Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2021, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (1): 137-142.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2020.0315
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhou JIN1( ), Hailong YU1, Wenwu ZHAO1, Guangjin ZHAO2, Xuejie HUANG1(
), Hailong YU1, Wenwu ZHAO1, Guangjin ZHAO2, Xuejie HUANG1( )
)
Received:2020-09-10
Revised:2020-09-28
Online:2021-01-05
Published:2021-01-08
CLC Number:
Zhou JIN, Hailong YU, Wenwu ZHAO, Guangjin ZHAO, Xuejie HUANG. Graphite/nano-Sn composite anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 137-142.
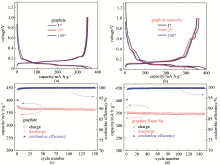
Fig.4
Charge-discharge curves in 1st, 2nd and 100th cycle for (a) graphite and (b) graphite/nano-Sn half-cells, Capacity retention and coulombic efficiency in 150 cycles for (c) graphite and (d) graphite/nano-Sn half-cells (All half-cells were cycled at 0.1 C for first cycle and 0.2 C for 2~150 cycles)"

| 1 | GUERARD D, HEROLD A. Intercalation of lithium into graphite and other carbons[J]. Carbon, 1975, 13: 337-45. |
| 2 | DAHN J. Phase-diagram of LixC6[J]. Physical Review B, 1991, 44: 9170-9177. |
| 3 | 孙方静, 韦连梅, 张家玮, 等. 锂离子电池快充石墨负极材料的研究进展及评价方法[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2017, 6(6): 1223-1230. |
| SUN Fangjing, WEI Lianmei, ZHANG Jiawei, et al. Research progress and evaluation methods of lithium-ion battery fast-charge graphite anode material[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2017, 6(6): 1223-1230. | |
| 4 | NIE Mengyun, CHALASANI D, ABRAHAM D P, et al. Lithium ion battery graphite solid electrolyte interphase revealed by microscopy and spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117: 1257-1267. |
| 5 | TARASCON M, ARMAND M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Nature, 2001, 414: 359-367. |
| 6 | BUQA H, GOERS M, HOLZAPFEL M, et al. High rate capability of graphite negative electrodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(2): A474-A481. |
| 7 | ZHAO Zhuo, JIA Xiaochuan, LI Jing, et al. Oxidative modification of natural graphite negative electrode[J]. New Carbon Material, 2013, 28(5): 385-390. |
| 8 | HAN Y J, KIM J D, YEO J S, et al. Coating of graphite anode with coal tar pitch as an effective precursor for enhancing the rate performance in Li-ion batteries: Effects of composition and softening points of coal tar pitch[J]. Carbon, 2015, 94: 432-438. |
| 9 | PARK M S, LEE J, LEE J W, et al. Tuning the surface chemistry of natural graphite anode by H3PO4 and H3BO3 treatments for improving electrochemical and thermal properties[J]. Carbon, 2013, 62: 278-287. |
| 10 | 李荣辉, 闫伟, 吴晓强, 等. 高容量高倍率的氮掺杂二次粒子石墨负极材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(1): 116-122. |
| LI Ronghui, YAN Wei, WU Xiaoqiang, et al. Nitrogen doped secondary particle graphite anode for high capacity and high rate Li ion battery[J]. | |
| Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 116-122. | |
| 11 | DU Zhijia, ZHANG Shichao, ZHAO F, et al. Improved electrochemical performance of Sn-Ni nanorods array for Li-ion battery[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2012, 7: 1180-1186. |
| 12 | TAN Chunhui, QI Gongwei, LI Yeping, et al. The improved performance of porous Sn-Ni alloy as anode materials for lithium-ion battery prepared by electrochemical dissolution treatment[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2013, 8: 1966-1975. |
| 13 | WU Chao, MAIER J, YU Yan. Sn-based nanoparticles encapsulated in a porous 3D graphene network: Advanced anodes for high-rate and long life Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25: 3488-3496. |
| 14 | TIRADO J. Inorganic materials for the negative electrode of lithium-ion batteries: State-of-the-art and future prospects[J]. Materials Science & Engineering Reports, 2003, 40: 103-136. |
| 15 | 徐辉, 仰榴青, 尹凡, 等. 无定形碳包覆锡基负极材料的制备及其电化学性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(4): 732-737. |
| XU Hui, YANG Liuqing, YIN Fan, et al. Preparation and electrochemical | |
| performance of amorphous carbon coated tin-based anode materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(4): 732-737. | |
| 16 | CUI Lifeng,SHENJian,CHENG Fangyi,et al.SnO2 nanoparticles@ |
| polypyrrole nanowires composite as anode materials for rechargeable | |
| lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196: 2195-2201. | |
| 17 | CHEN Chunhao, CHASON E, GUDURU P. Numerical solution of moving phase boundary and diffusion-induced stress of Sn anode in the lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164: E3661-E3670. |
| 18 | LIU Lilai, AN Maozhong, YANG Peixia, et al. Superior cycle performance and high reversible capacity of SnO2/graphene composite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: doi: 10.1038/srep09055. |
| 19 | JI Liwen, TAN Zhongkui, KUYKENDALL T, et al. Multilayer nanoassembly of Sn-nanopillar arrays sandwiched between graphene layers for high-capacity lithium storage[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4: 3611-3616. |
| 20 | XU Yunhua, LIU Qing, ZHU Yujie, et al. Uniform nano-Sn/C composite anodes for lithium ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2013, 13: 470-474. |
| 21 | ELLIS B, LEE K T, NAZAR L. Positive electrode materials for Li-ion and Li-batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22: 691-714. |
| [1] | Long CHEN, Quan XIA, Yi REN, Gaoping CAO, Jingyi QIU, Hao ZHANG. Research prospect on reliability of Li-ion battery packs under coupling of multiple physical fields [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2316-2323. |
| [2] | Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Apr. 1, 2022 to May 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2007-2022. |
| [3] | YAN Qiaoyi, WU Feng, CHEN Renjie, LI Li. Recovery and resource recycling of graphite anode materials for spent lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1760-1771. |
| [4] | DING Yi, YANG Yan, CHEN Kai, ZENG Tao, HUANG Yunhui. Intelligent fire protection of lithium-ion battery and its research method [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1822-1833. |
| [5] | WANG Can, MA Pan, ZHU Guoliang, WEI Shuimiao, YANG Zhilu, ZHANG Zhiyu. Effect of lithium acrylic-coated nature graphite on its electrochemical properties [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1706-1714. |
| [6] | Honghui WANG, Zeqin WU, Deren CHU. Thermal behavior of lithium titanate based Li ion batteries under slight over-discharging condition [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1305-1313. |
| [7] | Ronghan QIAO, Guanjun CEN, Xiaoyu SHEN, Mengyu TIAN, Hongxiang JI, Feng TIAN, Wenbin QI, Zhou JIN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2022 to Mar. 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1289-1304. |
| [8] | Zheng ZHENG, Xiaoshuai WANG, Bin LI, Tao HUANG, Peike LI. Adaptive interleaved control equalization for lithium-ion battery packs based on three-winding transformers [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1131-1140. |
| [9] | Qiannan LIU, Weiping HU, Zhe HU. Research progress of phosphorus-based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1201-1210. |
| [10] | Guanjun CEN, Jing ZHU, Ronghan QIAO, Xiaoyu SHEN, Hongxiang JI, Mengyu TIAN, Feng TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Dec. 1, 2021 to Jan. 31, 2022) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 1077-1092. |
| [11] | Zhiqiang ZHAO, Hengjun LIU, Xixiang XU, Yuanyuan PAN, Qinghao LI, Hongsen LI, Han HU, Qiang LI. Magnetometry technique in energy storage science [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 818-833. |
| [12] | Mengyu TIAN, Jing ZHU, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xiaoyu SHEN, Hongxiang JI, Feng TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yong YAN, Yida WU, Yuanjie ZHAN, Hailong YU, Liubin BEN, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries(Oct. 1, 2021 to Nov. 30, 2021) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 297-312. |
| [13] | Penghui LI, Caiwen WU, Jianpeng REN, Wenjuan WU. Research progress of lignin as electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 66-77. |
| [14] | Enda CI, Hui WANG, Xiaoqing LI, Ying ZHANG, Zhenying ZHANG, Jianqiang LI. Preparation and property enhancement of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate-lithium nitrate eutectic/expanded graphite composite phase change materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 30-37. |
| [15] | Yuyang LIU, Shunli WANG, Yanxin XIE, Weikang JI, Yixing ZHANG. Research on Li-ion battery modeling and SOC estimation based on online parameter identification and improved 2RC-PNGV model [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2312-2317. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
