储能科学与技术 ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (7): 2243-2258.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0362
收稿日期:2024-04-24
修回日期:2024-05-29
出版日期:2024-07-28
发布日期:2024-07-23
通讯作者:
郭新
E-mail:yhao_wang@hust.edu.cn;xguo@hust.edu.cn
作者简介:王宇豪(2001—),男,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为固态锂电池,E-mail:yhao_wang@hust.edu.cn;
基金资助:
Yuhao WANG( ), Zhiyong LI, Xin GUO(
), Zhiyong LI, Xin GUO( )
)
Received:2024-04-24
Revised:2024-05-29
Online:2024-07-28
Published:2024-07-23
Contact:
Xin GUO
E-mail:yhao_wang@hust.edu.cn;xguo@hust.edu.cn
摘要:
由于其良好的柔韧性、与电极兼容性好、易加工等特点,聚合物基电解质在固态锂电池中极具应用前景。聚合物基固态电池可在室温下稳定工作,在低温下(≤0 ℃),聚合物电解质离子电导率的降低和缓慢的锂离子传输动力学导致电池极化增大,放电容量急剧衰减,且低温下枝晶生长更加严重,极大限制了固态电池在低温环境中的应用。本文通过对近期相关文献进行探讨,首先介绍了聚合物基电解质在低温下应用面临的挑战和局限,接着阐述了聚合物基电解质的离子传导机制,通过实例重点阐述了低温聚合物基电解质的设计策略及应用,包括添加无机/有机填料、引入液体塑化剂、分子结构工程等优化聚合物基电解质体相离子传导的方法,以及原位聚合和构建良好的固体电解质界面/正极电解质界面等优化聚合物基电解质和电极间界面离子传输的方法。最后,评估并展望了低温聚合物基电解质的传输机制、设计原则、制备方法的不足及创新。本文有望促进聚合物基电解质及其固态锂电池在低温下的应用。
中图分类号:
王宇豪, 李志勇, 郭新. 聚合物基电解质在低温固态锂电池中的应用与挑战[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2243-2258.
Yuhao WANG, Zhiyong LI, Xin GUO. Applications and challenges of polymer-based electrolytes in low-temperature solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2243-2258.

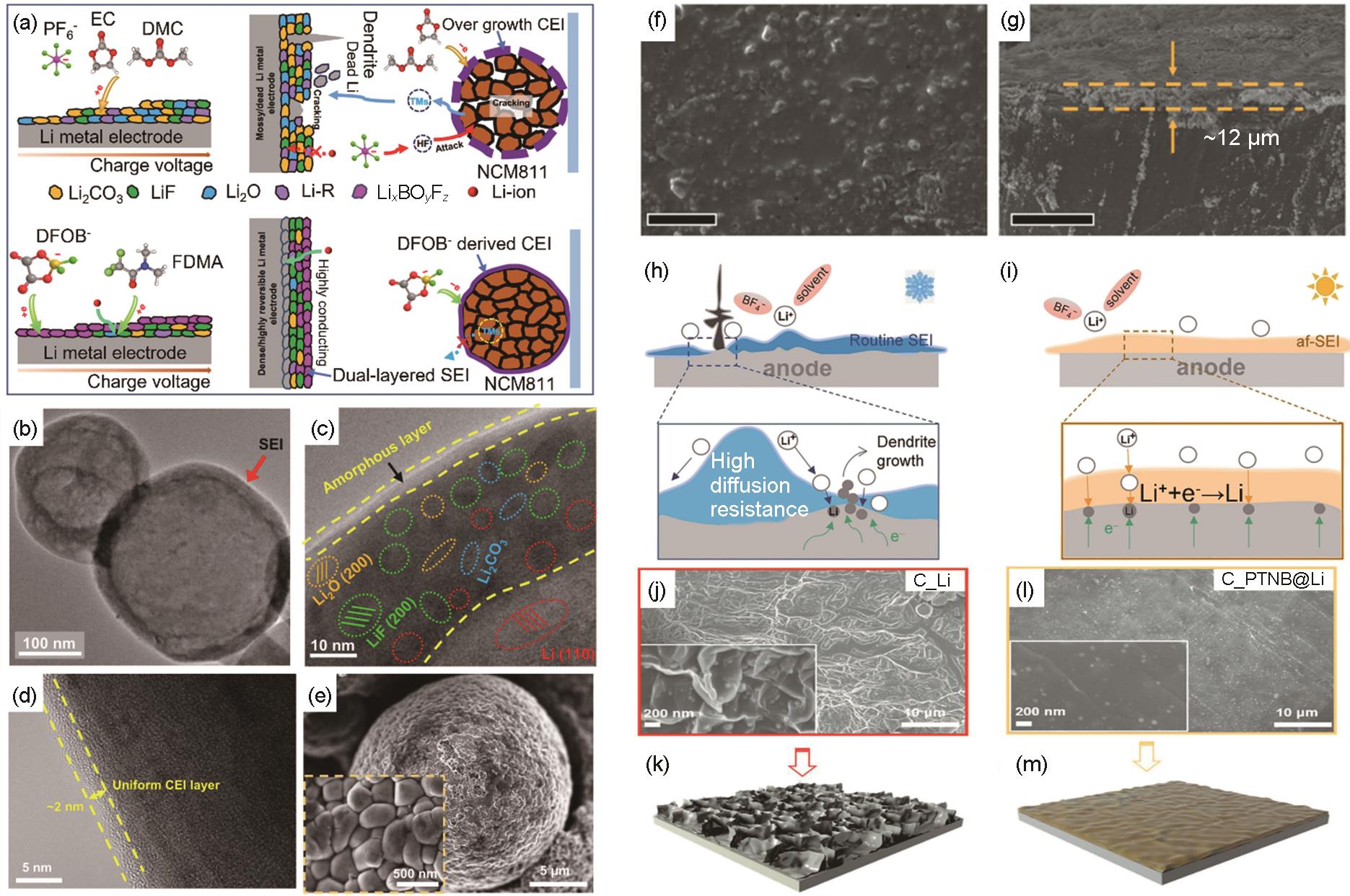
图7
高电导SEI/CEI的设计及构筑。(a) 在Li金属电极上形成的固体电解质界面相(SEI)和在Li||NCM811电池中正极侧CEI的形成过程示意图[76];(b),(c) 聚合物基电解质电池中沉积Li在不同尺度下的Cryo-TEM照片[76];(d) NCM811颗粒的TEM表征[76];(e) NCM811颗粒的SEM图像[76];Li金属在PDE中循环50圈后的SEM (f) 俯视图[77]和 (g) 横截面图[77];(h) 低温[78]和 (i) 环境温度[78]下SEI传导电荷和质子的示意图;(j),(k) Li||Li电池中的初始Li[79]和 (l),(m) PTNB@Li||PTNB@Li电池中PTNB@Li电极的形貌[79]"
| 1 | JAGUEMONT J, BOULON L, DUBÉ Y. A comprehensive review of lithium-ion batteries used in hybrid and electric vehicles at cold temperatures[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 164: 99-114. |
| 2 | WALDMANN T, HOGG B I, WOHLFAHRT-MEHRENS M. Li plating as unwanted side reaction in commercial Li-ion cells-A review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 384: 107-124. |
| 3 | HOLOUBEK J, YU M Y, YU S C, et al. An all-fluorinated ester electrolyte for stable high-voltage Li metal batteries capable of ultra-low-temperature operation[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(5): 1438-1447. |
| 4 | ZHONG S E, YU Y S, YANG Y, et al. Molecular engineering on solvation structure of carbonate electrolyte toward durable sodium metal battery at -40 ℃[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(18): 2301169. |
| 5 | JANEK J, ZEIER W G. A solid future for battery development[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(9): 16141. |
| 6 | HU Y S. Batteries: Getting solid[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(4): 16042. |
| 7 | XIE H X, FU Q G, LI Z, et al. Ultraviolet-cured semi-interpenetrating network polymer electrolytes for high-performance quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Chemistry, 2021, 27(28): 7773-7780. |
| 8 | ZHOU Q Y, XU B Y, CHIEN P H, et al. NASICON Li1.2Mg0.1Zr1.9(PO4)3 solid electrolyte for an all-solid-state Li-metal battery[J]. Small Methods, 2020, 4(12): 2000764. |
| 9 | 李泓. 全固态锂电池: 梦想照进现实[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2018, 7(2): 188-193. |
| LI H. All-solid lithium battery: Dreams may come[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(2): 188-193. | |
| 10 | 邹文洪, 樊佑, 张焱焱, 等. 安全固态锂电池室温聚合物基电解质的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(9): 5029-5044. |
| ZOU W H, FAN Y, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Research progress on room-temperature polymer-based electrolytes for safe solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(9): 5029-5044. | |
| 11 | XU B Y, LI X Y, YANG C, et al. Interfacial chemistry enables stable cycling of all-solid-state Li metal batteries at high current densities[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(17): 6542-6550. |
| 12 | CABAÑERO MARTÍNEZ M A, BOARETTO N, NAYLOR A J, et al. Are polymer-based electrolytes ready for high-voltage lithium battery applications? An overview of degradation mechanisms and battery performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(32): 2201264. |
| 13 | ZHOU Y M, ZHANG F R, HE P X, et al. Quasi-solid-state polymer plastic crystal electrolyte for subzero lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 46: 87-93. |
| 14 | MO S K, AN H W, LIU Q S, et al. Multistage bridge engineering for electrolyte and interface enables quasi-solid batteries to operate at -40 ℃[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 65: 103179. |
| 15 | LI Z, FU J L, ZHOU X Y, et al. Ionic conduction in polymer-based solid electrolytes[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(10): e2201718. |
| 16 | LI Z Y, REN Y, GUO X. Polymer-based electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries with a wide operating temperature range[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 7(24): 6305-6317. |
| 17 | YU T W, YANG X F, YANG R, et al. Progress and perspectives on typical inorganic solid-state electrolytes[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 885: 161013. |
| 18 | KARABELLI D, BIRKE K P, WEEBER M. A performance and cost overview of selected solid-state electrolytes: Race between polymer electrolytes and inorganic sulfide electrolytes[J]. Batteries, 2021, 7(1): 18. |
| 19 | YAO Z C, WANG Y T, WAN S, et al. Recent advances in designing solid-state electrolytes to reduce the working temperature of lithium batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 7(23): 6061-6084. |
| 20 | RATNER M A, SHRIVER D F. Ion transport in solvent-free polymers[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1988, 88(1): 109-124. |
| 21 | XUE Z G, HE D, XIE X L. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(38): 19218-19253. |
| 22 | ZHENG J, HU Y Y. New insights into the compositional dependence of Li-ion transport in polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(4): 4113-4120. |
| 23 | LIN Z Y, GUO X W, WANG Z C, et al. A wide-temperature superior ionic conductive polymer electrolyte for lithium metal battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 73: 104786. |
| 24 | FORD H O, PARK B, JIANG J Z, et al. Enhanced Li+ conduction within single-ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes via reduced cation–polymer interaction[J]. ACS Materials Letters, 2020, 2(3): 272-279. |
| 25 | HESS M. Non-linearity of the solid-electrolyte-interphase overpotential[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 244: 69-76. |
| 26 | SHI S Q, LU P, LIU Z Y, et al. Direct calculation of Li-ion transport in the solid electrolyte interphase[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(37): 15476-15487. |
| 27 | SHI S Q, QI Y, LI H, et al. Defect thermodynamics and diffusion mechanisms in Li2CO3 and implications for the solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(17): 8579-8593. |
| 28 | LI Y J, MAO E Y, MIN Z W, et al. Hybrid polymer-alloy-fluoride interphase enabling fast ion transport kinetics for low-temperature lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(19): 19459-19469. |
| 29 | LI Z, HUANG H M, ZHU J K, et al. Ionic conduction in composite polymer electrolytes: Case of PEO: Ga-LLZO composites[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(1): 784-791. |
| 30 | LI J, CAI Y J, CUI Y Y, et al. Fabrication of asymmetric bilayer solid-state electrolyte with boosted ion transport enabled by charge-rich space charge layer for -20~70 ℃ lithium metal battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 95: 107027. |
| 31 | ZHANG X Y, FU C K, CHENG S C, et al. Novel PEO-based composite electrolyte for low-temperature all-solid-state lithium metal batteries enabled by interfacial cation-assistance[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 56: 121-131. |
| 32 | HUANG X Y, HUANG S, WANG T Y, et al. Polyether-b-amide based solid electrolytes with well-adhered interface and fast kinetics for ultralow temperature solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(27): 2300683. |
| 33 | ALARCO P J, ABU-LEBDEH Y, ABOUIMRANE A, et al. The plastic-crystalline phase of succinonitrile as a universal matrix for solid-state ionic conductors[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3: 476-481. |
| 34 | FU C K, MA Y L, ZUO P J, et al. In-situ thermal polymerization boosts succinonitrile-based composite solid-state electrolyte for high performance Li-metal battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 496: 229861. |
| 35 | MINDEMARK J, LACEY M J, BOWDEN T, et al. Beyond PEO—Alternative host materials for Li+-conducting solid polymer electrolytes[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2018, 81: 114-143. |
| 36 | LEE M J, HAN J, LEE K, et al. Elastomeric electrolytes for high-energy solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Nature, 2022, 601: 217-222. |
| 37 | FU C K, ZHANG X, CUI C, et al. Molecular bridges stabilize lithium metal anode and solid-state electrolyte interface[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 432: 134271. |
| 38 | ZHOU X Y, ZHOU Y F, YU L, et al. Gel polymer electrolytes for rechargeable batteries toward wide-temperature applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2024, 53(10): 5291-5337. |
| 39 | TANG J Q, ZHAI B B, LIU J F, et al. A robust, freeze-resistant and highly ion conductive ionogel electrolyte towards lithium metal batteries workable at -30 ℃[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2021, 23(11): 6775-6782. |
| 40 | YU J, LIN X D, LIU J P, et al. In situ fabricated quasi-solid polymer electrolyte for high-energy-density lithium metal battery capable of subzero operation[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(2): 2102932. |
| 41 | GREEN M, KAYDANIK K, OROZCO M, et al. Closo-borate gel polymer electrolyte with remarkable electrochemical stability and a wide operating temperature window[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(16): 2106032. |
| 42 | LI S P, LORANDI F, WANG H, et al. Functional polymers for lithium metal batteries[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2021, 122: 101453. |
| 43 | WANG A L, XU H, ZHOU Q, et al. A new all-solid-state hyperbranched star polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries: Synthesis and electrochemical properties[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 212: 372-379. |
| 44 | HOMANN G, STOLZ L, NEUHAUS K, et al. Effective optimization of high voltage solid-state lithium batteries by using poly(ethylene oxide)-based polymer electrolyte with semi-interpenetrating network[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(46): 2006289. |
| 45 | JIANG Y, YAN X M, MA Z F, et al. Development of the PEO based solid polymer electrolytes for all-solid state lithium ion batteries[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(11): 1237. |
| 46 | WU Y X, LI Y, WANG Y, et al. Advances and prospects of PVDF based polymer electrolytes[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 64: 62-84. |
| 47 | NGUYEN A G, PARK C J. Insights into tailoring composite solid polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 675: 121552. |
| 48 | XI G, XIAO M, WANG S J, et al. Polymer-based solid electrolytes: Material selection, design, and application[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(9): 2007598. |
| 49 | WEN K H, XIN C Z, GUAN S D, et al. Ion-dipole interaction regulation enables high-performance single-ion polymer conductors for solid-state batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(32): e2202143. |
| 50 | HAN S T, WEN P, WANG H J, et al. Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2023, 22: 1515-1522. |
| 51 | WANG A X, GENG S X, ZHAO Z F, et al. In situ cross-linked plastic crystal electrolytes for wide-temperature and high-energy-density lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(17): 2201861. |
| 52 | XU S J, XU R G, YU T, et al. Decoupling of ion pairing and ion conduction in ultrahigh-concentration electrolytes enables wide-temperature solid-state batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(8): 3379-3387. |
| 53 | PAN J, ZHAO P, WANG N N, et al. Research progress in stable interfacial constructions between composite polymer electrolytes and electrodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(7): 2753-2775. |
| 54 | XU L, TANG S, CHENG Y, et al. Interfaces in solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(10): 1991-2015. |
| 55 | LI C, WANG Z Y, HE Z J, et al. An advance review of solid-state battery: Challenges, progress and prospects[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2021, 29: e00297. |
| 56 | ZHU X Q, WANG K, XU Y N, et al. Strategies to boost ionic conductivity and interface compatibility of inorganic-organic solid composite electrolytes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 36: 291-308. |
| 57 | RAJ V, AETUKURI N P B, NANDA J. Solid state lithium metal batteries-Issues and challenges at the lithium-solid electrolyte interface[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2022, 26(4): 100999. |
| 58 | TU Q S, BARROSO-LUQUE L, SHI T, et al. Electrodeposition and mechanical stability at lithium-solid electrolyte interface during plating in solid-state batteries[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2020, 1: 100106. |
| 59 | LYU Z L, ZHOU Q, ZHANG S, et al. Cyano-reinforced in situ polymer electrolyte enabling long-life cycling for high-voltage lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 37: 215-223. |
| 60 | 李卓, 郭新. 面向高比能固态电池的聚合物基电解质固化技术[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 212-230. |
| LI Z, GUO X. Solidification of polymer-based electrolytes for energy-density solid-state batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 212-230. | |
| 61 | ZHANG S H, XIE B, ZHUANG X C, et al. Great challenges and new paradigm of the in situ polymerization technology inside lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(17): 2314063. |
| 62 | DONG T T, XU G J, XIE B, et al. An electrode-crosstalk-suppressing smart polymer electrolyte for high safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024: e2400737. |
| 63 | REN W H, ZHANG Y F, LV R X, et al. In-situ formation of quasi-solid polymer electrolyte for improved lithium metal battery performances at low temperatures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 542: 231773. |
| 64 | MENG Y F, ZHOU D, LIU R L, et al. Designing phosphazene-derivative electrolyte matrices to enable high-voltage lithium metal batteries for extreme working conditions[J]. Nature Energy, 2023, 8: 1023-1033. |
| 65 | HE H, WANG Y, LI M, et al. In situ cross-linked fluorinated gel polymer electrolyte based on PEGDA-enabled lithium-ion batteries with a wide temperature operating range[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 467: 143311. |
| 66 | WU J R, WANG X S, LIU Q, et al. A synergistic exploitation to produce high-voltage quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5746. |
| 67 | TAN S, SHADIKE Z, LI J Z, et al. Additive engineering for robust interphases to stabilize high-Ni layered structures at ultra-high voltage of 4.8 V[J]. Nature Energy, 2022, 7: 484-494. |
| 68 | ZHANG S H, SUN F, DU X F, et al. In situ-polymerized lithium salt as a polymer electrolyte for high-safety lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(6): 2591-2602. |
| 69 | MA C, CUI W F, LIU X Z, et al. In situ preparation of gel polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries: Progress and perspectives[J]. InfoMat, 2022, 4(2): e12232. |
| 70 | WU H, TANG B, DU X F, et al. LiDFOB initiated in situ polymerization of novel eutectic solution enables room-temperature solid lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(23): 2003370. |
| 71 | LI Z, XIE H X, ZHANG X Y, et al. In situ thermally polymerized solid composite electrolytes with a broad electrochemical window for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(7): 3892-3900. |
| 72 | HOLOUBEK J, YIN Y J, LI M Q, et al. Exploiting mechanistic solvation kinetics for dual-graphite batteries with high power output at extremely low temperature[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(52): 18892-18897. |
| 73 | ZHANG S, XU K, JOW T. Low-temperature performance of Li-ion cells with a LiBF4-based electrolyte[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2003, 7(3): 147-151. |
| 74 | STOLZ L, GABERŠČEK M, WINTER M, et al. Different efforts but similar insights in battery R&D: Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy vs galvanostatic (constant current) technique[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(23): 10272-10278. |
| 75 | CHI S S, LIU Y C, ZHAO N, et al. Solid polymer electrolyte soft interface layer with 3D lithium anode for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 17: 309-316. |
| 76 | LI Z, YU R, WENG S T, et al. Tailoring polymer electrolyte ionic conductivity for production of low-temperature operating quasi-all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 482. |
| 77 | XIANG J W, ZHANG Y, ZHANG B, et al. A flame-retardant polymer electrolyte for high performance lithium metal batteries with an expanded operation temperature[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(6): 3510-3521. |
| 78 | DUAN J Y, CHEN J X, WANG F F, et al. Ambiently fostering solid electrolyte interphase for low-temperature lithium metal batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 87: 473-478. |
| 79 | CHEN Z, KIM G T, KIM J K, et al. Highly stable quasi-solid-state lithium metal batteries: Reinforced Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3/Li interface by a protection interlayer[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(30): 2101339. |
| 80 | XIANG J W, YUAN L X, SHEN Y, et al. Improved rechargeability of lithium metal anode via controlling lithium-ion flux[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(36): 1802352. |
| 81 | LIN D C, LIU Y Y, CUI Y. Reviving the lithium metal anode for high-energy batteries[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12: 194-206. |
| 82 | PASTA M, ARMSTRONG D, BROWN Z L, et al. 2020 roadmap on solid-state batteries[J]. Journal of Physics: Energy, 2020, 2(3): 032008. |
| 83 | SUNG J, KIM S Y, HARUTYUNYAN A, et al. Ultra-thin lithium silicide interlayer for solid-state lithium-metal batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(22): 2210835. |
| 84 | HAN X, WU T T, GU L H, et al. Li-MOF-based ions regulator enabling fast-charging and dendrite-free lithium metal anode[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(2): 107594. |
| 85 | LI T, CHEN Z Y, BAI F W, et al. Diluted low concentration electrolyte for interphase stabilization of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 81: 404-409. |
| [1] | 周洪, 辛竹琳, 付豪, 张强, 魏凤. 基于专利数据挖掘的固态锂电池关键材料分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2386-2398. |
| [2] | 李昌豪, 汪书苹, 杨献坤, 曾子琪, 周昕玥, 谢佳. 低温型锂离子电池中的非水电解质研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2286-2299. |
| [3] | 姜森, 陈龙, 孙创超, 王金泽, 李如宏, 范修林. 低温锂电池电解液的发展及展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2270-2285. |
| [4] | 陆洋, 闫帅帅, 马骁, 刘誌, 章伟立, 刘凯. 低温锂电池电解液的研究与应用[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2224-2242. |
| [5] | 廖世接, 魏颖, 黄云辉, 胡仁宗, 许恒辉. 间二氟苯稀释剂稳定电极界面助力低温锂金属电池[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2124-2130. |
| [6] | 李想, 刘德重, 袁开, 陈大鹏. 用于低温锂金属电池的固态电解质技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2327-2347. |
| [7] | 王美龙, 薛煜瑞, 胡文茜, 杜可遇, 孙瑞涛, 张彬, 尤雅. 低温磷酸铁锂电池用全醚高熵电解液的设计研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2131-2140. |
| [8] | 王浩天, 王永刚, 董晓丽. 基于有机电极材料的低温电池研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2259-2269. |
| [9] | 黄嘉琦, 熊杰明, 谭恩忠, 孙心语, 程李巍, 王华. 重新审视低温钠金属半电池[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2151-2160. |
| [10] | 徐雄文, 莫英, 周望, 姚环东, 洪娟, 雷化, 涂健, 刘继磊. 硬碳动力学特性对钠离子电池低温性能的影响及机制[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2141-2150. |
| [11] | 马国政, 陈金伟, 熊兴宇, 杨振忠, 周钢, 胡仁宗. SnSb-Li4Ti5O12 复合负极材料低温高倍率储锂特性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2107-2115. |
| [12] | 王文涛, 魏一凡, 黄鲲, 吕国伟, 张思瑶, 唐昕雅, 陈泽彦, 林清源, 母志鹏, 王昆桦, 才华, 陈军. 低温锂离子电池测试标准及研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2300-2307. |
| [13] | 林炜琦, 卢巧瑜, 陈宇鸿, 邱麟媛, 季钰榕, 管联玉, 丁翔. 低温钠离子电池正极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2348-2360. |
| [14] | 李征, 杨振忠, 王琼, 胡仁宗. 基于专利情报分析的锂离子电池用低温电解液的发展现状和研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2317-2326. |
| [15] | 程广玉, 刘新伟, 刘硕, 顾海涛, 王可. 调控电解液溶剂组分实现LCO/C低温18650电池循环寿命显著提升[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2171-2180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
