储能科学与技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (3): 883-897.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.1121
陈钊1( ), 梁沁沁2, 李玉婷1,3, 谢飞1(
), 梁沁沁2, 李玉婷1,3, 谢飞1( ), 唐彬2, 李建新2, 陆雅翔1, 陈爱兵3, 胡勇胜1(
), 唐彬2, 李建新2, 陆雅翔1, 陈爱兵3, 胡勇胜1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-27
修回日期:2024-12-10
出版日期:2025-03-28
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
谢飞,胡勇胜
E-mail:zchen@iphy.ac.cn;fxie@iphy.ac.cn;yshu@iphy.ac.cn
作者简介:陈钊(1998—),男,博士研究生,研究方向为钠离子负极材料及界面设计,E-mail:zchen@iphy.ac.cn;
基金资助:
Zhao CHEN1( ), Qinqin LIANG2, Yuting LI1,3, Fei XIE1(
), Qinqin LIANG2, Yuting LI1,3, Fei XIE1( ), Bin TANG2, Jianxin LI2, Yaxiang LU1, Aibing CHEN3, Yongsheng HU1(
), Bin TANG2, Jianxin LI2, Yaxiang LU1, Aibing CHEN3, Yongsheng HU1( )
)
Received:2024-11-27
Revised:2024-12-10
Online:2025-03-28
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Fei XIE, Yongsheng HU
E-mail:zchen@iphy.ac.cn;fxie@iphy.ac.cn;yshu@iphy.ac.cn
摘要:
负极材料是钠离子电池的重要组成部分,承担着接收并储存钠离子的重任从而影响电池的储能密度、功率密度、循环稳定性等。以锡为代表的合金类负极材料具有合适的电位和较高的理论比容量,是钠离子电池体系极具竞争力的负极材料。然而锡基负极,像合金类负极一样,具有钠化体积膨胀严重致颗粒粉化并失去电接触、固态电解质中间相不稳定、循环稳定性不佳等问题。本文通过对近期相关文献的分析,评述了钠离子电池领域锡基负极的研究现状,包括纯锡、锡碳复合、氧化锡、硫化锡、硒化锡、磷化锡等材料,并揭示了锡基合金类负极容量衰减的共性以及应对的改性策略。综合分析表明,针对锡基负极材料特点的活性物质的纳米化、相变过程调控和结构设计;对导电碳和黏结剂等非活性物质的改性与复合结构设计;电解质设计以及超高载量的锡箔形式负极等策略确实可以提升比容量、载量、倍率性能和循环稳定性等指标。众多策略对将在未来应用于钠离子电池体系,实现稳定、高倍率性能和高能量密度的锡基负极材料提出了合理构想。
中图分类号:
陈钊, 梁沁沁, 李玉婷, 谢飞, 唐彬, 李建新, 陆雅翔, 陈爱兵, 胡勇胜. 钠离子电池锡基合金类负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 883-897.
Zhao CHEN, Qinqin LIANG, Yuting LI, Fei XIE, Bin TANG, Jianxin LI, Yaxiang LU, Aibing CHEN, Yongsheng HU. Recent progress of tin-based alloy-type anode materials in Na-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 883-897.
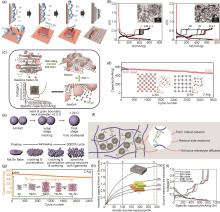
图3
(a) 阴极电沉积法纳米Sn纤维生长机理的简化描述[17];(b) Sn粉末∶3 μm石墨:PANa = 8∶1∶1 电极的电化学性能,左图为纳米Sn粉末电极的充放电曲线,右图微米Sn粉末电极的充放电曲线,插图为对应的粉末扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 图像[19];(c) SnNGnP的合成流程以及充放电曲线[20];(d) α-Sn与β-Sn负极的循环对比图,两种Sn晶体对应的结构如插图所示[25];(e) 高温烧结过程和Sn颗粒在电化学循环过程中的自修复相似性的示意图[26];(f) 聚丙烯酸 (PAA) 和甘油 (GLY) 的交联反应增强了电极的机械性能的示意图[28];(g) 微米Sn负极在0.01~1 V和0.01~0.62 V的循环对比图,不同的循环电压区间所对应的晶体结构如插图所示[29];(h) 负极中不同活性材料体积分数的体积容量与负极体积膨胀曲线,其中垂直虚线分别表示石墨 (Gr)、铝 (Al) 和硅 (Si) 的最大膨胀率[30];(i) 锡箔负极在0.1C循环100周中有代表性周数的充放电曲线[31]"
图4
(a) MWNTs@SnO2@C复合材料的制备示意图[39];(b) MWNTs@SnO2@C复合材料在50 mA/g和150 mA/g电流密度下的循环性能[39];(c) SnO2@SnS2@NG的制备流程示意图[41];(d) SnO2@SnS2@NG、SnO2@SnS2 、SnO2@NG和SnS2@NG在3 A/g的循环性能[41];(e) SnO2-x /C纳米纤维合成过程的示意图 (上图) 和形貌的扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 图 (下图)[37];(f) 充电/放电过程中,SnO2 (上图) 和 SnO2-x /C (下图) 电极的反应机制示意图[37];(g) 直接在铜基底上制造的氧化锡纳米螺旋阵列在经过放电和充电过程后结构发生变化的示意图[46];(h) 非晶态SnO x 纳米螺旋阵列,晶态SnO2 纳米颗粒和晶态SnO纳米颗粒所制成电极的循环性能对比[46]"
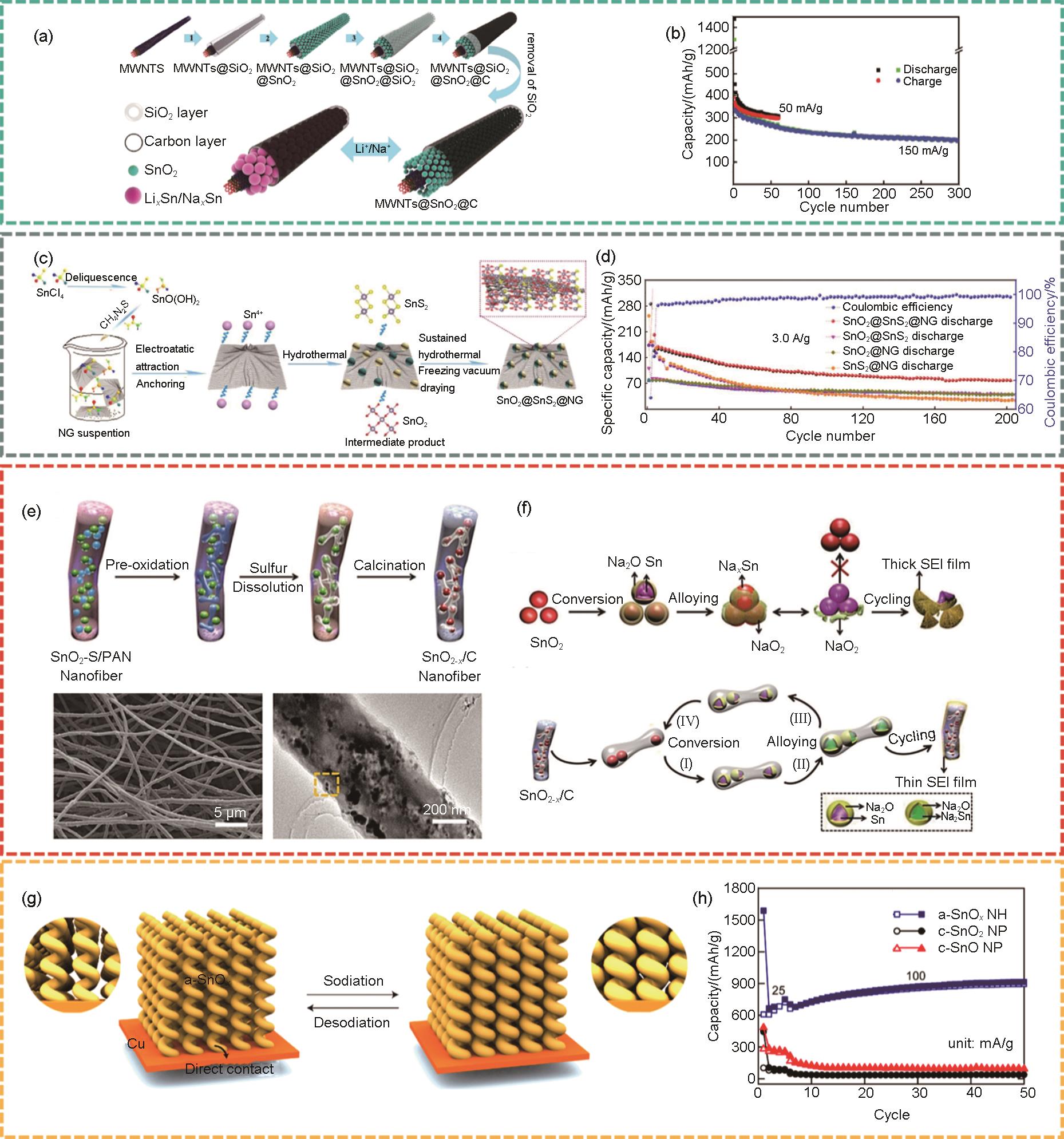
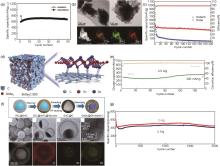
图6
(a) SnSe/C的循环性能图[51];(b) SnSe/C纳米复合材料的透射电子显微镜 (TEM) 图与对应的以及材料中碳 (C)、锡 (Sn) 和硒 (Se) 的EDS元素图谱[52];(c) SnSe/C和未改性的SnSe在0.5 A/g电流密度下的循环性能对比[52];(d) SnSe2 ⊂3DC缓冲多孔结构示意图[53];(e) SnSe2 ⊂3DC的2.5 A/g循环测试,其中初始活化2个循环时为0.13 A/g[53];(f) SnSe2@Se-C合成过程的示意图以及SnSe2@Se-C的SEM、TEM、高角度环形暗场扫描透射电子显微镜 (HAADF-STEM) 图像及相应的元素分布图[54];(g) SnSe2@Se-C的循环性能图[54]"
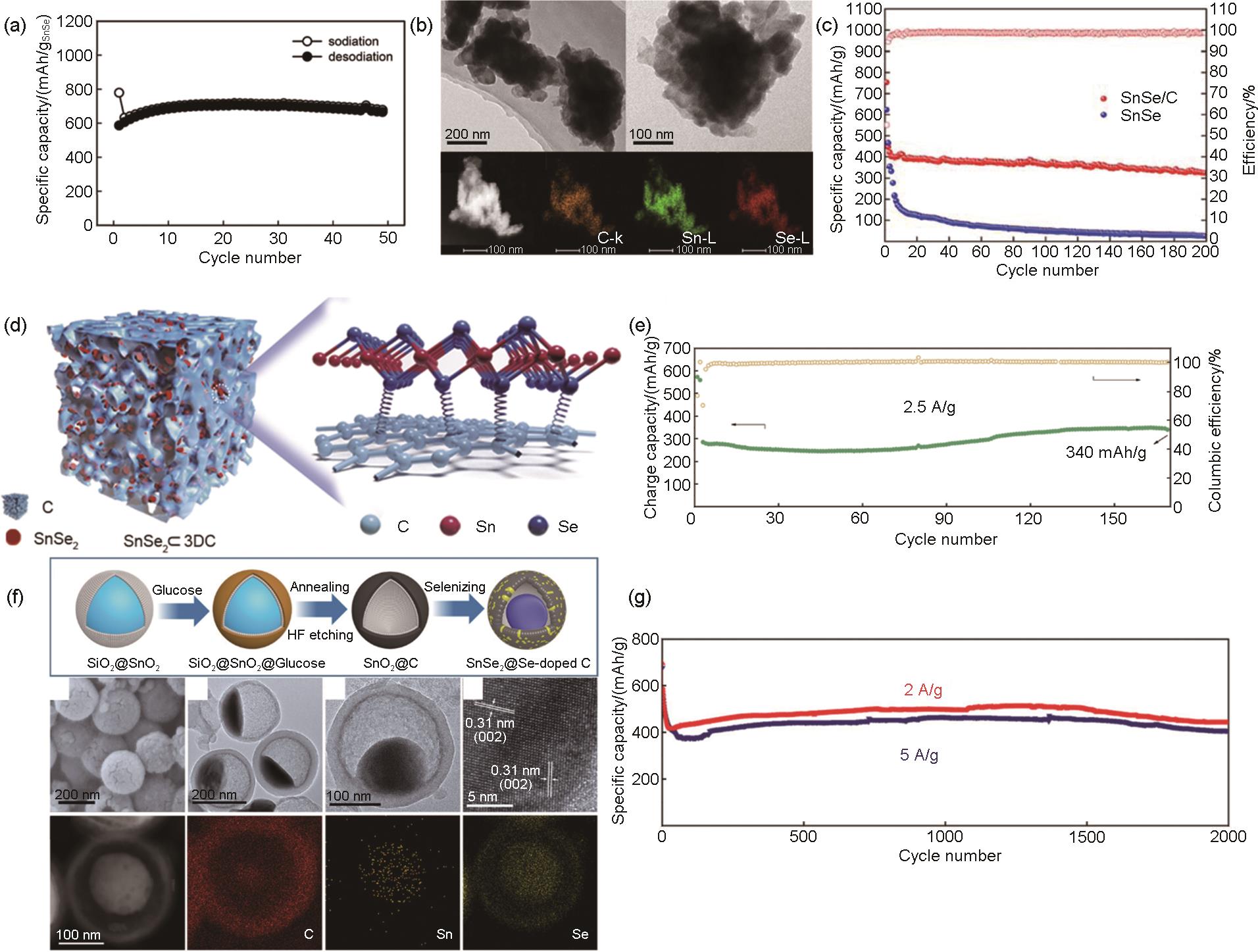
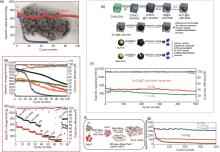
图7
(a) Sn4P3 和Sn的循环性能对比图[56];(b) Sn4P3@C蛋黄壳纳米立方体的合成及其相对于其他阳极材料的结构优势、Sn4P3@C蛋黄壳纳米立方体合成示意图和Sn4P3@C蛋黄壳纳米立方体在钠化/脱钠过程中相比Sn4P3/C和裸Sn4P3 的结构优势[57];(c) Sn4P3@C 蛋黄壳纳米立方体电极在1.0 A/g和2.0 A/g下的长期循环性能以及相应的库仑效率[57];Sn4P3@HC在NaClO4/EC:PC (橙色倒三角形)、NaClO4/EC:PC:FEC (红色菱形)、NaPF6/EC:PC (深青色六角形)、NaPF6/EC:PC:FEC (绿色圆圈)、NaPF6/DEGDME (黑色正方形) 和NaPF6/DEGDME:FEC (深灰色星形) 电解质中的 (d) 循环和 (e) 倍率测试图[58];(f) Sn4P3/NHC的合成路径示意图[59];(g) Sn4P3@HC在1 A/g电流密度下的循环性能图[60]"
| 1 | LI M H, WANG H F, LUO W, et al. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysts for electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(34): e2001848. DOI:10.1002/adma.202001848. |
| 2 | CHU S, CUI Y, LIU N. The path towards sustainable energy[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 16(1): 16-22. DOI:10.1038/nmat4834. |
| 3 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7(1): 19-29. DOI:10.1038/nchem.2085. |
| 4 | USISKIN R, LU Y X, POPOVIC J, et al. Fundamentals, status and promise of sodium-based batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2021, 6: 1020-1035. DOI:10.1038/s41578-021-00324-w. |
| 5 | HU Y S, LU Y X. 2019 Nobel prize for the Li-ion batteries and new opportunities and challenges in Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(11): 2689-2690. DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett. 9b02190. |
| 6 | LAO M M, ZHANG Y, LUO W B, et al. Alloy-based anode materials toward advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(48): 1700622. DOI:10.1002/adma.201700622. |
| 7 | WU X, LAN X X, HU R Z, et al. Tin-based anode materials for stable sodium storage: Progress and perspective[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(7): e2106895. DOI:10.1002/adma.202106895. |
| 8 | ZHOU L, CAO Z, WAHYUDI W, et al. Electrolyte engineering enables high stability and capacity alloying anodes for sodium and potassium ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(3): 766-776. DOI:10.1021/acsenergylett.0c00148. |
| 9 | ZHANG B, ROUSSE G, FOIX D, et al. Microsized Sn as advanced anodes in glyme-based electrolyte for Na-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(44): 9824-9830. DOI:10.1002/adma.201603212. |
| 10 | TIAN Y, AN Y L, ZHANG B. Approaching microsized alloy anodes via solid electrolyte interphase design for advanced rechargeable batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(31): 2302119. DOI:10.1002/aenm.202302119. |
| 11 | HUANG J Q, GUO X Y, DU X Q, et al. Nanostructures of solid electrolyte interphases and their consequences for microsized Sn anodes in sodium ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(5): 1550-1557. DOI:10.1039/C8EE03632B. |
| 12 | WANG J W, LIU X H, MAO S X, et al. Microstructural evolution of tin nanoparticles during in situ sodium insertion and extraction[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(11): 5897-5902. DOI:10.1021/nl303305c. |
| 13 | 周琳, 杨佯, 胡勇胜. 合金电极失效机制:体积膨胀?电解液分解? [J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(3): 813-20. |
| 14 | CHU C T, ZHOU L, CHENG Y, et al. Ultralow-concentration (0.1M) electrolyte for stable bulk alloy (Sn, Bi) anode in sodium-ion battery via regulating anions structure[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 482: 148915. DOI:10.1016/j.cej. 2024.148915. |
| 15 | ZHENG C, JI D L, YAO Q, et al. Electrostatic shielding boosts electrochemical performance of alloy-type anode materials of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(14): e202214258. DOI:10.1002/anie.202214258. |
| 16 | YAO Q, ZHENG C, JI D L, et al. Superior sodiophilicity and molecule crowding of crown ether boost the electrochemical performance of all-climate sodium-ion batteries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(27): e2312337121. DOI:10.1073/pnas. 2312337121. |
| 17 | NAM D H, KIM T H, HONG K S, et al. Template-free electrochemical synthesis of Sn nanofibers as high-performance anode materials for Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(11): 11824-11835. DOI:10.1021/nn505536t. |
| 18 | LI T, GULZAR U, BAI X, et al. Insight on the failure mechanism of Sn electrodes for sodium-ion batteries: Evidence of pore formation during sodiation and crack formation during desodiation[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(1): 860-866. DOI:10.1021/acsaem.8b01934. |
| 19 | FUKUNISHI M, HORIBA T, DAHBI M, et al. Optimizing micrometer-sized Sn powder composite electrodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochemistry, 2019, 87(1): 70-77. DOI:10. 5796/electrochemistry.18-00069. |
| 20 | PALANISELVAM T, GOKTAS M, ANOTHUMAKKOOL B, et al. Sodium storage and electrode dynamics of tin-carbon composite electrodes from bulk precursors for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(18): 1900790. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201900790. |
| 21 | LIU Z, ZHANG S, QIU Z P, et al. Tin nanodots derived from Sn2+/graphene quantum dot complex as pillars into graphene blocks for ultrafast and ultrastable sodium-ion storage[J]. Small, 2020, 16(38): e2003557. DOI:10.1002/smll.202003557. |
| 22 | PALANISELVAM T, BABU B, MOON H, et al. Tin-containing graphite for sodium-ion batteries and hybrid capacitors[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2021, 4(1): 173-182. DOI:10.1002/batt.202000196. |
| 23 | TAN M D, HAN S H, LI Z B, et al. Compact Sn/C composite realizes long-life sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(3): 3804-3813. DOI:10.1007/s12274-022-4255-0. |
| 24 | SAYED S Y, KALISVAART W P, LUBER E J, et al. Stabilizing tin anodes in sodium-ion batteries by alloying with silicon[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(10): 9950-9962. DOI:10.1021/acsaem.0c01641. |
| 25 | ZHU Y S, YAO Q, SHAO R W, et al. Microsized gray tin as a high-rate and long-life anode material for advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2022, 22(19): 7976-7983. DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c03334. |
| 26 | KIM C, KIM I, KIM H, et al. A self-healing Sn anode with an ultra-long cycle life for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(45): 22809-22818. DOI:10.1039/C8TA09544B. |
| 27 | PARK J H, CHOI Y S, KIM C, et al. Self-assembly of pulverized nanoparticles: An approach to realize large-capacity, long-lasting, and ultra-fast-chargeable Na-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(21): 9044-9051. DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02518. |
| 28 | YAO Q, ZHU Y S, ZHENG C, et al. Intermolecular cross-linking reinforces polymer binders for durable alloy-type anode materials of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(9): 2202939. DOI:10.1002/aenm.202202939. |
| 29 | ZHU Y S, QIAN Z, SONG J, et al. Voltage-modulated structure stress for enhanced electrochemcial performances: The case of μ-Sn in sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(8): 3588-3595. DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00489. |
| 30 | BOLES S T, TAHMASEBI M H. Are foils the future of anodes?[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(7): 1342-1346. DOI:10.1016/j.joule.2020.05.009. |
| 31 | KIM C, KIM H, SADAN M K, et al. Development and evaluation of Sn foil anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2021, 17(50): e2102618. DOI:10.1002/smll.202102618. |
| 32 | DIRICAN M, LU Y, GE Y Q, et al. Carbon-confined SnO2-electrodeposited porous carbon nanofiber composite as high-capacity sodium-ion battery anode material[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(33): 18387-18396. DOI:10.1021/acsami.5b04338. |
| 33 | SU D W, AHN H J, WANG G X. SnO2@graphene nanocomposites as anode materials for Na-ion batteries with superior electrochemical performance[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(30): 3131-3133. DOI:10.1039/c3cc40448j. |
| 34 | SHIMIZU M, USUI H, SAKAGUCHI H. Electrochemical Na-insertion/extraction properties of SnO thick-film electrodes prepared by gas-deposition[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 248: 378-382. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.09.046. |
| 35 | PATRA J, CHEN H C, YANG C H, et al. High dispersion of 1-nm SnO2 particles between graphene nanosheets constructed using supercritical CO2 fluid for sodium-ion battery anodes[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 28: 124-134. DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.08.044. |
| 36 | OEHL N, MICHALOWSKI P, KNIPPER M, et al. Size-dependent strain of Sn/SnOx core/shell nanoparticles[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(51): 30238-30243. DOI:10.1021/jp5096147. |
| 37 | MA D T, LI Y L, MI H W, et al. Robust SnO2- x nanoparticle-impregnated carbon nanofibers with outstanding electrochemical performance for advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed), 2018, 57(29): 8901-8905. DOI:10.1002/anie.201802672. |
| 38 | LIANG J J, YUAN C C, LI H H, et al. Growth of SnO2 nanoflowers on N-doped carbon nanofibers as anode for Li- and Na-ion batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2018, 10(2): 21. DOI:10.1007/s40820-017-0172-2. |
| 39 | ZHAO Y, WEI C, SUN S N, et al. Reserving interior void space for volume change accommodation: An example of cable-like MWNTs@SnO2@C composite for superior lithium and sodium storage[J]. Advanced Science, 2015, 2(6): 1500097. DOI:10.1002/advs.201500097. |
| 40 | WANG Y, SU D W, WANG C Y, et al. SnO2@MWCNT nanocomposite as a high capacity anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2013, 29: 8-11. DOI:10.1016/j.elecom.2013.01.001. |
| 41 | HUANG S F, WANG M, JIA P, et al. N-graphene motivated SnO2@SnS2 heterostructure quantum dots for high performance lithium/sodium storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 20: 225-233. DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2018.11.024. |
| 42 | CHEN W H, SONG K M, MI L W, et al. Synergistic effect induced ultrafine SnO2/graphene nanocomposite as an advanced lithium/sodium-ion batteries anode[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(20): 10027-10038. DOI:10.1039/C7TA01634D. |
| 43 | XIE X Q, CHEN S Q, SUN B, et al. 3D networked tin oxide/graphene aerogel with a hierarchically porous architecture for high-rate performance sodium-ion batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(17): 2948-2955. DOI:10.1002/cssc.201500149. |
| 44 | GABRIEL E, MA C R, GRAFF K, et al. Heterostructure engineering in electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries: Recent progress and perspectives[J]. eScience, 2023, 3(5): 100139. DOI:10.1016/j.esci.2023.100139. |
| 45 | LI Z T, FENG J Z, HU H, et al. An amorphous tin-based nanohybrid for ultra-stable sodium storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(39): 18920-18927. DOI:10.1039/C8TA05390A. |
| 46 | CHOI I Y, JO C, LIM W G, et al. Amorphous tin oxide nanohelix structure based electrode for highly reversible Na-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(6): 6513-6521. DOI:10.1021/acsnano.8b09773. |
| 47 | WANG J J, LUO C, MAO J F, et al. Solid-state fabrication of SnS2/C nanospheres for high-performance sodium ion battery anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(21): 11476-11481. DOI:10.1021/acsami.5b02413. |
| 48 | SUN W P, RUI X H, YANG D, et al. Two-dimensional tin disulfide nanosheets for enhanced sodium storage[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11371-11381. DOI:10.1021/acsnano.5b05229. |
| 49 | ZHANG Y D, ZHU P Y, HUANG L L, et al. Few-layered SnS2 on few-layered reduced graphene oxide as Na-ion battery anode with ultralong cycle life and superior rate capability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(3): 481-489. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201402833. |
| 50 | WANG Y P, ZHANG Y F, SHI J R, et al. Tin sulfide nanoparticles embedded in sulfur and nitrogen dual-doped mesoporous carbon fibers as high-performance anodes with battery-capacitive sodium storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 18: 366-374. DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2018.08.014. |
| 51 | KIM Y, KIM Y, PARK Y, et al. SnSe alloy as a promising anode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(1): 50-53. DOI:10.1039/c4cc06106c. |
| 52 | ZHANG Z A, ZHAO X X, LI J. SnSe/carbon nanocomposite synthesized by high energy ball milling as an anode material for sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 176: 1296-1301. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2015.07.140. |
| 53 | YANG K W, ZHANG X X, SONG K M, et al. Se–C bond and reversible SEI in facile synthesized SnSe2⊂3D carbon induced stable anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 337: 135783. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2020.135783. |
| 54 | XIAO S H, LI Z Z, LIU J T, et al. Se C bonding promoting fast and durable Na+ storage in yolk-shell SnSe2@Se C[J]. Small, 2020, 16(41): 2002486. DOI:10.1002/smll.202002486. |
| 55 | WANG W H, ZHANG J L, YU D Y W, et al. Improving the cycling stability of Sn4P3 anode for sodium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 364: 420-425. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2017.08.060. |
| 56 | KIM Y, KIM Y, CHOI A, et al. Tin phosphide as a promising anode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(24): 4139-4144. DOI:10.1002/adma.201305638. |
| 57 | MA L B, YAN P J, WU S K, et al. Engineering tin phosphides@carbon yolk-shell nanocube structures as a highly stable anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(32): 16994-17000. DOI:10.1039/c7ta04900e. |
| 58 | GÓMEZ-CÁMER J L, ACEBEDO B, ORTIZ-VITORIANO N, et al. Unravelling the impact of electrolyte nature on Sn4P3/C negative electrodes for Na-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(31): 18434-18441. DOI:10.1039/C9TA04288A. |
| 59 | PALANISELVAM T, MUKUNDAN C, HASA I, et al. Assessment on the use of high capacity "Sn4P3" /NHC composite electrodes for sodium-ion batteries with ether and carbonate electrolytes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(42): 2004798. DOI:10.1002/adfm.202004798. |
| 60 | WANG Y, SHI H T, NIU J R, et al. Self-healing Sn4P3@hard carbon co-storage anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 851: 156746. DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156746. |
| [1] | 王蕾, 刘少冕, 范凤兰, 杨子腾. 速生木基钠离子电池硬碳负极构效关系[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(3): 1107-1114. |
| [2] | 潘美玲, 孙楠楠, 赵志超. 二维VC2作为钠离子电池负极材料的理论研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(2): 497-504. |
| [3] | 王阳峰, 侯佳傲, 朱紫宸, 所聪, 侯栓弟. 钠离子电池硬碳闭孔结构研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(2): 555-569. |
| [4] | 常永刚, 张晋豪, 解炜, 李秀春, 王毅林, 陈成猛. 钠离子电池硬碳负极容量提升策略研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(2): 544-554. |
| [5] | 张李帅, 张艺菲, 马伊扬, 赵思博, 刘洪全, 石盛庭, 钟艳君. 铁基普鲁士蓝类似物钠离子电池正极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(2): 525-543. |
| [6] | 乌兰, 杨杰, 耿磊, 胡润, 彭尚龙. 钠离子电池正极表面残余碱转换钠补偿包覆层[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(1): 21-29. |
| [7] | 要义杰, 张峻伟, 赵燕君, 梁宏成, 赵冬妮. 界面动力学对钠离子电池低温性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(1): 30-41. |
| [8] | 郝定邦, 栗永利. 高倍率和长循环稳定性钠离子电池正极材料Na0.85Ni0.3Fe0.2Mn0.5O1.95F0.05 @CuO的性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2489-2498. |
| [9] | 姚远, 宗若奇, 盖建丽. 钠离子电池锑基及铋基金属负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2649-2664. |
| [10] | 范利君, 吴保周, 陈珂君. 不同形貌FeS2 的可控制备及储钠特性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2541-2549. |
| [11] | 谭仕荣, 尹文骥, 曾翠鸿, 黎小琼, 訚硕, 纪方力, 胡思江, 王红强, 李庆余. 高温淬火对钠离子电池锰基层状正极材料结构和性能的影响[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2399-2406. |
| [12] | 徐雄文, 莫英, 周望, 姚环东, 洪娟, 雷化, 涂健, 刘继磊. 硬碳动力学特性对钠离子电池低温性能的影响及机制[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2141-2150. |
| [13] | 林炜琦, 卢巧瑜, 陈宇鸿, 邱麟媛, 季钰榕, 管联玉, 丁翔. 低温钠离子电池正极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2348-2360. |
| [14] | 王立锋, 任乃青, 杨海, 姚雨, 余彦. 低温钠离子电池电解液研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2206-2223. |
| [15] | 李丹, 马铁, 刘汉浩, 郭丽. 高倍率钠离子电池炭包覆纳米铋负极材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(6): 1775-1785. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
