Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (1): 130-142.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0777
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yayun LIAO1,2( ), Feng ZHOU2, Yingxi ZHANG2, Tu'an LV2, Yang HE2, Xiaoyan CHEN2, Kaifu HUO2(
), Feng ZHOU2, Yingxi ZHANG2, Tu'an LV2, Yang HE2, Xiaoyan CHEN2, Kaifu HUO2( )
)
Received:2023-10-31
Revised:2023-11-15
Online:2024-01-05
Published:2024-01-22
Contact:
Kaifu HUO
E-mail:liaoyy20000702@163.com;kfhuo@hust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yayun LIAO, Feng ZHOU, Yingxi ZHANG, Tu'an LV, Yang HE, Xiaoyan CHEN, Kaifu HUO. Research progress on fast-charging graphite anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 130-142.
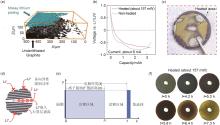
Fig. 2
Fast-charging graphite facing with the main challenge: (a) Li plating on the graphite anode at 100% DOD at 1 C[27]; (b) Voltage curves of graphite electrodes charged at the 2 C rate with or without local heating of the graphite electrode in coin cells[28]; (c) Li plating occurs on the surface of the high temperature area of the centrally heated graphite anode after fast charging[28]; (d) Li+ diffusion modes in graphite; (e) The concentration polarization diagram of the graphite electrode; (f) Photos of Li+ concentration distribution during the lithiating process of the graphite anode[35]"
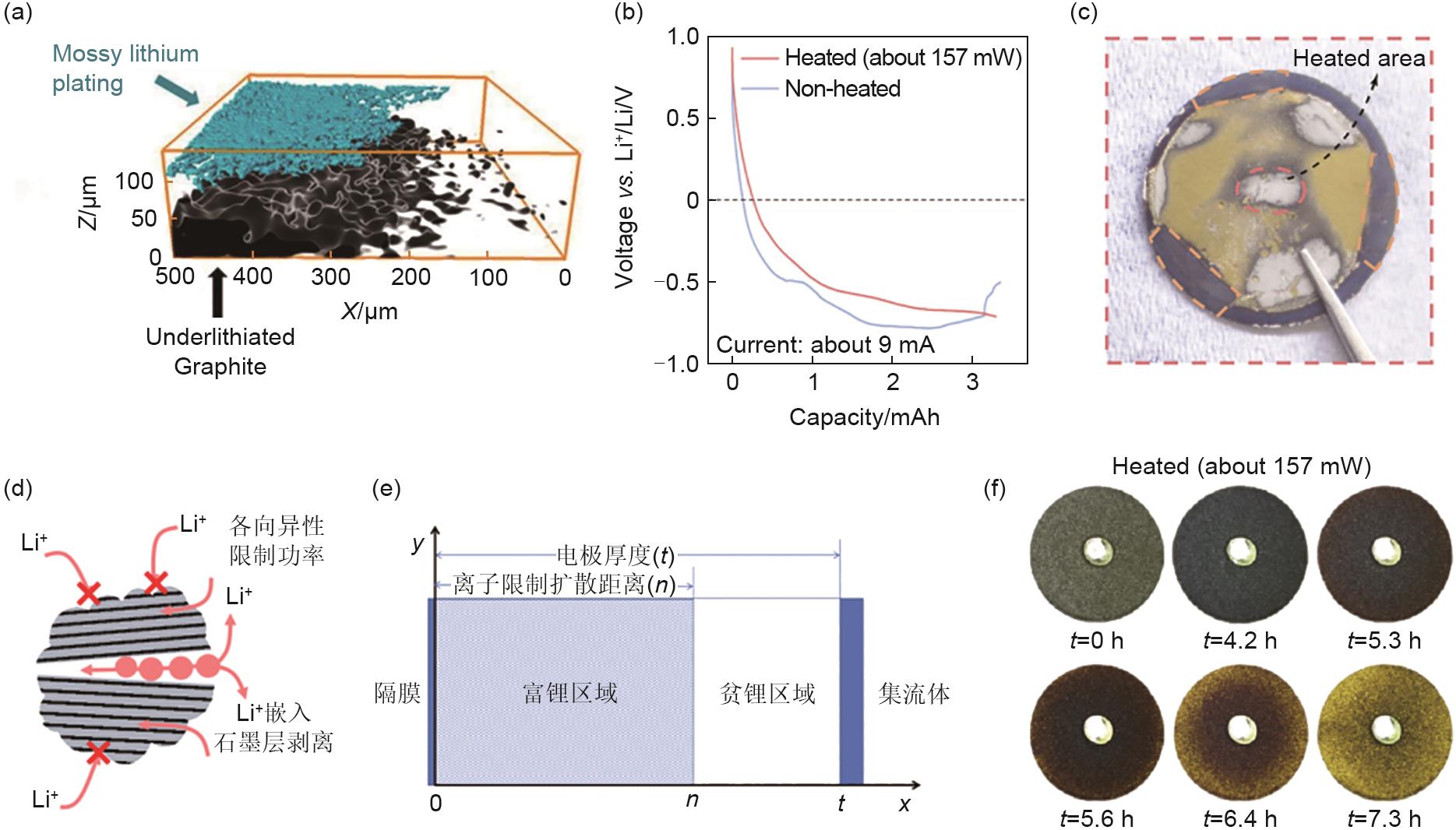

Fig. 3
Structure design of fast-charging graphite anode: (a) Schematic diagram of preparation of acid-treated graphite and KOH etched graphite, with the increase of the spacing between the KOH etched graphite layers, the surface pores are generated to promote Li+ diffusion and improve its fast charging performance[39]; (b) Voltage curves of GFms composite electrode under different discharge current densities, when the current is increased from 0.2 C to 30 C, the capacity retention rate is as high as 92%[40]; (c) A magnetic field is applied to make the graphite particles perpendicular to the collector and schematic diagram of the Li+ diffusion path, the structure shortens the Li+ diffusion distance and increases the Li+ diffusion rate[46]"
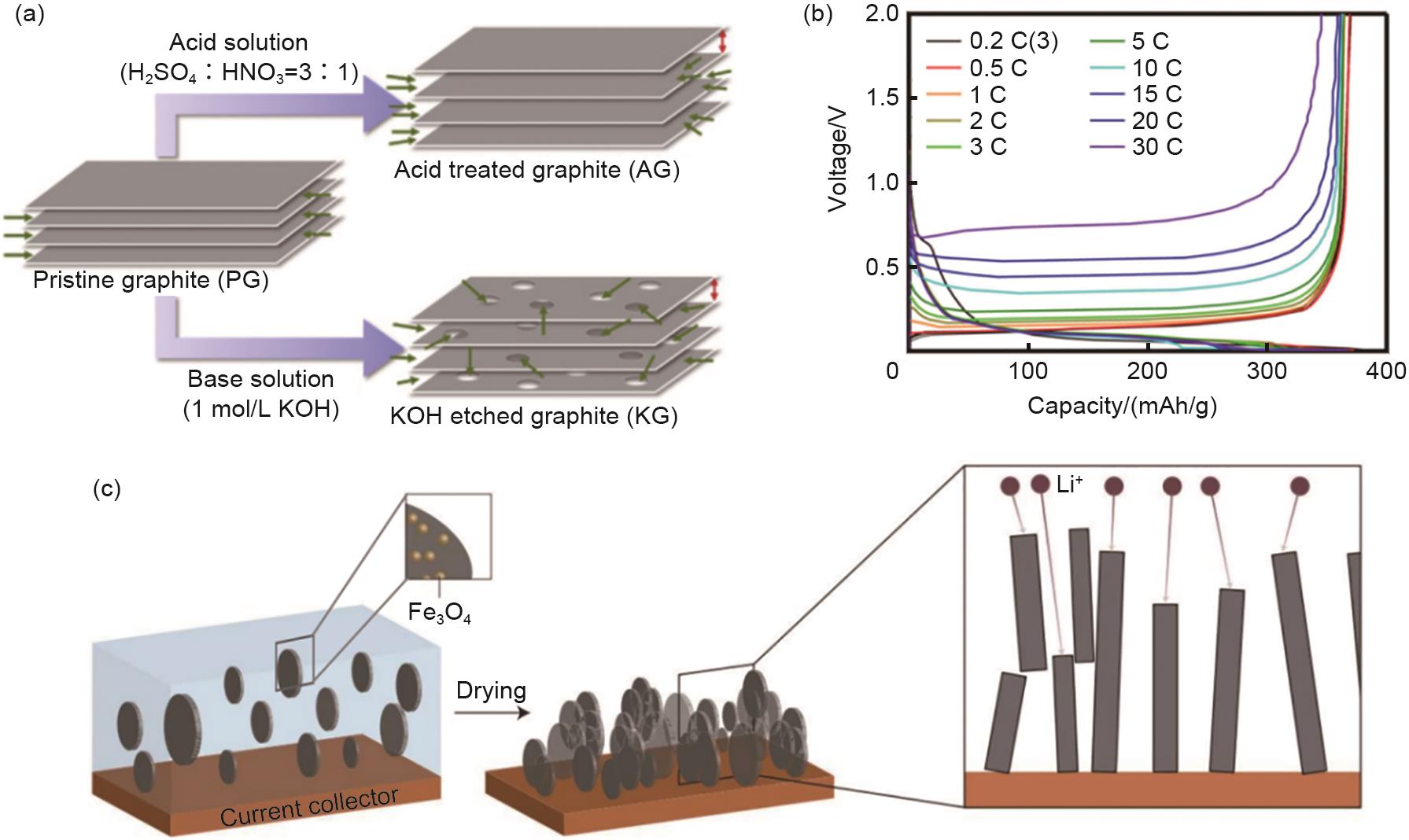
Table 1
Comparison of structure designing strategies and electrochemical properties of graphite anode materials"
| 改性策略 | 具体措施 | 比容量/(mAh/g) | 容量保持率 | 引用 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构设计 | 利用过氧化氢获得微膨胀层状球形石墨 | 188 (1 C) | — | [ |
| 采用热剥离制备开放式/半开放式孔结构的膨胀石墨 | 112 (3 A/g) | 500次循环后93 % (1 A/g) | [ | |
| 酸氧化和KOH蚀刻石墨 | 240 (0.6 A/g) | 1000次循环后96 % (1 A/g) | [ | |
| 利用中间相沥青制备多孔石墨泡沫(GFms) | 345.3 (30 C) | 50次循环后90.12% (1 C) | [ | |
| KOH腐蚀获得具有纳米级孔隙结构的石墨 | — | 100次循环后96.7% (2.5 C) | [ | |
| 空气氧化制备多通道石墨 | — | 3000次循环后85% (6 C) | [ | |
| 带通孔的石墨片和CNTs组成的复合电极 | 220 (8 C) | 500次循环后90% (4 C) | [ | |
| KOH高温蚀刻制备多通道结构石墨 | 125 (1 C) | 100次循环后74% (6 C) | [ | |
| 具有活化边缘的石墨 | 150.3 (10 C) | 700次循环后96.05% (5 C) | [ | |
| 施加磁场制备垂直排列的石墨负极 | 90 (2 C) | — | [ | |
| 采用激光测绘制备具有垂直多孔通道的3D石墨负极 | — | 600次循环后86% (6 C) | [ | |
| 在石墨表面生长垂直石墨烯薄片 | 105.4 (5 C) | — | [ |

Fig. 4
Chemical modification of graphite anode improves its charge-discharge performance: (a) Preparation process of SEAG, the electrode can achieve fast Li+ diffusion[56]; (b) Schematic diagram of synthesis of raw graphite and PTFE modified graphite, F doping is conducive to the fast Li+ diffusion in graphite[52]; (c) Rate performance of LNO and graphite half cells at 68—1360 mA/g, the LNO half cell rate performance has been significantly improved[58]"
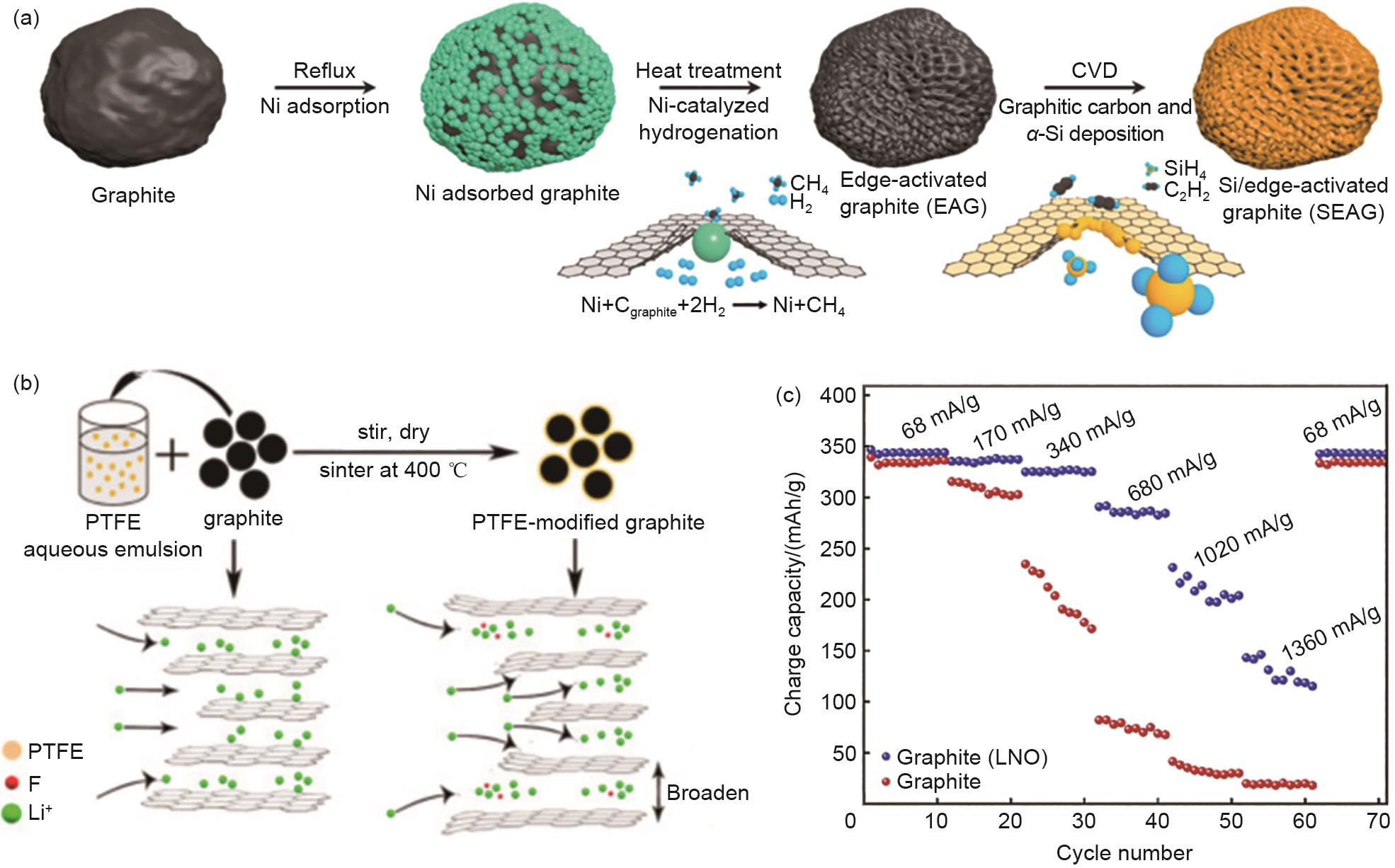
Table 2
Comparison of chemical modification strategies and electrochemical properties of graphite anode materials"
| 改性策略 | 具体措施 | 比容量/(mAh/g) | 容量保持率 | 引用 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化学修饰 | Si/边缘活化石墨复合电极 | 525 (3 C) | 50次循环后99.3% (3 C) | [ |
| 硼酸球磨石墨 | 330 (5 C) | — | [ | |
| 聚四氟乙烯改性石墨 | 318 (0.186 A/g) | 60次循环后98.2% (0.1 C) | [ | |
| N掺杂的空心结构石墨 | 305 (1 A/g) | 500次循环后98% (1 A/g) | [ | |
| 氯化钾与石墨混合制备掺K石墨 | 269.7 (1 C) | — | [ | |
| 石墨浆料中加入LNO制备掺F石墨 | 291.7 (0.68 A/g) | 200次循环后85.7% (0.34 A/g) | [ | |
| 利用H3PO4和H3BO3制备掺P、掺B石墨 | — | 掺P,掺B>95% (5 C/0.2 C) | [ |
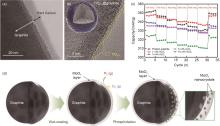
Fig. 5
Fast-charging graphite anode surface coating: (a) Microstructure diagram of hard carbon coated graphite[63]; (b) TiO2-x @graphite core-shell structure,the TiO2-x coating helps to reduce the interface resistance between the electrode and the electrolyte[66]; (c) Rate performance of graphite coated with Al2O3 of different thickness at different current densities,graphite with 1% Al2O3 has a reversible capacity of about 337.1 mAh/gat the current density of 100 mA/g[67]; and (d) MoO x -MoP x / graphite anode material preparation process, both MoO x and nanoscale MoP x can effectively inhibit Li plating during fast charging[68]"
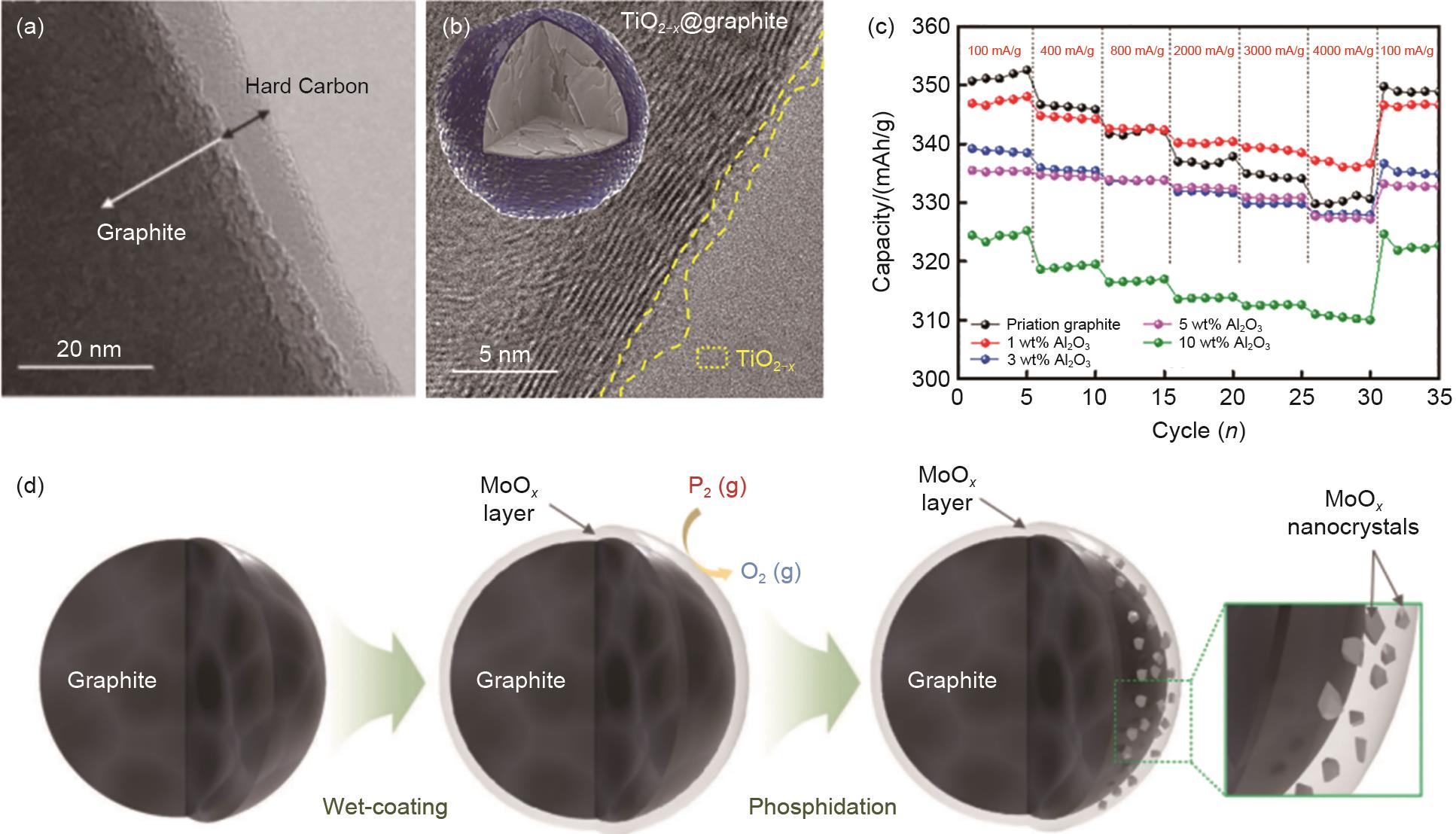
Table 3
Comparison of surface coating strategies and electrochemical properties of graphite anode materials"
| 改性策略 | 具体措施 | 比容量/(mAh/g) | 容量保持率 | 引用 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表面包覆 | 纳米级涡轮层状碳包覆石墨 | — | 300次循环后87% (0.17 A/g) | [ |
| 沥青包覆石墨 | 298 (5 C) | 83% (5 C/0.1 C) | [ | |
| TiO2-x @石墨 | 345.2 (10 C) | 98.2% (5 C/0.2 C) | [ | |
| Al2O3包覆石墨 | 327.7 (4 A/g) | 100次循环后97.2% (4 A/g) | [ | |
| MoO x -MoP x /石墨 | 143.3 (6 C) | 100次循环后86% (6 C) | [ | |
| SM包覆石墨 | — | 100次循环后72% (30 C) | [ | |
| PVDF包覆石墨 | — | 200次循环后96.3% (0.5 C) | [ |
| 1 | 李泓. 未来的电池将朝着更高的比能量发展[R/OL]. [2022-03-31]. http://guoqing.china.com.cn/2022-03/31/content_78140922.htm. |
| 2 | ZENG X Q, LI M, ABD EL-HADY D, et al. Commercialization of lithium battery technologies for electric vehicles[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(27): 1900161-1900185. |
| 3 | WANG G, YU M H, FENG X L. Carbon materials for ion-intercalation involved rechargeable battery technologies[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(4): 2388-2443. |
| 4 | ZHANG Z, ZHAO D, XU Y, et al. A review on electrode materials of fast-charging lithium-ion batteries[J]. The Chemical Record, 2022, 22(10): e202200127-e202200143. |
| 5 | XIA H R, ZHANG W, CAO S K, et al. A figure of merit for fast-charging Li-ion battery materials[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(6): 8525-8530. |
| 6 | USABC. USABC goals for low-cost / fast-charge advanced batteries for electric vehicles applications[R/OL]. [2022-12-20]. http://uscar.org/usabc/. |
| 7 | ZHU G L, ZHAO C Z, HUANG J Q, et al. Fast charging lithium batteries: Recent progress and future prospects[J]. Small, 2019, 15(15): e1805389. |
| 8 | BURNHAM A, DUFEK E J, STEPHENS T, et al. Enabling fast charging-Infrastructure and economic considerations[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 367: 237-249. |
| 9 | COLLIN R, MIAO Y, YOKOCHI A, et al. Advanced electric vehicle fast-charging technologies[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(10): 1839. |
| 10 | 柯承志, 肖本胜, 李苗, 等. 电极材料储锂行为及其机制的原位透射电镜研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(4): 1219-1236. |
| KE C Z, XIAO B S, LI M, et al. Research progress in understanding of lithium storage behavior and reaction mechanism of electrode materials through in situ transmission electron microscopy[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(4): 1219-1236. | |
| 11 | TOMASZEWSKA A, CHU Z Y, FENG X N, et al. Lithium-ion battery fast charging: A review[J]. eTransportation, 2019, 1: 100011. |
| 12 | WANG C Y, LIU T, YANG X G, et al. Fast charging of energy-dense lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nature, 2022, 611(7936): 485-490. |
| 13 | BABU B, SIMON P, BALDUCCI A. Fast charging materials for high power applications[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(29): 2001128-2001161. |
| 14 | HE J H, MENG J K, HUANG Y H. Challenges and recent progress in fast-charging lithium-ion battery materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023. 570: 232965-232981. |
| 15 | HUANG Q K, NI S Y, JIAO M L, et al. Aligned carbon-based electrodes for fast-charging batteries: A review[J]. Small, 2021, 17(48): 2007676-2007701. |
| 16 | LIU Y Y, SHI H D, WU Z S. Recent status, key strategies and challenging perspectives of fast-charging graphite anodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(11): 4834-4871. |
| 17 | WENG S T, YANG G J, ZHANG S M, et al. Kinetic limits of graphite anode for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 215. |
| 18 | LIU Q Q, DU C Y, SHEN B, et al. Understanding undesirable anode lithium plating issues in lithium-ion batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(91): 88683-88700. |
| 19 | MAO C Y, RUTHER R E, LI J L, et al. Identifying the limiting electrode in lithium ion batteries for extreme fast charging[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2018, 97: 37-41. |
| 20 | YANG X G, WANG C Y. Understanding the trilemma of fast charging, energy density and cycle life of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 402: 489-498. |
| 21 | LI L, ZHANG D, DENG J P, et al. Carbon-based materials for fast charging lithium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2021, 183: 721-734. |
| 22 | GOODENOUGH J B, KIM Y. Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(3): 587-603. |
| 23 | LIU Y Y, ZHU Y Y, CUI Y. Challenges and opportunities towards fast-charging battery materials[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(7): 540-550. |
| 24 | HEUBNER C, NIKOLOWSKI K, REUBER S, et al. Recent insights into rate performance limitations of Li-ion batteries[J]. Batteries & Supercaps, 2021, 4(2): 268-285. |
| 25 | ZHANG S S. Challenges and strategies for fast charge of Li-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(17): 3569-3577. |
| 26 | WEISS M, RUESS R, KASNATSCHEEW J, et al. Fast charging of lithium-ion batteries: A review of materials aspects[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(33): 2101126-2101162. |
| 27 | HO A S, PARKINSON D Y, FINEGAN D P, et al. 3D detection of lithiation and lithium plating in graphite anodes during fast charging[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(6): 10480-10487. |
| 28 | WANG H S, ZHU Y Y, KIM S C, et al. Underpotential lithium plating on graphite anodes caused by temperature heterogeneity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(47): 29453-29461. |
| 29 | YAO F, GÜNEŞ F, TA H Q, et al. Diffusion mechanism of lithium ion through basal plane of layered graphene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(20): 8646-8654. |
| 30 | SHI P C, LIN M, ZHENG H, et al. Effect of propylene carbonate-Li+ solvation structures on graphite exfoliation and its application in Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 247: 12-18. |
| 31 | ASENBAUER J, EISENMANN T, KUENZEL M, et al. The success story of graphite as a lithium-ion anode material-fundamentals, remaining challenges, and recent developments including silicon (oxide) composites[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2020, 4(11): 5387-5416. |
| 32 | DIDIER C, PANG W K, GUO Z P, et al. Phase evolution and intermittent disorder in electrochemically lithiated graphite determined using in operando neutron diffraction[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(6): 2518-2531. |
| 33 | VETTER J, NOVÁK P, WAGNER M R, et al. Ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 147(1/2): 269-281. |
| 34 | GUO Y T, LI X H, GUO H J, et al. Visualization of concentration polarization in thick electrodes[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 51: 476-485. |
| 35 | YANG W, XIE H M, SHI B Q, et al. In-situ experimental measurements of lithium concentration distribution and strain field of graphite electrodes during electrochemical process[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 423: 174-182. |
| 36 | WAN J Y, XIE J, KONG X A, et al. Ultrathin, flexible, solid polymer composite electrolyte enabled with aligned nanoporous host for lithium batteries[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(7): 705-711. |
| 37 | 郭德超, 曾燮榕, 邓飞, 等. 微膨石墨锂离子电池负极材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 新型炭材料, 2015, 30(5): 419-424. |
| GUO D C, ZENG X R, DENG F, et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of expanded graphites as anode materials for a lithium-ion battery[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2015, 30(5): 419-424. | |
| 38 | SON D K, KIM J, RAJ M R, et al. Elucidating the structural redox behaviors of nanostructured expanded graphite anodes toward fast-charging and high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2021, 175: 187-201. |
| 39 | KIM J, NITHYA JEGHAN S M, LEE G. Superior fast-charging capability of graphite anode via facile surface treatment for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 305: 110325. |
| 40 | LIM S, KIM J H, YAMADA Y, et al. Improvement of rate capability by graphite foam anode for Li secondary batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 355: 164-170. |
| 41 | SHIM J H, LEE S H. Characterization of graphite etched with potassium hydroxide and its application in fast-rechargeable lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 324: 475-483. |
| 42 | CHENG Q A, ZHANG Y. Multi-channel graphite for high-rate lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(5): A1104-A1109. |
| 43 | XU J, WANG X, YUAN N Y, et al. Graphite-based lithium ion battery with ultrafast charging and discharging and excellent low temperature performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 430: 74-79. |
| 44 | CHENG Q, YUGE R, NAKAHARA K, et al. KOH etched graphite for fast chargeable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 284: 258-263. |
| 45 | DU P, ZHANG B, CAO L, et al. Designed graphite with an activated edge for fast-charging lithium-ion storage properties[J]. Chemical Communications, 2022, 58(53): 7372-7375. |
| 46 | BILLAUD J, BOUVILLE F, MAGRINI T, et al. Magnetically aligned graphite electrodes for high-rate performance Li-ion batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2016, 1: 16097. |
| 47 | CHEN K H, NAMKOONG M J, GOEL V, et al. Efficient fast-charging of lithium-ion batteries enabled by laser-patterned three-dimensional graphite anode architectures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 471: 228475. |
| 48 | MU Y B, HAN M S, LI J Y, et al. Growing vertical graphene sheets on natural graphite for fast charging lithium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2021, 173: 477-484. |
| 49 | LI S Q, WANG K, ZHANG G F, et al. Fast charging anode materials for lithium-ion batteries: Current status and perspectives[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(23): 2200796-2200831. |
| 50 | CHEN X Y, ZHOU W, LIU J L, et al. Sulfur / nitrogen / oxygen tri-doped carbon nanospheres as an anode for potassium ion storage[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 77: 338-347. |
| 51 | YEO J S, PARK T H, SEO M H, et al. Enhancement of the rate capability of graphite via the introduction of boron-oxygen functional groups[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2013, 8(1): 1308-1315. |
| 52 | KANG S X, LUN H, QI Y X, et al. Boosted electrochemical performance of graphite anode enabled by polytetrafluoroethylene-derived F-doping[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2021, 261: 124214. |
| 53 | YANG X Y, ZHAN C Z, REN X L, et al. Nitrogen-doped hollow graphite granule as anode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2021, 303: 122500. |
| 54 | SHIM J, STRIEBEL K A. Electrochemical characterization of thermally oxidized natural graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 164(2): 862-867. |
| 55 | LIN Y X, HUANG Z H, YU X L, et al. Mildly expanded graphite for anode materials of lithium ion battery synthesized with perchloric acid[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 116: 170-174. |
| 56 | KIM N, CHAE S, MA J, et al. Fast-charging high-energy lithium-ion batteries via implantation of amorphous silicon nanolayer in edge-plane activated graphite anodes[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 812. |
| 57 | WU Y, WANG L Y, LI Y F, et al. KCl-modified graphite as high performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries with excellent rate performance[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(24): 13052-13058. |
| 58 | QI W B, BEN L B, YU H L, et al. Improving the electrochemical cycling performance of anode materials via facile in situ surface deposition of a solid electrolyte layer[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 424: 150-157. |
| 59 | PARK M S, LEE J, LEE J W, et al. Tuning the surface chemistry of natural graphite anode by H3PO4 and H3BO3 treatments for improving electrochemical and thermal properties[J]. Carbon, 2013, 62: 278-287. |
| 60 | IM U S, HWANG J U, YUN J H, et al. The effect of mild activation on the electrochemical performance of pitch-coated graphite for the lithium-ion battery anode material[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 278: 128421. |
| 61 | WU Y S, WANG Y H, LEE Y H. Performance enhancement of spherical natural graphite by phenol resin in lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 426(1/2): 218-222. |
| 62 | LIN J H, CHEN C Y. Thickness-controllable coating on graphite surface as anode materials using glucose-based suspending solutions for lithium-ion battery[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 436: 128270. |
| 63 | LIM Y G, PARK J W, PARK M S, et al. Hard carbon-coated natural graphite electrodes for high-energy and power lithium-ion capacitors[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2015, 36(1): 150-155. |
| 64 | CAI W L, YAN C, YAO Y X, et al. Rapid lithium diffusion in Order@Disorder pathways for fast-charging graphite anodes[J]. Small Structures, 2020, 1(1): 2000010-2000015. |
| 65 | HAN Y J, KIM J, YEO J S, et al. Coating of graphite anode with coal tar pitch as an effective precursor for enhancing the rate performance in Li-ion batteries: Effects of composition and softening points of coal tar pitch[J]. Carbon, 2015, 94: 432-438. |
| 66 | KIM D S, CHUNG D J, BAE J, et al. Surface engineering of graphite anode material with black TiO2- x for fast chargeable lithium ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 258: 336-342. |
| 67 | KIM D S, KIM Y E, KIM H. Improved fast charging capability of graphite anodes via amorphous Al2O3 coating for high power lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 422: 18-24. |
| 68 | LEE S M, KIM J, MOON J, et al. A cooperative biphasic MoOx-MoPx promoter enables a fast-charging lithium-ion battery[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 39. |
| 69 | SHI Q, LIU W J, QU Q T, et al. Robust solid/electrolyte interphase on graphite anode to suppress lithium inventory loss in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2017, 111: 291-298. |
| 70 | LUO J, WU C G, SU L Y, et al. A proof-of-concept graphite anode with a lithium dendrite suppressing polymer coating[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 406: 63-69. |
| 71 | HAN H, PARK H, KIL K C, et al. Microstructure control of the graphite anode with a high density for Li ion batteries with high energy density[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 166: 367-371. |
| 72 | CHEN K H, GOEL V, NAMKOONG M J, et al. Enabling 6 C fast charging of Li-ion batteries with graphite/hard carbon hybrid anodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(5): 2003336-2003347. |
| 73 | 何月德, 刘洪波, 石磊, 等. 改性球形微晶石墨用作锂离子电池负极材料的研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(11): 44-46, 61. |
| HE Y D, LIU H B, SHI L, et al. Study on modified spherical microcrystalline graphite as anode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 36(11): 44-46, 61. | |
| 74 | 何月德, 刘洪波, 洪泉, 等. 酚醛树脂炭包覆对天然微晶石墨电化学性能的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2013, 44(16): 2397-2400, 2405. |
| HE Y D, LIU H B, HONG Q, et al. Investigation on pyrolitic carbon-coated microcrystalline graphite as anode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2013, 44(16): 2397-2400, 2405. | |
| 75 | SUN Y L, HAN F, ZHANG C Z, et al. FeCl3 intercalated microcrystalline graphite enables high volumetric capacity and good cycle stability for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Technology, 2019, 7(4): 1801091-1801099. |
| 76 | HUANG P, LIU B, ZHANG J L, et al. Silicon/carbon composites based on natural microcrystalline graphite as anode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2021, 27(5): 1957-1966. |
| 77 | 韩峰, 张春梅, 王剑秋.一种改性沥青包覆微晶石墨负极材料及其制备方法:CN115579470A.2023-01-06. |
| HAN F, ZHANG C M, WANG J Q. A modified asphalt coated microcrystalline graphite anode material and its preparation method: CN115579470A.2023-01-06. | |
| 78 | 石磊, 邵浩明, 王志勇, 等.一种快充型微晶石墨负极材料及其制备方法:CN110395725B.2021-08-17. |
| SHI L, SHAO H M, WANG Z Y, et al. A fast charging microcrystalline graphite anode material and its preparation method: CN110395725B.2021-08-17. | |
| 79 | 周海辉, 吴璇, 赖俊辉, 等.石墨负极材料、其制备方法和锂离子电池:CN111668480B.2023-07-28. |
| ZHOU H H, WU X, LAI J H, et al. Graphite anode material, its preparation method,and lithium-ion battery: CN111668480B.2023-07-28. | |
| 80 | 周奇, 周晓航, 娄忠良.一种天然微晶石墨负极材料的制备方法及负极材料与应用:CN111115623B.2022-02-18. |
| ZHOU Q, ZHOU X H, LOU L L. Preparation method and application of a natural microcrystalline graphite anode material: CN111115623B.2022-02-18. | |
| 81 | GUO H, WANG Z S, XING B L, et al. Carbon nanosheets prepared with a vermiculite template for high-performance lithium-ion batteries via space-confined carbonization strategy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 933: 167721. |
| 82 | 周奇, 文博, 谢志勇. 微晶石墨改性用作锂离子电池负极材料[J]. 功能材料, 2023, 54(2): 2167-2173. |
| ZHOU Q, WEN B, XIE Z Y. Microcrystalline graphite modified as lithium-ion battery anode material[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2023, 54(2): 2167-2173. |
| [1] | Guobin ZHONG, Xin YAO, Yongchao LIU, Qian HOU, Hongfa XIANG. Challenges and prospects of high-safety composite separators for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1794-1806. |
| [2] | Ziwei TANG, Yupu SHI, Yuchan ZHANG, Yibo ZHOU, Huiling DU. Prediction of lithium-ion battery capacity degradation trajectory based on Informer [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1658-1666. |
| [3] | Nana FENG, Ming YANG, Zhouli HUI, Ruijie WANG, Hongyang NING. Prediction of the remaining useful life of lithium batteries based on Antlion optimization Gaussian process regression [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1643-1652. |
| [4] | Gaoqi LIAN, Min YE, Qiao WANG, Yan LI, Yuchuan MA, Yiding SUN, Penghui DU. State-of-charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries in rapid temperature-varying environments based on improved battery model and optimized adaptive cubature Kalman filter [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1667-1676. |
| [5] | Xinbing XIE, Kaiyue YANG, Xiaozhong DU. Mechanical behavior and structure of lithium-ion battery electrode calendering process [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1699-1706. |
| [6] | Lin HE, Jiangyan LIU, Bin LIU, Kuining LI, Shuai DAI. Generalized impact of data distribution diversity on SOC prediction of lithium battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1677-1687. |
| [7] | Yalu HAN, Yige CHEN, Huifang DI, Jiehuan LIN, Zhenbing WANG, Yang ZHANG, Fangyuan SU, Chengmeng CHEN. Research progress on failure of lithium-ion batteries under different service conditions [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1338-1349. |
| [8] | Ge LI, Xiangdong KONG, Yuedong SUN, Fei CHEN, Yuebo YUAN, Xuebing HAN, Yuejiu ZHENG. Method for sorting the dynamic characteristics of lithium-ion battery consistency based on production line big data [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1188-1196. |
| [9] | Ruizi WANG, Xunliang LIU, Ruifeng DOU, Wenning ZHOU, Juan FANG. A comparative study on diffusion-induced stress and thermal stress during discharge of ternary soft pack lithium-ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1128-1141. |
| [10] | Yuting WANG, Qiutong LI, Yiming HU, Xin GUO. Techniques for monitoring internal signals of lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(4): 1253-1265. |
| [11] | Xiaoyu SHEN, Congbo YIN. SOH estimation of lithium-ion batteries using a convolutional Fastformer [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 990-999. |
| [12] | Zhiguo ZHANG, Huaqing LI, Li WANG, Xiangming HE. Characteristics and preparation of metallized plastic current collectors for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 749-758. |
| [13] | Jian LIU, Libo YU, Zhenxing WU, Jiegang MOU. Effect of thermal characteristics of lithium-ion battery charging and discharging equipment on air cooling [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 914-923. |
| [14] | Meiling WU, Lei NIU, Shiyou LI, Dongni ZHAO. Research progress on cathode prelithium additives used in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 759-769. |
| [15] | Xiaolei LI, Jian GAO, Weidong ZHOU, Hong LI. Application of COMSOL multiphysics in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 546-567. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
