Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (3): 825-840.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0751
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chengfan JIANG( ), Jun HUANG(
), Jun HUANG( ), Haibo XIE
), Haibo XIE
Received:2023-10-24
Revised:2023-12-08
Online:2024-03-28
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
Jun HUANG
E-mail:jiangcf9872@163.com;huangj@gzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Chengfan JIANG, Jun HUANG, Haibo XIE. Improving the initial coulombic efficiency of hard carbon materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 825-840.
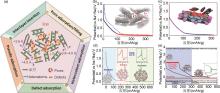
Fig. 1
(a) Multiple sodium storage mechanisms of hard carbon[11]; (b) Sodium insertion into carbon nanosheets and subsequent pore filling[12]; (c) Typical Potential and Capacity Curve of Hard Carbon in Sodium Half-cell[13]; (d) Schematic illustration of the Na-ion storage in hard carbons according to the “adsorption-intercalation” mechanism[14]; (e) Typical potential vs. capacity profile for hard carbons in sodium cells with the associated parameters of interest, such as the irreversible capacity, IR drop, and Na plating[12]"
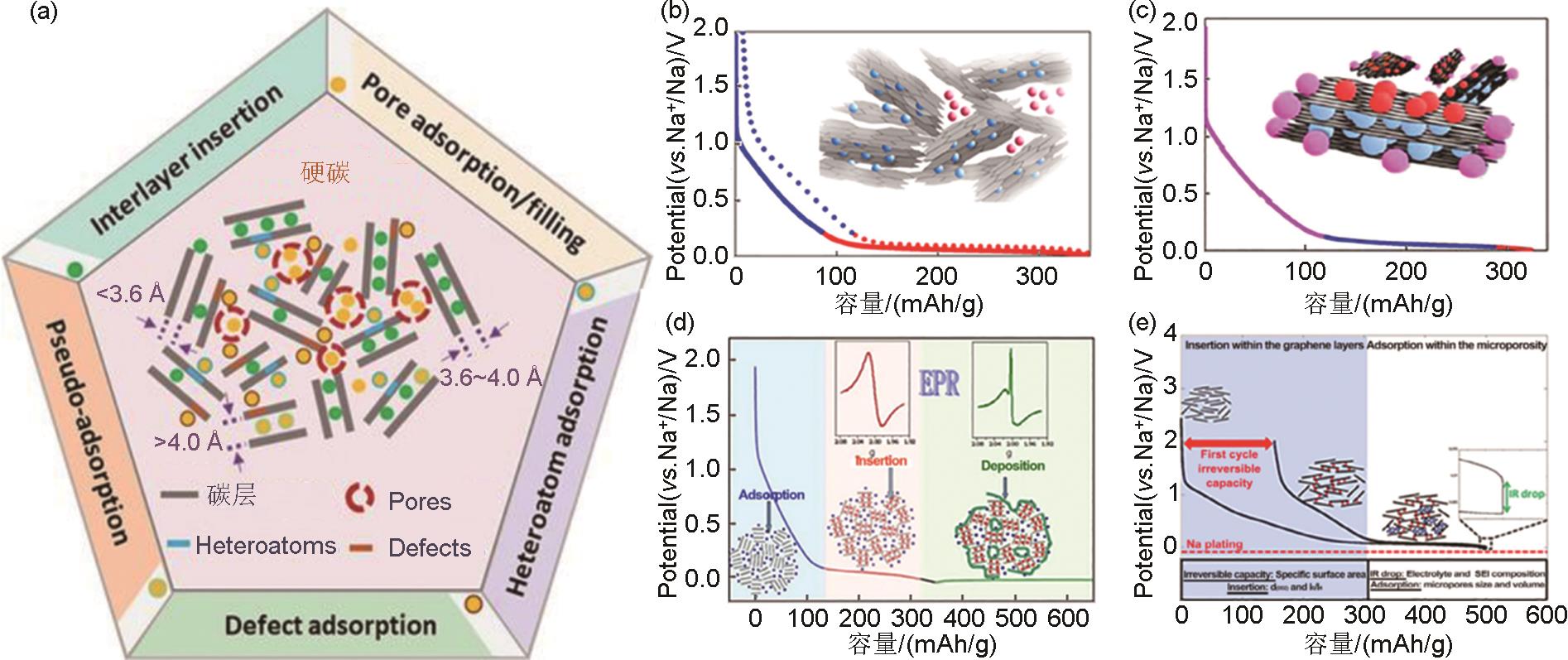
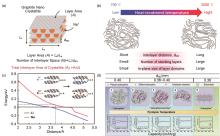
Fig. 3
(a) Structure of graphitic crystallites[18]; (b) Schematics of hard carbon structures obtained at 700 and 2000 ℃ and their structural parameters[19]; (c) Theoretical energy cost for Na and Li ions insertion into carbon as a function of carbon interlayer distance[16]; (d) Schematic illustration of the evolution of the microstructure, sodium storage mechanism and behavior with the pyrolysis temperature of HCs[17]"
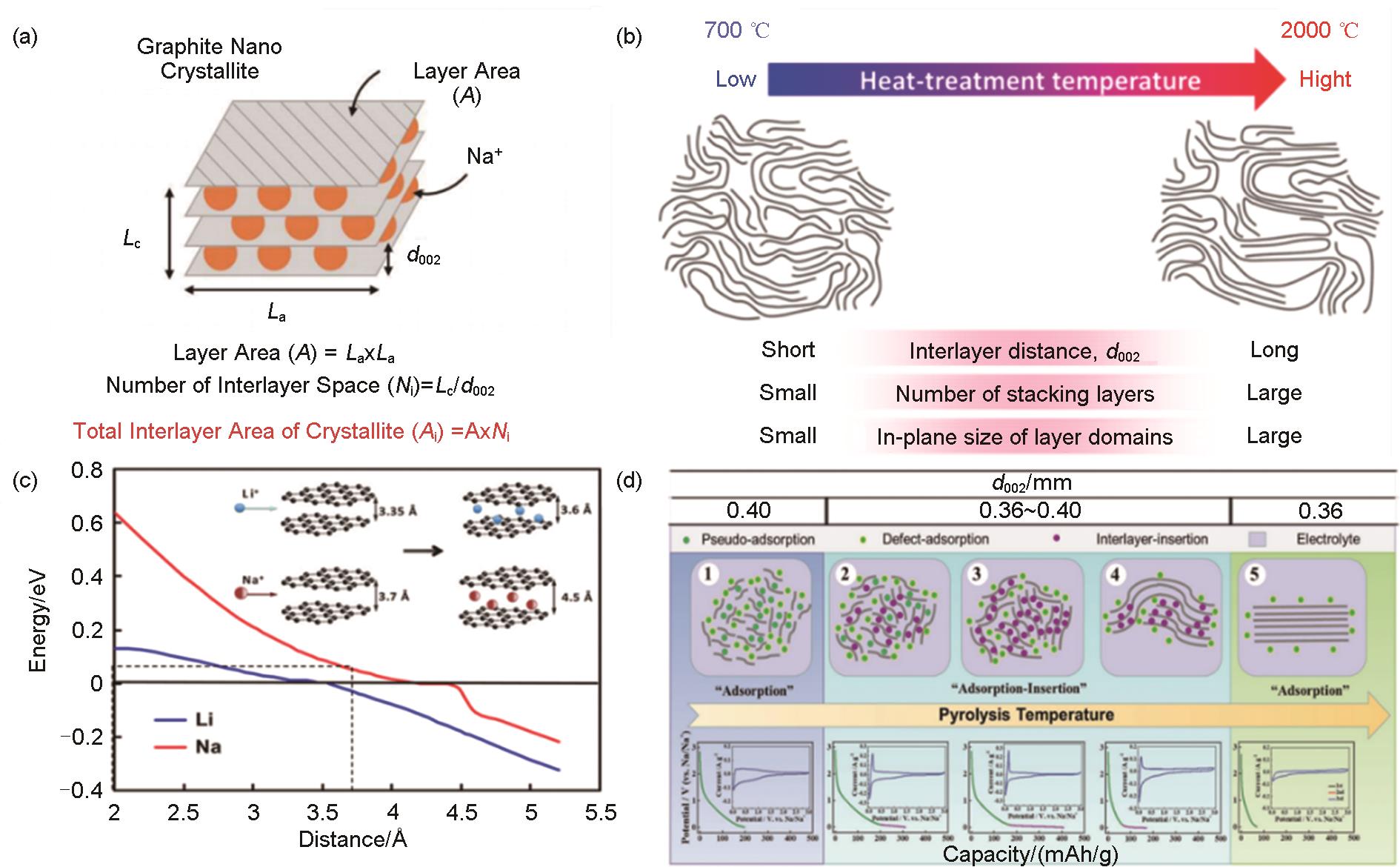
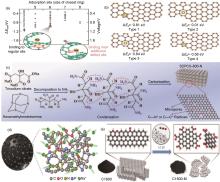
Fig. 4
(a) DFT calculation of chemical adsorption energy of sodium atoms on hard carbon with different structures [24]; (b) DFT calculation of intrinsic defect adsorption energy of sodium atoms[20]; (c) Hard carbon materials prepared by introducing defects rich in pyridine nitrogen during the heat treatment process by adding a nitrogen source[21]; (d) Hard carbon materials prepared by doping multiple elements [22]; (e) Synthesis of carboxyl rich hard carbon by ball milling method [23]"

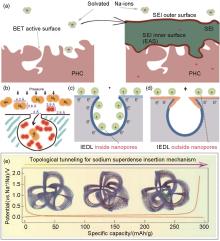
Fig. 8
(a) The behavior of SEI in different pores on the electrolyte accessible surface of the anode[49]; (b) Schematic diagram of commercial carbon molecular sieve[56], Schematic diagram of the formation mechanism of solid electrolyte interface between (c) typical porous carbon and (d) screened carbon after 5 cycles [32]; (e) The insertion mechanism of sodium in topological carbon[50]"
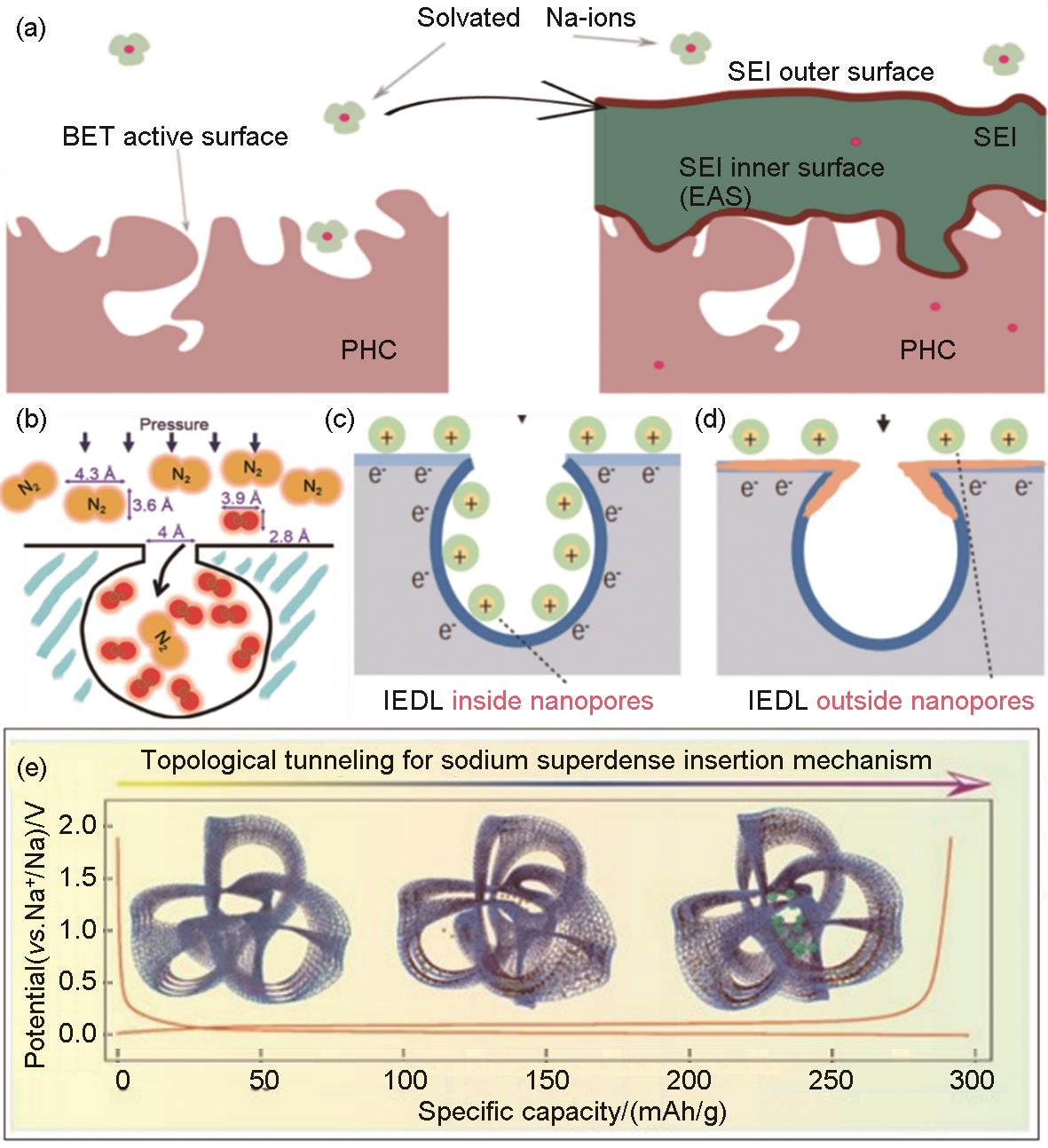
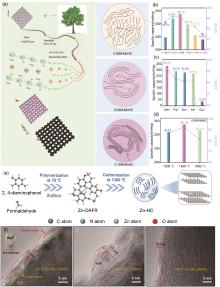
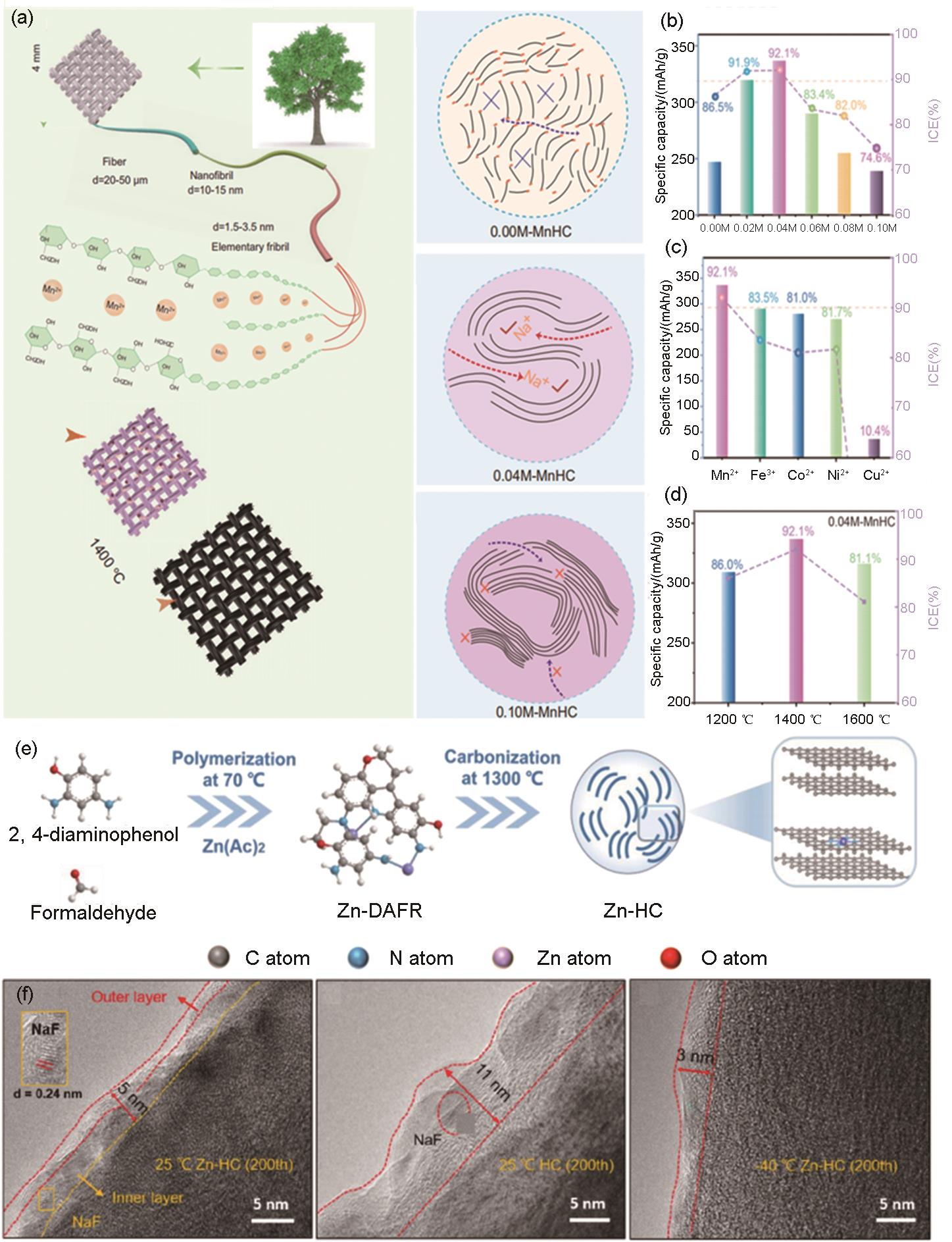
Fig. 9
(a) Mn2+ regulates the carbon layer structure of hard carbon materials; (b) The reversible capacity and ICE change of hard carbon modified by manganese chloride of different concentrations; (c) The reversible capacity and ICE change of hard carbon modified by various metal chloride salts at the optimal concentration; (d) The reversible capacity and ICE of manganese chloride modified hard carbon at different carbonization temperatures with optimal concentration[53]; (e) Schematic illustration of the synthesis for Zn-HC; (f) HRTEM images of Zn-HC and HC electrodes[6]"
| 1 | HUANG J, YUAN K, CHEN Y W. Wide voltage aqueous asymmetric supercapacitors: Advances, strategies, and challenges[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(4): 2108107. |
| 2 | NISHI Y. The development of lithium ion secondary batteries[J]. The Chemical Record, 2001, 1(5): 406-413. |
| 3 | BLOMGREN G E. The development and future of lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2016, 164(1): A5019. |
| 4 | YOSHINO A. The birth of the lithium-ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(24): 5798-5800. |
| 5 | ROBERTS S, KENDRICK E. The re-emergence of sodium ion batteries: testing, processing, and manufacturability[J]. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 2018: 23-33. |
| 6 | LU Z, WANG J, FENG W, et al. Zinc single-atom-regulated hard carbons for high-rate and low-temperature sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023: 2211461. |
| 7 | JIN Q, WANG K, FENG P, et al. Surface-dominated storage of heteroatoms-doping hard carbon for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 27: 43-50. |
| 8 | DING J, ZHANG H, ZHOU H, et al. Sulfur-grafted hollow carbon spheres for potassium-ion battery anodes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(30): 1900429. |
| 9 | XU Y S, GUO S J, TAO X S, et al. High-performance cathode materials for potassium-ion batteries: Structural design and electrochemical properties[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(36): 2100409. |
| 10 | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: present and future[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529-3614. |
| 11 | SUN N, QIU J, XU B. Understanding of sodium storage mechanism in hard carbons: Ongoing development under debate[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(27): 2200715. |
| 12 | BOMMIER C, SURTA T W, DOLGOS M, et al. New mechanistic insights on Na-ion storage in nongraphitizable carbon[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(9): 5888-5892. |
| 13 | IRISARRI E, PONROUCH A, PALACIN M R. Hard carbon negative electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(14): A2476. |
| 14 | DOU X, HASA I, SAUREL D, et al. Hard carbons for sodium-ion batteries: Structure, analysis, sustainability, and electrochemistry[J]. Materials Today, 2019, 23: 87-104. |
| 15 | CHU Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Reconfiguring hard carbons with emerging sodium-ion batteries: A perspective[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023: 2212186. |
| 16 | CAO Y, XIAO L, SUSHKO M L, et al. Sodium ion insertion in hollow carbon nanowires for battery applications[J]. Nano letters, 2012, 12(7): 3783-3787. |
| 17 | SUN N, GUAN Z, LIU Y, et al. Extended "adsorption-insertion" model: a new insight into the sodium storage mechanism of hard carbons[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(32): 1901351. |
| 18 | KATSUYAMA Y, NAKAYASU Y, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Rational route for increasing intercalation capacity of hard carbons as sodium-ion battery anodes[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(21): 5762-5768. |
| 19 | KUBOTA K, SHIMADZU S, YABUUCHI N, et al. Structural analysis of sucrose-derived hard carbon and correlation with the electrochemical properties for lithium, sodium, and potassium insertion[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(7): 2961-2977. |
| 20 | GUO R, LV C, XU W, et al. Effect of intrinsic defects of carbon materials on the sodium storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(9): 1903652. |
| 21 | GAN Q, QIN N, GU S, et al. Extra sodiation sites in hard carbon for high performance sodium ion batteries[J]. Small Methods, 2021, 5(9): 2100580. |
| 22 | WANG G, SHAO M, DING H, et al. Multiple active sites of carbon for high-rate surface-capacitive sodium-ion storage[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(38): 13584-13589. |
| 23 | SUN F, WANG H, QU Z, et al. Carboxyl‐dominant oxygen rich carbon for improved sodium ion storage: synergistic enhancement of adsorption and intercalation mechanisms[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(1): 2002981. |
| 24 | DERINGER V L, MERLET C, HU Y, et al. Towards an atomistic understanding of disordered carbon electrode materials[J]. Chemical communications, 2018, 54(47): 5988-5991. |
| 25 | LU P, SUN Y, XIANG H, et al. 3D amorphous carbon with controlled porous and disordered structures as a highrate anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(8): 1702434. |
| 26 | SHEN F, LUO W, DAI J, et al. Ultra-thick, low-tortuosity, and mesoporous wood carbon anode for high-performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(14): 1600377. |
| 27 | DAHN J R, XING W, GAO Y. The "falling cards model" for the structure of microporous carbons[J]. Carbon, 1997, 35(6): 825-830. |
| 28 | KITSU L L, ANTONIO E N, MARTINEZ T D, et al. Revealing the sodium storage mechanisms in hard carbon pores[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 2302171. |
| 29 | ZHANG M, LI Y, WU F, et al. Boost sodium-ion batteries to commercialization: Strategies to enhance initial Coulombic efficiency of hard carbon anode[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 82: 105738. |
| 30 | LI Z, CHEN Y, JIAN Z, et al. Defective hard carbon anode for Na-ion batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(14): 4536-4542. |
| 31 | WANG Z, FENG X, BAI Y, et al. Probing the energy storage mechanism of quasi-metallic Na in hard carbon for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(11): 2003854. |
| 32 | LI Q, LIU X, TAO Y, et al. Sieving carbons promise practical anodes with extensible low-potential plateaus for sodium batteries[J]. National Science Review, 2022, 9(8): nwac084. |
| 33 | XU T, QIU X, ZHANG X, et al. Regulation of surface oxygen functional groups and pore structure of bamboo-derived hard carbon for enhanced sodium storage performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139514. |
| 34 | MARSH H, REINOSO F R. Activated carbon[M]. Elsevier, 2006. |
| 35 | LIU Y, MERINOV B V, GODDARD III W A. Origin of low sodium capacity in graphite and generally weak substrate binding of Na and Mg among alkali and alkaline earth metals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(14): 3735-3739. |
| 36 | TSAI P, CHUNG S C, LIN S, et al. Ab initio study of sodium intercalation into disordered carbon[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(18): 9763-9768. |
| 37 | LIANG Z, FAN X, ZHENG W, et al. Adsorption and formation of small Na clusters on pristine and double-vacancy graphene for anodes of Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2017, 9(20): 17076-17084. |
| 38 | SUN D, LUO B, WANG H, et al. Engineering the trap effect of residual oxygen atoms and defects in hard carbon anode towards high initial Coulombic efficiency[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 64: 103937. |
| 39 | LIN Q, ZHANG J, KONG D, et al. Deactivating defects in graphenes with Al2O3 nanoclusters to produce long-life and high-rate sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(1): 1803078. |
| 40 | GHIMBEU C M, GÓRKA J, SIMONE V, et al. Insights on the Na+ ion storage mechanism in hard carbon: Discrimination between the porosity, surface functional groups and defects[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 44: 327-335. |
| 41 | HANKEL M, YE D, WANG L, et al. Lithium and sodium storage on graphitic carbon nitride[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(38): 21921-21927. |
| 42 | WANG X, LI G, HASSAN F M, et al. Sulfur covalently bonded graphene with large capacity and high rate for high-performance sodium-ion batteries anodes[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 15: 746-754. |
| 43 | DENG X, XIE K, LI L, et al. Scalable synthesis of self-standing sulfur-doped flexible graphene films as recyclable anode materials for low-cost sodium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2016, 107: 67-73. |
| 44 | QIE L, CHEN W, XIONG X, et al. Sulfur-doped carbon with enlarged interlayer distance as a high-performance anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced science, 2015, 2(12): doi: 10.1002/advs.201500195. |
| 45 | GUO M, HUANG J, KONG X, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of porous phosphorus-doped carbon nanotubes and their use in the oxygen reduction reaction and lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2016, 31(3): 352-362. |
| 46 | WU F, DONG R, BAI Y, et al. Phosphorus-doped hard carbon nanofibers prepared by electrospinning as an anode in sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2018, 10(25): 21335-21342. |
| 47 | LI Z, MA L, SURTA T W, et al. High capacity of hard carbon anode in Na-ion batteries unlocked by PO x Do**[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1(2): 395-401. |
| 48 | SONG M, YI Z, XU R, et al. Towards enhanced sodium storage of hard carbon anodes: Regulating the oxygen content in precursor by low-temperature hydrogen reduction[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 51: 620-629. |
| 49 | ZHENG Y, LU Y, QI X, et al. Superior electrochemical performance of sodium-ion full-cell using poplar wood derived hard carbon anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 18: 269-279. |
| 50 | HE X X, LAI W H, LIANG Y, et al. Achieving all-plateau and high-capacity sodium insertion in topological graphitized carbon[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023: 2302613. |
| 51 | YU Z L, XIN S, YOU Y, et al. Ion-catalyzed synthesis of microporous hard carbon embedded with expanded nanographite for enhanced lithium/sodium storage[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(45): 14915-14922. |
| 52 | GE P, HOU H, CAO X, et al. Multidimensional evolution of carbon structures underpinned by temperature-induced intermediate of chloride for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(6): 1800080. |
| 53 | ZHAO J, HE X X, LAI W H, et al. Catalytic defect-repairing using manganese ions for hard carbon anode with high-capacity and high-initial-coulombic-efficiency in sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023: 2300444. |
| 54 | KOMABA S, MURATA W, ISHIKAWA T, et al. Electrochemical Na insertion and solid electrolyte interphase for hard-carbon electrodes and application to Na-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(20): 3859-3867. |
| 55 | TANG Z, WANG H, WU P F, et al. Electrode-electrolyte interfacial chemistry modulation for ultra-high rate sodium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2022, 134(18): e202200475. |
| 56 | 张俊, 李琦, 陶莹, 等. 钠离子电池筛分型碳:缘起与进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(9): 2825-2833. |
| ZHANG J, LI Q, TAO Y, et al. Sieving carbons for sodium ion batteries: origin and progress[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2825-2833. | |
| 57 | DONG Y, YUAN S, ZHAO W, et al. Tailoring natural anthracite carbon materials towards considerable electrochemical properties with exploration of ester/ether-based electrolyte[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(17): 9668-9681. |
| 58 | JIANG N, CHEN L, JIANG H, et al. Introducing the solvent co-intercalation mechanism for hard carbon with ultrafast sodium storage[J]. Small, 2022, 18(15): 2108092. |
| 59 | XIAO B, SOTO F A, GU M, et al. Lithium-pretreated hard carbon as high-performance sodium-ion battery anodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(24): 1801441. |
| 60 | DOSE W M, JOHNSON C S. Cathode pre-lithiation/sodiation for next-generation batteries[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2022, 31: 100827. |
| 61 | MOEEZ I, JUNG H G, LIM H D, et al. Presodiation strategies and their effect on electrode-electrolyte interphases for high-performance electrodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(44): 41394-41401. |
| 62 | MA R, FAN L, CHEN S, et al. Offset initial sodium loss to improve coulombic efficiency and stability of sodium dual-ion batteries[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2018, 10(18): 15751-15759. |
| 63 | LIU W, CHEN X, ZHANG C, et al. Gassing in Sn-anode sodium-ion batteries and its remedy by metallurgically prealloying Na[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2019, 11(26): 23207-23212. |
| 64 | LIU M, YANG Z, SHEN Y, et al. Chemically presodiated Sb with a fluoride-rich interphase as a cycle-stable anode for high-energy sodium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(9): 5639-5647. |
| 65 | PARK K, YU B C, GOODENOUGH J B. Electrochemical and chemical properties of Na2NiO2 as a cathode additive for a rechargeable sodium battery[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(19): 6682-6688. |
| 66 | TANG J, KYE D K, POL V G. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of sodium powder as electrode additive to improve cycling performance of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 396: 476-482. |
| 67 | 陈杰, 陈伟伦, 张旭, 等. 钠离子电池预钠化技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(11): 3487-3496. |
| CHEN J, CHEN W L, ZHANG X, et al. Research progress in pre-sodium technology for sodium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology. 2022, 11(11): 3487-3496. |
| [1] | Ke LI, Yifan HAO, Zhenhua FANG, Jing WANG, Songtong ZHANG, Xiayu ZHU, Jingyi QIU, Hai MING. Development and military application analysis of high-power chemical power supply system [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 436-461. |
| [2] | Jinya ZHANG, Wenbo ZHOU, Ziyiyi CHENG. Performance comparison of metal foam and fin phase-change energy storage system based on LBM [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 598-607. |
| [3] | Xiaoyun SUN, Deren WANG, Lin MENG, Zhongshan REN, Sensen LI. Design and optimization of cell structure and negative electrode materials for high areal capacity zinc-bromine flow batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 370-380. |
| [4] | Fei HAO, Junming WANG, Chunwei DONG, Linlin WEI, Yang DONG, Zhijiang SU, Wenbing LIANG. Preparation and research of three-dimensional silicon carbon anodes with a hollow structure [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 325-332. |
| [5] | Jiangtian ZHU, Yuan ZHANG, Yibin LUO, Huiting YANG, Jie LI, Xiaoqin SUN. Optimization of 5G communication base station cabinet based on heat storage of phase change material [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2789-2798. |
| [6] | Haoran CAI, Lijue YAN, Xu YANG, Huilin PAN. Structural evolution and sodium-storage performance of O3/P2-Na x Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 multiphasic cathode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2707-2714. |
| [7] | Ding ZHANG, Zixian YE, Zhenming LIU, Qun YI, Lijuan SHI, Huijuan GUO, Yi HUANG, Li WANG, Xiangming HE. Research progress of black phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2482-2490. |
| [8] | Wenda ZAN, Rui ZHANG, Fei DING. Development and application of electrochemical models for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2302-2318. |
| [9] | Zhun FENG. Ultra-flexible halloysite/polyaniline composite electrode based on graphene electrode [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(6): 1794-1803. |
| [10] | Shedong LI, Yingying SONG, Yuhua BIAN, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Status and challenges in the development of room-temperature sodium-sulfur batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1315-1331. |
| [11] | Jidong ZHANG, Zhan YANG, Jianguo HUANG. Fabrication and electrochemical performance of micro-nanostructured C/TiO2/CuMoO4 fibrous composite based on natural cellulose [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1616-1624. |
| [12] | Chuan HU, Zhiwei HU, Zhendong LI, Shuai LI, Hao WANG, Liping WANG. Tailoring LiPF6-base electrolyte solvation structure toward a stable Lithium-rich manganese-based cathode interface [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1604-1615. |
| [13] | Junpeng GUO, Qi SUN, Yuefang CHEN, Yuwen ZHAO, Huan YANG, Zhijia ZHANG. Preparation of three-dimensional multistage iron oxide/carbon nanofiber integrated electrode and sodium storage performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1469-1479. |
| [14] | Ting TING, Qihang LIN, Changyang LIU, Liuzhen BIAN, Chao SUN, QI Ji, Jihua PENG, Shengli AN. Research progress in modification of manganese dioxide as cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 754-767. |
| [15] | Heqing TIAN, Zhaoyang KOU, Junjie ZHOU, Yinsheng YU. Molecular dynamics simulation of structure and thermal properties of LiCl-KCl molten salt nanofluids [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 654-660. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
