Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (3): 770-787.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0771
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhipeng WEN1( ), Kai PAN1(
), Kai PAN1( ), Yi WEI1, Jiawen GUO1, Shanli QIN1, Wen JIANG1, Lian WU2,3(
), Yi WEI1, Jiawen GUO1, Shanli QIN1, Wen JIANG1, Lian WU2,3( ), Huan LIAO1
), Huan LIAO1
Received:2023-10-30
Revised:2023-11-20
Online:2024-03-28
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
Kai PAN, Lian WU
E-mail:wenzhipeng_01@sina.com;pankai_09@sina.com;wulian@gdcri.com
CLC Number:
Zhipeng WEN, Kai PAN, Yi WEI, Jiawen GUO, Shanli QIN, Wen JIANG, Lian WU, Huan LIAO. Research progress in lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode material modification[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 770-787.
Table 1
Preparation method of LiMn1-x Fe x PO4 material"
| 分类 | 制备方法 | 技术简介 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 固相法 | 高温固相法 | 将煅烧分解后可产生挥发性气体的锂源、磷源、铁源、锰源等混合均匀,干燥后在惰性气体保护下烧结,再通过粉碎、筛分除铁等步骤得到磷酸锰铁锂正极材料 | 工艺简单,过程易控,比较容易实现大规模工业生产 | 合成周期长,能耗大,尺寸较大且分布不均匀 |
| 碳热还原法 | 采用还原性的碳源,在高温条件下将Fe3+还原为Fe2+,再将二价铁源与其他原料混合,经煅烧、研磨得到磷酸锰铁锂成品 | 采用廉价三价铁源代替昂贵的二价铁源,可大幅降低生产成本 | 需严格控制碳源的用量,过多或过少都会产生杂质,降低材料的性能 | |
| 液相法 | 水热法/溶剂热法 | 原材料加入溶剂或水中溶解,在高温高压的条件下反应,然后经干燥、研磨、煅烧等步骤得到磷酸锰铁锂正极材料 | 产品结晶度高、粒径尺寸可控,电化学性能优良 | 高温高压的反应条件对设备要求严格,环保压力大 |
| 溶胶-凝胶法 | 各种原料一起溶解在水或者乙醇中,搅拌较长的时间使各组分形成均匀的溶胶,再通过升高温度使体系发生凝胶化,再经过高温焙烧后得到成品 | 产品颗粒粒径均匀且细小,不易团聚,制备过程简单且能耗较低 | 需要控制的影响因素多,干燥、焙烧时间较长,合成周期长 | |
| 共沉淀法 | 可溶性亚铁盐、锰盐、锂盐、磷酸盐等原材料溶于溶剂中,通过调控体系的pH值或加入沉淀剂,使反应物在溶液中形成沉淀,再经离心、洗涤、干燥、煅烧后,得到LiMnFeO4成品 | 产物粒径均匀,材料廉价易得,合成工艺简单,热处理温度低,周期短 | 纳米级沉淀过滤困难,后续废液处理困难,环保压力大 | |
| 喷雾干燥 | 原材料通过液相混合、球磨混合等方式充分混合均匀后,用压力喷雾干燥机进行造粒并直接烧结制备出LiMnFeO4成品 | 产品颗粒球形度高,振实密度高 | 较难得到均一的包覆层 | |
| 其他方法 | 静电纺丝法 | 利用高压电场将电极材料前驱体与有机高分子物质混合液拉伸成极细的纤维,再经高温煅烧后得到纤维状LiMnFeO4材料 | 制备过程简单,纤维状LiMnFeO4材料具有较高的比表面积和孔隙度 | 设备成本较高,有机高分子物质容易受到氧化、水解等因素的影响,其稳定性较差 |
| 模板法 | 模板法是以模板为主体构型去控制、影响和修饰最终产物的形貌,控制尺寸进而改善材料性能的一种合成方法 | 能够控制、影响和修饰目标物质的形貌 | 反应条件苛刻、设备要求高、后处理工序复杂 | |
Table 2
A sum of surface coating modification for LiMn1-x Fe x PO4 materials to improve electrical conductivity"
| 材料 | 合成方法 | 包覆材料 | 倍率性能/(mAh/g) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@C | 水热法 | 碳 | 156.4(0.05 C)、151(0.1 C)、147.6(0.2 C)、145.7(0.5 C)、137.3(1 C)、134.5(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4@C | 喷雾干燥和高温煅烧 | 碳 | 153.8(0.1 C)、114.0(5 C)、95.5(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4@C | 湿法球磨和高温固相 | 碳 | 164.7(0.1 C)、137.7(1 C)、 | [ |
| LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C | 生物衍生琼脂辅助溶胶-凝胶法 | 碳 | 143(1 C)、123(2 C)、 96(5 C)、88(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4/C | 机械化学活化辅助高温碳热还原 | 碳 | 155(0.1 C)、140(1 C)、 122.9(2 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.7Fe0.3 PO4@GO | 高温碳热还原 | 石墨烯 | 116(10 C)、83(30 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.25Mn0.75PO4/C/ rGO | 砂磨辅助喷雾干燥 | 碳和还原石墨烯 | 143.8(1 C)、139.8(2 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C/rGO | 溶剂热法 | 碳和还原石墨烯 | 159.5(0.05 C)、118.7(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C | 喷雾热解法 | 碳 | 151(0.1 C)、133(1 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@N-C | 溶剂热法 | 掺N碳 | 154.7(0.1 C)、110.0(5 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4@N-C | 溶胶-凝胶和静电纺丝 | 掺N碳 | 169.9(0.1 C)、93(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@N-C | 生物矿化法 | 掺N石墨烯 | 168.8(0.05 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@N/S | 溶剂热法 | 掺N/S碳 | 166.83(0.1 C)、96.47(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@N/S-C | 溶剂热法 | 掺N/S碳 | 159.2(0.1 C)、145.7(1 C)、117.3(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@N/S-C | 溶剂热法 | 掺N/S碳 | 156.4(0.1 C)、149.2(1 C)、116.4(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO 4@P-C | 溶胶-凝胶和水热法 | 掺P碳 | 157.8(0.2 C)、93.6(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4@F-C | 溶剂热法 | 掺F碳 | 161.3(0.2 C)、130.0(20 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@B-C | 溶胶-凝胶法 | 掺B碳涂层 | 151.1(0.1 C)、132.5(1 C)、102.5 (5 C)、82.3(10 C)、 | [ |
| LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4@B/P-C | 溶胶-凝胶和水热法 | B/P双掺杂碳包覆 | 159.6(0.1 C)、97.1(20 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@LiAlO2@C | 溶剂热法 | LiAlO2和碳 | 137.6(0.05 C)、113.2(5 C) | [ |
| 0.9LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4·0.1Na3V2(PO4)2F3/C | 溶剂热法 | Na3V2(PO4)2F3和碳 | 125.5(1 C)、106.4(3 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.5Fe 0.5PO4@C-3Li3VO4 | 湿式球磨法 | Li3VO4和碳 | 156(0.1 C)、144(1 C)、125(10C) | [ |
| C/LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@Li0.33La0.56TiO3(3%) | 高温煅烧 | Li0.33La0.56TiO3和碳 | 146(0.05 C)、131.3(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@/NS-C@ Li2ZrO3(1%) | 溶剂热合成和煅烧 | Li2ZrO3和掺N/S碳 | 166.8(0.1 C)、118.9(5 C) | [ |
| C/ LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4@Li2SiO3(1%) | 固相反应和原位镀膜法 | Li2SiO3和碳 | 157.6(0.1 C)、106.3(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@Li3PO4/C | 固相法结合冷冻干燥法 | Li3PO4和碳 | 150(0.1 C)、144(1 C)、136(5 C) | [ |
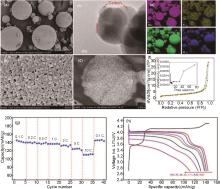
Fig. 7
SEM images of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 for the micron-size secondary particles (a) and nanosized primary particles (b); (c) HR-TEM image of the nanosized primary particles; (d) A cross-section SEM image of one single micron-size secondary particle; (e) EDX mapping images of Mn, Fe, P, O elements of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 secondary particles; (f) Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms; (g) Rate performance and (h) the corresponding charge-discharge profiles at different rates of Li/ LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 half cells [61]"
Table3
A sum of morphology control modification for LiMn1-x Fe x PO4 materials to improve electrical conductivity"
| 材料 | 合成方法 | 形貌 | 倍率性能/(mAh/g) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C | 溶剂热法 | 纳米椭球 | 150.9(0.05 C)、134.6(1 C)、107.5(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 | 固相法 | 微米球 | 122(0.2 C)、118(0.5 C)、113(1 C)、109(2 C)、106(3 C) | [ |
| LiMn 0.5Fe0.5PO4 | 高温固相法 | 纳米球 | 141(0.1 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.1Mn0.9PO4 | 溶剂热法 | 纺锤状纳米 | 129.7(0.1 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 | 水热法 | 纳米棒 | 106.4(0.1 C) | [ |
| LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C | 溶剂热法 | 纳米棒 | 157(0.2 C)、119(5 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C | 溶剂热法 | 纳米棒 | 140(0.1 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4@C | 喷雾干燥法 | 微纳球 | 144.9(0.1 C)、140.2(0.2 C)、125.2(5 C)、110.5(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 | 机械化学液相活化 | 微纳球 | 159(0.1 C)、130(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 | 共沉淀法、喷雾干燥法、高温烧结法 | 微纳球 | 156(0.1 C)、147(1 C)、133(10 C) | [ |
| LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C | 高温固相法、液相法、喷雾干燥法 | 微纳球 | 162.5(0.1 C)、101.2(10 C) | [ |
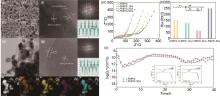
Fig. 9
(a)—(d) SEM images of LFMP/C, LFMP/C-1Ca, LFMP/C-3Ca, and LFMP/C-5Ca, respectively; (e) TEM images and (f) HRTEM with corresponding FFT images of LFMP/C; (g) HRTEM with corresponding FFT images of LFMP/C-3Ca; (h), (i) EDS maps of LFMP/C-3Ca sample;(m) Nyquist plots and (n) fitting results (Inset is equivalent circuit) of LFMP/C, LFMP/C-1Ca, LFMP/C-3Ca, and LFMP/C-5Ca; (o) calculated DLi+ for the LFMP/C and LFMP/C-3Ca during discharge (Inset is corresponding GITT curves)[74]"
Table 4
A sum of ion doping modification for LiMn1-x Fe x PO4 materials to improve electrical conductivity"
| 掺杂元素 | 最佳掺杂量 | 倍率性能/(mAh/g) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | Li0.97Na0.03Mn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C | 141.7(0.05C)、125.0(1C) 、89.5(5C) | [ |
| Na+ | Li0.98Na0.02Fe0.65Mn0.35PO4/C | 136.3(0.1C) | [ |
| K+ | Li0.97K0.03Fe0.95Mn0.05PO4/C | 145.07(5C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiFe0.48Mn0.48Mg0.04PO4 | 152.2 (0.1C)、146.3 (10C)、107.8 (20C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiMn0.6Fe0.39Mg0.01PO4/C | 159.6 (0.2C) 、124.5 (10C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiMn0.8Fe0.19Mg0.01PO4/C | 146.6 (0.1C) 、116.0 (5C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiFe0.7Mn0.25Mg0.05PO4/C | 163.2 (0.1C)、155.2 (0.2C) 、149.1 (0.5C) 、142.0 (1C) | [ |
| Co2+ | LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4-1%Co/C | 165 (0.1C) 、154 (1C) 、150 (5C)、147(10C) | [ |
| Ni2+ | LiMn0.6Fe0.38Ni0.02PO4/C | 159.3 (0.2C)、149.8 (1C) 、143.5 (2C) 、135.7 (5C)、125.1 (10C) 、115.4 (15C) | [ |
| Ni2+ | LiMn0.8Fe0.19Ni0.01PO4/C | 157.3(0.5C)、119.1(10C)、102.5(20C) | [ |
| Ca2+ | LiFe0.497Mn0.5Ca0.03PO4@C | 162.6 (0.1C) 、105.7 (10C)、53.1 (50C) | [ |
| Zn2+ | LiMn0.9Fe0.05Zn0.05PO4/C | 151.3 (0.1C) 、128.4 (1C) | [ |
| Cr3+ | LiFe0.4Mn0.595Cr0.005PO4/C | 164.0 (0.1C) 、156.2 (0.5C) 、147.5 (2C)、139.3 (5C) | [ |
| V3+ | LiMn0.8Fe0.155V0.03□0.015PO4(□为Fe空位) | 155 (0.1C) | [ |
| Y3+ | LiFe0.5Mn0.49Y0.01PO4@C | 160 (0.1C) 、44.89 (10C) | [ |
| Ti4+ | LiMn0.6Fe0.38Ti0.02PO4/C | 143.5 (1C) 、126.8 (10C) | [ |
| Nb5+ | LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C-1%Nb | 152 (0.1C) 、115 (5C) | [ |
| 1 | PORTHAULT H, LE CRAS F, FRANGER S. Synthesis of LiCoO2 thin films by sol/gel process[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(19): 6262-6267. |
| 2 | PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, GOODENOUGH J B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(4): 1188-1194. |
| 3 | GAO X L, LIU X H, XIE W L, et al. Multiscale observation of Li plating for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Rare Metals, 2021, 40(11): 3038-3048. |
| 4 | YANG S C, ZHOU C C, WANG Q, et al. Highly aligned ultra-thick gel-based cathodes unlocking ultra-high energy density batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2022, 5(4): 1332-1339. |
| 5 | 王伟东, 仇卫华, 丁倩倩, 等. 锂离子电池三元材料: 工艺技术及生产应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2015. |
| WANG W D, QIU W H, DING Q Q. Nickel cobalt manganese based cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2015. | |
| 6 | NWACHUKWU I M, NWANYA A C, EKWEALOR A B C, et al. Recent progress in Mn and Fe-rich cathode materials used in Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 54: 105248. |
| 7 | PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, GOODENOUGH J B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(4): 1188. |
| 8 | PADHI A K, NANJUNDASWAMY K S, MASQUELIER C, et al. Effect of structure on the Fe3+/Fe2+ redox couple in iron phosphates[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(5): 1609-1613. |
| 9 | WI S, PARK J, LEE S, et al. Insights on the delithiation/lithiation reactions of LixMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 mesocrystals in Li+ batteries by in situ techniques[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 39: 371-379. |
| 10 | DENG Y F, YANG C X, ZOU K X, et al. Recent advances of Mn-rich LiFe1- yMnyPO4 (0.5≤y≤1.0) cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(13): 1601958. |
| 11 | JIANG F, QU K, WANG M S, et al. Atomic scale insight into the fundamental mechanism of Mn doped LiFePO4[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2020, 4(6): 2741-2751. |
| 12 | 杨毅. 锂离子电池正极材料LiFexMn1- x PO4/C溶剂热法制备及改性研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2021. |
| YANG Y. Solvothermal preparation and modification of LiFexMn1- x PO4/C cathode material for lithium ion batteries[D].Nanning: Guangxi University, 2021. | |
| 13 | 董林涛, 孙德业, 刘建, 等. 不同铁源对磷酸锰铁锂电化学性能的影响[J]. 电源技术, 2020, 44(1): 9-12, 20. |
| DONG L T, SUN D Y, LIU J, et al. Effect of different iron sources on electrochemical properties of lithium manganese iron phosphate[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 44(1): 9-12, 20. | |
| 14 | LI S Q, MENG X Y, YI Q, et al. Structural and electrochemical properties of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 as a cathode material for flexible lithium-ion batteries and self-charging power pack[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 52: 510-516. |
| 15 | DU K, ZHANG L H, CAO Y B, et al. Synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C by co-precipitation method and its electrochemical performances as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 136(2/3): 925-929. |
| 16 | ZOU Q Q, ZHU G N, XIA Y Y. Preparation of carbon-coated LiFe0.2Mn0.8PO4 cathode material and its application in a novel battery with Li4Ti5O12 anode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 206: 222-229. |
| 17 | 刘帅杰, 孙妍, 邓子昭. 磷酸锰铁锂正极材料研究进展[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2023:1-10. |
| LIU S J,SUN Y, DENG Z Z. Research progress of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2023, 1-10. | |
| 18 | 饶媛媛, 王康平, 曾晖. 磷酸锰铁锂材料在锂电池中的研究进展[J]. 电源技术, 2016, 40(2): 455-457. |
| RAO Y Y, WANG K P, ZENG H. Development of LiMnxFe1- xPO4 cathodes in lithium ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 40(2): 455-457. | |
| 19 | 庄慧. 磷酸锰铁锂基正极材料的组成调控、制备优化与电化学性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. |
| ZHUANG H. Composition control, preparation optimization and electrochemical performance of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4-based cathode materials[D].Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 20 | GUAN P Y, ZHOU L, YU Z L, et al. Recent progress of surface coating on cathode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 43: 220-235. |
| 21 | 田世宇. 高压实密度磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的合成与性能研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2022. |
| TIAN S Y. Synthesis and performance study of high compaction density lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials[D].Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2022. | |
| 22 | YI T, Peng P, Fang Z, et al. Carbon-coated LiMn1 -xFexPO4 (0≤x≤0.5) nanocomposites as high-performance cathode materials for Li-ion battery[J]. Composites Part B, 2019, 175: 107067. |
| 23 | HUANG S L, LIN W Z, LI L W, et al. Pathway for high-energy density LiMnFePO4 cathodes[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2023, 33(1): 126-131. |
| 24 | XIONG Y L, WEI Y, RONG W Y, et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of carbon-coated LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 113001. |
| 25 | LU C H, SUBBURAJ T, CHIOU H T, et al. Facile sol-gel synthesis of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials fostered by bio-derived natural agar[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(2): 1051-1056. |
| 26 | PODGORNOVA O A, VOLFKOVICH Y M, SOSENKIN V E, et al. Increasing the efficiency of carbon coating on olivine-structured cathodes by choosing a carbon precursor[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2022, 907: 116059. |
| 27 | CHEN Z W, WANG W G, DUAN J G, et al. Highly efficient synthesis of nano LiMn0.90Fe0.10PO4/C composite via mechanochemical activation assisted calcination[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(11): 18483-18490. |
| 28 | DING D, MAEYOSHI Y, KUBOTA M, et al. Highly improved performances of LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4 cathode with in situ electrochemically reduced graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 793: 627-634. |
| 29 | XIE X M, ZHANG B C, HU G R, et al. A new route for green synthesis of LiFe0.25Mn0.75PO4/C@rGO material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 853: 157106. |
| 30 | WU K P, YIN S, WANG S, et al. Construction of submicron-sized LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C enwrapped into graphene framework for advanced Li-storage[J]. Carbon, 2020, 169: 55-64. |
| 31 | WANG Y Z, HU G R, CAO Y B, et al. Highly atom-economical and environmentally friendly synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/rGO/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 354: 136743. |
| 32 | YANG L T, XIA Y G, FAN X, et al. Constructing durable carbon layer on LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 with superior long-term cycling performance for lithium-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 191: 200-206. |
| 33 | ZHANG K, LI Z X, LI X, et al. Perspective on cycling stability of lithium-iron manganese phosphate for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Rare Metals, 2023, 42(3): 740-750. |
| 34 | FAN R Z, FAN C L, HU Z, et al. Construction of high performance N-doped carbon coated LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 nanocrystal cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 876: 160090. |
| 35 | CHEN W Y, XU D H, CHEN Y C, et al. In situ electrospinning synthesis of N-doped C nanofibers with uniform embedding of Mn doped MFe1- xMnxPO4 (M = Li, Na) as a high performance cathode for lithium/sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2020, 7(19): 2000684. |
| 36 | HOU Y K, PAN G L, SUN Y Y, et al. LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/carbon Nanospheres@Graphene nanoribbons prepared by the biomineralization process as the cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(19): 16500-16510. |
| 37 | GUO L Q, REN L, WAN L, et al. Heterogeneous carbon/N-doped reduced graphene oxide wrapping LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 composite for higher performance of lithium ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 476: 513-520. |
| 38 | ZHANG B Q, WANG S Z, LIU L, et al. One-pot solvothermal synthesis of S-doped LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@N/S-doped C core-shell structured composites for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Letters, 2022, 323: 132586. |
| 39 | SONG Z Y, CHEN S L, DU S, et al. Construction of high-performance LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode by using quinoline soluble substance from coal pitch as carbon source for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 927: 166921. |
| 40 | LIANG Y L, CHEN S L, FAN C L, et al. High-performance LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode prepared by using the toluene-soluble component of pitch as a carbon source[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(13): 19103-19119. |
| 41 | CUI X L, TUO K Y, DONG H, et al. Modification of phosphorus-doped carbon coating enhances the electrochemical performance of LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4 cathode material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 885: 160946. |
| 42 | YAN X, SUN D Y, WANG Y Q, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4 nanoplates from multiple interface modification by using fluorine-doped carbon coating[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(6): 4637-4644. |
| 43 | ZENG T T, HU Z, ZHOU Z Y, et al. Boron-catalyzed graphitization carbon layer enabling LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathode superior kinetics and Li-storage properties[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(2): 2201390. |
| 44 | TUO K Y, MAO L P, DING H, et al. Boron and phosphorus dual-doped carbon coating improves electrochemical performances of LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4 cathode materials[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(8): 8003-8015. |
| 45 | YI T F, LI Y, FANG Z K, et al. Improving the cycling stability and rate capability of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C nanorod as cathode materials by LiAlO2 modification[J]. Journal of Materiomics, 2020, 6(1): 33-44. |
| 46 | ZHANG Z J, HU G R, CAO Y B, et al. Novel synergistic 0.9LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4·0.1Na3V2(PO4)2F3/C nano-hybrid cathode with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 303: 29-34. |
| 47 | YU M, LI J, NING X H. Improving electrochemical performance of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode by hybrid coating of Li3VO4 and carbon[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 368: 137597. |
| 48 | CHANG H, LI Y, FANG Z K, et al. Construction of carbon-coated LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@Li0.33La0.56TiO3 nanorod composites for high-performance Li-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(28): 33102-33111. |
| 49 | ZHANG B Q, WANG S Z, LIU L, et al. Enhancement of Li2ZrO3 modification of the cycle life of N/S-doped LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C composite cathodes for lithium ion batteries[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2023, 39(14): 5187-5198. |
| 50 | LIU X C, OUYANG B X, HAO R, et al. Li2SiO3 modification of C/LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 for high performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(16): e202200609. |
| 51 | LI Y C, XING B Y, WANG Z G, et al. Constructing a hierarchical LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode via comodification of Li3PO4 and graphite for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(9): 10983-10993. |
| 52 | PENG Z D, ZHANG B C, HU G R, et al. Green and efficient synthesis of micro-nano LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C composite with high-rate performance for Li-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 387: 138456. |
| 53 | 张凯成. 磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的合成与改性研究[D]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2022. |
| ZHANG K C. Study on synthesis and modification of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode material[D].Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2022. | |
| 54 | LUO T, ZENG T T, CHEN S L, et al. Structure, performance, morphology and component transformation mechanism of LiMn0·8Fe0·2PO4/C nanocrystal with excellent stability[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 834: 155143. |
| 55 | YANG L, CHANG W G, XIE C G, et al. Rational design of the micron-sized particle size of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathode material with enhanced electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries[J]. Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(1): 015527. |
| 56 | WANG L, LI Y, WU J, et al. Synthesis mechanism and characterization of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C composite cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 839: 155653. |
| 57 | DAI Z J, WANG L, HE X M, et al. Morphology regulation of nano LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4 by solvothermal synthesis for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 112: 144-148. |
| 58 | XU C C, WANG Y, LI L, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis mechanism and electrochemical performance of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 cathode material[J]. Rare Metals, 2019, 38(1): 29-34. |
| 59 | DENG Z W, WANG Q, PENG D C, et al. Fast precipitation-induced LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C nanorods with a fine size and large exposure of the (010) faces for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 794: 178-185. |
| 60 | XIONG J W, WANG Y Z, WANG Y Y, et al. PVP-assisted solvothermal synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nanorods as cathode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(7): 9018-9024. |
| 61 | ZHANG X, HOU M Y, TAMIRATE A G, et al. Carbon coated nano-sized LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 porous microsphere cathode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448: 227438. |
| 62 | LI J L, WANG Y, WU J H, et al. Preparation of enhanced-performance LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries by using a divalent transition-metal phosphate as an Intermediate[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2017, 4(1): 175-182. |
| 63 | 熊俊威. 锂离子电池正极材料LiFe0.2Mn0.8PO4制备及性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. |
| XIONG J W. Preparation and properties of cathode material LiFe0.2Mn0.8PO4 for lithium ion batteries[D].Jinan: Shandong University, 2017. | |
| 64 | LI R, FAN C L, ZHANG W H, et al. Structure and performance of Na+ and Fe2+ co-doped Li1- xNaxMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nanocapsule synthesized by a simple solvothermal method for lithium ion batteries[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 10501-10510. |
| 65 | QIAO S P, ZHU L Z, HAN E S, et al. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of Na and Mg coDoped LiFe0.65Mn0.35PO4/C cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2019, 14(12): 10616-10629. |
| 66 | GENG J, ZOU Z G, WANG T X, et al. Synthesis and electrochemical behavior of K+ and Mn2+ Co-doped LiFePO4/C as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries and the mechanism of modification[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2023, 933: 117275. |
| 67 | JANG D, PALANISAMY K, KIM Y, et al. Structural and electrochemical properties of doped LiFe0.48Mn0.48Mg0.04PO4 as cathode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Science and Technology, 2013, 4(3): 102-107. |
| 68 | ZHANG K C, CAO J R, TIAN S Y, et al. The prepared and electrochemical property of Mg-doped LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2021, 27(11): 4629-4637. |
| 69 | CHU X, CHEN W, FANG H S. Hydrothermal synthesis of olivine phosphates in the presence of excess phosphorus: A case study of LiMn0.8Fe0.19Mg0.01PO4[J]. Ionics, 2021, 27(8): 3259-3269. |
| 70 | XIA K, LIANG R, LUO Y, et al. Solid-state preparation and electrochemical properties of Mg2+-doped LiFe0.7Mn0.3PO4/C as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2022, 17(12): 221273. |
| 71 | LIU S J, ZHENG J G, ZHANG B, et al. Engineering manganese-rich phospho-olivine cathode materials with exposed crystal{0 1 0}facets for practical Li-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 139986. |
| 72 | TIAN S Y, ZHANG K C, CAO J R, et al. Spherical Ni-doped LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C composites with high-rate performance[J]. Ionics, 2021, 27(7): 2877-2887. |
| 73 | WANG Y, YANG H, WU C Y, et al. Facile and controllable one-pot synthesis of nickel-doped LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 nanosheets as high performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(35): 18674-18683. |
| 74 | LIU W F, LIU X C, HAO R, et al. Contribution of calcium ion doping to the rate property for LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2023, 929: 117117. |
| 75 | YI H H, HU C L, HE X M, et al. Electrochemical performance of LiMnPO4 by Fe and Zn co-doping for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2015, 21(3): 667-671. |
| 76 | XIAO P, CAI Y Y, CHEN X P, et al. Improved electrochemical performance of LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C with Cr3+ doping[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(50): 31558-31566. |
| 77 | WU T, LIU J, SUN L, et al. V-insertion in Li(Fe, Mn)FePO4[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 383: 133-143. |
| 78 | ZHENG J W, YANG J W, WU J M, et al. Y3+ doping and electrochemical properties of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4@C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 960: 170610. |
| 79 | JIN H B, ZHANG J H, QIN L, et al. Dual modification of olivine LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 cathodes with accelerated kinetics for high-rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(2): 1029-1034. |
| [1] | Xueling ZHANG, Qiang YE, Junheng GU, Haoyun XUN, Qi ZHANG, Chuanxiao CHENG, Tingxiang JIN, Yeqiang ZHANG. Preparation and adsorption heat storageperformance study of MgSO4-LiCl@MEG composite heat storage materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2778-2788. |
| [2] | Zhengguang ZHAO, Zhenying CHEN, Guangqun ZHAI, Xi ZHANG, Xiaodong ZHUANG. Preparation of Sc/O-doped sulfide electrolyte for all-solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2412-2423. |
| [3] | Wenzhe HAN, Qingsong LAI, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Advances toward manganese-based layered oxide cathodes for potassium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1364-1379. |
| [4] | Yanqin GUO, Zhen ZENG, Hongguang ZHANG, Ziye LING, Zhengguo ZHANG, Xiaoming FANG. Investigation of heat transfer enhancement mechanism and performance of phase change materials using expanded graphite in double helical coils [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(12): 3678-3689. |
| [5] | Fa MAO, Xuelai ZHANG, Weisan HUA. Research progress of aluminum potassium sulfate dodecahydrate phase-change material for thermal energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(1): 120-130. |
| [6] | Binwei ZHANG, Zidong WEI, Shigang SUN. The recent progress and future opportunities of Na2S cathode for room temperature sodium sulfur batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2811-2824. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yan, WANG Hai, LIU Zhaomeng, ZHANG Deliu, WANG Jiadong, LI Jianzhong, GAO Xuanwen, LUO Wenbin. Research progress of nickel-rich ternary cathode material ncm for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1693-1705. |
| [8] | LI Yitao, SHEN Kaier, PANG Quanquan. Advance in organics enhanced sulfide-based solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1902-1918. |
| [9] | Chaochao WEI, Chuang YU, Zhongkai WU, Linfeng PENG, Shijie CHENG, Jia XIE. Research progress of Li3PS4 solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1368-1382. |
| [10] | Liangtao XIONG, Jifen WANG, Huaqing XIE, Xuelai ZHANG. Effect of vacancy defects on thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene by molecular dynamics [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1322-1330. |
| [11] | Xiaohan FENG, Jie SUN, Jianhao HE, Yihua WEI, Chenggang ZHOU, Ruimin SUN. Research progress in LiFePO4 cathode material modification [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(2): 467-486. |
| [12] | Sifei ZHOU, Jun LI, Xiaofei WANG, Daoming ZHANG, Haoliang XUE. Research progress in the conductivity model of lithium battery electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 3688-3698. |
| [13] | Linsen ZHANG, Shiqi WANG, Lixia WANG, Yanhua SONG. Synthesis and performances of Li+ modified g-C3N4 for PEO-based composite solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 3463-3469. |
| [14] | Minhui LIAO, Daxiang YANG, Yang ZHOU, Renjie WAN, Ruiping LIU, Qiang WANG. Preparation and properties study of glass fiber cloth-based multilayer composite solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(10): 3090-3099. |
| [15] | Sifei ZHOU, Jun LI, Daoming ZHANG, Haoliang XUE, Xiaofei WANG. Statistics method-based optimization of electrolyte conductivity of lithium-ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(10): 3364-3370. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
