Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2022, Vol. 11 ›› Issue (6): 1749-1759.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0722
Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Chunhui( ), HE Ziying, ZHANG Chenxi(
), HE Ziying, ZHANG Chenxi( ), LIN Xianqing, XIAO Zhexi, WEI Fei(
), LIN Xianqing, XIAO Zhexi, WEI Fei( )
)
Received:2021-12-31
Revised:2022-01-11
Online:2022-06-05
Published:2022-06-13
Contact:
ZHANG Chenxi, WEI Fei
E-mail:chemych@126.com;cxzhang@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn;wf-dce@tsinghua.edu.cn
CLC Number:
YU Chunhui, HE Ziying, ZHANG Chenxi, LIN Xianqing, XIAO Zhexi, WEI Fei. The analyses and suppressing strategies of silicon anode with the electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1749-1759.
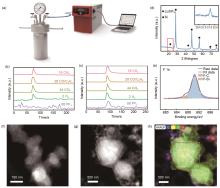
Fig. 1
Study of the chemical reaction. (a) Illustration of the experiment; (b) and (c) MS results of the electrolyte and Si after the reaction, respectively; (d) XRD data of Si after the reaction; (e) F1s spectrum results for Si@C after the reaction; TEM image of Si@C before (f) and after (g) reaction; (h) EDS Mapping of Si@C after reaction"
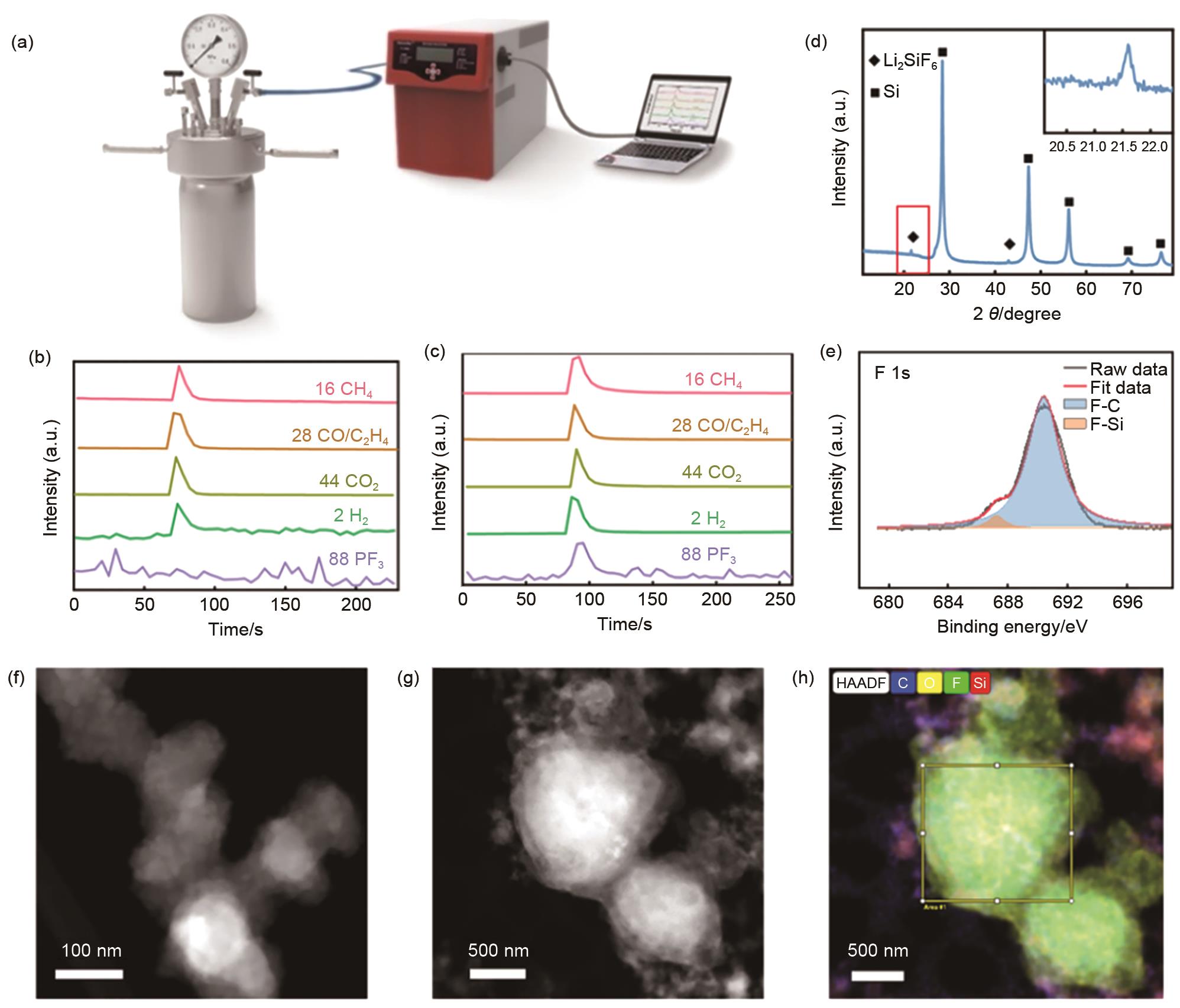
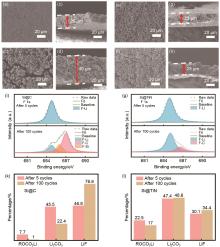
Fig. 7
The Comparison of Si@C and Si@TiN after different cycles. (a) SEM image of fresh Si@C; (b) SEM image of Si@C after 5 cycles; (c) Top-view SEM image of fresh Si@C; (d) Top-view SEM image of Si@C after 5 cycles; (e) SEM image of fresh Si@TiN; (f) SEM image of Si@TiN after 5 cycles; (g) Top-view SEM image of fresh Si@TiN; (h) Top-view SEM image of Si@C after 5 cycles; (i) XPS data of Si@C after different cycles; (j) XPS data of Si@TiN after different cycles; (k) Relative percentage of different components for Si@C; (l) Relative percentage of different components for Si@TiN"
| 1 | SUN Y M, LIU N, CUI Y. Promises and challenges of nanomaterials for lithium-based rechargeable batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16071. |
| 2 | DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: A battery of choices[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058): 928-935. |
| 3 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 4 | GOODENOUGH J B, KIM Y. Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(3): 587-603. |
| 5 | LU Y X, RONG X H, HU Y S, et al. Research and development of advanced battery materials in China[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 23: 144-153. |
| 6 | LUO F, LIU B N, ZHENG J Y, et al. Review—nano-silicon/carbon composite anode materials towards practical application for next generation Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(14): A2509-A2528. |
| 7 | AUPPERLE F, VON ASPERN N, BERGHUS D, et al. The role of electrolyte additives on the interfacial chemistry and thermal reactivity of Si-anode-based Li-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(9): 6513-6527. |
| 8 | VEITH G M, BAGGETTO L, SACCI R L, et al. Direct measurement of the chemical reactivity of silicon electrodes with LiPF6-based battery electrolytes[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2014, 50(23): 3081-3084. |
| 9 | SEYFERTH D. Dimethyldichlorosilane and the direct synthesis of methylchlorosilanes. the key to the silicones industry[J]. Organometallics, 2001, 20(24): 4978-4992. |
| 10 | YU C H, LIN X Q, CHEN X, et al. Suppressing the side reaction by a selective blocking layer to enhance the performance of Si-based anodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(7): 5176-5184. |
| 11 | 姜晓萍, 左翔, 蔡烽, 等. 六氟磷酸锂的热分解动力学研究[J]. 电源技术, 2012, 36(4): 467-469. |
| JIANG X P, ZUO X, CAI F, et al. Decomposition kinetics research of LiFP6 at elevated temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 36(4): 467-469. | |
| 12 | YANG H, ZHUANG G V, ROSS P N J. Thermal stability of LiPF6 salt and Li-ion battery electrolytes containing LiPF6[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 161(1): 573-579. |
| 13 | GAVRITCHEV K, SHARPATAYA G A, SMAGIN A, et al. Calorimetric study of thermal decomposition of lithium hexafluorophosphate[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2003, 73: 71-83. |
| 14 | YU C H, CHEN X, XIAO Z X, et al. Silicon carbide as a protective layer to stabilize Si-based anodes by inhibiting chemical reactions[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(8): 5124-5132. |
| 15 | WANG X L, BAI S Z, LI F, et al. Effect of plasma nitriding and titanium nitride coating on the corrosion resistance of titanium[J]. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2016, 116(3): 450-456. |
| 16 | FERRAZ E P, SVERZUT A T, FREITAS G P, et al. Bone tissue response to plasma-nitrided titanium implant surfaces[J]. Journal of Applied Oral Science: Revista FOB, 2015, 23(1): 9-13. |
| 17 | GUO L T, WU H T, LIU X C, et al. Effect of fluoride corrosion on the bonding strength of Ti-porcelain under static loads[J]. Materials Letters, 2009, 63(28): 2486-2488. |
| 18 | RIZZI M, GATTI G, MIGLIARIO M, et al. Effect of zirconium nitride physical vapor deposition coating on preosteoblast cell adhesion and proliferation onto titanium screws[J]. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2014, 112(5): 1103-1110. |
| 19 | GUO L T, LIU X C, HE Z Y, et al. Effect of fluoride corrosion on the bonding strength of Ti-porcelain[J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(14): 2200-2202. |
| 20 | NAKAGAWA M, MATONO Y, MATSUYA S, et al. The effect of Pt and Pd alloying additions on the corrosion behavior of titanium in fluoride-containing environments[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(15): 2239-2246. |
| 21 | LIU X Y, CHU P K, DING C X. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: Reports, 2004, 47(3/4): 49-121. |
| 22 | 刘马林. 流化床-化学气相沉积技术在先进核燃料制备中的应用进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(4): 1646-1653. |
| LIU M L. Research activities on FB-CVD technology application in advanced nuclear fuel fabrication[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(4): 1646-1653. | |
| 23 | LIU R Z, ZHAO J, LIU M L, et al. Preparation, performance and nuclear applications of silicon carbide materials prepared by FB-CVD method[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 48(3): 381-390. |
| 24 | KATOH Y, SNEAD L L. Silicon carbide and its composites for nuclear applications-Historical overview[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2019, 526: doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2019.151849. |
| 25 | KOYANAGI T, TERRANI K, HARRISON S, et al. Additive manufacturing of silicon carbide for nuclear applications[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2021, 543: doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat. 2020.152577. |
| [1] | Shunmin YI, Linbo XIE, Li PENG. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on VF-DW-DFN [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2305-2315. |
| [2] | Qingwei ZHU, Xiaoli YU, Qichao WU, Yidan XU, Fenfang CHEN, Rui HUANG. Semi-empirical degradation model of lithium-ion battery with high energy density [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2324-2331. |
| [3] | Yuzuo WANG, Jin WANG, Yinli LU, Dianbo RUAN. Study on the effects of pore structure on lithium-storage performances for soft carbon [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2023-2029. |
| [4] | Wei KONG, Jingtao JIN, Xipo LU, Yang SUN. Study on cooling performance of lithium ion batteries with symmetrical serpentine channel [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2258-2265. |
| [5] | YAN Qiaoyi, WU Feng, CHEN Renjie, LI Li. Recovery and resource recycling of graphite anode materials for spent lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1760-1771. |
| [6] | WANG Yuzuo, DENG Miao, WANG Jin, YANG Bin, LU Yinli, JIN Ge, RUAN Dianbo. Study on the effects of carbonization temperature on lithium-storage kinetics for soft carbon [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1715-1724. |
| [7] | WANG Can, MA Pan, ZHU Guoliang, WEI Shuimiao, YANG Zhilu, ZHANG Zhiyu. Effect of lithium acrylic-coated nature graphite on its electrochemical properties [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1706-1714. |
| [8] | LIU Hangxin, CHEN Xiantao, SUN Qiang, ZHAO Chenxi. Cycle performance characteristics of soft pack lithium-ion batteries under vacuum environment [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1806-1815. |
| [9] | Guangyu CHENG, Xinwei LIU, Yueni MEI, Honghui GU, Cheng YANG, Ke WANG. Capacity fading analysis of lithium-ion battery after high temperature storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1339-1349. |
| [10] | Yanwen DAI, Aiqing YU. Combined CNN-LSTM and GRU based health feature parameters for lithium-ion batteries SOH estimation [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1641-1649. |
| [11] | Xuan WANG, Qiang YE. The aggravation of side reactions caused by insufficient localized liquid supply in an all-vanadium redox flow battery stack [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1455-1467. |
| [12] | Ce ZHANG, Siwu LI, Jia XIE. Research progress on the prelithiation technology of alloy-type anodes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1383-1400. |
| [13] | Chunjing LIN, Danhua LI, Haoran WEN, Tianyi MA, Hong CHANG, Peixiang CHANG, Haiqiang LI, Shiqiang LIU. Research on swelling force characteristics of power battery during charging [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1627-1633. |
| [14] | Qiaomin KE, Jian GUO, Yiwei WANG, Wenjiong CAO, Man CHEN, Fangming JIANG. The effect of liquid-cooled thermal management on thermal runaway of power battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1634-1640. |
| [15] | Jun WANG, Lin RUAN, Yanliang QIU. Research progress on rapid heating methods for lithium-ion battery in low-temperature [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1563-1574. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
