Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (3): 777-791.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0684
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yiming YAO( ), Weiling LUAN(
), Weiling LUAN( ), Ying CHEN, Min SUN
), Ying CHEN, Min SUN
Received:2022-11-21
Revised:2022-11-30
Online:2023-03-05
Published:2023-04-14
Contact:
Weiling LUAN
E-mail:ecustyaoyiming@163.com;luan@ecust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yiming YAO, Weiling LUAN, Ying CHEN, Min SUN. Recent progress in aging degradation of lithium-ion battery materials via in-situ optical microscopy[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 777-791.

Fig. 1
Several typical structures of in situ optical microscope reaction cells (a) glass plate clamped type[15]; (b) glass cuvette type[16]; (c) glass tube type[17]; (d) capillary tube type[18]; (e) coin cell type[19]; (f) pouch cell type[20]; (g) electrode draped mold[21]; (h) electrode edge-to-edge mold[22]; (i) electrode face-to-face mold[24]"


Fig. 8
Morphological evolution of the i-Li island [52] (a) configuration of the optical cell with an i-Li island between the NMC and Li electrodes; (b) Li islands in the initial state (t=0 h) and intermediate states (t=3 h) during the charging phase h) optical microscope images; (c) optical microscope images of Li islands in the initial state (t=0 h) and intermediate state (t=3 h) during the discharge"
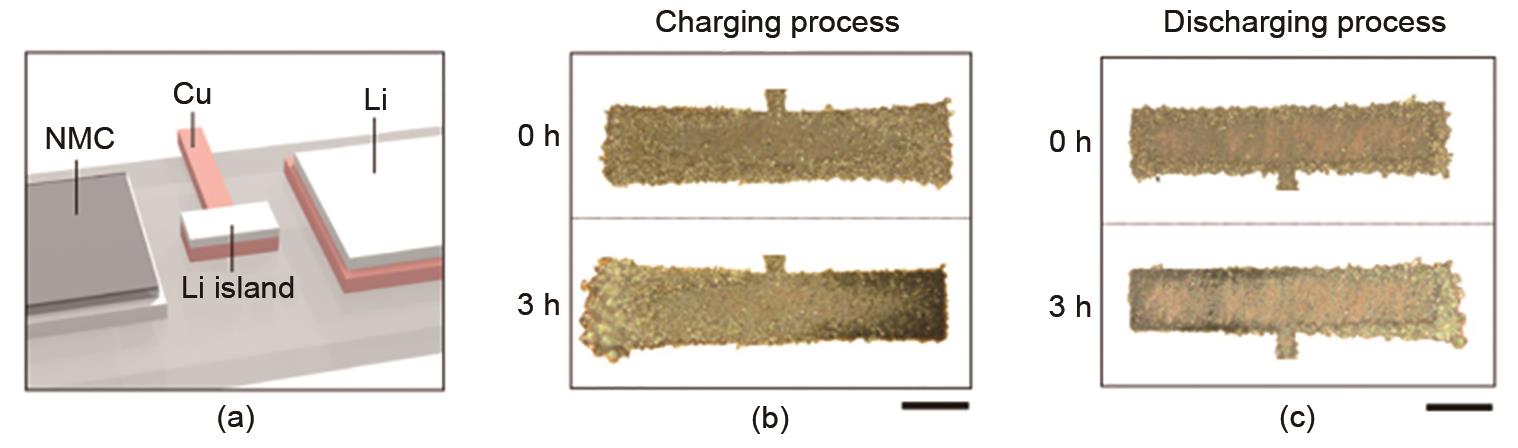

Fig. 9
The morphological evolution process of graphite anode surface and the corresponding external characteristic curves[22] (a) voltage curves of graphite during a 10 min OCV rest period for two cells; (b) local optical images of the graphite surfaces at different points in time during the OCV rest; (c) dV/dt curves associated with the two voltage profiles; (d) blue of graphite during the extended 50 min OCV rest period"
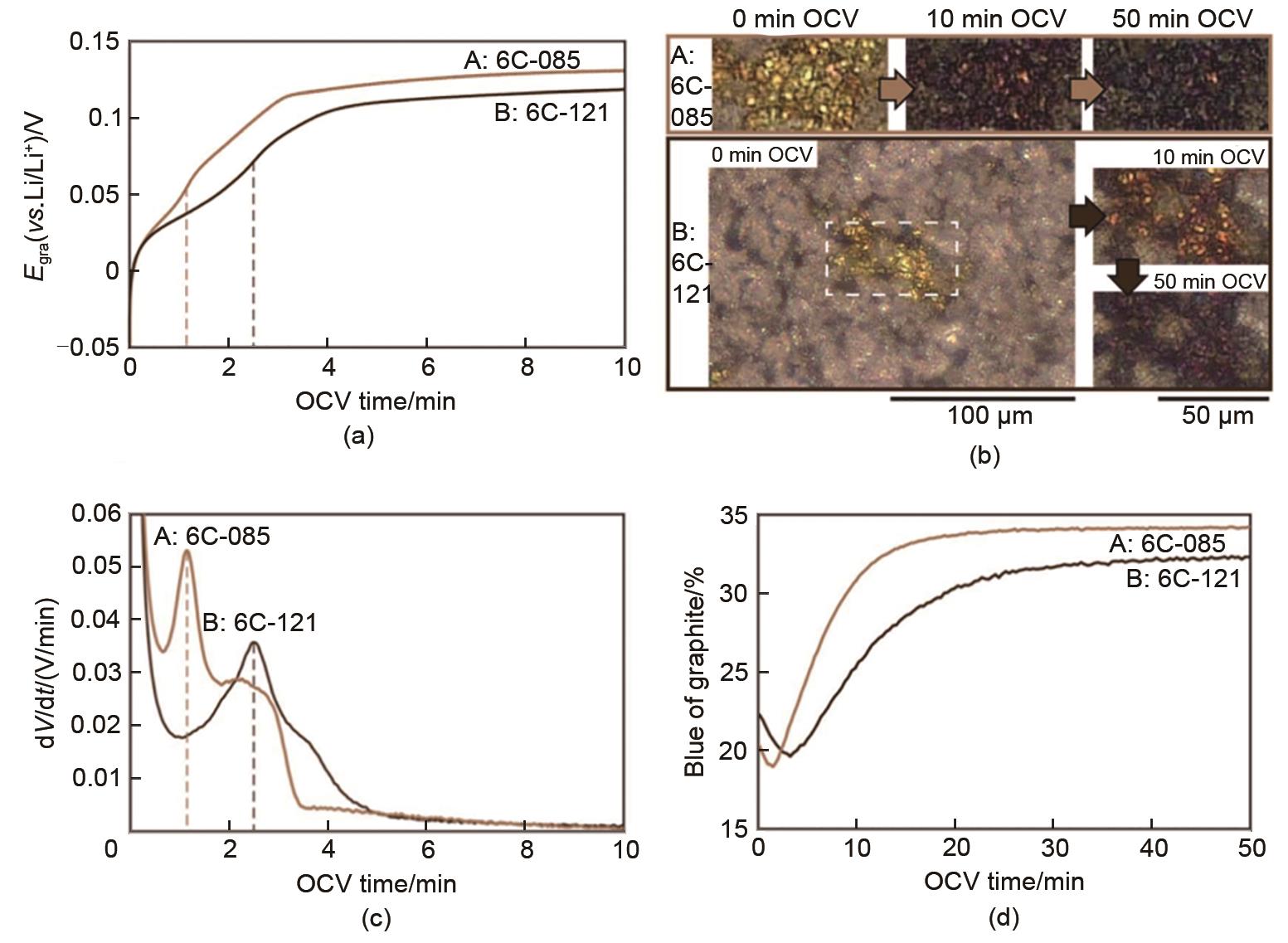

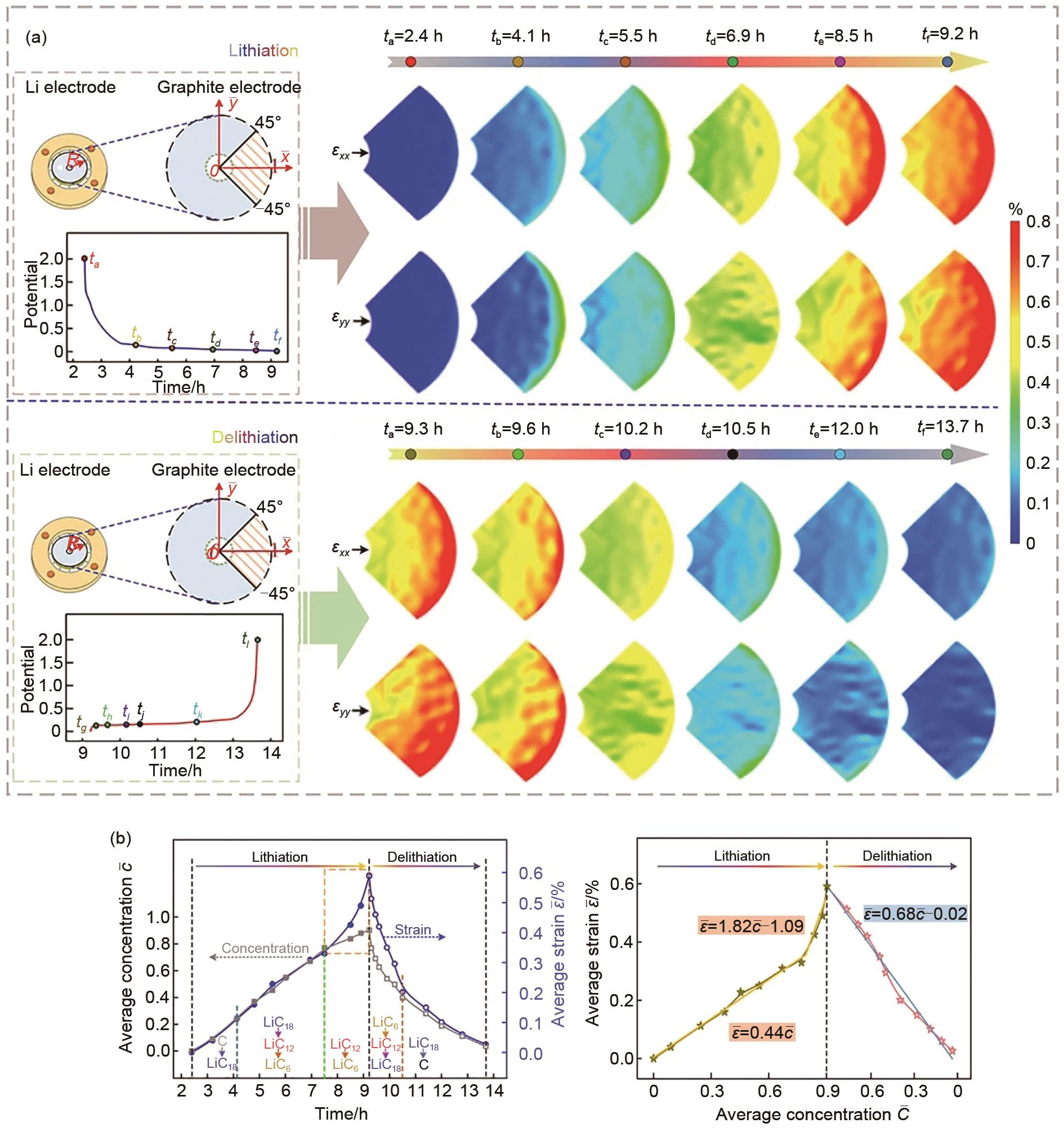
Fig. 14
Evolution of strain field on graphite anode surface with lithium concentration changing[83] (a) evolution of the strain field on the surface of the graphite anode; (b) average concentration and average in-plane strain as a function of time on the surface of the graphite anode, respectively"
| 1 | 缪平, 姚祯, JOHN L, 等. 电池储能技术研究进展及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(3): 670-678. |
| MIAO P, YAO Z, JOHN L, et al. Current situations and prospects of energy storage batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 670-678. | |
| 2 | LIU D Q, SHADIKE Z, LIN R Q, et al. Review of recent development of in situ/operando characterization techniques for lithium battery research[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(28): doi: 10.1002/adma.201806620. |
| 3 | WALDMANN T, ITURRONDOBEITIA A, KASPER M, et al. Review—post-mortem analysis of aged lithium-ion batteries: Disassembly methodology and physico-chemical analysis techniques[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(10): doi: 10.1149/2.1211609jes. |
| 4 | YANG H C, TANG P, PIAO N, et al. In-situ imaging techniques for advanced battery development[J]. Materials Today, 2022, 57: 279-294. |
| 5 | 柯承志, 肖本胜, 李苗, 等. 电极材料储锂行为及其机制的原位透射电镜研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(4): 1219-1236. |
| KE C Z, XIAO B S, LI M, et al. Research progress in understanding of lithium storage behavior and reaction mechanism of electrode materials through in situ transmission electron microscopy[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(4): 1219-1236. | |
| 6 | 李文俊, 郑杰允, 谷林, 等. 锂电池原位与非原位表征技术研究[J]. 电化学, 2015, 21(2): 99-114. |
| LI W J, ZHENG J Y, GU L, et al. Researches on In-situ and ex-situ characterization techniques in lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2015, 21(2): 99-114. | |
| 7 | WANG X, ZHOU H, CHEN Z H, et al. Synchrotron-based X-ray diffraction and absorption spectroscopy studies on layered LiNixMnyCozO2 cathode materials: A review[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 49: 181-208. |
| 8 | TAO S W, LI M, LYU M Q, et al. In operando closed-cell transmission electron microscopy for rechargeable battery characterization: Scientific breakthroughs and practical limitations[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 96: doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107083. |
| 9 | 于川茗, 李林, 蔡毅超. 扫描电镜在电池材料领域的应用[J]. 电子显微学报, 2021, 40(3): 339-347. |
| YU C M, LI L, CAI Y C. The application of scanning electron microscopy in the field of battery materials[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2021, 40(3): 339-347. | |
| 10 | NEUPANE S, VALENCIA-RAMÍREZ A, LOSADA-PÉREZ P, et al. In operando atomic force microscopy imaging of electrochemical interfaces: A short perspective[J]. Physica Status Solidi (a), 2021, 218(24): doi: 10.1002/pssa.202100470. |
| 11 | SWALLOW J G, WOODFORD W H, MCGROGAN F P, et al. Effect of electrochemical charging on elastoplastic properties and fracture toughness of LixCoO2[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(11): doi: 10.1149/2.0141411jes. |
| 12 | STIASZNY B, ZIEGLER J C, KRAUß E E, et al. Electrochemical characterization and post-mortem analysis of aged LiMn2O4-Li(Ni0.5Mn0.3Co0.2)O2/graphite lithium ion batteries. Part I: Cycle aging[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 251: 439-450. |
| 13 | CHEN Y X, TORRES-CASTRO L, CHEN K H, et al. Operando detection of Li plating during fast charging of Li-ion batteries using incremental capacity analysis[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 539: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.231601. |
| 14 | HAFNER C, BERNTHALER T, KNOBLAUCH V, et al. The materialographic preparation and microstructure characterization of lithium ion accumulators[J]. Practical Metallography, 2012, 49: 75-85. |
| 15 | NISHIKAWA K, NAITO H, KAWASE M, et al. Morphological variation of electrodeposited Li in ionic liquid[J]. ECS Transactions, 2012, 41(41): 3-10. |
| 16 | CONDER J, MARINO C, NOVáK P, et al. Do imaging techniques add real value to the development of better post-Li-ion batteries?[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(8): 3304-3327. |
| 17 | SUN Y M, SEH Z W, LI W Y, et al. In-operando optical imaging of temporal and spatial distribution of polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 11: 579-586. |
| 18 | BAI P, LI J, BRUSHETT F R, et al. Transition of lithium growth mechanisms in liquid electrolytes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(10): 3221-3229. |
| 19 | THOMAS-ALYEA K E, JUNG C, SMITH R B, et al. In situ observation and mathematical modeling of lithium distribution within graphite[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(11): doi: 10.1149/2.0061711jes. |
| 20 | OTOYAMA M, SAKUDA A, HAYASHI A, et al. Optical microscopic observation of graphite composite negative electrodes in all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2018, 323: 123-129. |
| 21 | ARISE I, MIYAHARA Y, MIYAZAKI K, et al. Functional role of aramid coated separator for dendrite suppression in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2022, 169(1): doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac4b1e. |
| 22 | CHEN Y X, CHEN K H, SANCHEZ A J, et al. Operando video microscopy of Li plating and re-intercalation on graphite anodes during fast charging[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(41): 23522-23536. |
| 23 | SANCHEZ A J, KAZYAK E, CHEN Y X, et al. Plan-view Operando video microscopy of Li metal anodes: Identifying the coupled relationships among nucleation, morphology, and reversibility[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(3): 994-1004. |
| 24 | OTOYAMA M, KOWADA H, SAKUDA A, et al. Operando confocal microscopy for dynamic changes of Li+ ion conduction path in graphite electrode layers of all-solid-state batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020, 11(3): 900-904. |
| 25 | 吕思奇, 李娜, 陈浩森, 等. 电池电极过程可视化与定量化技术的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(3): 795-817. |
| LYU S Q, LI N, CHEN H S, et al. Progresses in visualization and quantitative analysis of the electrode process in rechargeable batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 795-817. | |
| 26 | GAO T, HAN Y, FRAGGEDAKIS D, et al. Interplay of lithium intercalation and plating on a single graphite particle[J]. Joule, 2021, 5(2): 393-414. |
| 27 | ARAI H, YAGUCHI A, NISHIMURA Y, et al. Operando optical analysis of LiFePO4 composite electrodes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(7): 3776-3780. |
| 28 | AZHAGURAJAN M, NAKATA A, ARAI H, et al. Effect of vanillin to prevent the dendrite growth of Zn in zinc-based secondary batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(12): doi: 10.1149/2.0221712jes. |
| 29 | FENG Y, NGO T D T, PANAGOPOULOU M, et al. Lithiation of pure and methylated amorphous silicon: Monitoring by operando optical microscopy and ex situ atomic force microscopy[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 302: 249-258. |
| 30 | WAN J Y, BAO W Z, LIU Y, et al. In situ investigations of Li-MoS2 with planar batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(5): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201401742. |
| 31 | ZHANG Y W, FINCHER C, MCPROUTY S, et al. In-operando imaging of polysulfide catholytes for Li-S batteries and implications for kinetics and mechanical stability[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 434: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226727. |
| 32 | SONG Y X, SHI Y, WAN J, et al. Direct tracking of the polysulfide shuttling and interfacial evolution in all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries: A degradation mechanism study[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(8): 2496-2506. |
| 33 | AGRAWAL S, BAI P. Dynamic interplay between phase transformation instabilities and reaction heterogeneities in particulate intercalation electrodes[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2022, 3(5): doi: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.100854. |
| 34 | LODICO J J, LAI C H, WOODALL M, et al. Irreversibility at macromolecular scales in the flake graphite of the lithium-ion battery anode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 436: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226841. |
| 35 | 孟德超, 马紫峰, 李林森. 锂离子电池介尺度电化学反应非均匀性[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(9): 4869-4881. |
| MENG D C, MA Z F, LI L S. Mesoscale reaction heterogeneities in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(9): 4869-4881. | |
| 36 | YANG L, CHEN H S, SONG W L, et al. Effect of defects on diffusion behaviors of lithium-ion battery electrodes: in situ optical observation and simulation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(50): 43623-43630. |
| 37 | SHI B Q, HAN B, XIE H M, et al. C-rate related diffusion process of the graphite electrode by in situ experiment and analysis[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 378: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138151. |
| 38 | FUKUMITSU H, OMORI M, TERADA K, et al. Development of in situ cross-sectional Raman imaging of LiCoO2 cathode for Li-ion battery[J]. Electrochemistry, 2015, 83(11): 993-996. |
| 39 | HAN X B, LU L G, ZHENG Y J, et al. A review on the key issues of the lithium ion battery degradation among the whole life cycle[J]. eTransportation, 2019, 1: doi: 10.1016/j.etran.2019.100005. |
| 40 | LI Z, HUANG J, YANN LIAW B, et al. A review of lithium deposition in lithium-ion and lithium metal secondary batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 254: 168-182. |
| 41 | 任东生, 冯旭宁, 韩雪冰, 等. 锂离子电池全生命周期安全性演变研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2018, 7(6): 957-966. |
| REN D S, FENG X N, HAN X B, et al. Recent progress on evolution of safety performance of lithium-ion battery during aging process[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(6): 957-966. | |
| 42 | EDGE J S, O'KANE S, PROSSER R, et al. Lithium ion battery degradation: What You need to know[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2021, 23(14): 8200-8221. |
| 43 | REN D S, HSU H, LI R H, et al. A comparative investigation of aging effects on thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries[J]. eTransportation, 2019, 2: doi: 10.1016/j.etran.2019.100034. |
| 44 | FEAR C, ADHIKARY T, CARTER R, et al. In operando detection of the onset and mapping of lithium plating regimes during fast charging of lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(27): 30438-30448. |
| 45 | LOVE C T, BATURINA O A, SWIDER-LYONS K E. Observation of lithium dendrites at ambient temperature and below[J]. ECS Electrochemistry Letters, 2015, 4(2): doi: 10.1149/2.0041502eel. |
| 46 | KÜHNLE H, KNOBBE E, FIGGEMEIER E. In situ optical investigations of lithium depositions on pristine and aged lithium metal electrodes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(2): doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abdeeb. |
| 47 | KONG L X, XING Y J, PECHT M G. In-situ observations of lithium dendrite growth[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 8387-8393. |
| 48 | SHI Y, WAN J, LIU G X, et al. Interfacial evolution of lithium dendrites and their solid electrolyte interphase shells of quasi-solid-state lithium-metal batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(41): 18120-18125. |
| 49 | REN D S, SMITH K, GUO D X, et al. Investigation of lithium plating-stripping process in Li-ion batteries at low temperature using an electrochemical model[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(10): doi: 10.1149/2.0661810jes. |
| 50 | WALDMANN T, HOGG B I, WOHLFAHRT-MEHRENS M. Li plating as unwanted side reaction in commercial Li-ion cells-A review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 384: 107-124. |
| 51 | SANCHEZ A J, KAZYAK E, CHEN Y X, et al. Lithium stripping: Anisotropic evolution and faceting of pits revealed by operando 3-D microscopy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(37): 21013-21023. |
| 52 | LIU F, XU R, WU Y C, et al. Dynamic spatial progression of isolated lithium during battery operations[J]. Nature, 2021, 600(7890): 659-663. |
| 53 | 周宇, 邓哲, 黄震宇, 等. 锂离子电池负极析锂检测方法的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50(1): 84-100. |
| ZHOU Y, DENG Z, HUANG Z Y, et al. Research progress on detection methods for lithium plating in anode of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2022, 50(1): 84-100. | |
| 54 | HE X, SCHMOHL S, WIEMHÖFER H D. Direct observation and suppression effect of lithium dendrite growth for polyphosphazene based polymer electrolytes in lithium metal cells[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6(4): 1166-1176. |
| 55 | LI W Y, YAO H B, YAN K, et al. The synergetic effect of lithium polysulfide and lithium nitrate to prevent lithium dendrite growth[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: doi: 10.1038/ncomms8436. |
| 56 | RODRIGUEZ R, LOEFFLER K E, EDISON R A, et al. Effect of the electrolyte on the cycling efficiency of lithium-limited cells and their morphology studied through in situ optical imaging[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(11): 5830-5835. |
| 57 | WAN G J, GUO F H, LI H, et al. Suppression of dendritic lithium growth by in situ formation of a chemically stable and mechanically strong solid electrolyte interphase[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(1): 593-601. |
| 58 | HAN B, FENG D Y, LI S, et al. Self-regulated phenomenon of inorganic artificial solid electrolyte interphase for lithium metal batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(5): 4029-4037. |
| 59 | LI Q, QUAN B G, LI W J, et al. Electro-plating and stripping behavior on lithium metal electrode with ordered three-dimensional structure[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 45: 463-470. |
| 60 | YU C, DU Y, HE R H, et al. Hollow SiOx/C microspheres with semigraphitic carbon coating as the "lithium host" for dendrite-free lithium metal anodes[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(4): 3905-3912. |
| 61 | GUAN R Z, LIU S, WANG C, et al. Lithiophilic Sn sites on 3D Cu current collector induced uniform lithium plating/stripping[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 425: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130177. |
| 62 | CHEN X, XIE J, LU Y H, et al. Two-dimensional lithiophilic YFδ enabled lithium dendrite removal for quasi-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2021, 7(2): 355-365. |
| 63 | YANG J, FENG T T, ZHI C, et al. Bimetallic composite induced ultra-stable solid electrolyte interphase for dendrite-free lithium metal anode[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 599: 819-827. |
| 64 | DE VASCONCELOS L S, XU R, XU Z R, et al. Chemomechanics of rechargeable batteries: Status, theories, and perspectives[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(15): 13043-13107. |
| 65 | KONDRAKOV A O, SCHMIDT A, XU J, et al. Anisotropic lattice strain and mechanical degradation of high- and low-nickel NCM cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(6): 3286-3294. |
| 66 | OBROVAC M N, CHRISTENSEN L. Structural changes in silicon anodes during lithium insertion/extraction[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2004, 7(5): doi: 10.1149/1.1652421. |
| 67 | TIMMONS A, DAHN J R. Isotropic volume expansion of particles of amorphous metallic alloys in composite negative electrodes for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2007, 154(5): doi: 10.1149/1.2711075. |
| 68 | DOKKO K. In situ observation of LiNiO2 single-particle fracture during Li-ion extraction and insertion[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 1999, 3(3): 125. |
| 69 | 陈莹, 栾伟玲, 陈浩峰, 等. 基于应力场的锂离子电池正极多尺度失效研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 918-923. |
| CHEN Y, LUAN W L, CHEN H F, et al. Multi-scale failure behavior of cathode in lithium-ion batteries based on stress field[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 918-923. | |
| 70 | 王亚楠, 李华, 王正坤, 等. 扩散应力诱导的锂离子电池失效机理研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1071-1087. |
| WANG Y N, LI H, WANG Z K, et al. Progress on failure mechanism of lithium ion battery caused by diffusion induced stress[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1071-1087. | |
| 71 | WALDMANN T, MOLINERO M B, WILDNER L, et al. Cross-sectional in situ optical microscopy with simultaneous electrochemical measurements for lithium-ion full cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2022, 169(5): doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac6c57. |
| 72 | 高金辉, 陈英龙, 孟繁慧, 等. 锂离子电池原位光学显微观测[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(1): 53-59. |
| GAO J H, CHEN Y L, MENG F H, et al. Research on in situ optical microscopic observation in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 53-59. | |
| 73 | YOON D H, MARINARO M, AXMANN P, et al. Study of the binder influence on expansion/contraction behavior of silicon alloy negative electrodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(16): doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abcf4f. |
| 74 | HERNANDEZ C R, ETIEMBLE A, DOUILLARD T, et al. A facile and very effective method to enhance the mechanical strength and the cyclability of Si-based electrodes for Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(6): doi: 10.1002/aenm. 201701787. |
| 75 | LEWIS J A, TIPPENS J, CORTES F J Q, et al. Chemo-mechanical challenges in solid-state batteries[J]. Trends in Chemistry, 2019, 1(9): 845-857. |
| 76 | SUN M H, LIU T F, YUAN Y F, et al. Visualizing lithium dendrite formation within solid-state electrolytes[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(2): 451-458. |
| 77 | CHEN Y, CHEN H F, LUAN W L. Shakedown, ratcheting and fatigue analysis of cathode coating in lithium-ion battery under steady charging-discharging process[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2021, 150: doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2021.104366. |
| 78 | 冯小龙, 杨乐, 张明亮, 等. 锂离子电池内部力学与温度参量在位表征方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(6): 1062-1075. |
| FENG X L, YANG L, ZHANG M L, et al. Failure mechanics inner lithium ion batteries: In-situ multi-field experimental methods[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(6): 1062-1075. | |
| 79 | JANGID M K, MUKHOPADHYAY A. Real-time monitoring of stress development during electrochemical cycling of electrode materials for Li-ion batteries: Overview and perspectives[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(41): 23679-23726. |
| 80 | QI Z F, SHAN Z Q, MA W H, et al. Strain analysis on electrochemical failures of nanoscale silicon electrode based on three-dimensional in situ measurement[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(2): doi: 10.3390/app10020468. |
| 81 | QI Y, HARRIS S J. In situ observation of strains during lithiation of a graphite electrode[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(6): doi: 10.1149/1.3377130. |
| 82 | XU Z Y, SHI X L, ZHUANG X Q, et al. Chemical strain of graphite-based anode during lithiation and delithiation at various temperatures[J]. Research (Washington, D C), 2021, 2021: doi: 10.34133/2021/9842391. |
| 83 | XIE H M, YANG W, KANG Y L, et al. In-situ strain field measurement and mechano-electro-chemical analysis of graphite electrodes via fluorescence digital image correlation[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2021, 61(8): 1249-1260. |
| 84 | AHMED R A, EBECHIDI N, REISYA I, et al. Pressure-induced interfacial contacts and the deformation in all solid-state Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 521: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230939. |
| [1] | Fan YANG, Jiarui HE, Ming LU, Lingxia LU, Miao YU. SOC estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on BP-UKF algorithm [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 552-559. |
| [2] | Wenkai ZHU, Xing ZHOU, Yajie LIU, Tao ZHANG, Yuanming SONG. Real time state of charge estimation method of lithium-ion battery based on recursive gated recurrent unit neural network [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 570-578. |
| [3] | Zhifu WANG, Wei LUO, Yuan YAN, Song XU, Wenmei HAO, Conglin ZHOU. Fault diagnosis of lithium-ion battery sensors using GAPSO-FNN [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 602-608. |
| [4] | Deliu ZHANG, Yan ZHANG, Hai WANG, Jiadong WANG, Xuanwen GAO, Chaomeng LIU, Dongrun YANG, Wenbin LUO. Optimization of high nickel cathode materials for lithium ion batteries by magnesium doped heterogeneous aluminum oxide coating [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 339-348. |
| [5] | Yue PAN, Xuebing HAN, Minggao OUYANG, Huahua REN, Wei LIU, Yuejun YAN. Research on the detection algorithm for internal short circuits in lithium-ion batteries and its application to real operating data [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 198-208. |
| [6] | Xiaolong HE, Xiaolong SHI, Ziyang WANG, Luhao HAN, Bin YAO. Experimental study on thermal runaway characteristics of vehicle NCM lithium-ion batteries under overcharge, overheating, and their combined effects [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 218-226. |
| [7] | Linwang DENG, Tianyu FENG, Shiwei SHU, Bin GUO, Zifeng ZHANG. Nondestructive lithium plating online detection for lithium-ion batteries: A review [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 263-277. |
| [8] | Linwang DENG, Tianyu FENG, Shiwei SHU, Zifeng ZHANG, Bin GUO. Review of a fast-charging strategy and technology for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2879-2890. |
| [9] | Zhizhan LI, Jinlei QIN, Jianing LIANG, Zhengrong LI, Rui WANG, Deli WANG. High-nickel ternary layered cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries: Research progress, challenges and improvement strategies [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2900-2920. |
| [10] | Xiaoyu CHEN, Mengmeng GENG, Qiankun WANG, Jiani SHEN, Yijun HE, Zifeng MA. Electrochemical impedance feature selection and gaussian process regression based on the state-of-health estimation method for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2995-3002. |
| [11] | Yang WANG, Xu LU, Yuxin ZHANG, Long LIU. Thermal runaway exhaust strategy of power battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2480-2487. |
| [12] | Qingsong ZHANG, Yang ZHAO, Tiantian LIU. Effects of state of charge and battery layout on thermal runaway propagation in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2519-2525. |
| [13] | Yong MA, Xiaohan LI, Lei SUN, Dongliang GUO, Jinggang YANG, Jianjun LIU, Peng XIAO, Guangjun QIAN. Parameter design of lithium-ion batteries based on a three-dimensional electrochemical thermal coupling lithium precipitation model [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2600-2611. |
| [14] | Liang TANG, Xiaobo YIN, Houfu WU, Pengjie LIU, Qingsong WANG. Demand for safety standards in the development of the electrochemical energy storage industry [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2645-2652. |
| [15] | Liping HUO, Weiling LUAN, Zixian ZHUANG. Development trend of lithium-ion battery safety technology for energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(8): 2671-2680. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
