Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (5): 1427-1443.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0260
• Special Issue on Key Materials and Recycling Technologies for Energy Storage Batteries • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qi ZHANG1,2( ), Xiaodong LI1,2, Wenwen WANG1,2, Xiao LIU1,2(
), Xiaodong LI1,2, Wenwen WANG1,2, Xiao LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2023-04-25
Revised:2023-04-28
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-05-29
Contact:
Xiao LIU
E-mail:zhangqi01@tyut.edu.cn;liuxiao@tyut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Qi ZHANG, Xiaodong LI, Wenwen WANG, Xiao LIU. Rational design of multifunctional cellulose based materials for their application in emerging energy storage[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1427-1443.
Table 1
The mechanical properties of several different materials[4, 6-9]"
| Material | Density/(kg/m3) | Ultimate tensile strength/GPa | Ultimate tensile modulus/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose nanofibers | 1500 | 2~6 | 145 |
| Cellulose nanocrystals | 1500 | — | 150 |
| Cellulose nanofiber films | ~1400 | 0.2 | 10 |
| Cellulose nanofiber wet spun fiber | ~1400 | 0.321 | 23.6 |
| Carbon fiber | 1700 | 1~4 | 100~400 |
| Kevlar/polyaramid (high modulus grade) | 1450 | 2.8~3.6 | 120 |
| E-glass fiber | 2600 | 2 | 73 |
| Steel (high carbon) | 7850 | 750~900 | 210 |
| Titanium (Ti 99.5) | 4500 | 250~1.1 | 102~110 |
| Single walled carbon nanotube | — | 300 | 1002 |

Fig. 3
(a) Reaction scheme illustration of the simultaneous occurrence of cellulose hydrolysis and esterification of hydroxyl groups using a mixture of acetic and hydrochloric acid as example[11]. (b) The preparation of nanocellulose under the pretreatment by the natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES) composed of lactate (LA) and choline chloride (CC)[19]. (c) Schematic diagram of the fabrication of CNCs through MwDES pretreatment and a subsequent high-intensity ultrasonication process. Optical photographs and polarized optical microscope images of the MwDES-pretreated CFs and the corresponding CNC suspensions: (d), (h) MwDES-70, (e), (i) MwDES-80, (f), (j) MwDES-90, and (g), (k) MwDES-100[21]"
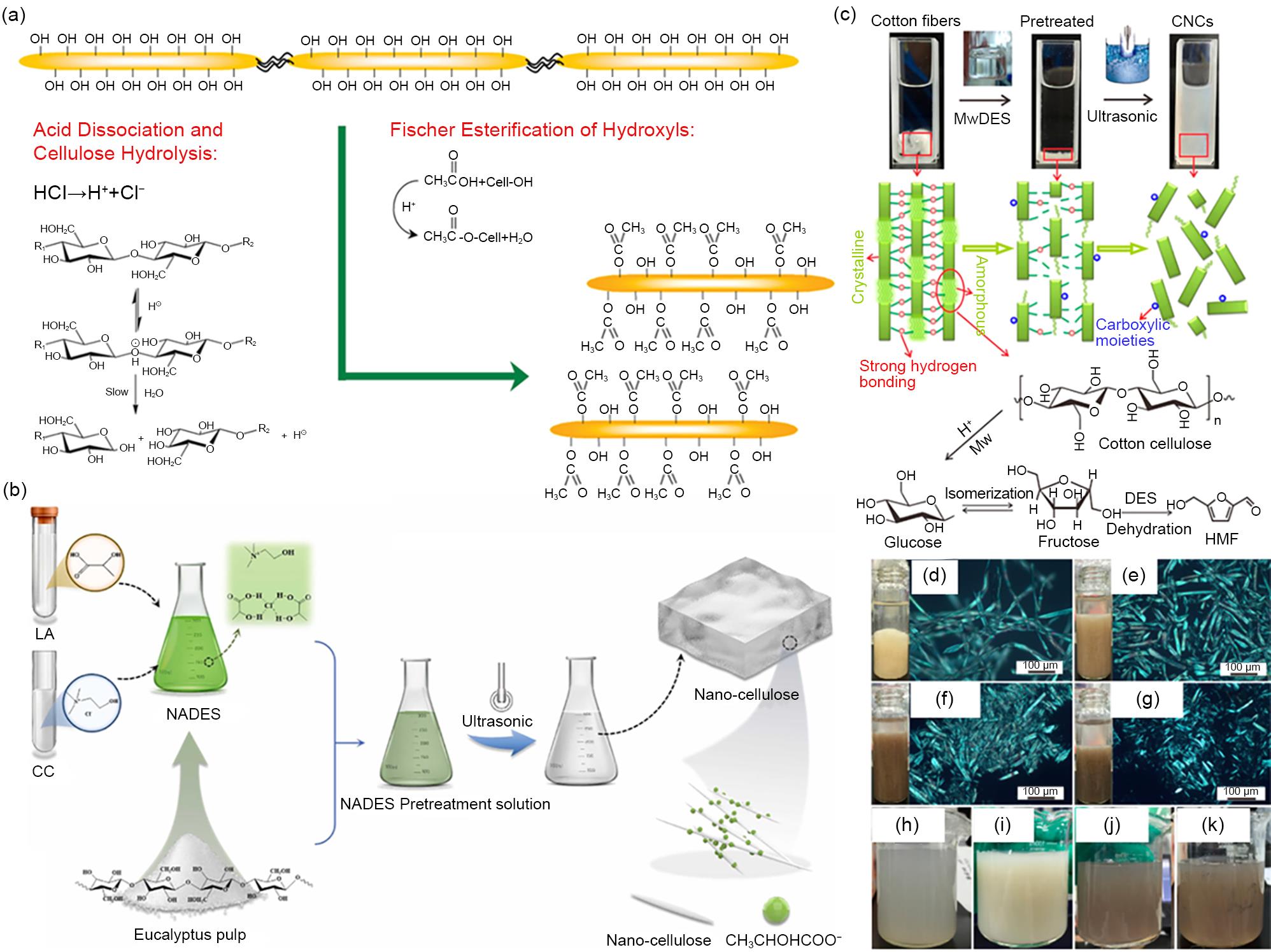
Fig. 5
Cooling wood demonstrates passive daytime radiative cooling. Photos of (a) natural wood and (b) cooling wood. (c) SEM image of the cooling wood showing the aligned wood channels. (d) SEM image of partially aligned cellulose nanofibers of the cooling wood. (e) Schematic diagram of the wood structure strongly scattering solar irradiance. (f) Schematic diagram of infrared emission by molecular vibration of the cellulose functional groups. (g) Setup of the real-time measurement of the sub-ambient cooling performance of the cooling wood[29]. (h) Fabrication process of the cooling lignocellulosic bulk by low cost cellulose and silicon dioxide. (i) Bending stress curves, (j) tensile stress curves for the cooling lignocellulosic bulk and pure wood fibers bulk. (k) Schematic diagram of the cooling lignocellulosic bulk with infrared emission and scattering solar irradiance. (l) Schematic diagram of the thermal box for demonstrating radiative cooling performance. (m) A 2-day continuous measurement of radiative cooling power, the ambient temperature (black) and the surface temperature (red) of a cooling lignocellulosic bulk under direct thermal testing[30]"
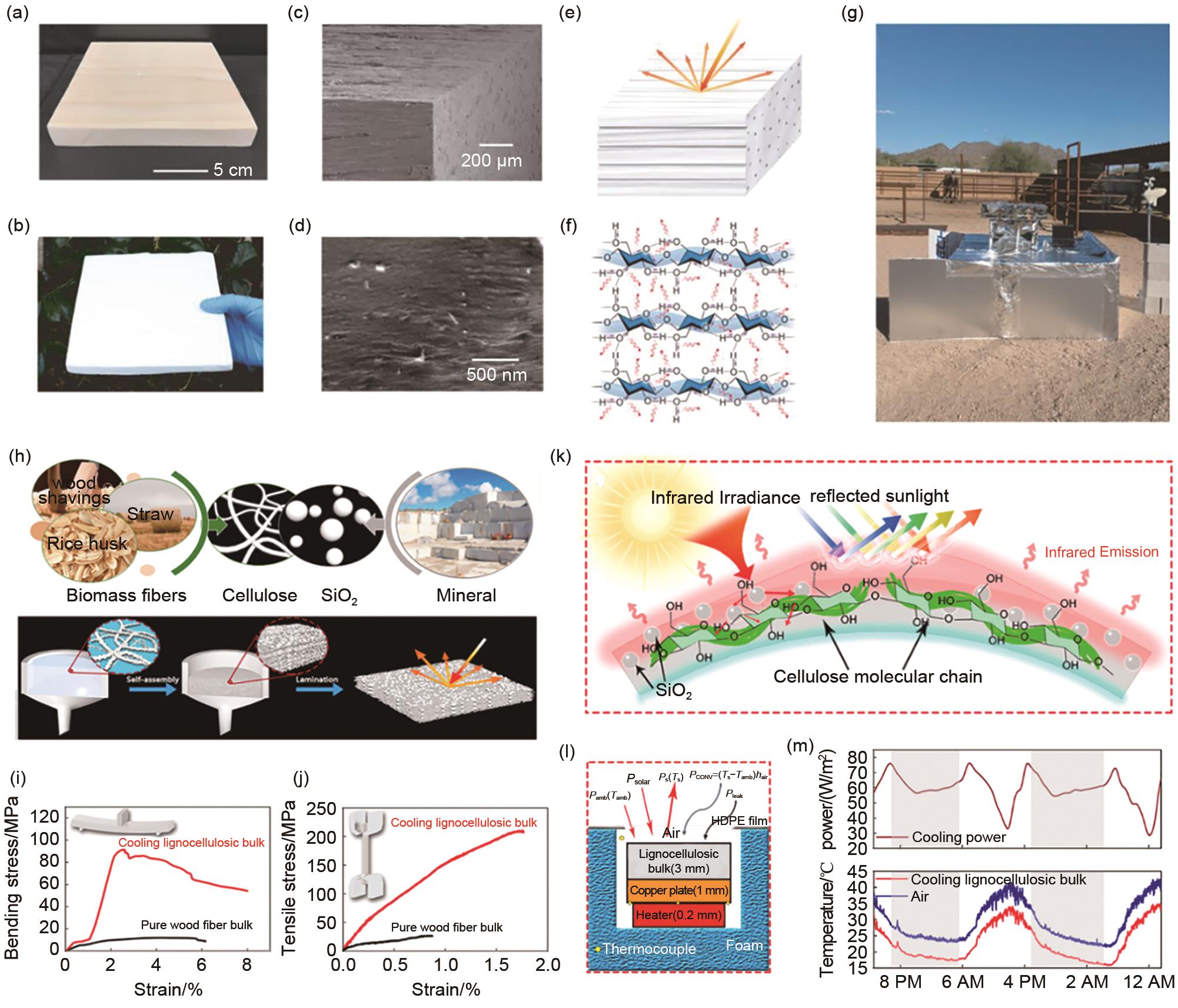
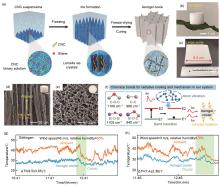
Fig. 6
Construction and characterization of aerogel coolers. (a)—(c) Preparation process for ultralight and upscaling aerogel coolers. (d) Interior and top surface morphology of aerogel coolers. (e) Chemical bonds and proposed mechanism of radiative emittance of aerogel cooler. (f) Cooling performance of aerogel coolers at a wind speed of 6 m/s and a relative humidity of 30%. (g), (h) Cooling performance of aerogel coolers at a wind speed of 3 m/s and a relative humidity of 70%[31]"

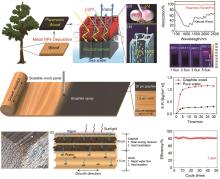
Fig. 7
Design of plasmonic wood. (a) A tree transports water from the bottom upward and absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis, (b) the natural wood decorated with plasmonic metal nanoparticles (c) a schematic of light is guided into the wood lumen and is fully absorbed for steam generation, (d) Schematic of plasmonic effect of two adjacent metal nanoparticles (NPs), (e) Zoomed-in schematic illustrating the water transport along microchannels in wood, (f) Absorption curves for plasmonic wood decorated with Pd nanoparticles and natural wood, (g) IR pictures of plasmonic wood under various illumination intensities[38], (h) Schematic of the scalable device manufacturing process, (i) SEM image of mesoporous wood with the wood lumens aligned along the wood growth direction (j) Schematic showing the solar steam generation mechanism of the graphite-coated wood, Evaporation rate (k) and Cycling performance (l) of graphite coated wood under 1 Sun condition[39]"
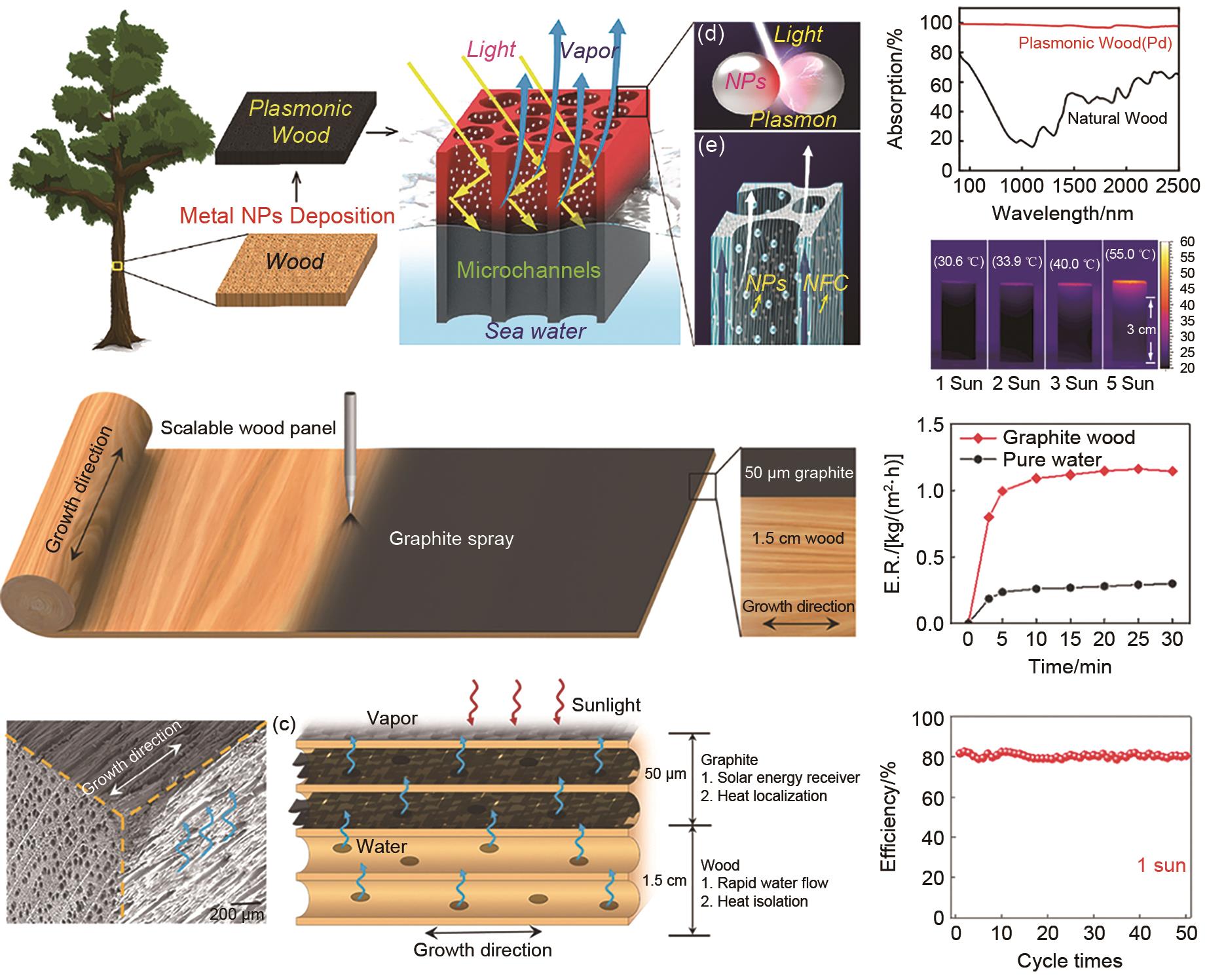
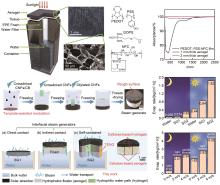
Fig. 8
(a) Schematic diagram of a typical solar steam generation device, (b) Optical microscope picture of PEDOT:PSS-NFC aerogel, (c) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of PEDOT:PSS-NFC aerogel, (d) Chemical structures of PEDOT:PSS, GOPS, and NFC, (e) The absorptance of PEDOT:PSS-NFC film, 1 mm thick aerogel, and 2 mm thick aerogel[40], The preparation process of all-cellulose-based steam generator (SG2) (f) and schematic illustration of interface interaction (g) in the steam generators, (h) Water evaporation rates in dark and light conditions, (i) water evaporation rates of SG2 under different solar intensities and air flows[41]"
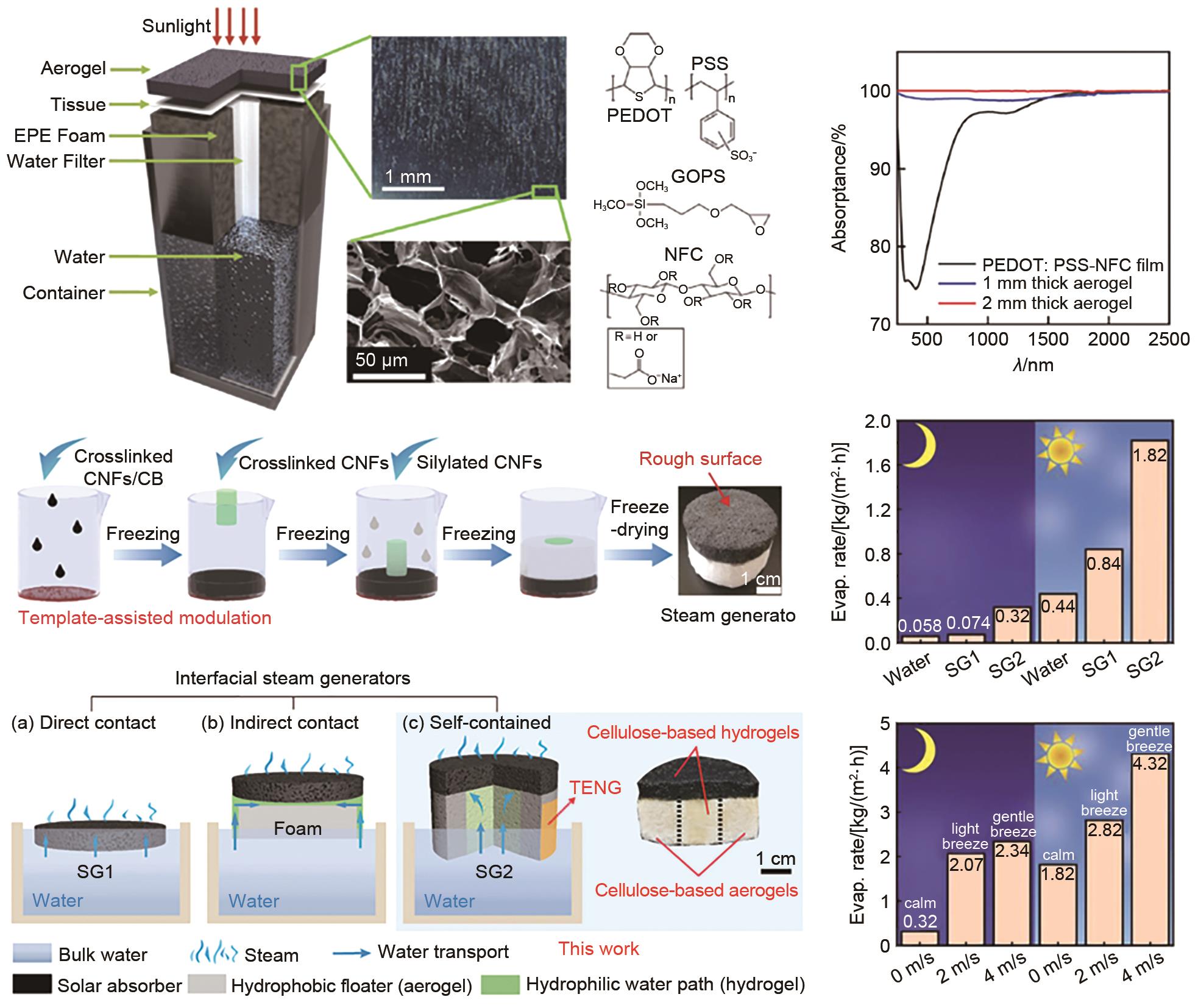

Fig. 9
(a) Schematic of synthesis procedure for CNF@c-MOF hybrid nanofibers, (b) Photograph of an origami folded by CNF@Ni-HITP nanopaper[43], (c) gold-patterned cellulose films reineforced by nano Si pellets. Resistance measurements as a function of bending angle (d), bending cycle (e), and number of folds (f)[44], (g) Fabrication process of flexible hydrophobic cellulose paper (HCP), (h) The photo of TENG constructed by HCP (i) VOC signals under walking behavior using HCPTENG[45]"
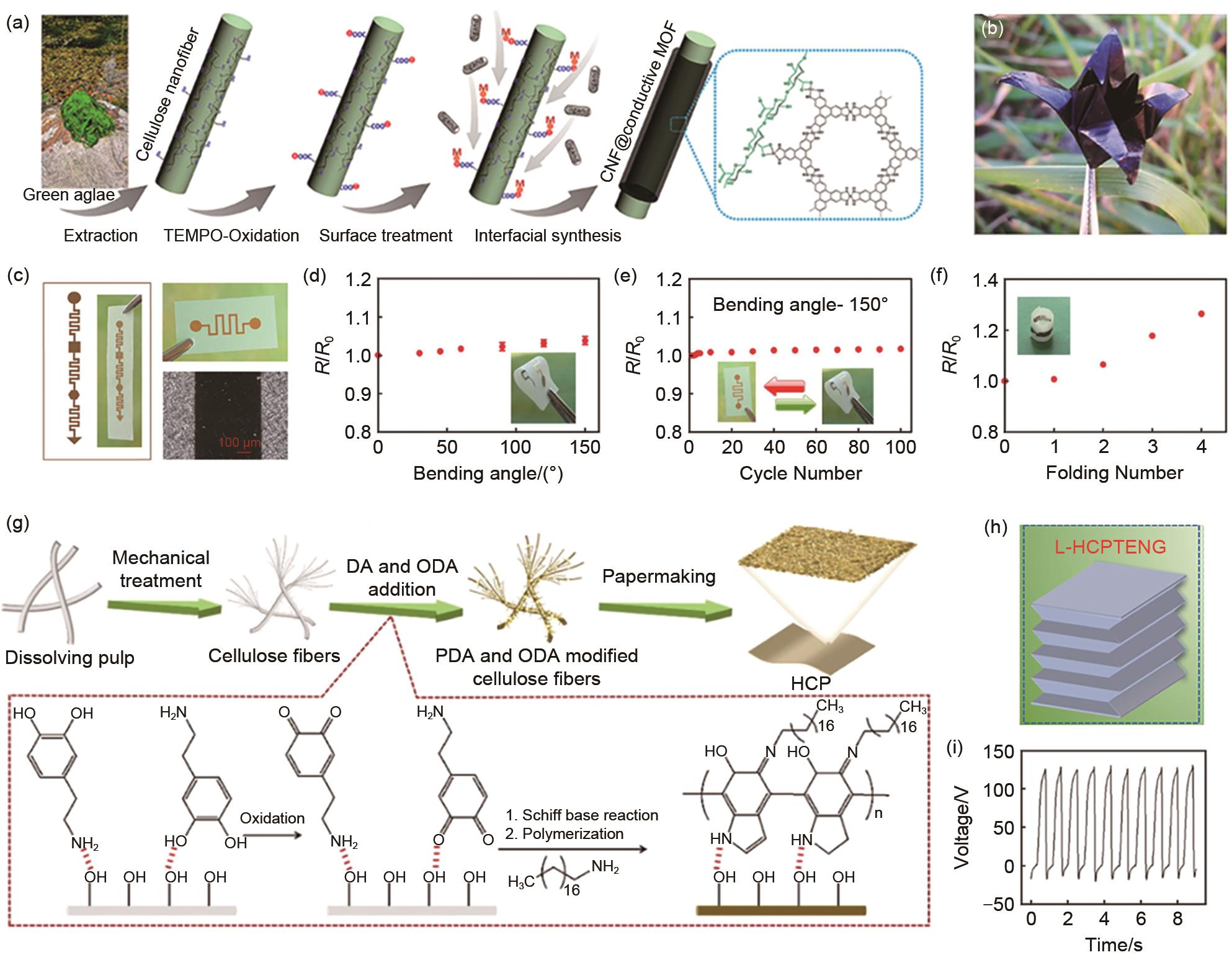

Fig. 10
Schematic illustration of the tree-inspired tri-pathway design for flexible Li-O2 cells. (a) Multiphase transport (e.g., water, ions, and nutrients) are essential for photosynthesis in trees. (b) A tri-pathway structural design was realized by chemically treating natural wood to remove lignin and hemicellulose (endowing it with flexibility) and subsequent CNT/Ru coating to provide electron conductivity and catalytic activity to enable the noncompetitive triphase transport of Li+, electrons, and oxygen gas[46]"

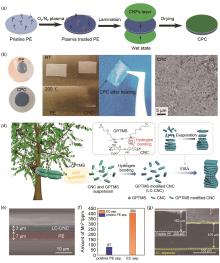
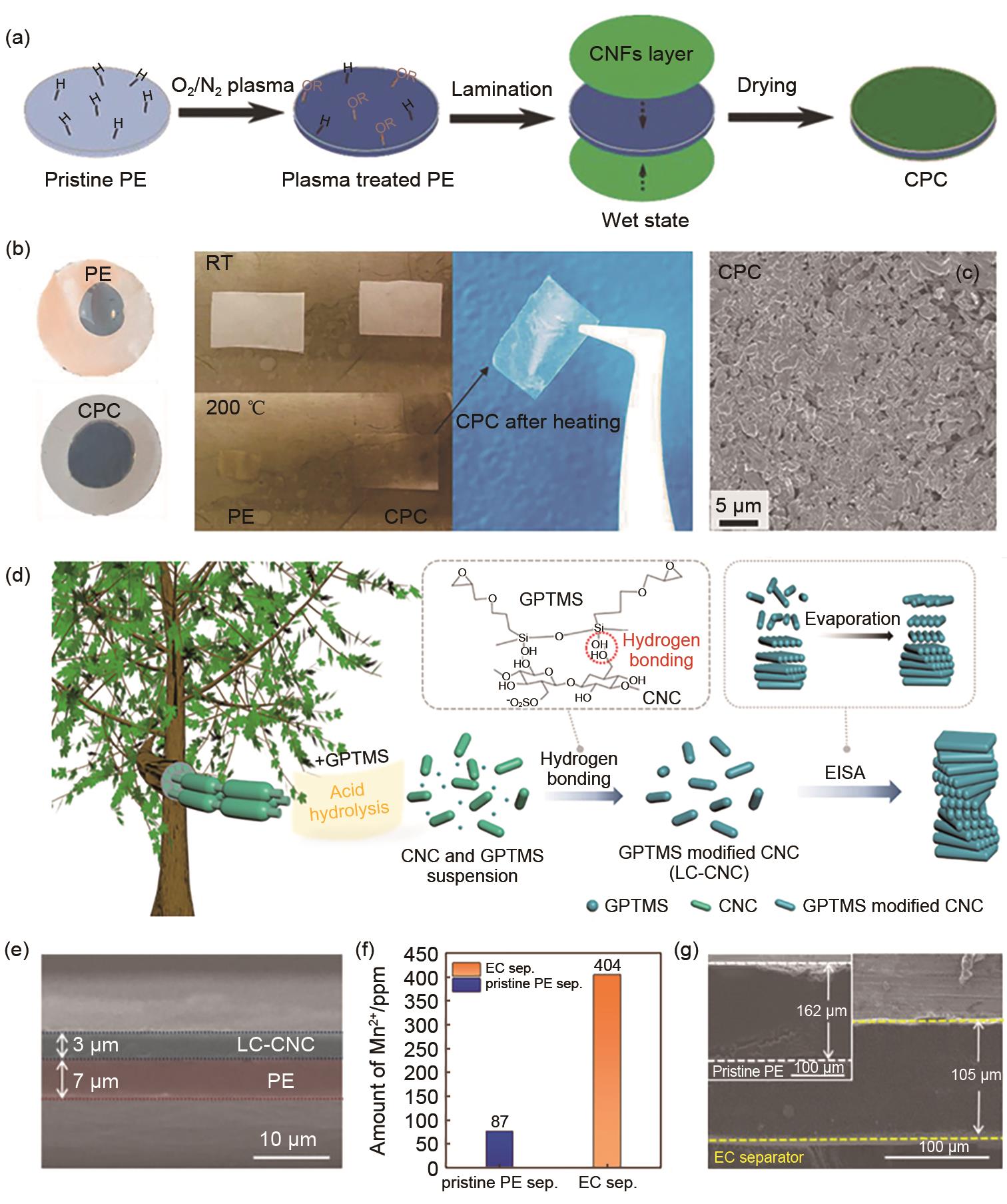
Fig. 11
(a) Schematic illustration of the manufacturing of the CPC separator, (b) Wettability and thermal stability of pristine PE and CPC separators, (c) SEM images of the Li deposits on Cu electrodes used in Li/Cu cells comprising a CPC (right) separator at a deposition current density of 1.5 mA/cm2[49], (d) Schematic illustration depicting the evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) process-driven fabrication of the self-assembled chiral nematic liquid crystalline cellulose nanocrystal (LC-CNC) layer on a polyethylene (PE) separator and its chemical structure, (e) Cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the EC separator (consisting of the LC-CNC layer (thickness ~3 μm) and PE separator (~7 μm), (f) Cross-sectional SEM image of the Li-metal after the unidirectional Li plating using the EC separator (vs. pristine PE separator (inset) for 90 h, (g) Amount of Mn2+ ions trapped by the EC separator (vs. pristine PE separator)[53]"
| 1 | 付时雨. 纤维素的研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2019, 38(6): 54-64. |
| FU S Y. Progress in cellulose research[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2019, 38(6): 54-64. | |
| 2 | PINKERT A, MARSH K N, PANG S S, et al. Ionic liquids and their interaction with cellulose[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2009, 109(12): 6712-6728. |
| 3 | CHEN C J, HU L B. Nanocellulose toward advanced energy storage devices: Structure and electrochemistry[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(12): 3154-3165. |
| 4 | SAITO T, KURAMAE R, WOHLERT J, et al. An ultrastrong nanofibrillar biomaterial: The strength of single cellulose nanofibrils revealed via sonication-induced fragmentation[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14(1): 248-253. |
| 5 | LI J, CHEN C, ZHU J Y, et al. In situ wood delignification toward sustainable applications[J]. Accounts of Materials Research, 2021, 2(8): 606-620. |
| 6 | SEHAQUI H, LIU A D, ZHOU Q, et al. Fast preparation procedure for large, flat cellulose and cellulose/inorganic nanopaper structures[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2010, 11(9): 2195-2198. |
| 7 | IWAMOTO S, ISOGAI A, IWATA T. Structure and mechanical properties of wet-spun fibers made from natural cellulose nanofibers[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2011, 12(3): 831-836. |
| 8 | HUANG X S. Fabrication and properties of carbon fibers[J]. Materials, 2009, 2(4): 2369-2403. |
| 9 | YU M F, FILES B S, AREPALLI S, et al. Tensile loading of ropes of single wall carbon nanotubes and their mechanical properties[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(24): 5552-5555. |
| 10 | 祁明辉, 易锬, 莫琪, 等. 硫酸水解辅助高压均质法制备小麦秸秆纳米纤维素[J]. 中国造纸学报, 2020, 35(3): 1-8. |
| QI M H, YI T, MO Q, et al. Preparation of wheat straw nanocellulose by acid hydrolysis assisted high pressure homogenization[J]. Transactions of China Pulp and Paper, 2020, 35(3): 1-8. | |
| 11 | BRAUN B, DORGAN J R. Single-step method for the isolation and surface functionalization of cellulosic nanowhiskers[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10(2): 334-341. |
| 12 | CAI J, ZHANG L N. Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience, 2005, 5(6): 539-548. |
| 13 | HUANG J C, ZHONG Y, ZHANG L N, et al. Distinctive viewpoint on the rapid dissolution mechanism of α-chitin in aqueous potassium hydroxide-urea solution at low temperatures[J]. Macromolecules, 2020, 53(13): 5588-5598. |
| 14 | SWATLOSKI R P, SPEAR S K, HOLBREY J D, et al. Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(18): 4974-4975. |
| 15 | TARDY B L, MATTOS B D, OTONI C G, et al. Deconstruction and reassembly of renewable polymers and biocolloids into next generation structured materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(22): 14088-14188. |
| 16 | ABBOTT A P, CAPPER G, DAVIES D L, et al. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures[J]. Chemical Communications, 2003(1): 70-71. |
| 17 | 胡鹏程, 江伟,钟丽娟, 低共熔溶剂的应用研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2018, 38(10): 53-57. |
| 18 | CHOI Y H, VAN SPRONSEN J, DAI Y T, et al. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology?[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(4): 1701-1705. |
| 19 | WU X Y, YUAN Y, HONG S, et al. Controllable preparation of nano-cellulose via natural deep eutectic solvents prepared with lactate and choline chloride[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2023, 194: 116259. |
| 20 | LI P P, SIRVIÖ J A, HAAPALA A, et al. Cellulose nanofibrils from nonderivatizing urea-based deep eutectic solvent pretreatments[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(3): 2846-2855. |
| 21 | LIU Y Z, GUO B T, XIA Q Q, et al. Efficient cleavage of strong hydrogen bonds in cotton by deep eutectic solvents and facile fabrication of cellulose nanocrystals in high yields[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(9): 7623-7631. |
| 22 | WU Z T, CHEN S Y, LI J, et al. Insights into hierarchical structure-property-application relationships of advanced bacterial cellulose materials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(12): 2214327. |
| 23 | SHEN X P, ZHAO D W, XIE Y J, et al. Cellulose gel mechanoreceptors-principles, applications and prospects[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023: 2214317. |
| 24 | RAHMANIAN V, PIRZADA T, WANG S Y, et al. Cellulose-based hybrid aerogels: Strategies toward design and functionality[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(51): 2102892. |
| 25 | CHEN Y M, ZHANG L, YANG Y, et al. Recent progress on nanocellulose aerogels: Preparation, modification, composite fabrication, applications[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(11): 2005569. |
| 26 | ZHAO D W, ZHU Y, CHENG W K, et al. Cellulose-based flexible functional materials for emerging intelligent electronics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(28): 2000619. |
| 27 | WANG Z H, LEE Y H, KIM S W, et al. Why cellulose-based electrochemical energy storage devices?[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(28): 2000892. |
| 28 | TIAN Y P, SHAO H, LIU X J, et al. Superhydrophobic and recyclable cellulose-fiber-based composites for high-efficiency passive radiative cooling[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(19): 22521-22530. |
| 29 | LI T, ZHAI Y, HE S, et al., A radiative cooling structural material[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6442): 760-763. |
| 30 | CHEN Y P, DANG B K, FU J Z, et al. Cellulose-based hybrid structural material for radiative cooling[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(1): 397-404. |
| 31 | CAI C Y, WEI Z C, DING C X, et al. Dynamically tunable all-weather daytime cellulose aerogel radiative supercooler for energy-saving building[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(10): 4106-4114. |
| 32 | GUO Y H, LU H Y, ZHAO F, et al. Biomass-derived hybrid hydrogel evaporators for cost-effective solar water purification[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(11): 1907061. |
| 33 | LI Y J, GAO T T, YANG Z, et al. 3D-printed, all-in-one evaporator for high-efficiency solar steam generation under 1 Sun illumination[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(26): 1700981. |
| 34 | QI H S, WEI T Q, ZHAO W, et al. An interfacial solar-driven atmospheric water generator based on a liquid sorbent with simultaneous adsorption-desorption[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(43): 1903378. |
| 35 | LI R Y, WANG W B, SHI Y F, et al. Advanced material design and engineering for water-based evaporative cooling[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.2209460. |
| 36 | CHEN Y M, LI S J, LI X L, et al. Liquid transport and real-time dye purification via lotus petiole-inspired long-range-ordered anisotropic cellulose nanofibril aerogels[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(12): 20666-20677. |
| 37 | CHEN G G, LI T, CHEN C J, et al. A highly conductive cationic wood membrane[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(44): 1902772. |
| 38 | ZHU M W, LI Y J, CHEN F J, et al. Plasmonic wood for high-efficiency solar steam generation[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(4): 1701028. |
| 39 | LI T, LIU H, ZHAO X P, et al. Scalable and highly efficient mesoporous wood-based solar steam generation device: Localized heat, rapid water transport[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(16): 1707134. |
| 40 | HAN S B, RUOKO T P, GLADISCH J, et al. Cellulose-conducting polymer aerogels for efficient solar steam generation[J]. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2020, 4(7): 2000004. |
| 41 | LI N, QIAO L F, HE J T, et al. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation and self-powered water wave detection based on an all-cellulose monolithic design[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(7): 2008681. |
| 42 | ZHANG Y, ZHU W K, ZHANG C, et al. Atmospheric water harvesting by large-scale radiative cooling cellulose-based fabric[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(7): 2618-2626. |
| 43 | ZHOU S Y, KONG X Y, ZHENG B, et al. Cellulose nanofiber @ conductive metal-organic frameworks for high-performance flexible supercapacitors[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(8): 9578-9586. |
| 44 | KADUMUDI F B, TRIFOL J, JAHANSHAHI M, et al. Flexible and green electronics manufactured by origami folding of nanosilicate-reinforced cellulose paper[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(42): 48027-48039. |
| 45 | LIN C M, HUANG H, ZHAO H H, et al. Acid- and alkali-resistant and high-performance cellulose paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator by controlling the surface hydrophobicity[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(41): 13669-13679. |
| 46 | CHEN C J, XU S M, KUANG Y D, et al. Nature-inspired tri-pathway design enabling high-performance flexible Li-O2 batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(9): 1802964. |
| 47 | YU B C, PARK K, JANG J H, et al. Cellulose-based porous membrane for suppressing Li dendrite formation in lithium-sulfur battery[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1(3): 633-637. |
| 48 | ZHAO D W, CHEN C J, ZHANG Q, et al. High performance, flexible, solid-state supercapacitors based on a renewable and biodegradable mesoporous cellulose membrane[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(18): 1700739. |
| 49 | PAN R J, XU X X, SUN R, et al. Nanocellulose modified polyethylene separators for lithium metal batteries[J]. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2018, 14(21): e1704371. |
| 50 | FU J, ZHANG J, SONG X P, et al. A flexible solid-state electrolyte for wide-scale integration of rechargeable zinc-air batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(2): 663-670. |
| 51 | ZHANG J, JIANG G P, GOLEDZINOWSKI M, et al. Green solid electrolyte with cofunctionalized nanocellulose/graphene oxide interpenetrating network for electrochemical gas sensors[J]. Small Methods, 2017, 1(11): 1700237. |
| 52 | ZHANG J, FU J, SONG X P, et al. Laminated cross-linked nanocellulose/graphene oxide electrolyte for flexible rechargeable zinc-air batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(14): 1600476. |
| 53 | SEO J Y, LEE Y H, KIM J H, et al. Electrode-customized separator membranes based on self-assembled chiral nematic liquid crystalline cellulose nanocrystals as a natural material strategy for sustainable Li-metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 50: 783-791. |
| 54 | YANG J L, ZHAO X X, ZHANG W, et al. Inside back cover: “pore-hopping” ion transport in cellulose-based separator towards high-performance sodium-ion batterie[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(15): https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202302568. |
| 55 | LIU L M, QIN Y Y, WANG K, et al. Rational design of nanostructured metal/C interface in 3D self-supporting cellulose carbon aerogel facilitating high-performance Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(20): https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.2103681. |
| 56 | CHEN Z M, WANG X F, XUE B C, et al. Self-templating synthesis of 3D hollow tubular porous carbon derived from straw cellulose waste with excellent performance for supercapacitors[J]. ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(7): 1390-1400. |
| 57 | WU Z Y, LIANG H W, CHEN L F, et al. Bacterial cellulose: A robust platform for design of three dimensional carbon-based functional nanomaterials[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49(1): 96-105. |
| 58 | BOMMIER C, XU R, WANG W, et al. Self-activation of cellulose: A new preparation methodology for activated carbon electrodes in electrochemical capacitors[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 13: 709-717. |
| 59 | HAO P, ZHAO Z H, TIAN J, et al. Hierarchical porous carbon aerogel derived from bagasse for high performance supercapacitor electrode[J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(20): 12120-12129. |
| 60 | JIANG L L, LI L, LUO S, et al. Configuring hierarchical Ni/NiO 3D-network assisted with bamboo cellulose nanofibers for high-performance Ni-Zn aqueous batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(27): 14651-14660. |
| 61 | LIU K, MO R W, DONG W J, et al. Nature-derived, structure and function integrated ultra-thick carbon electrode for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(38): 20072-20081. |
| 62 | WANG F, CHEONG J Y, LEE J, et al. Pyrolysis of enzymolysis-treated wood: Hierarchically assembled porous carbon electrode for advanced energy storage devices[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(31): 2101077. |
| 63 | XIE F, XU Z, JENSEN A C S, AU H, et al. Hard-soft carbon composite anodes with synergistic sodium storage performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29: doi:10.1002/adfm. 201901072. |
| [1] | Jiwei LI, Ruihan LIU, Taolin LU, Long PAN, Changjun MA, Qingbo LI, Zhiyun ZHAO, Wen YANG, Jingying XIE. Early fault diagnosis of lithium-ion battery pack based on improved local outlier detection and standard deviation method [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, (): 1-10. |
| [2] | Xuanchen WANG, Da WANG, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Research progress and prospect of potassium ion battery electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1409-1426. |
| [3] | Junlong ZHOU, Lukang ZHAO, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Advances in the research of quantum dots anode for alkali metal ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1392-1408. |
| [4] | Yongshi YU, Xianming XIA, Hongyang HUANG, Yu YAO, Xianhong RUI, Guobin ZHONG, Wei SU, Yan YU. Research progress on sodium metal anode modified by artificial interface layer [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1380-1391. |
| [5] | Wenzhe HAN, Qingsong LAI, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Advances toward manganese-based layered oxide cathodes for potassium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1364-1379. |
| [6] | Shangzhuo LI, Yutong LONG, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Advances toward polyanionic cathode materials for potassium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1348-1363. |
| [7] | Yuwen ZHAO, Huan YANG, Junpeng GUO, Yi ZHANG, Qi SUN, Zhijia ZHANG. Application of magnetic metal elements in sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1332-1347. |
| [8] | Shedong LI, Yingying SONG, Yuhua BIAN, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Status and challenges in the development of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1315-1331. |
| [9] | Xinyu LI, Xuebing HAN, Languang LU, Jianqiu LI, Minggao OUYANG. Optimization of an impedance model for power Li-ion batteries based on a large multiplier current pulse [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1686-1694. |
| [10] | Chuan HU, Zhiwei HU, Zhendong LI, Shuai LI, Hao WANG, Liping WANG. Tailoring LiPF6-base electrolyte solvation structure toward a stable Lithium-rich manganese-based cathode interface [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1604-1615. |
| [11] | Yuhua BIAN, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Jianguo LI, Da WANG, Shangzhuo LI, Wenbin LUO. Role of CoS2/NC in ether-based electrolytes as high-performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1500-1509. |
| [12] | Yifan HAO, Xiayu ZHU, Jing WANG, Jingyi QIU, Hai MING, Zhenhua FANG. Analysis of battery nondestructive testing and monitoring methods [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1713-1737. |
| [13] | Wenchao SHI, Yu LIU, Bomian ZHANG, Qi LI, Chunhua HAN, Liqiang MAI. Research progress and prospect on electrolyte additives for stabilizing the zinc anode interface in aqueous batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603. |
| [14] | Jing ZHU, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Junfeng HAO, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yida WU, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2023 to Mar. 31, 2023) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1553-1569. |
| [15] | Lei LEI, Peng GAO, Nana FENG, Kunpeng CAI, Hai ZHANG, Yang ZHANG. The influences of multifactors in the synthesis progress on the characteristics of lithium lanthanum zirconate solid electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1625-1635. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
