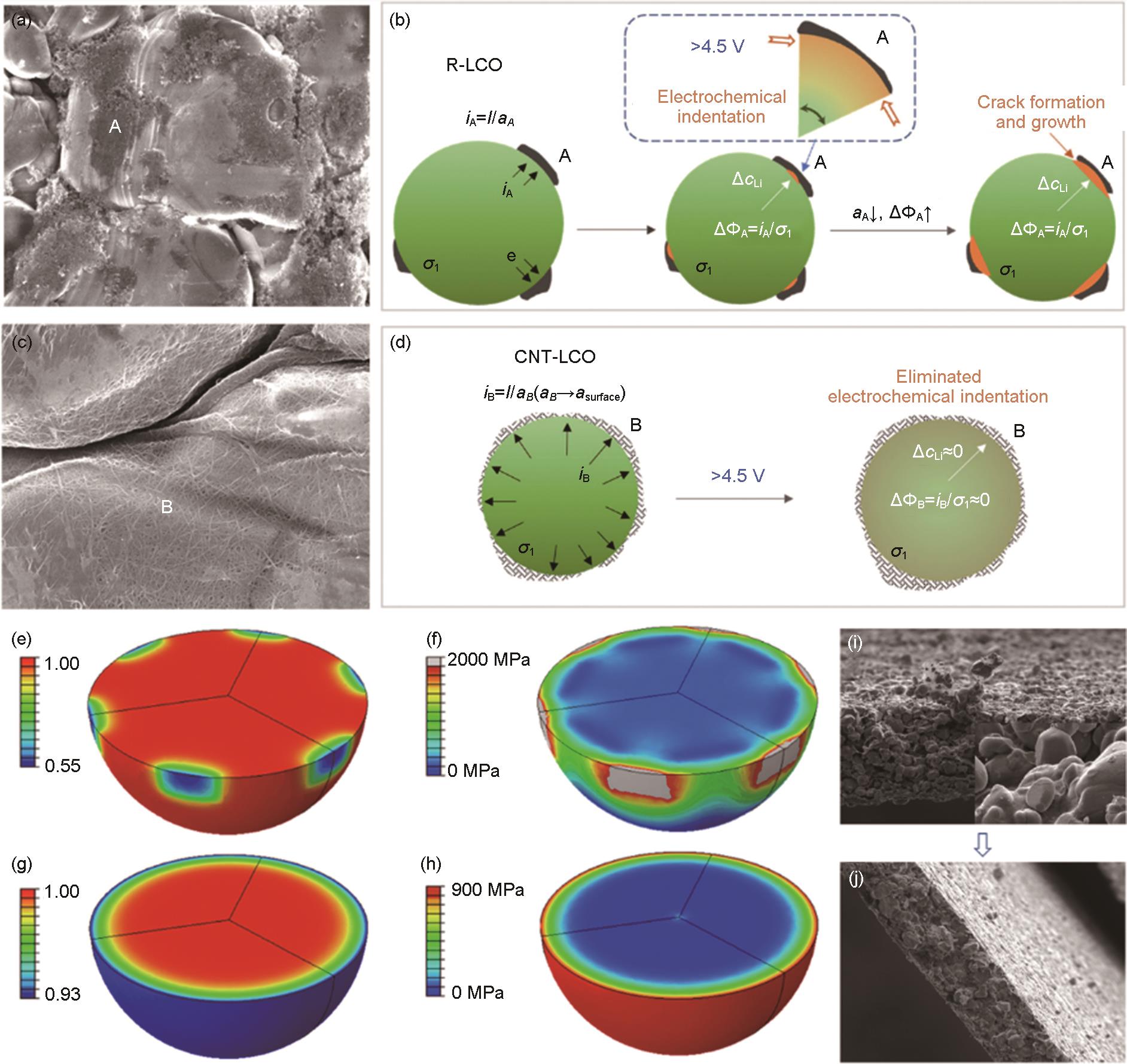
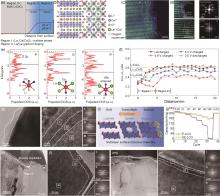
图16
(a) La3+ 和Ca2+ 的表面结构和化学势分布 μ 示意图, δ 表示氧的非化学计量;(b) 表面原子结构示意图。(c) HAADF-STEM图显示La-LCO表面由虚线分隔的区域I、II和III组成,比例尺为2 nm;(d) 区域I (上,钙钛矿La1-w Ca w CoO3-δ ) 和区域III (下) 的HAADF-STEM和对应的FFT图,比例尺为5 nm;(e) LCO(左)、未应变的LaCoO3 (中等) 和-8%的应变LaCoO3 (右) 的PDOS图和氧的局域结构示意图 (插图), EF 表示费米能级,实线表示O 2p的平均能量;(f) 不同深度和电压下的钴离子价态[156];(g) 表面Li3PO4 的TEM图;(h) 表面和近表面结构和衍射图谱分析;(i) SE-LCO的表面结构示意图;(j) 倍率性能对比;(k) P-LCO表面阶梯状降解的TEM图,和对应的 (l) 表面结构和电子衍射图;(m) SE-LCO平滑表面的TEM图,和对应的 (n) 表面结构和电子衍射图[33]"
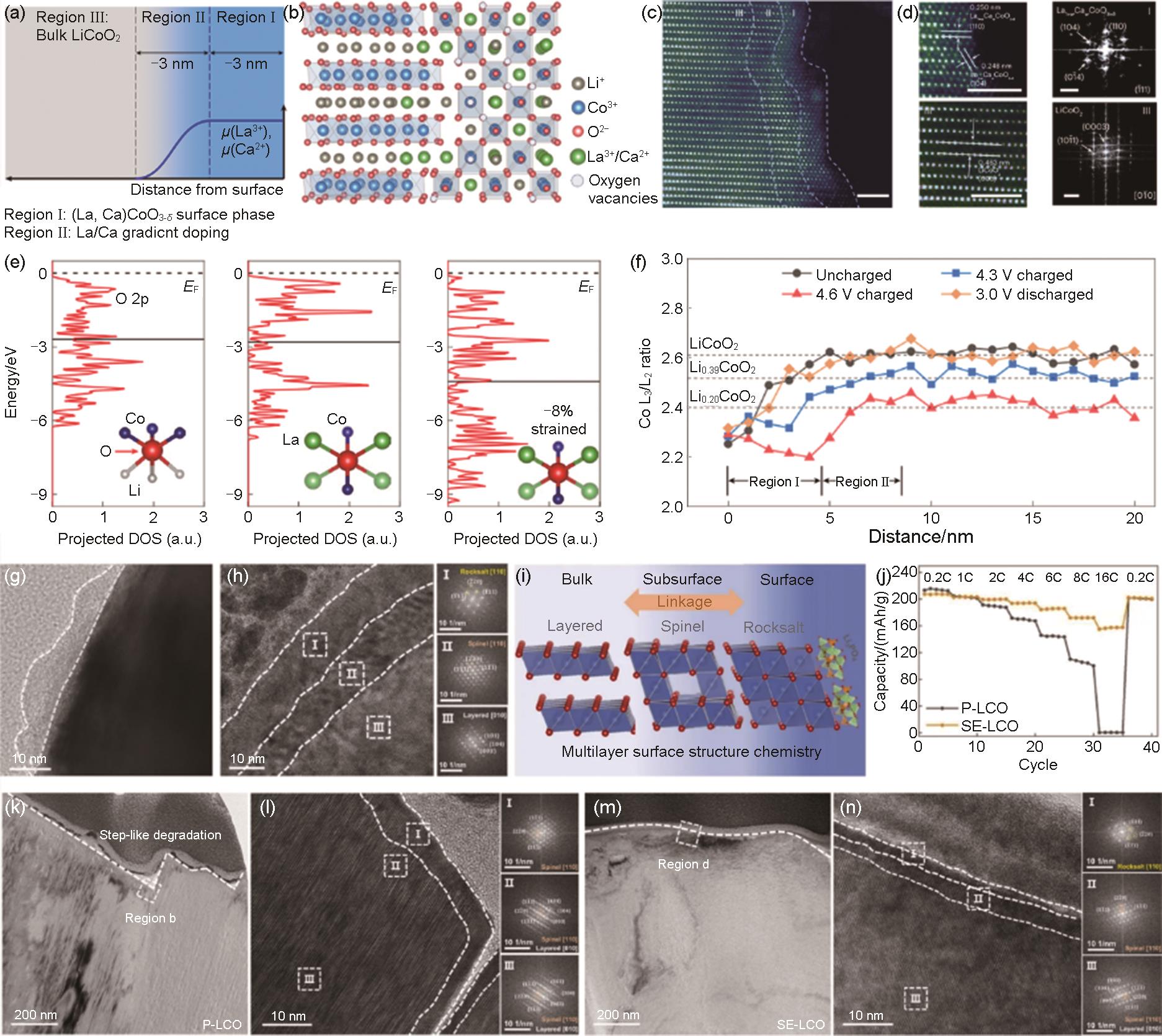
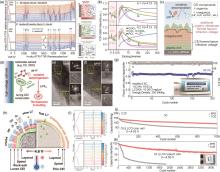
图18
(a) 初始充电时LCO/电解质界面的原位ATR-FTIR图谱,电流密度为25 mA/g,在拐点电压下收集的图谱用红色表示,右侧为不同电压下Li+-溶剂化 (充电) 过程中LCO/电解质界面电解质溶剂化构型示意图;(b) 5次循环后从扣式电池中提取的4.1 V和4.2 V循环LCO正极 (低于/高于弯曲电压) 的TOF-SIMS表征。具有代表性的无机和有机碎片的归一化深度剖面说明了CEI体系结构;(c) 充电截止电压低于/高于弯曲电压时形成的CEI结构示意图[162];(d) SPTF添加剂在碳酸脂溶剂中的作用机制;(e),(f) 长循环后的钴酸锂的HRTEM图;(g) 1 Ah的LCO/石墨软包全电池[163];(h) LCO电池在4.6 V下稳定循环的示意图;(i) 0.2 C下第4周循环的 (003) 峰异位XRD图谱,FPE (上) 和TCE (下);(j) Gr||LCO纽扣电池在3~4.55 V的3 C循环性能;(k) Gr||LCO软包电池在3~4.55 V电压下的循环性能[164]"
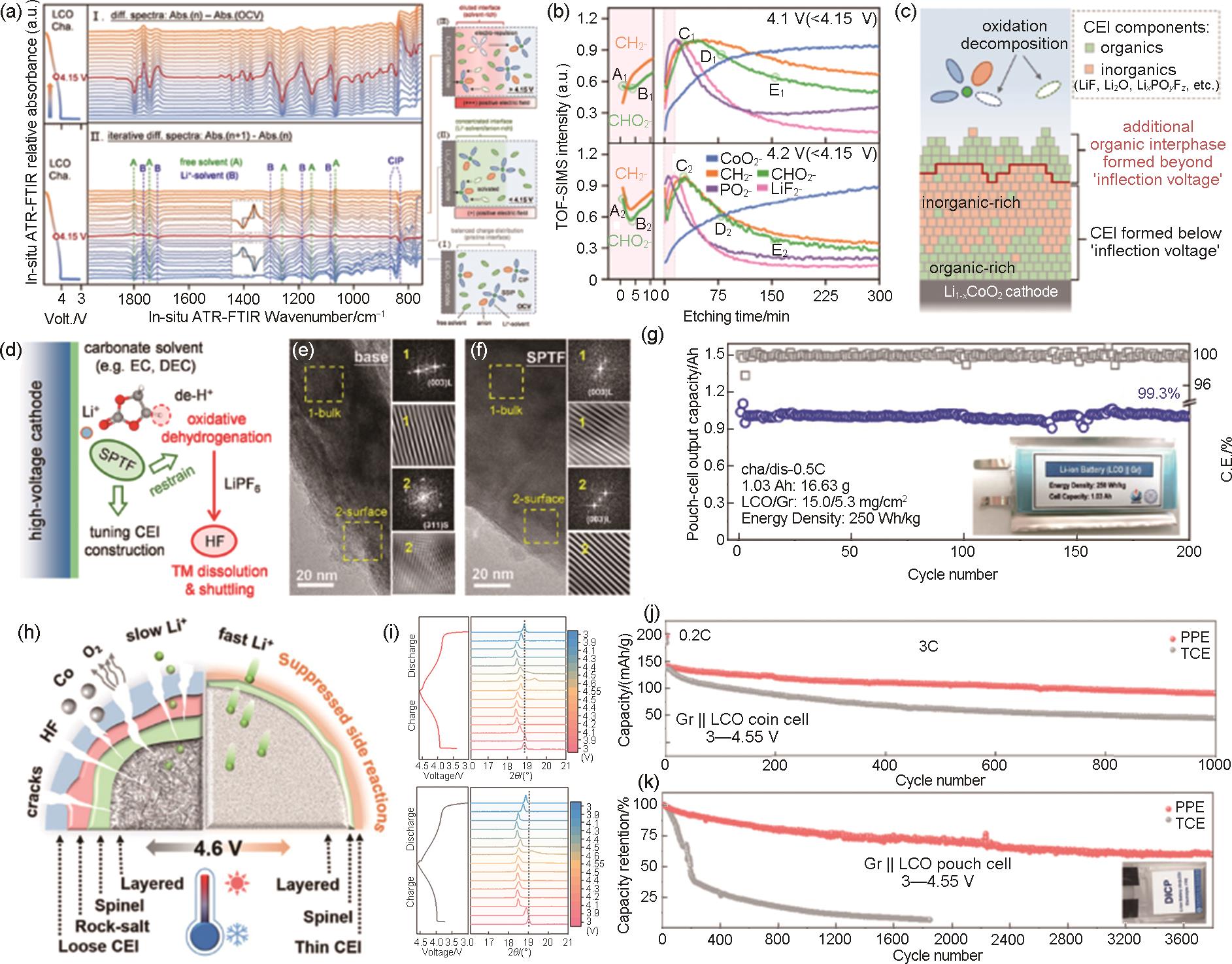
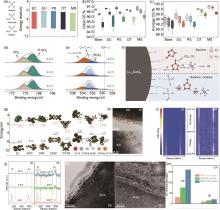
图19
(a) 砜、磺酸盐和硫酸盐的代表性官能团 (左),以及EC、磺烷 (SU)、1,3-丙烷磺酮 (PS)、1,3,2-二氧杂噻烷2,2-二氧化物 (DT) 和亚甲基甲磺酸盐 (MS) 的HOMO-LUMO能级 (右);不同充电截止电压下的LCO||Li电池的 (b) 初始库仑效率和 (c) 平均库仑效率(每种物质的充电截止电压依次为4.2、4.4和4.6 V);循环100次后,不同截止电压下LCO表面的 (d) S 2p 和 (e) O 1s 的XPS光谱;(f) 高电压LCO用MS添加剂的作用机理[165];(g) 不同分子HOMO和LUMO的计算值;(h) LCO电极在BE (上) 和DE (下) 电解液中1C下循环50圈后的TEM图;(i) LCO电极在BE和DE电解液中的 in-situ Raman光谱,首圈,0.5 mV/s;(j) 不同充/放电状态的Raman光谱;LCO电极在 (k) BE和 (l) DE电解液中循环2周后的TEM图,0.2 C;(m) 循环10、50、100次后不同电解液中钴离子的含量[166]"
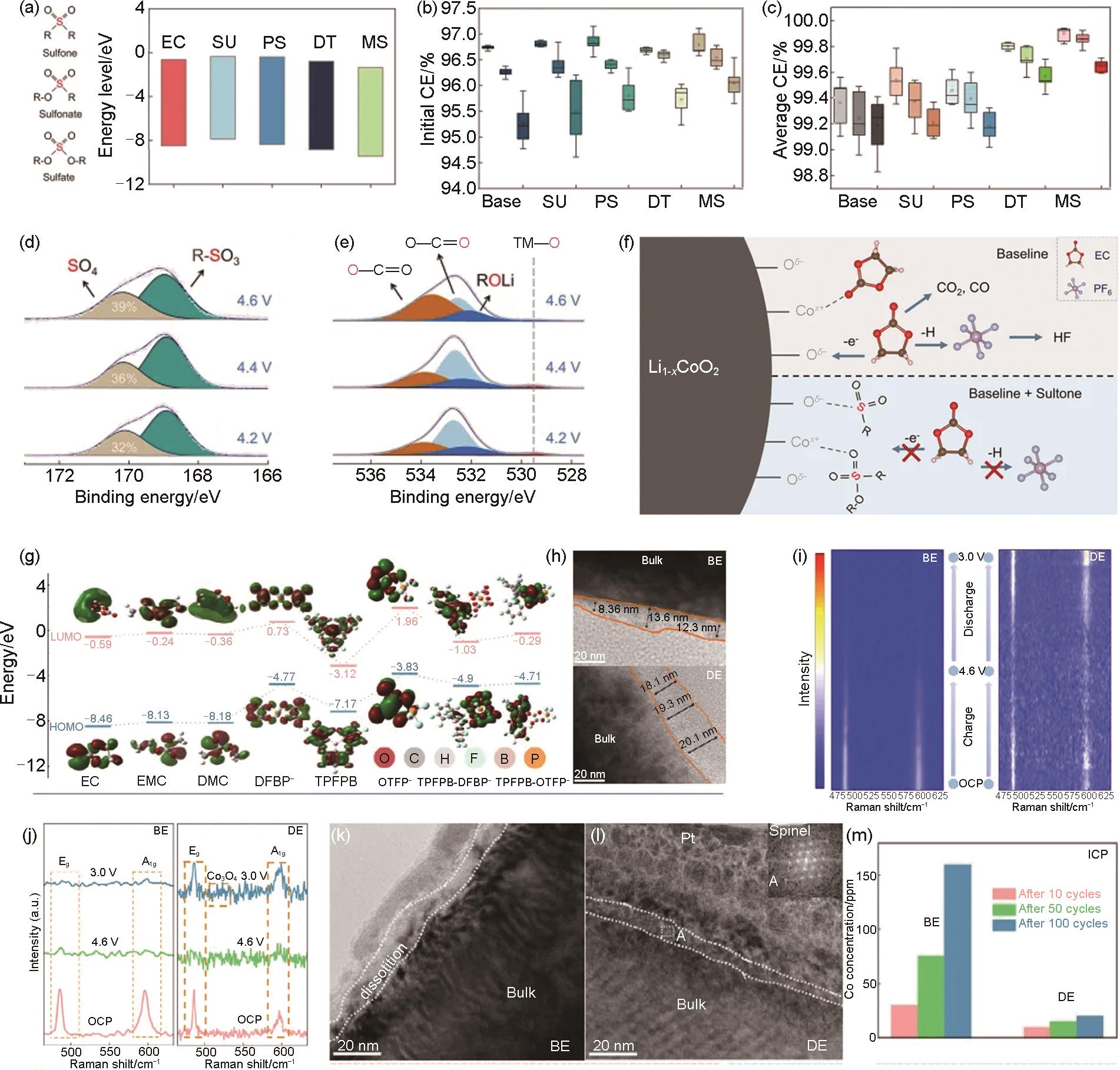
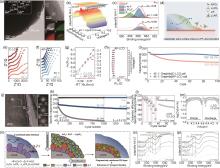
图20
(a) AP-LCO的TEM和EDS图;(b) 首次充电后IR谱图中Al-O-P信号的演化过程;(c) 45 ℃循环前后的F 1s XPS;(d) AP-LCO上CEI的化学和形态演变示意图;温度相关EIS谱图对比 (e) C-LCO和(f)AP-LCO;(g)C-LCO和AP-LCO的活化能(Ea,第102圈,45 ℃);(h) AP-LCO的CEI层电阻变化(RCEI,第2和第102圈,45 ℃);(i)Graphite||LCO电池的循环性能,1C,3~4.6V,45 ℃[169];(j) Z-LCO的HRTEM和对应的FFT图;LCO和Z-LCO的 (k) 循环性能,1C,(l) 倍率性能,和 (m) GITT测试,3~4.6V;(n) Z-LCO的CEI层致密化过程示意图;(o) LCO和 (p) Z-LCO在TEY模式下O K-edge的sXAS测试,第1, 10圈[170]"
| 1 | MANTHIRAM A, GOODENOUGH J B. Layered lithium cobalt oxide cathodes[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6(3): 323. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-020-00764-8. |
| 2 | CHU S, MAJUMDAR A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7411): 294-303. DOI: 10.1038/nature11475. |
| 3 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. DOI: 10.1126/science.1212741. |
| 4 | KATO Y, HORI S, SAITO T, et al. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16030. DOI: 10.1038/nenergy.2016.30. |
| 5 | DRESSELHAUS M S, THOMAS I L. Alternative energy technologies[J]. Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 332-337. DOI: 10.1038/35104599. |
| 6 | WANG L L, CHEN B B, MA J, et al. Reviving lithium cobalt oxide-based lithium secondary batteries-toward a higher energy density[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(17): 6505-6602. DOI: 10.1039/C8CS00322J. |
| 7 | ADAM A, WANDT J, KNOBBE E, et al. Fast-charging of automotive lithium-ion cells: in situ lithium-plating detection and comparison of different cell designs[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(13): 130503. DOI: 10.1149/1945-7111/abb564. |
| 8 | SCROSATI B, GARCHE J. Lithium batteries: Status, prospects and future[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(9): 2419-2430. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.11.048. |
| 9 | MEINTZ A, ZHANG J C, VIJAYAGOPAL R, et al. Enabling fast charging-vehicle considerations[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 367: 216-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.07.093. |
| 10 | TOMASZEWSKA A, CHU Z Y, FENG X N, et al. Lithium-ion battery fast charging: A review[J]. eTransportation, 2019, 1: 100011. DOI: 10.1016/j.etran.2019.100011. |
| 11 | LI N, CHEN Z P, REN W C, et al. Flexible graphene-based lithium ion batteries with ultrafast charge and discharge rates[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(43): 17360-17365. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1210072109. |
| 12 | KANG B, CEDER G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7235): 190-193. DOI: 10.1038/nature07853. |
| 13 | ZHANG S S. The effect of the charging protocol on the cycle life of a Li-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 161(2): 1385-1391. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.06.040. |
| 14 | GOODENOUGH J B, KIM Y. Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(3): 587-603. DOI: 10.1021/cm901452z. |
| 15 | PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, GOODENOUGH J B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(4): 1188. DOI: 10.1149/1.1837571. |
| 16 | ZHENG J M, MYEONG S, CHO W, et al. Li- and Mn-rich cathode materials: Challenges to commercialization[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(6): 1601284. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201601284. |
| 17 | PARK J Y, JO M, HONG S, et al. Mechanism of degradation of capacity and charge/discharge voltages of high-Ni cathode during fast long-term cycling without voltage margin[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(29): 2201151. DOI: 10.1002/aenm. 202201151. |
| 18 | WANG R, CHEN X, HUANG Z Y, et al. Twin boundary defect engineering improves lithium-ion diffusion for fast-charging spinel cathode materials[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3085. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23375-7. |
| 19 | MANTHIRAM A, KNIGHT J C, MYUNG S T, et al. Nickel-rich and lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes: Progress and perspectives[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(1): 1501010. DOI: 10. 1002/aenm.201501010. |
| 20 | OH J, LEE S Y, KIM H, et al. Overcharge-induced phase heterogeneity and resultant twin-like layer deformation in lithium cobalt oxide cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(32): 2203639. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202203639. |
| 21 | JOHNSTON W D, HEIKES R R, SESTRICH D. The preparation, crystallography, and magnetic properties of the LixCo(1- x)O system[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1958, 7(1): 1-13. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3697(58)90175-6. |
| 22 | DELMAS C, FOUASSIER C, HAGENMULLER P. Structural classification and properties of the layered oxides[J]. Physica B+C, 1980, 99(1): 81-85. DOI: 10.1016/0378-4363(80)90214-4. |
| 23 | LIN C, LI J Y, YIN Z W, et al. Structural understanding for high-voltage stabilization of lithium cobalt oxide[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(6): 2307404. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202307404. |
| 24 | THACKERAY M M, DAVID W I F, BRUCE P G, et al. Lithium insertion into manganese spinels[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1983, 18(4): 461-472. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5408(83)90138-1. |
| 25 | WANG J J, SUN X L. Olivine LiFePO4: The remaining challenges for future energy storage[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(4): 1110-1138. DOI: 10.1039/C4EE04016C. |
| 26 | ENSLING D, CHERKASHININ G, SCHMID S, et al. Nonrigid band behavior of the electronic structure of LiCoO2 thin film during electrochemical Li deintercalation[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(13): 3948-3956. DOI: 10.1021/cm501480b. |
| 27 | AMATUCCI G G, TARASCON J M, KLEIN L C. Cobalt dissolution in LiCoO2-based non-aqueous rechargeable batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1996, 83(1/2): 167-173. DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(95)00231-6. |
| 28 | WU Z X, ZENG G F, YIN J H, et al. Unveiling the evolution of LiCoO2 beyond 4.6 V[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(11): 4806-4817. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c01954. |
| 29 | VAN DER VEN A, AYDINOL M K, CEDER G, et al. First-principles investigation of phase stability in LixCoO2[J]. Physical Review B, 1998, 58(6): 2975-2987. DOI: 10.1103/physrevb. 58.2975. |
| 30 | NI L S, ZHANG S, DI A D, et al. Challenges and strategies towards single-crystalline Ni-rich layered cathodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(31): 2201510. DOI: 10.1002/aenm. 202201510. |
| 31 | CHEN Z H, DAHN J R. Methods to obtain excellent capacity retention in LiCoO2 cycled to 4.5 V[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2004, 49(7): 1079-1090. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2003.10.019. |
| 32 | LI S, SUN Y, GAO A, et al. Sustainable LiCoO2 by collective glide of CoO6 slabs upon charge/discharge[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(20): e2120060119. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2120060119. |
| 33 | WANG X H, REN H Y, DU Y H, et al. Tuning surface chemistry to reduce the step-like degradation of LiCoO2 at 4.6 V[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 125: 109537. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109537. |
| 34 | LI J Y, LIN C, WENG M Y, et al. Structural origin of the high-voltage instability of lithium cobalt oxide[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(5): 599-605. DOI: 10.1038/s41565-021-00855-x. |
| 35 | WANG Z X, LIU L J, CHEN L Q, et al. Structural and electrochemical characterizations of surface-modified LiCoO2 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148(3/4): 335-342. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00071-1. |
| 36 | MA X S, WANG J K, WANG Z H, et al. Engineering strategies for high-voltage LiCoO2 based high-energy Li-ion batteries[J]. Electron, 2024, 2(3): e33. DOI: 10.1002/elt2.33. |
| 37 | ZHANG J N, LI Q H, OUYANG C Y, et al. Trace doping of multiple elements enables stable battery cycling of LiCoO2 at 4.6 V[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(7): 594-603. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-019-0409-z. |
| 38 | YU Z Z, TONG Q L, ZHAO G Q, et al. Combining surface holistic Ge coating and subsurface Mg doping to enhance the electrochemical performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(22): 25490-25500. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c04666. |
| 39 | CEDER G, CHIANG Y M, SADOWAY D R, et al. Identification of cathode materials for lithium batteries guided by first-principles calculations[J]. Nature, 1998, 392(6677): 694-696. DOI: 10.1038/33647. |
| 40 | WANG H S, RUS E, SAKURABA T, et al. CO2 and O2 evolution at high voltage cathode materials of Li-ion batteries: A differential electrochemical mass spectrometry study[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(13): 6197-6201. DOI: 10.1021/ac403317d. |
| 41 | TAKAMATSU D, KOYAMA Y, ORIKASA Y, et al. First In Situ observation of the LiCoO2 electrode/electrolyte interface by total-reflection X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(46): 11597-11601. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201203910. |
| 42 | TAKAMATSU D, NAKATSUTSUMI T, MORI S, et al. Nanoscale observation of the electronic and local structures of LiCoO2 thin film electrode by depth-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2011, 2(20): 2511-2514. DOI: 10.1021/jz2011226. |
| 43 | TEBBE J L, HOLDER A M, MUSGRAVE C B. Mechanisms of LiCoO2 cathode degradation by reaction with HF and protection by thin oxide coatings[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(43): 24265-24278. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b07887. |
| 44 | NAKAYAMA K, KOBAYASHI S, ISHIKAWA R, et al. Atomic-scale and nanoscale structural changes in LiCoO2 due to irreversible delithiation accompanied by oxygen release[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2024: acs.chemmater.4c02084. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c02084. |
| 45 | SONG Y Z, WANG L, SHENG L, et al. The significance of mitigating crosstalk in lithium-ion batteries: A review[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(5): 1943-1963. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE00441D. |
| 46 | ZHANG S S. Understanding of performance degradation of LiNi0.80Co0.10Mn0.10O2 cathode material operating at high potentials[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 41: 135-141. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.05.013. |
| 47 | XIA H, LU L, MENG Y S, et al. Phase transitions and high-voltage electrochemical behavior of LiCoO2 thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2007, 154(4): A337. DOI: 10.1149/1.2509021. |
| 48 | SEONG W M, YOON K, LEE M H, et al. Unveiling the intrinsic cycle reversibility of a LiCoO2 electrode at 4.8-V cutoff voltage through subtractive surface modification for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Lett, 2019, 19(1): 29-37. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02902. |
| 49 | JIANG Y Y, QIN C D, YAN P F, et al. Origins of capacity and voltage fading of LiCoO2 upon high voltage cycling[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(36): 20824-20831. DOI: 10.1039/C9TA06579B. |
| 50 | YANG X G, ZHANG G S, GE S H, et al. Fast charging of lithium-ion batteries at all temperatures[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(28): 7266-7271. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1807115115. |
| 51 | XIA H R, ZHANG W, CAO S K, et al. A figure of merit for fast-charging Li-ion battery materials[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(6): 8525-8530. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03922. |
| 52 | ZHANG Y X, KIM J C, SONG H W, et al. Recent achievements toward the development of Ni-based layered oxide cathodes for fast-charging Li-ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(9): 4195-4218. DOI: 10.1039/d2nr05701h. |
| 53 | XU Z R, JIANG Z S, KUAI C G, et al. Charge distribution guided by grain crystallographic orientations in polycrystalline battery materials[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 83. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13884-x. |
| 54 | BESLI M M, SUBBARAMAN A, POUR SAFAEI F R, et al. A study of model-based protective fast-charging and associated degradation in commercial smartphone cells: Insights on cathode degradation as a result of lithium depositions on the anode[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(12): 2003019. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202003019. |
| 55 | JIANG Z S, LI J Z, YANG Y, et al. Machine-learning-revealed statistics of the particle-carbon/binder detachment in lithium-ion battery cathodes[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2310. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16233-5. |
| 56 | TANIM T R, YANG Z Z, COLCLASURE A M, et al. Extended cycle life implications of fast charging for lithium-ion battery cathode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 656-666. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.07.001. |
| 57 | 杲齐新, 赵景腾, 李国兴. 锂离子电池快速充电研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(7): 2166-2184. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0287. |
| GAO Q X, ZHAO J T, LI G X. Research progress on fast-charging lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2166-2184. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0287. | |
| 58 | YANG Y, XU R, ZHANG K, et al. Quantification of heterogeneous degradation in Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(25): 1900674. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201900674. |
| 59 | PARK J, ZHAO H B, KANG S D, et al. Fictitious phase separation in Li layered oxides driven by electro-autocatalysis[J]. Nature Materials, 2021, 20(7): 991-999. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-021-00936-1. |
| 60 | LIU W G, ZHENG J Q, ZHANG Z, et al. The capacity decay mechanism of the 100% SOC LiCoO2/graphite battery after high-temperature storage[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 580: 233330. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2023.233330. |
| 61 | SUN Z Y, LI F K, DING J Y, et al. High-voltage and high-temperature LiCoO2 operation via the electrolyte additive of electron-defect boron compounds[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(6): 2478-2487. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c00324. |
| 62 | MENG T, YANG S S, PENG Y T, et al. Deciphering interphase instability of lithium metal batteries with localized high-concentration electrolytes at elevated temperatures[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 71: 103598. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103598. |
| 63 | SHEN Y B, WANG L C, JIANG J Z, et al. Stabilization of high-voltage layered oxide cathode by multi-electron rare earth oxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 140249. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140249. |
| 64 | ZHANG Z J, ZHANG H Z, WU Y P, et al. Advances in doping strategies for sodium transition metal oxides cathodes: A review[J]. Frontiers in Energy, 2024, 18(2): 141-159. DOI: 10.1007/s11708-024-0918-8. |
| 65 | HUANG Y Y, ZHU Y C, FU H Y, et al. Mg-pillared LiCoO2: Towards stable cycling at 4.6 V[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(9): 4682-4688. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202014226. |
| 66 | YOON M, DONG Y H, YOO Y, et al. Unveiling nickel chemistry in stabilizing high-voltage cobalt-rich cathodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(6): 1907903. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201907903. |
| 67 | KIM J, KANG H, GO N, et al. Egg-shell structured LiCoO2 by Cu2+ substitution to Li+ sites via facile stirring in an aqueous copper(ii) nitrate solution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(47): 24892-24900. DOI: 10.1039/C7TA07232E. |
| 68 | ZHANG J N, LI Q H, LI Q, et al. Improved electrochemical performances of high voltage LiCoO2 with tungsten doping[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2018, 27(8): 088202. DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/8/088202. |
| 69 | TAN X H, ZHAO T Q, SONG L T, et al. Simultaneous near-surface trace doping and surface modifications by gas-solid reactions during one-pot synthesis enable stable high-voltage performance of LiCoO2[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(30): 2200008. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202200008. |
| 70 | ER-RAMI F E, DUFFIET M, HINKLE S, et al. Understanding the role of Al doping of LiCoO2 on the mechanisms upon cycling up to high voltages (≥4.6 V vs Li+/Li)[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(10): 4384-4393. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c04338. |
| 71 | KONG W J, WONG D, AN K, et al. Stabilizing the anionic redox in 4.6 V LiCoO2 cathode through adjusting oxygen magnetic moment[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(31): 2202679. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202202679. |
| 72 | KIM S H, KIM C S. Improving the rate performance of LiCoO2 by Zr doping[J]. Journal of Electroceramics, 2009, 23(2): 254-257. DOI: 10.1007/s10832-008-9414-5. |
| 73 | ZHU Z, WANG H, LI Y, et al. A surface Se-substituted LiCo[O2- δSeδ] cathode with ultrastable high-voltage cycling in pouch full-cells[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(50): 2005182. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202005182. |
| 74 | LIU Q, SU X, LEI D, et al. Approaching the capacity limit of lithium cobalt oxide in lithium ion batteries via lanthanum and aluminium doping[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(11): 936-943. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-018-0180-6. |
| 75 | HUANG W Y, ZHAO Q, ZHANG M J, et al. Surface design with cation and anion dual gradient stabilizes high-voltage LiCoO2[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(20): 2200813. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202200813. |
| 76 | KONG W J, ZHANG J C, WONG D, et al. Tailoring Co3d and O2p band centers to inhibit oxygen escape for stable 4.6 V LiCoO2 cathodes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(52): 27102-27112. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202112508. |
| 77 | LIU A, LI J, SHUNMUGASUNDARAM R, et al. Synthesis of Mg and Mn doped LiCoO2 and effects on high voltage cycling[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(7): A1655-A1664. DOI: 10.1149/2.1381707jes. |
| 78 | SONG S C, LI Y W, YANG K, et al. Interplay between multiple doping elements in high-voltage LiCoO2[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(9): 5702-5710. DOI: 10.1039/d0ta09931g. |
| 79 | CHEN S X, WANG C W, ZHOU Y, et al. Co/Li-dual-site doping towards LiCoO2 as a high-voltage, fast-charging, and long-cycling cathode material[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(10): 5295-5304. DOI: 10.1039/D1TA10612K. |
| 80 | LI X Q, ZHOU L M, WANG H, et al. Dopants modulate crystal growth in molten salts enabled by surface energy tuning[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(35): 19675-19680. DOI: 10.1039/D1TA02351A. |
| 81 | YAO Z Q, FU T J, PAN T, et al. Modulating the spin state to stabilize the surface and bulk structure for durable 4.6 V LiCoO2 cathodes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(48): 2408152. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202408152. |
| 82 | WU Q, ZHANG B, LU Y Y. Progress and perspective of high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 74: 283-308. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem. 2022.07.007. |
| 83 | JUNG H G, GOPAL N V, PRAKASH J, et al. Improved electrochemical performances of LiM0.05Co0.95O1.95F0.05 (M=Mg, Al, Zr) at high voltage[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 68: 153-157. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.02.057. |
| 84 | HU B, LOU X B, LI C, et al. Reversible phase transition enabled by binary Ba and Ti-based surface modification for high voltage LiCoO2 cathode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 438: 226954. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226954. |
| 85 | CHENG J H, PAN C J, NITHYA C, et al. Effect of Mg doping on the local structure of LiMgyCo1- yO2 cathode material investigated by X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 252: 292-297. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.10.130. |
| 86 | ZHANG W, ZHANG X Y, CHENG F Y, et al. Enabling stable 4.6 V LiCoO2 cathode through oxygen charge regulation strategy[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 76: 557-565. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.09.034. |
| 87 | YOON W S, KIM K B, KIM M G, et al. Oxygen contribution on Li-ion intercalation-deintercalation in LiAlyCo1- yO2 investigated by O K-edge and co L-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149(10): A1305. DOI: 10.1149/1.1503074. |
| 88 | ZHU Z, KUSHIMA A, YIN Z Y, et al. Anion-redox nanolithia cathodes for Li-ion batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16111. DOI: 10.1038/nenergy.2016.111. |
| 89 | QIAO Y, JIANG K Z, DENG H, et al. A high-energy-density and long-life lithium-ion battery via reversible oxide-peroxide conversion[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(11): 1035-1044. DOI: 10.1038/s41929-019-0362-z. |
| 90 | YOON W S, KIM K B, KIM M G, et al. Oxygen contribution on Li-ion intercalation-deintercalation in LiCoO2 investigated by O K-edge and co L-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(10): 2526-2532. DOI: 10.1021/jp013735e. |
| 91 | KANNAN A M, RABENBERG L, MANTHIRAM A. High capacity surface-modified LiCoO2 cathodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2003, 6(1): A16-A18. DOI: 10.1149/1.1526782. |
| 92 | LEE E, PERSSON K A. Structural and chemical evolution of the layered Li-excess LixMnO3 as a function of Li content from first-principles calculations[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(15): 1400498. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201400498. |
| 93 | YAN P F, ZHENG J M, TANG Z K, et al. Injection of oxygen vacancies in the bulk lattice of layered cathodes[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(6): 602-608. DOI: 10.1038/s41565-019-0428-8. |
| 94 | ZHANG D H, WANG J Q, LIN Y G, et al. Present situation and future prospect of renewable energy in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 76: 865-871. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.023. |
| 95 | SI Z, SHI B Z, HUANG J, et al. Titanium and fluorine synergetic modification improves the electrochemical performance of Li(Ni0.8Co0.1Mn0.1)O2[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(14): 9354-9363. DOI: 10.1039/D1TA00124H. |
| 96 | YANG S Q, WANG P B, WEI H X, et al. Li4V2Mn(PO4)4-stablized Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 cathode materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 63: 103889. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.103889. |
| 97 | SUN Z H, XU L Q, DONG C Q, et al. A facile gaseous sulfur treatment strategy for Li-rich and Ni-rich cathode materials with high cycling and rate performance[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 63: 103887. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.103887. |
| 98 | ZHU Z, WANG H, LI Y, et al. A surface Se-substituted LiCo[O2- δSeδ] cathode with ultrastable high-voltage cycling in pouch full-cells[J]. Advanced Materials,2020. |
| 99 | HUANG Y Y, ZHU Y C, FU H Y, et al. Mg-pillared LiCoO2: Towards stable cycling at 4.6 V[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(9): 4682-4688. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202014226. |
| 100 | YAO Y T, XUE Z Y, LI C Y, et al. Progress and perspective of doping strategies for lithium cobalt oxide materials in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 71: 103666. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103666. |
| 101 | CHO W, MYEONG S, KIM N, et al. Critical role of cations in lithium sites on extended electrochemical reversibility of co-rich layered oxide[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(21): 1605578. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201605578. |
| 102 | GOODENOUGH J B, PARK K S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(4): 1167-1176. DOI: 10.1021/ja3091438. |
| 103 | WANG M J, YU F D, SUN G, et al. Co-regulating the surface and bulk structure of Li-rich layered oxides by a phosphor doping strategy for high-energy Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(14): 8302-8314. DOI: 10.1039/C9TA00783K. |
| 104 | TAN X H, ZHAO T Q, SONG L T, et al. Simultaneous near-surface trace doping and surface modifications by gas-solid reactions during one-pot synthesis enable stable high-voltage performance of LiCoO2[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(30): 2200008. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202200008. |
| 105 | ZHENG W, LIANG G M, GUO H, et al. Enhancing the reaction kinetics and structural stability of high-voltage LiCoO2 via polyanionic species anchoring[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(12): 4147-4156. DOI: 10.1039/D4EE00726C. |
| 106 | MIN S H, JO M R, CHOI S Y, et al. A layer-structured electrode material reformed by a PO4 -O2 hybrid framework toward enhanced lithium storage and stability[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(7): 1501717. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201501717. |
| 107 | WAN J J, ZHU J P, XIANG Y X, et al. Revealing the correlation between structure evolution and electrochemical performance of high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 54: 786-794. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2020.06.027. |
| 108 | HONG Y S, HUANG X J, WEI C X, et al. Hierarchical defect engineering for LiCoO2 through low-solubility trace element doping[J]. Chem, 2020, 6(10): 2759-2769. DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2020.07.017. |
| 109 | WANG L L, MA J, WANG C, et al. A novel bifunctional self-stabilized strategy enabling 4.6 V LiCoO2 with excellent long-term cyclability and high-rate capability[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(12): 1900355. DOI: 10.1002/advs.201900355. |
| 110 | ZHANG Z J, WANG J, SUN X Y, et al. Improved stability of single-crystal LiCoO2 cathodes at 4.8 V through solvation structure regulation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(48): 2411409. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202411409. |
| 111 | LIU T C, YU L, LIU J J, et al. Understanding Co roles towards developing co-free Ni-rich cathodes for rechargeable batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6(3): 277-286. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-021-00776-y. |
| 112 | CHAE B G, PARK S Y, SONG J H, et al. Evolution and expansion of Li concentration gradient during charge-discharge cycling[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3814. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24120-w. |
| 113 | BI Y J, TAO J H, WU Y Q, et al. Reversible planar gliding and microcracking in a single-crystalline Ni-rich cathode[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6522): 1313-1317. DOI: 10.1126/science.abc3167. |
| 114 | ZHU Z, YU D W, SHI Z, et al. Gradient-morph LiCoO2 single crystals with stabilized energy density above 3400 Wh·L-1[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(6): 1865-1878. DOI: 10.1039/D0EE00231C. |
| 115 | KANG K, CEDER G. Factors that affect Li mobility in layered lithium transition metal oxides[J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(9): 094105. DOI: 10.1103/physrevb.74.094105. |
| 116 | LU W, ZHANG J S, XU J J, et al. In situ visualized cathode electrolyte interphase on LiCoO2 in high voltage cycling[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(22): 19313-19318. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b03024. |
| 117 | ZHOU A J, LIU Q, WANG Y, et al. Al2O3 surface coating on LiCoO2 through a facile and scalable wet-chemical method towards high-energy cathode materials withstanding high cutoff voltages[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(46): 24361-24370. DOI: 10.1039/C7TA07312G. |
| 118 | WU R, CAO T C, LIU H, et al. Ultralong lifespan for high-voltage LiCoO2 enabled by in situ reconstruction of an atomic layer deposition coating layer[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(22): 25524-25533. DOI: 10.1021/acsami. 2c05129. |
| 119 | YASUHARA S, YASUI S, TERANISHI T, et al. Enhancement of ultrahigh rate chargeability by interfacial nanodot BaTiO3 treatment on LiCoO2 cathode thin film batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(3): 1688-1694. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett. 8b04690. |
| 120 | CHENG T, MA Z T, QIAN R C, et al. Achieving stable cycling of LiCoO2 at 4.6 V by multilayer surface modification[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(2): 2001974. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202001974. |
| 121 | ORIKASA Y, TAKAMATSU D, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Origin of surface coating effect for MgO on LiCoO2 to improve the interfacial reaction between electrode and electrolyte[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2014, 1(9): 1400195. DOI: 10.1002/admi.201400195. |
| 122 | SUN Y K, YOON C S, MYUNG S T, et al. Role of AlF3 coating on LiCoO2 particles during cycling to cutoff voltage above 4.5 V[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2009, 156(12): A1005. DOI: 10.1149/1.3236501. |
| 123 | GU R, MA Z T, CHENG T, et al. Improved electrochemical performances of LiCoO2 at elevated voltage and temperature with an in situ formed spinel coating layer[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(37): 31271-31279. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b08264. |
| 124 | TAN X H, MAO D D, ZHAO T Q, et al. Long-term highly stable high-voltage LiCoO2 synthesized via a solid sulfur-assisted one-pot approach[J]. Small, 2022, 18(26): 2202143. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202202143. |
| 125 | PANG P P, WANG Z, DENG Y M, et al. Delayed phase transition and improved cycling/thermal stability by spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 modification for LiCoO2 cathode at high voltages[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(24): 27339-27349. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c02459. |
| 126 | QIAN J W, LIU L, YANG J X, et al. Electrochemical surface passivation of LiCoO2 particles at ultrahigh voltage and its applications in lithium-based batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 4918. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07296-6. |
| 127 | FAN T J, KAI W, HARIKA V K, et al. Operating highly stable LiCoO2 cathodes up to 4.6 V by using an effective integration of surface engineering and electrolyte solutions selection[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(33): 2204972. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202204972. |
| 128 | XIE J, ZHAO J, LIU Y Y, et al. Engineering the surface of LiCoO2 electrodes using atomic layer deposition for stable high-voltage lithium ion batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2017, 10(11): 3754-3764. DOI: 10.1007/s12274-017-1588-1. |
| 129 | QU S S, WU W B, WU Y F, et al. Sputtering coating of lithium fluoride film on lithium cobalt oxide electrodes for reducing the polarization of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(12): 3393. DOI: 10.3390/nano11123393. |
| 130 | WANG P F, MENG Y, WANG Y J, et al. Oxygen framework reconstruction by LiAlH4 treatment enabling stable cycling of high-voltage LiCoO2[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 44: 487-496. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.041. |
| 131 | YANG X R, WANG C W, YAN P F, et al. Pushing lithium cobalt oxides to 4.7 V by lattice-matched interfacial engineering[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(23): 2200197. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202200197. |
| 132 | ZHANG X L, PENG B, ZHAO L P, et al. NASICON-structured LiZr2(PO4)3 surface modification improves ionic conductivity and structural stability of LiCoO2 for a stable 4.6 V cathode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(14): 16204-16213. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c00533. |
| 133 | WANG Y, ZHANG Q H, XUE Z C, et al. An in situ formed surface coating layer enabling LiCoO2 with stable 4.6 V high-voltage cycle performances[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(28): 2001413. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202001413. |
| 134 | SHARIFI-ASL S, SOTO F A, FOROOZAN T, et al. Anti-oxygen leaking LiCoO2[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(23): 1901110. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201901110. |
| 135 | WANG X, WU Q, LI S Y, et al. Lithium-aluminum-phosphate coating enables stable 4.6 V cycling performance of LiCoO2 at room temperature and beyond[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 37: 67-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.01.031. |
| 136 | CHENG T, CHENG Q, HE Y, et al. A hybrid ionic and electronic conductive coating layer for enhanced electrochemical performance of 4.6 V LiCoO2[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(36): 42917-42926. DOI: 10.1021/acsami. 1c12882. |
| 137 | MAO S L, SHEN Z Y, ZHANG W D, et al. Outside-In nanostructure fabricated on LiCoO2 surface for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(11): 2104841. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202104841. |
| 138 | LUCERO M, HOLSTUN T M, YAO Y D, et al. Dual-shell silicate and alumina coating for long lasting and high capacity lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 68: 314-323. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.11.014. |
| 139 | YAO J, LI Y Y, XIONG T T, et al. Scalable precise nanofilm coating and gradient Al doping enable stable battery cycling of LiCoO2 at 4.7 V[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(32): e202407898. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202407898. |
| 140 | BI Z H, YI Z L, ZHANG L Z, et al. Ultrathin dense LiF coverage coupled with a near-surface gradient fluorination lattice enables fast-charging long-life 4.6 V LiCoO2[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(8): 2765-2775. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE03464J. |
| 141 | ZHANG W J, QIU C F, LIN Z, et al. Modification of Li3PO4 layer effectively boosting lithium storage and thermal safety performance for LiCoO2 batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 99: 615-626. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2024.08.010. |
| 142 | WANG J X, LIU Z M, YAN G C, et al. Improving the electrochemical performance of lithium vanadium fluorophosphate cathode material: Focus on interfacial stability[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 329: 553-557. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2016.08.131. |
| 143 | WU K, RAN P L, WANG B T, et al. Diffusion-optimized long lifespan 4.6 V LiCoO2: Homogenizing cycled bulk-to-surface Li concentration with reduced structure stress[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(14): 2308258. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202308258. |
| 144 | DONG W J, YE B, CAI M Z, et al. Superwettable high-voltage LiCoO2 for low-temperature lithium ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(2): 881-888. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.2c02434. |
| 145 | ZHU R N, ZHANG S J, GUO Q X, et al. More than just a protection layer: Inducing chemical interaction between Li3BO3 and LiNi0·5Mn1·5O4 to achieve stable high-rate cycling cathode materials[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 342: 136074. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136074. |
| 146 | DENG Y L, MOU J R, WU H L, et al. A superior Li2SiO3-composited LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for high-voltage and high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 235: 19-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.066. |
| 147 | LV D D, WANG L, HU P F, et al. Li2O-B2O3-Li2SO4 modified LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode material for enhanced electrochemical performance[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 247: 803-811. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.068. |
| 148 | JO M R, KIM Y I, KIM Y, et al. Lithium-ion transport through a tailored disordered phase on the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 surface for high-power cathode materials[J]. ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(8): 2248-2254. DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201402109. |
| 149 | JO M R, NAM K M, LEE Y, et al. Phosphidation of Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles and their electrochemical and biocompatible superiority for lithium rechargeable batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(41): 11474-11476. DOI: 10.1039/c1cc15320j. |
| 150 | BRAMNIK N N, BRAMNIK K G, BAEHTZ C, et al. Study of the effect of different synthesis routes on Li extraction-insertion from LiCoPO4[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 145(1): 74-81. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.12.036. |
| 151 | EOM J, CHO J. M3(PO4)2-nanoparticle-coated LiCoO2 vs LiCo0.96M0.04O2(M=Mg and Zn) on electrochemical and storage characteristics[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2008, 155(3): A201. DOI: 10.1149/1.2827993. |
| 152 | HU G R, DENG X R, PENG Z D, et al. Comparison of AlPO4- and Co3(PO4)2-coated LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 cathode materials for Li-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(5): 2567-2573. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2007.10.040. |
| 153 | ZHU Z, XU S L, WANG Z J, et al. Avoiding electrochemical indentations: A CNT-cocooned LiCoO2 electrode with ultra-stable high-voltage cycling[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(16): 6102-6112. DOI: 10.1039/D4EE00722K. |
| 154 | LIU Z W, SHI L F, YUE K, et al. Stalling CO2 evolution at high voltage by a catalytically induced LiF-rich interphase[J]. Materials Today, 2025, 85: 69-81. DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod. 2025.02.017. |
| 155 | YASUHARA S, YASUI S, TERANISHI T, et al. Enhancement of ultrahigh rate chargeability by interfacial nanodot BaTiO3 treatment on LiCoO2 cathode thin film batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(3): 1688-1694. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett. 8b04690. |
| 156 | CAI M Z, DONG Y H, XIE M, et al. Stalling oxygen evolution in high-voltage cathodes by lanthurization[J]. Nature Energy, 2023, 8(2): 159-168. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-022-01179-3. |
| 157 | LI Z J, YI H C, REN H Y, et al. Multiple surface optimizations for a highly durable LiCoO2 beyond 4.6 V[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(46): 2307913. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202307913. |
| 158 | ZHANG W, CHENG F Y, WANG M, et al. Collective surface enabling an ultralong life of LiCoO2 at high voltage and elevated temperature[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(42): 2304008. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202304008. |
| 159 | HUANG W Y, LI J Y, ZHAO Q H, et al. Mechanochemically robust LiCoO2 with ultrahigh capacity and prolonged cyclability[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(32): 2405519. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202405519. |
| 160 | ZHANG M, HUANG W Y, TANG J Y, et al. Precise synthesis of 4.75 V-tolerant LiCoO2 with homogeneous delithiation and reduced internal strain[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(2): 1563-1573. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c10976. |
| 161 | KIM S, LEE J A, LEE D G, et al. Designing electrolytes for stable operation of high-voltage LiCoO2 in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(1): 262-270. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c02534. |
| 162 | LUO H Y, JI X Y, ZHANG B D, et al. Revealing the dynamic evolution of electrolyte configuration on the cathode-electrolyte interface by visualizing (de) solvation processes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(51): e202412214. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202412214. |
| 163 | YAN Y W, WENG S T, FU A, et al. Tailoring electrolyte dehydrogenation with trace additives: Stabilizing the LiCoO2 cathode beyond 4.6 V[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(8): 2677-2684. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.2c01433. |
| 164 | ZHANG A P, BI Z H, WANG G R, et al. Regulating electrode/electrolyte interfacial chemistry enables 4.6 V ultra-stable fast charging of commercial LiCoO2[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(9): 3021-3031. DOI: 10.1039/D4EE00676C. |
| 165 | YANG H Y, ZHAO Y J, QIN T, et al. Chemically active sulfonate additive with transition metal and oxygen dual-site deactivation for high-voltage LiCoO2[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(9): 4475-4484. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.4c01898. |
| 166 | ZHANG H, HUANG Y X, WANG Y, et al. In-situ constructed protective bilayer enabling stable cycling of LiCoO2 cathode at high-voltage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 62: 102951. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2023.102951. |
| 167 | WU D X, ZHU C L, WANG H P, et al. Mechanically and thermally stable cathode electrolyte interphase enables high-temperature, high-voltage Li||LiCoO2 batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(7): e202315608. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202315608. |
| 168 | SUN Z Y, ZHOU H B, LUO X H, et al. Design of a novel electrolyte additive for high voltage LiCoO2 cathode lithium-ion batteries: Lithium 4-benzonitrile trimethyl borate[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 503: 230033. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2021.230033. |
| 169 | LI Z J, ZHAO W G, REN H Y, et al. Tuning surface reconfiguration for durable cathode/electrolyte interphase of LiCoO2 at 45 ℃[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(46): 2402223. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202402223. |
| 170 | REN H Y, HU J X, JI H C, et al. Densification of cathode/electrolyte interphase to enhance reversibility of LiCoO2 at 4.65 V[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(40): 2408875. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202408875. |
| 171 | REN H Y, ZHENG G R, LI Y H, et al. Stabilizing LiCoO2 at 4.6 V by regulating anti-oxidative solvents[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(20): 7944-7957. DOI: 10.1039/D4EE02049A. |
| 172 | SRIVASTAVA I, BOLINTINEANU D S, LECHMAN J B, et al. Controlling binder adhesion to impact electrode mesostructures and transport[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(31): 34919-34930. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.0c08251. |
| 173 | CAO Y L, CAI H S, XU X, et al. Fucoidan cross-linking polyacrylamide as multifunctional aqueous binder stabilizes LiCoO2 to 4.6 V[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(40): 2405911. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202405911. |
| 174 | 高桂红, 刘福园, 李珅珅, 等. 二元导电剂对锂浆料电池性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(11): 3299-3306. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0505. |
| GAO G H, LIU F Y, LI S S, et al. Effect of binary composite conductive agent on the performance of lithium slurry battery[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(11): 3299-3306. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0505. | |
| 175 | WU X S, XIA S X, HUANG Y Q, et al. High-performance, low-cost, and dense-structure electrodes with high mass loading for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(34): 1903961. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201903961. |
| 176 | CHEN C J, ZHANG Y, LI Y J, et al. Highly conductive, lightweight, low-tortuosity carbon frameworks as ultrathick 3D current collectors[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(17): 1700595. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201700595. |
| 177 | ZHENG J X, GARCIA-MENDEZ R, ARCHER L A. Engineering multiscale coupled electron/ion transport in battery electrodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(12): 19014-19025. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c08719. |
| 178 | SHI Y, WEN L, PEI S F, et al. Choice for graphene as conductive additive for cathode of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019, 30: 19-26. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2018.03.009. |
| 179 | YAN L J, WANG K, LUO S, et al. Sandwich-structured cathodes with cross-stacked carbon nanotube films as conductive layers for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(8): 4047-4057. DOI: 10.1039/C6TA10024D. |
| 180 | USSEGLIO-VIRETTA F L E, MAI W, COLCLASURE A M, et al. Enabling fast charging of lithium-ion batteries through secondary-/dual-pore network: Part I—Analytical diffusion model[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 342: 136034. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136034. |
| 181 | ZHANG X, HUI Z Y, KING S, et al. Tunable porous electrode architectures for enhanced Li-ion storage kinetics in thick electrodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(13): 5896-5904. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02142. |
| 182 | HUANG H, LI Z Q, GU S, et al. Dextran sulfate lithium as versatile binder to stabilize high-voltage LiCoO2 to 4.6 V[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(44): 2101864. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202101864. |
| 183 | LI S P, XIONG R Y, HAN Z L, et al. Unveiling low-tortuous effect on electrochemical performance toward ultrathick LiFePO4 electrode with 100 mg·cm-2 area loading[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 515: 230588. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230588. |
| 184 | HE R J, TIAN G L, LI S P, et al. Enhancing the reversibility of lithium cobalt oxide phase transition in thick electrode via low tortuosity design[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(6): 2429-2436. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c00123. |
| 185 | ZHU C B, USISKIN R E, YU Y, et al. The nanoscale circuitry of battery electrodes[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6369): eaao2808. DOI: 10.1126/science.aao2808. |
| 186 | LIU Z M, ZENG Y Q, TAN J Y, et al. Revealing the degradation pathways of layered Li-rich oxide cathodes[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2024, 19(12): 1821-1830. DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01773-4. |
| [1] | 刘佳辉, 卞伟翔, 李大伟. 锂电池石墨复合电极力-电耦合性能原位测量分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2240-2247. |
| [2] | 陈峥, 多功东, 申江卫, 沈世全, 刘昱, 魏福星. 基于容量增量分析与VMD-GWO-KELM的锂电池健康状态估计[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2476-2487. |
| [3] | 阮晶晶, 巫湘坤, 李勇慧, 赵冲冲, 李珅珅, 王童飞, 梁圣杰, 高桂红. 低成本干法石墨厚电极的制备与性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2248-2255. |
| [4] | 韩丹丹, 张武卫, 张亮, 王宗江. 核壳结构LiMn1-y Fe y PO4/C正极材料设计与电化学性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(6): 2215-2222. |
| [5] | 周海洋, 张振东, 盛雷, 朱泽华, 张晓军, 张春风. 储能用锂电池浸没式热性能调控仿真及热安全实验研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1866-1874. |
| [6] | 宋海飞, 王乐红, 原义栋, 赵天挺, 陈捷. 基于改进卡尔曼算法的电池采样电压滤波估计[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 2106-2113. |
| [7] | 曾州岚, 尚雷, 胡志金, 王宗凡, 辛小超, 刘瑛. 高容量锂离子电池正极补锂材料Li5FeO4@C的性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1875-1883. |
| [8] | 莫子鸣, 饶宗昕, 杨建飞, 杨孟昊, 蔡黎明. 锂离子电池过充热失控气热模型构建及关键参数影响分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(5): 1784-1796. |
| [9] | 彭磊, 倪照鹏, 于越, 孙福鹏, 夏修龙, 张鹏, 孙思博. 过充导致三元锂电池电动汽车火灾的试验研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1484-1495. |
| [10] | 申江卫, 折亦鑫, 舒星, 刘永刚, 魏福星, 夏雪磊, 陈峥. 基于短时随机充电数据和优化卷积神经网络的锂电池健康状态估计[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1585-1595. |
| [11] | 刘瑞昊, 马小乐, 张宇萱, 朱曰莹, 刘仕强, 白广利. 基于绝热量热仪的锂离子电池热物性参数测试影响因素研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1596-1602. |
| [12] | 董作林, 宋金岩, 孟子迪. 基于模态分解和深度学习的锂离子电池寿命预测[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1645-1653. |
| [13] | 徐桂培, 刘浩, 赖洁文, 卢毅锋, 黄辉, 邸会芳, 王振兵. 干法电极技术在超级电容器和锂离子电池中的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1445-1460. |
| [14] | 岳金明, 刘媛丽, 陈一霞, 禹习谦, 李泓. GC-MS检测锂离子电池电解液分离条件的研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1564-1573. |
| [15] | 廖兴群, 杨睿, 于立娟, 胡大林, 肖峰, 胡菁, 卢周广. 多功能电解液添加剂2,6-吡啶二甲腈稳定高电压钴酸锂[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1331-1339. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
