Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (5): 1500-1509.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0001
• Special Issue on Key Materials and Recycling Technologies for Energy Storage Batteries • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuhua BIAN( ), Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO(
), Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO( ), Jianguo LI, Da WANG, Shangzhuo LI, Wenbin LUO
), Jianguo LI, Da WANG, Shangzhuo LI, Wenbin LUO
Received:2023-01-03
Revised:2023-01-13
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-05-29
Contact:
Xuanwen GAO
E-mail:2001520@stu.neu.edu.cn;gaoxuanwen@mail.neu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yuhua BIAN, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Jianguo LI, Da WANG, Shangzhuo LI, Wenbin LUO. Role of CoS2/NC in ether-based electrolytes as high-performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1500-1509.
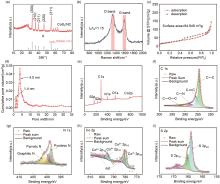
Fig. 2
(a) XRD pattern; (b) Raman spectra; (c) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms; (d) the pore size distribution curves; (e) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) survey spectra of CoS2/NC, and high-resolution XPS spectra of (f) C 1s, (g) N 1s, (h) Co 2p, and (i) S 2p elements in the CoS2/NC"
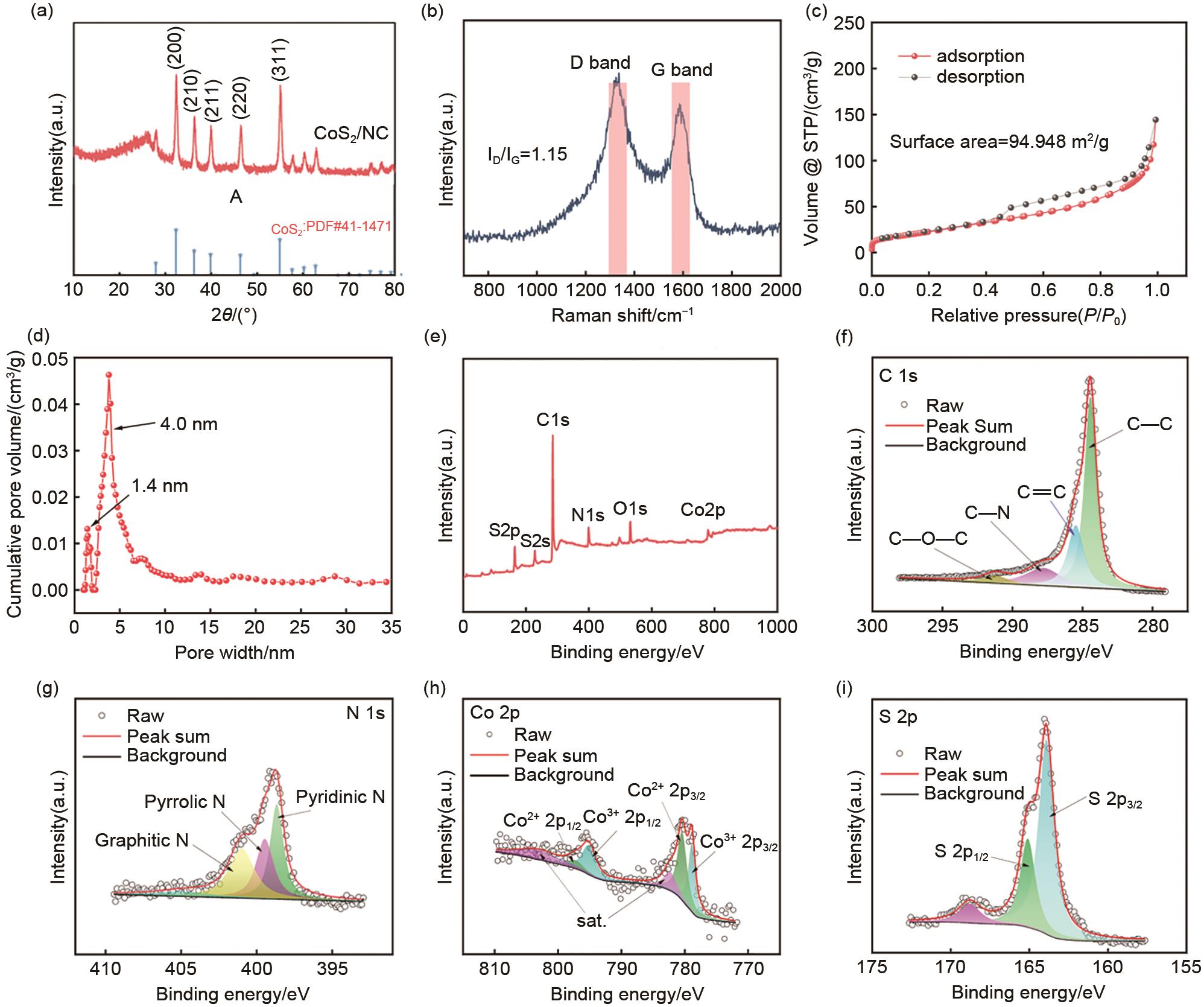

Fig. 3
Cyclic voltammogram (CV) profiles of CoS2/NC in (a) DME, (b) EC/DEC electrolyte at a scan rate of 0.1 mV/s, (c) Rate performance, Discharge/charge curves of CoS2/NC at different current densities in (d) DME, (e) EC/DEC electrolyte, (f) Nyquist plots, (g) Cycling performance at 0.6A/g and the coulombic efficiency, (h) Optical photograph and (i) UV spectrum of Na2S6 with electrolyte stability test"
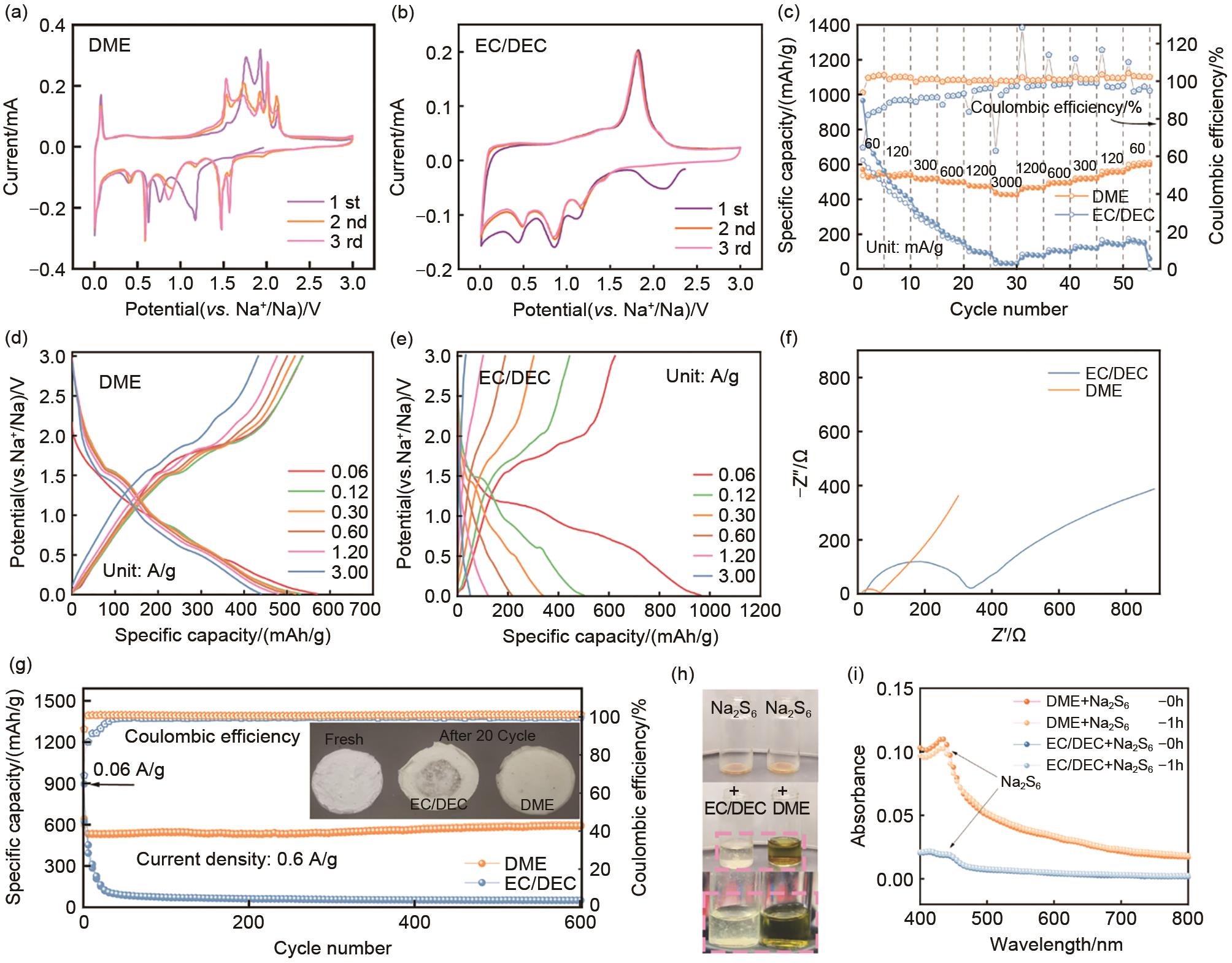

Fig. 5
(a) CV curres of the CoS2/NC electrode in DME electrolyte at a scan rate from 0.1 to 5 mV/s, (b) Plots of peak current versus the corresponding sweep rate for the CoS2/NC electrode in DME electrolyte, (c) Illustration of the pseudocapacitive fraction at the scan rate of 1.0 mV/s for the CoS2/NC electrode in DME electrolyte, (d) Charge contribution percentage of the pseudocapacitive part to the whole capacity of the CoS2/NC electrode in DME electrolyte, (e) CV profiles of the CoS2/NC electrode in EC/DEC electrolyte at a scan rate from 0.1 to 5 mV/s, (f) Plots of peak current versus the corresponding sweep rate for the CoS2/NC electrode in EC/DEC electrolyte, (g) Illustration of the pseudocapacitive fraction at the scan rate of 1.0 mV/s for the CoS2/NC electrode in EC/DEC electrolyte, (h) Charge contribution percentage of the pseudocapacitive part to the whole capacity of the CoS2/NC electrode in EC/DEC electrolyte"
| 1 | STEPHAN A K. The age of Li-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 20193(11): 2583-2584. |
| 2 | LI M, LU J. Lattice strain blights lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nature, 2022: doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-01179-z. |
| 3 | WINTER M, BARNETT B, XU K. Before Li ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(23): 11433-11456. |
| 4 | LI M, LU J. Cobalt in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6481): 979-980. |
| 5 | MANTHIRAM A. Electrical energy storage: Materials challenges and prospects[J]. MRS Bulletin, 2016, 41(8): 624-631. |
| 6 | CHU S Y, GUO S H, ZHOU H S. Advanced cobalt-free cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(23): 13189-13235. |
| 7 | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: Present and future[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529-3614. |
| 8 | VAALMA C, BUCHHOLZ D, WEIL M, et al. A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3(4): 1-11. |
| 9 | LAO M M, ZHANG Y, LUO W B, et al. Alloy-based anode materials toward advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017: doi: 10.1002/adma.201700622. |
| 10 | LI L, ZHENG Y, ZHANG S L, et al. Recent progress on sodium ion batteries: Potential high-performance anodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(9): 2310-2340. |
| 11 | HUANG Y, WANG Z, GUAN M, et al. Sodium-ion batteries: Toward rapid-charging sodium-ion batteries using hybrid-phase molybdenum sulfide selenide-based anodes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020: doi: 10.1002/adma.202003534. |
| 12 | CAO L, GAO X W, ZHANG B, et al. Bimetallic sulfide Sb2S3@FeS2 hollow nanorods as high-performance anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(3): 3610-3620. |
| 13 | LI C C, WANG B, CHEN D, et al. Topotactic transformation synthesis of 2D ultrathin GeS2 nanosheets toward high-rate and high-energy-density sodium-ion half/full batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(1): 531-540. |
| 14 | CHEN L, LUO N J, HUANG S P, et al. Metal-organic framework-derived hollow structure CoS2/nitrogen-doped carbon spheres for high-performance lithium/sodium ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(28): 3951-3954. |
| 15 | HUANG P F, YING H J, ZHANG S L, et al. Multidimensional synergistic architecture of Ti3C2 MXene/CoS2@N-doped carbon for sodium-ion batteries with ultralong cycle lifespan[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132396. |
| 16 | LI Z W, FENG W J, LIN Y Q, et al. Flaky CoS2 and graphene nanocomposite anode materials for sodium-ion batteries with improved performance[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(74): 70632-70637. |
| 17 | LIU X, ZHANG K, LEI K X, et al. Facile synthesis and electrochemical sodium storage of CoS2 micro/nano-structures[J]. Nano Research, 2016, 9(1): 198-206. |
| 18 | MIAO W F, ZHANG Y, LI H T, et al. ZIF-8/ZIF-67-derived 3D amorphous carbon-encapsulated CoS/NCNTs supported on CoS-coated carbon nanofibers as an advanced potassium-ion battery anode[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(10): 5504-5512. |
| 19 | PAN Y L, CHENG X D, GONG L L, et al. Double-morphology CoS2 anchored on N-doped multichannel carbon nanofibers as high-performance anode materials for Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(37): 31441-31451. |
| 20 | PAN Y L, CHENG X D, HUANG Y J, et al. CoS2 nanoparticles wrapping on flexible freestanding multichannel carbon nanofibers with high performance for Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(41): 35820-35828. |
| 21 | ABDUL RAZZAQ A, YUAN X T, CHEN Y J, et al. Anchoring MOF-derived CoS2 on sulfurized polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for high areal capacity lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(3): 1298-1306. |
| 22 | SHADIKE Z, CAO M H, DING F, et al. Improved electrochemical performance of CoS2-MWCNT nanocomposites for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(52): 10486-10489. |
| 23 | SONG Z Y, WANG G, CHEN Y, et al. Construction of hierarchical NiS@C/rGO heterostructures for enhanced sodium storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 435: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134633. |
| 24 | TAO M L, DU G Y, YANG T T, et al. MXene-derived three-dimensional carbon nanotube network encapsulate CoS2 nanoparticles as an anode material for solid-state sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(6): 3018-3026. |
| 25 | WANG P Y, SUN S M, JIANG Y, et al. Hierarchical microtubes constructed by MoS2 nanosheets with enhanced sodium storage performance[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11): 15577-15586. |
| 26 | WANG J J, YUE X Y, XIE Z K, et al. MOFs-derived transition metal sulfide composites for advanced sodium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 404-426. |
| 27 | ZHANG N, YANG Y, FENG X R, et al. Sulfur encapsulation by MOF-derived CoS2 embedded in carbon hosts for high-performance Li-S batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(37): 21128-21139. |
| 28 | ZHANG W M, YUE Z W, WANG Q M, et al. Carbon-encapsulated CoS2 nanoparticles anchored on N-doped carbon nanofibers derived from ZIF-8/ZIF-67 as anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122548. |
| 29 | XIAO F P, YANG X M, WANG D H, et al. Metal-organic framework derived CoS2 wrapped with nitrogen-doped carbon for enhanced lithium/sodium storage performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(11): 12809-12820. |
| 30 | LIN D M, SHI X L, LI K K, et al. Ether-induced phase transition toward stabilized layered structure of MoS2 with extraordinary sodium storage performance[J]. ACS Materials Letters, 2022: doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.2c00262. |
| 31 | TAO H W, ZHOU M, WANG R X, et al. TiS2 as an advanced conversion electrode for sodium-ion batteries with ultra-high capacity and long-cycle life[J]. Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany), 2018, 5(11): doi: 10.1002/advs.201801021. |
| 32 | WANG Z Y, DONG K Z, WANG D, et al. A nanosized SnSb alloy confined in N-doped 3D porous carbon coupled with ether-based electrolytes toward high-performance potassium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(23): 14309-14318. |
| 33 | LI Y, WU F, LI Y, et al. Ether-based electrolytes for sodium ion batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(11): 4484-4536. |
| 34 | YIN X C, REN Y, WU L B, et al. Construction of polysulfides defense system for greatly improving the long cycle life of metal sulfide anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 71: 210-217. |
| 35 | HU M X, JU Z Y, BAI Z C, et al. Revealing the critical factor in metal sulfide anode performance in sodium-ion batteries: An investigation of polysulfide shuttling issues[J]. Small Methods, 2019: doi:10.1002/smtd.201900673. |
| 36 | YIN X C, REN Y, GUO S, et al. Investigating the origin of the enhanced sodium storage capacity of transition metal sulfide anodes in ether-based electrolytes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022: doi:10.1002/adfm.202110017 |
| 37 | SHI X, SONG H H, LI A, et al. Sn-Co nanoalloys embedded in porous N-doped carbon microboxes as a stable anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(12): 5873-5879. |
| 38 | ZHAO S Y, JIA H N, WANG Y, et al. Engineering monodispersed 2 nm Sb2S3 particles embedded in a porphyrin-based MOF-derived mesoporous carbon network via an adsorption method to construct a high-performance sodium-ion battery anode[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(33): 12524-12531. |
| 39 | ZHANG S P, WANG G, ZHANG Z L, et al. 3D graphene networks encapsulated with ultrathin SnS Nanosheets@Hollow mesoporous carbon spheres nanocomposite with pseudocapacitance-enhanced lithium and sodium storage kinetics[J]. Small (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2019, 15(14): doi: 10.1002/smll.201900565. |
| 40 | ZHAO S M, LI J L, CHEN H X, et al. Synthesis of Bi2S3/MoS2 nanorods and their enhanced electrochemical performance for aluminum ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 2020, 17(3): doi:10.1115/1.4045784. |
| [1] | Chuan HU, Zhiwei HU, Zhendong LI, Shuai LI, Hao WANG, Liping WANG. Tailoring LiPF6-base electrolyte solvation structure toward a stable Lithium-rich manganese-based cathode interface [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1604-1615. |
| [2] | Wenchao SHI, Yu LIU, Bomian ZHANG, Qi LI, Chunhua HAN, Liqiang MAI. Research progress and prospect on electrolyte additives for stabilizing the zinc anode interface in aqueous batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603. |
| [3] | Kangkang QU, Yahua LIU, Die HONG, Zhaoxi SHEN, Xiaozhao HAN, Xu ZHANG. Research progress on positive electrolytes for neutral aqueous organic redox flow battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1570-1588. |
| [4] | Yongli YI, Ran YU, Wu LI, Yi JIN, Zheren DAI. Preparation of Mo, Al-doped Li7La3Zr2O12-based composite solid electrolyte and performance of all-solid-state batterys [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1490-1499. |
| [5] | Shedong LI, Yingying SONG, Yuhua BIAN, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Status and challenges in the development of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1315-1331. |
| [6] | Xuanchen WANG, Da WANG, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Research progress and prospect of potassium ion battery electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1409-1426. |
| [7] | Yongshi YU, Xianming XIA, Hongyang HUANG, Yu YAO, Xianhong RUI, Guobin ZHONG, Wei SU, Yan YU. Research progress on sodium metal anode modified by artificial interface layer [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1380-1391. |
| [8] | Jing ZHU, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Junfeng HAO, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yida WU, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2023 to Mar. 31, 2023) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1553-1569. |
| [9] | Lei LEI, Peng GAO, Nana FENG, Kunpeng CAI, Hai ZHANG, Yang ZHANG. The influences of multifactors in the synthesis progress on the characteristics of lithium lanthanum zirconate solid electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1625-1635. |
| [10] | Weibin HUANG, Biao ZHANG, Jincheng FAN, Wei YANG, Hanbo ZOU, Shengzhou CHEN. Preparation and modification of ZIF-8 composite PEO based solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1083-1092. |
| [11] | Cai TANG, Jiangmin JIANG, Xinfeng WANG, Guangfa LIU, Yanhua CUI, Quanchao ZHUANG. Research progress of Li/CF x primary batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1093-1109. |
| [12] | Zhiwen WANG, Qiang YE. Investigation of the mixing loss and guiding strategy of the electrolyte flow in the tanks of a redox flow battery system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1148-1157. |
| [13] | Mai FENG, Nan CHEN, Renjie CHEN. Research progress of low-temperature electrolyte for lithium-ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 792-807. |
| [14] | Kaiyuan XUE, Yan WANG, Junwei LANG, Tian HE, Zuoqiang DAI, Zongmin ZHENG. The progress in applications of dicationic ionic liquids in the energy storage and conversion system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 808-821. |
| [15] | Xiaoyu SHEN, Jing ZHU, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Junfeg HAO, Mengyu TIAN, Hongxiang JI, Zhou JIN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Dec. 1, 2022 to Jan. 31, 2023) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 639-653. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
