Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (2): 357-365.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0555
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ke XU1( ), Juexi CHEN1, Yao MENG1, Zhiye YUAN2, Xingyan WANG1(
), Juexi CHEN1, Yao MENG1, Zhiye YUAN2, Xingyan WANG1( )
)
Received:2022-09-28
Revised:2022-10-25
Online:2023-02-05
Published:2023-02-24
Contact:
Xingyan WANG
E-mail:1971778912@qq.com;xywangxtu@xtu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Ke XU, Juexi CHEN, Yao MENG, Zhiye YUAN, Xingyan WANG. Preparation of Cu-NiCoP microspheres and their supercapacitive performance[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 357-365.
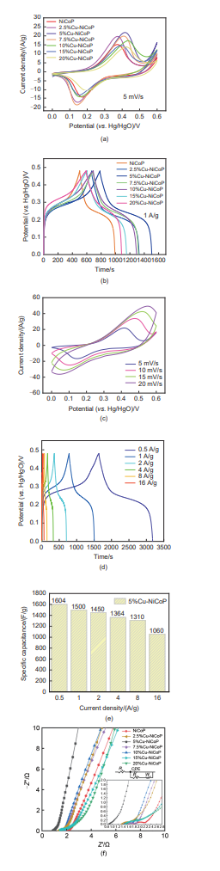
Fig. 3
(a) CV curves of Cu-NiCoP at 5 mV/s scanning speed; (b) GCD curves of Cu-NiCoP at 1 A/g current density; (c) CV curves of 5% Cu-NiCoP at different scanning speeds; (d) GCD curves of 5% Cu-NiCoP at different current densities; (e) Specific capacitance plot of 5% Cu-NiCoP; and (f) EIS curves of Cu-NiCoP"


Fig. 4
(a) CV curves of AC and 5% Cu-NiCoP; (b) CV curves of 5% Cu-NiCoP||AC in the voltage window of 1.3—1.7 V; (c) CV curves of 5% Cu-NiCoP||AC at different scanning speeds; (d) GCD curves of 5% Cu-NiCoP||AC at different current densities; (e) Cycle life diagram of 5% Cu-NiCoP||AC; and (f) Ragone diagram of 5% Cu-NiCoP||AC"

| 1 | SIMON P, GOGOTSI Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors[J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(11): 845-854. |
| 2 | ARBIZZANI C, YU Y, LI J, et al. Good practice guide for papers on supercapacitors and related hybrid capacitors for the Journal of Power Sources[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 450: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227636. |
| 3 | YI M, XIANG F F, YUE X Q, et al. Porous Ni2P/Co2(P2O7) heterojunction nanosheets as an advanced electrode for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 604: doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154503. |
| 4 | ZONG Q, LIU C F, YANG H, et al. Tailoring nanostructured transition metal phosphides for high-performance hybrid supercapacitors[J]. Nano Today, 2021, 38: doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101201. |
| 5 | SUN M, LIU H J, QU J H, et al. Earth-rich transition metal phosphide for energy conversion and storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(13): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201600087. |
| 6 | ZHANG L, CHANG C, HSU C W, et al. Hollow nanocubes composed of well-dispersed mixed metal-rich phosphides in N-doped carbon as highly efficient and durable electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction at high current densities[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(37): 19656-19663. |
| 7 | JIANG J, LI Z P, HE X R, et al. Novel skutterudite CoP3-based asymmetric supercapacitor with super high energy density[J]. Small, 2020, 16(31): doi: 10.1002/smll.202000180. |
| 8 | SIVAKUMAR P, JUNG M G, RAJ C J, et al. 1D interconnected porous binary transition metal phosphide nanowires for high performance hybrid supercapacitors[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(11): 17005-17014. |
| 9 | XU W C, WANG T, WANG H X, et al. Free-standing amorphous nanoporous nickel cobalt phosphide prepared by electrochemically delloying process as a high performance energy storage electrode material[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 17: 300-308. |
| 10 | ZHOU Q F, GONG Y, TAO K Y. Calcination/phosphorization of dual Ni/Co-MOF into NiCoP/C nanohybrid with enhanced electrochemical property for high energy density asymmetric supercapacitor[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 320: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.134582. |
| 11 | KONG M L, WANG Z, WANG W Y, et al. NiCoP nanoarray: A superior pseudocapacitor electrode with high areal capacitance[J]. Chemistry (Weinheim an Der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2017, 23(18): 4435-4441. |
| 12 | CHU X Y, MENG F L, YANG H, et al. Cu-doped layered double hydroxide constructs the performance-enhanced supercapacitor via band gap reduction and defect triggering[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(2): 2192-2201. |
| 13 | ELSHAHAWY A M, GUAN C, LI X, et al. Sulfur-doped cobalt phosphide nanotube arrays for highly stable hybrid supercapacitor[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 39: 162-171. |
| 14 | JIN Y H, ZHAO C C, JIANG Q L, et al. Preparation and electrochemical capacitive performance of hollow urchin-like Ni2P/CoP bimetallic phosphides for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 219: 59-63. |
| 15 | 佟永丽, 武祥. 金属有机框架衍生的Co3O4电极材料及其电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(3): 1035-1043. |
| TONG Y L, WU X. Electrochemical performance of Co3O4 electrode materials derived from Co metal-organic framework[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 1035-1043. | |
| 16 | 陈帅, 陈灵, 江浩. 氮掺杂无定形氧化钒纳米片阵列用于快充型准固态超级电容器[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(3): 945-951. |
| CHEN S, CHEN L, JIANG H. Nitrogen-doped amorphous vanadium oxide nanosheet arrays for rapid-charging quasi-solid asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 945-951. | |
| 17 | LIANG H F, XIA C, JIANG Q, et al. Low temperature synthesis of ternary metal phosphides using plasma for asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Nano Energy, 2017, 35: 331-340. |
| 18 | DONG Y X, YUE X Q, LIU Y, et al. Hierarchical core-shell-structured bimetallic nickel-cobalt phosphide nanoarrays coated with nickel sulfide for high-performance hybrid supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 628: 222-232. |
| 19 | ZHANG P, YANG Z H. Three-dimensional Cu-Co-Se-P nanocomposites as flexible supercapacitor electrodes[J].Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2022, 33(10): 7396-7402. |
| 20 | PAN Y, CHEN Y J, LIN Y, et al. Cobalt nickel phosphide nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes as advanced hybrid catalysts for hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(38): 14675-14686. |
| 21 | BLANCHARD P E R, GROSVENOR A P, CAVELL R G, et al. X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectroscopy of metal-rich phosphides M2P and M3P (M = Cr-Ni)[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(22): 7081-7088. |
| 22 | MOOSAVIFARD S E, FANI S, RAHMANIAN M. Hierarchical CuCo2S4 hollow nanoneedle arrays as novel binder-free electrodes for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2016, 52(24): 4517-4520. |
| 23 | WU X Y, LI S M, LIU J H, et al. Multiplex compounds of Ni, Cu, Co-based oxyphosphide nanowire arrays grown on Ni foam: A well-designed free-standing anode for high-capacity lithium storage[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 799: 406-414. |
| 24 | LEDENDECKER M, KRICK CALDERÓN S, PAPP C, et al. The synthesis of nanostructured Ni5P4 films and their use as a non-noble bifunctional electrocatalyst for full water splitting[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(42): 12361-12365. |
| 25 | LIU Y, FU N, ZHANG G, et al. Design of hierarchical Ni‐Co@Ni‐Co layered double hydroxide core-shell structured nanotube array for high-performance flexible all-solid-state battery-type supercapacitors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(8): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201605307. |
| 26 | HE S X, LI Z W, MI H Y, et al. 3D nickel-cobalt phosphide heterostructure for high-performance solid-state hybrid supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 467: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228324. |
| 27 | LEI X Y, GE S C, TAN Y H, et al. High capacity and energy density of Zn-Ni-Co-P nanowire arrays as an advanced electrode for aqueous asymmetric supercapacitor[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(8): 9158-9168. |
| 28 | LI X L, HUANG J J, WANG L, et al. Hierarchical honeycomb-like networks of CuCo-P@Ni(OH)2 nanosheet arrays enabling high-performance hybrid supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 838: doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155626. |
| 29 | SALEH A A, AHMED N, BIBY A H, et al. Supercapattery electrode materials by design: Plasma-induced defect engineering of bimetallic oxyphosphides for energy storage[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 603: 478-490. |
| 30 | LYU L L, HOOCH ANTINK W, LEE B H, et al. Zeolitic imidazole framework sacrificial template-assisted synthesis of NiCoP nanocages doped with multiple metals for high-performance hybrid supercapacitors[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(10): 10553-10564. |
| 31 | ANDIKAEY Z, ENSAFI A A, REZAEI B. Iron-doped cobalt copper phosphide/phosphate composite with 3D hierarchical flower-like structures as electrodes for hybrid supercapacitors[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 393: doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139061. |
| 32 | LIU Q S, HU R, QI J Q, et al. Facile synthesis of hierarchical NiCoP nanowires@NiCoP nanosheets core-shell nanoarrays for high-performance asymmetrical supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(3): 1157-1169. |
| 33 | LIU W F, GAO H X, ZHANG Z, et al. CoP/Cu3P heterostructured nanoplates for high-rate supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 437: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135352. |
| [1] | Chaochao WEI, Chuang YU, Zhongkai WU, Linfeng PENG, Shijie CHENG, Jia XIE. Research progress of Li3PS4 solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1368-1382. |
| [2] | Qiannan LIU, Weiping HU, Zhe HU. Research progress of phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1201-1210. |
| [3] | Yongli TONG, Xiang WU. Electrochemical performance of Co3O4 electrode materials derived from Co metal-organic framework [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 1035-1043. |
| [4] | Zhun NIU, Xueyan ZHANG, Jiawei FENG, Liguo JIN, Yonghui SHI, Jiayi YU, Zichao LI, Zhijun FENG. Preparation and electrochemical properties of FeSe2-C three-dimensional conductive composites [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(11): 3470-3477. |
| [5] | Jian LI, Lixin ZHANG, Ruiyi LI, Xiao YANG, Ting ZHANG. High-pressure gaseous hydrogen storage vessels: Current status and prospects [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(5): 1835-1844. |
| [6] | Dangling LIU, Shimin WANG, Zhihui GAO, Lufu XU, Shubiao XIA, Hong GUO. Properties of three-dimensional NZSPO/PAN-[PEO-NATFST] sodium-battery-composite solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 931-937. |
| [7] | Xinxin ZHU, Wei JIANG, Zhengwei WAN, Shu ZHAO, Zeheng LI, Liguang WANG, Wenbin NI, Min LING, Chengdu LIANG. Research progress in electrolyte and interfacial issues of solid lithium sulfur batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 848-862. |
| [8] | Chunyan YANG, Yunlong MA, Xiaoqiong FENG, Shiying ZHANG, Changsheng AN, Jingfeng LI. Research progress of carbon-based materials in aluminum-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 432-439. |
| [9] | Jin WANG, Jianquan WANG, Dianbo RUAN, Jiao XIE, Bin YANG. Preparation and electrochemical performances of Si/activated carbon composites [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 104-110. |
| [10] | Jixian WANG, Sikan PENG, Wenzheng NAN, Xiang CHEN, Chen WANG, Shaojiu YAN, Shenglong DAI. Preparation of graphene-coated Li1.22Mn0.52Ni0.26O2 using a spray drying method for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 111-117. |
| [11] | Jiajing ZHU, Yun GAO. Research progress of water-in-salt electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(S1): 13-22. |
| [12] | Caiwen WU, Lijing HUANG, Chunyang ZOU, Bowen LI, Wenjuan WU. Research progress of the lignin in application energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(6): 1737-1746. |
| [13] | Mengying MA, Huilin PAN, Yongsheng HU. Progress in electrolyte research for non-aqueous sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1234-1250. |
| [14] | MA Tengfei, MA Chao, SUN Rui, JI Hongmei, YANG Gang. Freeze-drying assisted synthesis of mno/reduced graphene composite and the improved rate cyclic performance for lithium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 1044-1051. |
| [15] | XIONG Xiaolin, YUE Jinming, ZHOU Anxing, SUO Liumin, HU Yongsheng, LI Hong, HUANG Xuejie. Electrochemical performance of spinel LiMn2O4 inWater-in-salt aqueouselectrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(2): 375-384. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
